Asia Pacific Negative Pressure Wound Therapy Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report By Device (Conventional, Single-Use, Accessories), Component (Canisters & Dressings, Pumps), Wound Type (Chronic, Acute), Indication (Surgical, Pressure Ulcers, Venous Ulcers, Diabetic Foot, Burns, Others), End User (Hospitals, ASCs, Home Care, Others), and Country (India, China, Japan, South Korea, Australia) – Industry Analysis From 2025 to 2033.
Asia Pacific Negative Pressure Wound Therapy Market Size
The size of the Asia Pacific negative pressure wound therapy market was worth USD 715 million in 2024. The Asia Pacific market is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 5.6% from 2025 to 2033 and be worth USD 1,168 million by 2033 from USD 755 million in 2025.
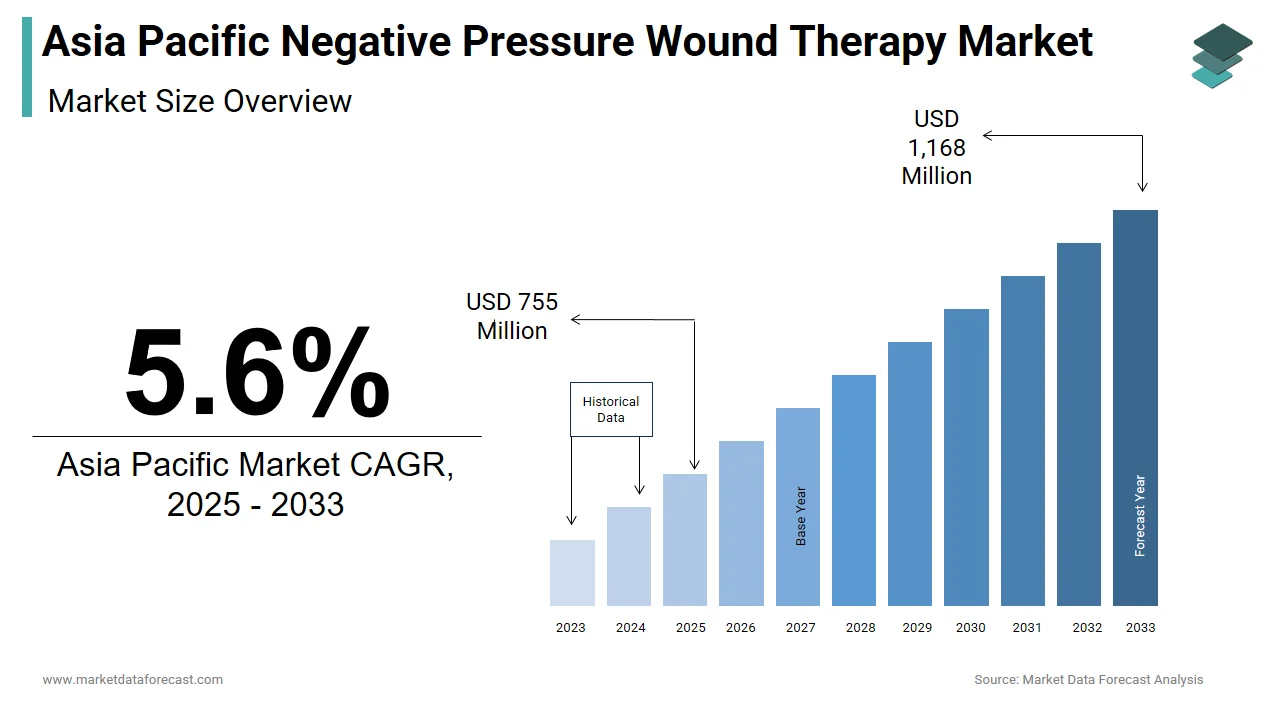
The Asia Pacific negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) market encompasses the use of advanced medical devices that apply controlled sub-atmospheric pressure to wounds to promote healing. These systems are widely used in managing chronic wounds such as diabetic ulcers, pressure sores, surgical incisions, and traumatic injuries. The therapy enhances granulation tissue formation, removes excess exudate, and reduces bacterial load, making it a preferred solution in both hospital and homecare settings.
MARKET DRIVERS
Rising Incidence of Chronic Wounds Due to Diabetic Population Growth
One of the most significant drivers of the Asia Pacific negative pressure wound therapy market is the escalating prevalence of diabetes, which leads to chronic foot ulcers and other non-healing wounds requiring advanced interventions. Countries such as China, India, and Indonesia are experiencing a rapid surge in diabetic patients due to sedentary lifestyles, urbanization, and poor dietary habits. According to the International Diabetes Federation, India alone reported over 77 million cases of diabetes in 2023, while China accounted for more than 141 million cases. A large proportion of these patients develop diabetic foot ulcers, with approximately 15% progressing to severe infections or amputations if left untreated. As per the Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism, diabetic foot ulcers contribute to nearly 25% of diabetes-related hospital admissions in India, necessitating timely and effective wound care solutions. In response, hospitals and rehabilitation centers across the region are increasingly adopting NPWT to accelerate healing and reduce infection risks.
Increasing Number of Surgical Procedures and Post-Operative Complications
Another key driver fueling the growth of the Asia Pacific negative pressure wound therapy market is the surge in surgical procedures and associated post-operative complications such as dehiscence, infections, and delayed healing. With the expansion of healthcare infrastructure and rising disposable incomes, more patients are opting for elective and emergency surgeries, particularly in countries like South Korea, Japan, and Australia. Similarly, in China, the National Health Commission reported a 20% increase in major surgeries between 2021 and 2023, including orthopedic, cardiothoracic, and bariatric operations known for higher postoperative wound complication rates. As per the British Journal of Surgery, negative pressure wound therapy has demonstrated a 30–40% reduction in surgical site infections when applied prophylactically after high-risk procedures. Hospitals in Thailand and Malaysia have also integrated NPWT into their standard post-operative protocols, especially for obese and elderly patients who are more prone to healing delays.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Cost of Negative Pressure Wound Therapy Systems
A primary restraint impeding the widespread adoption of negative pressure wound therapy in the Asia Pacific region is the high cost associated with NPWT systems, particularly disposable components and branded devices. While traditional wound care methods, such as gauze dressing,s remain more affordable, NPWT requires continuous investment in single-use canisters, adhesive drapes, and pump units, which can be financially burdensome for low-income patients and public healthcare institutions. In Indonesia, where out-of-pocket healthcare expenditure accounts for a major share of total health spending, only 10% of patients in rural areas can afford sustained NPWT treatment, limiting its accessibility.
Limited Awareness and Training Among Healthcare Professionals
Despite the proven efficacy of negative pressure wound therapy, limited awareness and insufficient training among healthcare professionals continue to hinder its full-scale adoption in the Asia Pacific region. Many clinicians, especially those practicing in rural and semi-urban hospitals, lack formal education on the appropriate indications, contraindications, and application techniques for NPWT. In Bangladesh, the Directorate General of Health Services found that over 60% of public hospitals lacked certified wound care specialists, contributing to the underutilization of evidence-based treatment modalities. As per the Singapore Nursing Board, even in well-developed healthcare systems, only half of the nursing staff were trained in operating NPWT devices effectively, leading to inconsistent patient outcomes. Furthermore, the absence of standardized wound care curricula in medical and nursing schools across several Asia Pacific countries exacerbates the knowledge gap, slowing down the integration of NPWT into mainstream clinical practice.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Expansion of Home Healthcare and Ambulatory Wound Care Services
A significant opportunity driving the Asia Pacific negative pressure wound therapy market is the rapid expansion of home healthcare and ambulatory wound care services, particularly in urban centers and aging societies. Governments and private healthcare providers are increasingly promoting outpatient wound management to reduce hospital readmissions and optimize resource utilization. In Australia, the Department of Health introduced new rebates under Medicare for home-based wound care services, encouraging the use of lightweight and user-friendly NPWT systems. As per the Indian Journal of Community Medicine, over 1.5 million patients in India opted for home healthcare services in 2023, with diabetic foot ulcer management accounting for a significant share. Companies such as Smith & Nephew and Mölnlycke Health Care are launching miniaturized NPWT pumps designed for self-application, enhancing compliance and convenience.
Integration of Smart and Connected NPWT Devices
The emergence of smart and connected negative pressure wound therapy devices represents a transformative opportunity for market expansion in the Asia Pacific region. These next-generation systems incorporate IoT-enabled sensors, remote monitoring capabilities, and real-time data analytics to enhance patient adherence and clinical decision-making. In Japan, where the aging population is growing rapidly, manufacturers such as KCI (a subsidiary of Acelity) have introduced cloud-connected NPWT platforms that allow caregivers to track therapy progress and receive alerts for device malfunctions or dressing leaks. Moreover, AI-powered predictive analytics integrated into these devices assist clinicians in adjusting pressure levels and identifying potential complications before they escalate.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Regulatory Hurdles and Complex Approval Processes
A major challenge constraining the growth of the Asia Pacific negative pressure wound therapy market is the fragmented regulatory landscape and complex approval mechanisms for NPWT devices across different countries. Unlike the United States or European Union, where streamlined pathways exist for medical device clearances, the Asia Pacific lacks a unified regulatory framework, causing significant delays in product launches. In China, the National Medical Products Administration revised its registration requirements in 2023, mandating additional clinical validation data for imported NPWT products, thereby increasing compliance costs. Similarly, in India, the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization enforces stringent quality checks that delay market entry for smaller international players.
Limited Reimbursement Policies and Insurance Coverage
The lack of comprehensive reimbursement policies and inadequate health insurance coverage for negative pressure wound therapy poses a significant challenge in the Asia Pacific region, particularly in emerging economies. While developed countries such as Australia and Japan offer partial or full coverage for NPWT under national health schemes, most Southeast Asian nations provide little to no financial assistance, discouraging widespread usage. According to the World Bank, out-of-pocket healthcare expenditures in countries like Myanmar, Nepal, and Cambodia exceed 60% , restricting access to expensive wound care treatments.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
Segments Covered |
By Device, Component, Wound Type, Indication, End User, and Region. |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional and Country-Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, Drivers, Restraints, Opportunities, Challenges; PESTLE Analysis; Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Countries Covered |
India, China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, New Zealand, Thailand, Malaysia, Vietnam, Philippines, Indonesia, Singapore, Rest of APAC |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Acelity, Smith & Nephew, Mölnlycke Health Care AB, Convatec Group, Cardinal Health, Paul Hartmann AG, Deroyal, Lohmann & Rauscher International, Cork Medical, Chongqing Sunshine Medical Industry and Trading, Wuhan VSD Medical Science & Technology. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Device Insights
The conventional NPWT devices segment captured 52.6% of the Asia Pacific negative pressure wound therapy market in 2024 by making it the largest category. This dominance is primarily attributed to their widespread use in hospitals and long-term care centers for managing complex wounds such as surgical dehiscence, traumatic injuries, and post-amputation healing. According to a report by the Japanese Society of Wound Healing, over 60% of tertiary care hospitals in Japan utilize conventional NPWT systems for high-risk surgical wound management. In China, the National Health Commission emphasized the importance of advanced wound care in its "Healthy China 2030" initiative, leading to increased procurement of reusable and durable NPWT units across public hospitals. As per the Indian Journal of Surgery, conventional NPWT devices are preferred for prolonged wound healing scenarios due to their flexibility in pressure settings and compatibility with various dressings.
The single-use NPWT devices segment is projected to grow at the fastest CAGR of 14.5% over the forecast period and is driven by increasing demand for portable, cost-effective, and patient-friendly wound care solutions in home and ambulatory settings. These disposable units offer ease of use, lightweight design, and reduced maintenance costs, making them ideal for diabetic foot ulcers and minor surgical wounds. In Australia, the Department of Health reported that home-based NPWT usage rose by 25% following Medicare's inclusion of single-use pumps under partial reimbursement coverage. Moreover, companies like Medela and B. Braun have introduced compact, battery-operated models tailored for elderly patients, enhancing accessibility and compliance.
By Component Insights
In 2024, the canisters and dressings component accounted for 58% of the Asia Pacific negative pressure wound therapy market and is propelled by its recurring consumption nature and essential role in every NPWT application. Unlike pumps, which are often reused, canisters and dressings require frequent replacement depending on wound severity and treatment duration. In India, the Association of Diabetes Foot Care Specialists found that diabetic foot ulcer patients typically require dressing changes every 2–3 days, escalating demand for compatible foam and gauze materials. With increasing awareness about infection control and enhanced healing outcomes, the reliance on high-quality, absorbent dressings and biocompatible canisters continues to drive this segment’s overwhelming share in the market.
The pumps segment is anticipated to register a CAGR of approximately 12%, which reflects growing investments in next-generation NPWT systems featuring smart controls, wireless connectivity, and miniaturized designs. These advancements cater to both clinical and homecare settings, where portability and ease of operation are critical. According to a white paper published by the Korean Ministry of Food and Drug Safety, the approval rate for innovative NPWT pump models doubled in 2023 compared to the previous year, signaling a shift toward technologically superior alternatives. Furthermore, local startups in Indonesia and Vietnam are developing affordable, reusable pump variants to capture budget-conscious segments, accelerating growth across diverse healthcare environments.
By Wound Type Insights
The chronic wounds segment held the largest share of the Asia Pacific negative pressure wound therapy market at around 64% in 2023. This is primarily due to the region’s expanding population suffering from diabetes, vascular diseases, and age-related immobility. According to the International Diabetes Federation, Asia accounts for a significant share of the global diabetic population, with complications such as foot ulcers driving extensive demand for advanced wound care. Similarly, Japan’s aging demographic, where more than 30% of the population is aged above 65, has led to a surge in pressure sores and venous ulcers necessitating prolonged treatment. Also, healthcare professionals increasingly prefer NPWT for chronic wound management due to its ability to accelerate granulation tissue formation and reduce amputation risks.
The acute wounds segment is projected to grow at the highest CAGR of nearly 13%. It is propelled by the rising number of trauma cases, emergency surgeries, and burn center admissions across major APAC countries. According to the World Health Organization, road traffic accidents account for over 200,000 annual deaths in the Asia Pacific, many of which result in severe open wounds requiring immediate NPWT intervention. In addition, the rise in cosmetic and orthopedic surgeries has contributed to the expanded use of NPWT for acute surgical incisions.
By Indication Insights
The diabetic foot ulcer indication segment contributed a 38.7% of the Asia Pacific negative pressure wound therapy market in 2024 and is making it the largest sub-segment due to the exponential rise in diabetes-related complications. In Malaysia, the Ministry of Health found that diabetic foot complications contribute to nearly 40% of lower limb amputations, prompting aggressive adoption of advanced wound therapies, including NPWT. As per the Asian Pacific Association for the Study of Diabetes, negative pressure wound therapy has demonstrated a 50% faster healing time compared to traditional dressings in controlled DFU trials, reinforcing its clinical relevance. Hospitals in Thailand and the Philippines have also incorporated NPWT into diabetes foot clinics supported by national health initiatives.
The surgical and traumatic wounds segment is expected to expand at the highest CAGR of about 13%, and is caused by increasing hospitalization rates, surgical volumes, and trauma-related injuries across the region. In addition, road traffic accidents and industrial injuries in rapidly urbanizing economies like India and Indonesia have amplified demand for NPWT in emergency wound care.
COUNTRY LEVEL ANALYSIS
China held the largest share of 28.5% in the Asia Pacific negative pressure wound therapy market. This is owing to its vast patient pool, growing prevalence of diabetes and vascular diseases, and increasing investment in wound care infrastructure. With a vast number of diabetic patients, the country faces a significant burden of non-healing foot ulcers and post-surgical complications. The Ministry of Science and Technology funded several R&D initiatives in 2023 aimed at developing cost-effective NPWT solutions tailored for domestic use.
Japan had established a healthcare infrastructure and high adoption rates. It is distinguished by its mature healthcare system, aging population, and early adoption of advanced wound care technologies. Also, research institutions such as the University of Tokyo have collaborated with domestic medtech firms to refine NPWT algorithms for better healing outcomes. As a result, Japan remains a key innovation hub and early adopter of next-generation negative pressure wound therapy systems.
India is a rapidly expanding market due to the rising chronic disease burden. This is emerging as one of the fastest-growing markets due to the proliferation of lifestyle diseases, increasing access to specialty wound care centers, and expanding private healthcare infrastructure. The Indian Council of Medical Research estimates that over 77 million people suffer from diabetes, many of whom develop foot ulcers requiring timely intervention. In response, the Ministry of Health launched the “National Diabetic Foot Care Program” to strengthen ulcer management practices and reduce amputation rates. Private hospital chains such as Apollo and Fortis have introduced dedicated wound healing departments equipped with NPWT systems.
Australia has strong reimbursement policies and advanced clinical adoption. It is characterized by well-established reimbursement frameworks, high healthcare expenditure, and early adoption of evidence-based wound care practices. Medicare provides partial coverage for NPWT in both hospital and home settings, especially for diabetic foot ulcers and post-surgical complications. The Department of Veterans’ Affairs includes NPWT in its approved equipment list for elderly veterans prone to pressure injuries. Local research bodies such as the Wound Management Innovation CRC have conducted extensive studies validating the efficacy of negative pressure wound therapy, influencing clinical guidelines nationwide.
South Korea occupies a smaller share of the Asia Pacific NPWT market and is known for its proactive approach to medical technology adoption and digital health integration. The country’s Ministry of Food and Drug Safety has streamlined regulatory pathways for NPWT device approvals, facilitating quicker market entry for innovative products.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
Some of the noteworthy companies in the APAC negative pressure wound therapy market profiled in this report are Acelity, Smith & Nephew, Mölnlycke Health Care AB, Convatec Group, Cardinal Health, Paul Hartmann AG, Deroyal, Lohmann & Rauscher International, Cork Medical, Chongqing Sunshine Medical Industry and Trading, and Wuhan VSD Medical Science & Technology.
TOP LEADING PLAYERS IN THE MARKET
Smith & Nephew (United Kingdom-based)
Smith & Nephew is a global leader in advanced wound care and holds a strong presence in the Asia Pacific negative pressure wound therapy market. The company offers a comprehensive portfolio of NPWT systems, including both conventional and single-use devices tailored for hospital and homecare settings. Its focus on innovation has led to the development of smart, lightweight pumps that enhance patient mobility and ease of use. Smith & Nephew actively collaborates with regional healthcare providers and regulatory bodies to improve product accessibility. By investing in clinical education and digital integration initiatives, the company continues to drive adoption of evidence-based wound management solutions across multiple surgical and chronic wound applications in the Asia Pacific region.
Acelity L.P. and its subsidiaries (United States-based)
Acelity, along with its subsidiary KCI, plays a critical role in shaping the Asia Pacific NPWT landscape through its pioneering technologies such as the V.A.C. Therapy System. The company’s solutions are widely recognized for their efficacy in managing complex wounds, including diabetic foot ulcers and post-surgical injuries. Acelity's commitment to research and development has resulted in next-generation NPWT platforms that offer improved healing outcomes and reduced hospital stays. Through strategic partnerships and localized distribution networks, the company enhances its reach across emerging markets. Acelity also emphasizes training programs for clinicians to ensure optimal utilization of its products, reinforcing its leadership position and long-term growth potential in the Asia Pacific region.
Medela LLC (Switzerland-based)
Medela is a key player in the Asia Pacific negative pressure wound therapy market due to its expertise in developing innovative, patient-centric NPWT solutions. Known for its portable and user-friendly devices, Medela focuses on improving patient compliance and comfort, particularly in homecare environments. The company’s dedication to integrating advanced engineering with clinical insights positions it as a preferred choice among healthcare professionals and patients alike. In the Asia Pacific region, Medela strengthens its market presence by expanding its distribution channels and engaging in educational outreach programs for caregivers and medical staff.
TOP STRATEGIES USED BY KEY MARKET PARTICIPANTS
One of the primary strategies adopted by leading players in the Asia Pacific negative pressure wound therapy market is product innovation and differentiation. Companies are continuously investing in R&D to develop next-generation NPWT devices that offer enhanced portability, ease of use, and compatibility with various wound types. This includes the introduction of smart, connected units that support remote monitoring and real-time data analysis for improved patient outcomes.
Another crucial strategy involves expanding regional distribution networks and strengthening local partnerships. Major firms are collaborating with hospitals, clinics, and government agencies to ensure wider availability of NPWT systems and consumables. These efforts include setting up regional service centers, offering specialized training, and engaging with local distributors to penetrate underserved markets effectively.
Lastly, companies are increasingly investing in clinician education and clinical validation programs to bridge knowledge gaps and promote broader adoption of NPWT. By organizing hands-on workshops, simulation labs, and certification courses, firms ensure that healthcare professionals are proficient in using advanced NPWT technologies, thereby increasing device utilization and reinforcing long-term market growth.
COMPETITION OVERVIEW
The competition in the Asia Pacific negative pressure wound therapy market is characterized by a mix of globally established medical device manufacturers and emerging regional players striving for market share. Multinational corporations leverage their extensive product portfolios, technological expertise, and well-established distribution networks to maintain dominance, particularly in developed economies such as Japan, Australia, and South Korea. However, local and domestic firms are gaining traction by offering cost-effective alternatives and tailoring products to suit specific clinical needs in emerging markets like India, China, and Southeast Asia. The market remains highly dynamic, fueled by continuous innovation, evolving treatment preferences, and increasing investment in healthcare infrastructure. Strategic collaborations, joint ventures, and acquisitions are frequently employed to strengthen regional footholds and expand product offerings. Additionally, companies face growing pressure to differentiate themselves through enhanced product features, integrated digital solutions, and superior after-sales support.
RECENT MARKET DEVELOPMENTS
- In February 2023, Smith & Nephew launched a new line of compact, battery-powered NPWT devices in Singapore, specifically designed for home use. This initiative aimed at expanding access to advanced wound care solutions for patients suffering from chronic ulcers and post-surgical wounds while enhancing the company’s presence in Southeast Asia.
- In June 2023, Medela entered into a strategic collaboration with a major Indian distributor to significantly increase the availability of its portable NPWT systems in private hospitals and specialty clinics. This move was intended to address the rising demand for user-friendly negative pressure wound therapy options among diabetic foot ulcer patients across tier-2 and tier-3 cities.
- In October 2023, Acelity partnered with a Japanese telehealth platform to integrate remote monitoring capabilities into its V.A.C. Therapy System. This initiative targeted elderly patients requiring long-term wound care and aligned with the country’s push toward digital health-enabled homecare services.
- In March 2024, B. Braun expanded its wound care division in Thailand by establishing a dedicated training center for healthcare professionals specializing in NPWT application. The facility provided hands-on instruction on best practices, ensuring better clinical outcomes and supporting broader adoption of negative pressure wound therapy in the country.
- In November 2024, Mölnlycke Health Care introduced a subsidized program for NPWT dressings and canisters in partnership with public hospitals in the Philippines. The initiative was designed to reduce financial barriers for low-income patients and encourage increased usage of negative pressure wound therapy in treating non-healing wounds within the public healthcare system.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This Asia Pacific negative pressure wound therapy market research report is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Device
- Conventional NPWT Devices
- Single-Use NPWT Devices
- Accessories
By Component
- Canisters and Dressings
- Pumps
By Wound Type
- Chronic Wounds
- Acute Wounds
By Indication
- Surgical and Traumatic Wounds
- Pressure Ulcers
- Venous Ulcers
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer
- Burns
- Others
By End User
- Hospitals and Clinics
- Ambulatory Surgical Centers
- Home Care Settings
- Others
By Country
- India
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Thailand
- Malaysia
- Vietnam
- Philippines
- Indonesia
- Singapore
- Rest Of APAC
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the size of the APAC Negative Pressure Wound Therapy Market?
The APAC Negative Pressure Wound Therapy Market is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 5.6% from 2025 to 2033.
What factors are driving the growth of the APAC Negative Pressure Wound Therapy Market?
Factors such as the increasing prevalence of chronic wounds and an aging population, growing awareness about the benefits of NPWT, and a rise in the number of surgical procedures are majorly driving the APAC Negative Pressure Wound Therapy Market
Which countries in the APAC region are expected to have the highest growth in the NPWT market?
China and India are expected to have the highest growth in the APAC Negative Pressure Wound Therapy Market due to their large populations and increasing healthcare expenditures.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from
$ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: sales@marketdataforecast.com
