Asia Pacific Oilseed Processing Market Research Report - Segmented Based on Type, Process, Application, and Country (India, China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, New Zealand, Thailand, Malaysia, Vietnam, Philippines, Indonesia, Singapore & Rest of APAC)- Analysis on Size, Share, Trends, & Growth Forecast from 2025 to 2033
Asia Pacific Oilseed Processing Market Size
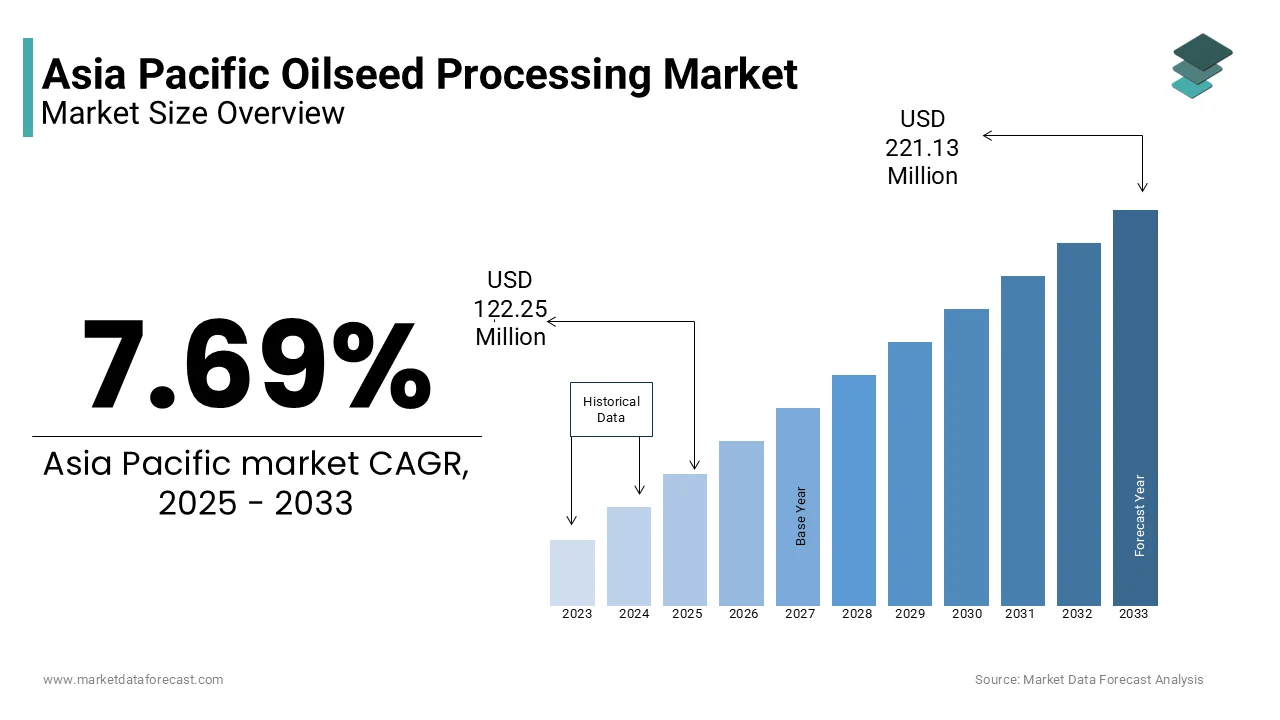
Asia Pacific Oilseed Processing market size was valued at USD 113.52 million in 2024 and the market size is expected to reach USD 221.13 million by 2033 from USD 122.25 million in 2025. The market is growing at a CAGR of 7.69% during the forecast period.
The Asia Pacific Oilseed Processing Market refers to the industrial transformation of oil-bearing seeds such as soybeans, rapeseed (canola), sunflower, cottonseed, and palm kernels into edible oils, protein-rich meals, and biofuel feedstocks. This market plays a crucial role in meeting the region’s growing demand for food, livestock feed, and renewable energy sources. The sector encompasses mechanical pressing, solvent extraction, refining, and value addition processes that ensure quality and efficiency in oil production.
According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), Asia accounts for a significant portion of global oilseed production, with China, India, Indonesia, and Malaysia serving as key contributors.
MARKET DRIVERS
Surge in Urbanization and Changing Dietary Habits
One of the major drivers of the Asia Pacific Oilseed Processing Market is the rapid pace of urbanization and the corresponding shift in dietary preferences toward processed and packaged foods. As populations migrate to cities and disposable incomes rise, there is a growing reliance on ready-to-eat meals, fast food, and convenience products that require substantial quantities of refined vegetable oils.
According to the World Bank, the urban population in the Asia Pacific region increased to nearly 51% in 2023 from 45% in 2015, with countries like China, India, and Indonesia witnessing some of the fastest urban growth rates globally. This trend has led to a surge in commercial frying, baking, and food manufacturing activities that depend heavily on soybean, palm, and canola oils.
In response, oilseed processors have expanded their capacities to meet this rising demand. For instance, according to the Wilmar International, one of the largest agribusiness companies in Asia, there was an increase in edible oil sales across its regional markets in 2023, particularly in Southeast Asia and India.
Additionally, changing consumer awareness regarding health benefits associated with certain oils has spurred demand for low-saturated-fat alternatives such as sunflower and rice bran oil. This convergence of demographic shifts, economic growth, and health consciousness is significantly boosting the Asia Pacific Oilseed Processing Market, ensuring sustained expansion in both traditional and emerging oil varieties.
Expansion of Biofuel Mandates and Green Energy Policies
Another critical driver shaping the Asia Pacific Oilseed Processing Market is the increasing adoption of biofuel mandates and renewable energy policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions and dependence on fossil fuels. Governments across the region are promoting biodiesel blending programs that utilize vegetable oils derived from oilseeds such as palm, soybean, and mustard.
Similarly, India launched its National Biofuel Policy, aiming to achieve a 20% ethanol and biodiesel blending target by 2025–2026. According to the Union Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas, the country’s biodiesel consumption grew by 18% in 2023, with state-owned refiners sourcing significant volumes from non-edible oilseeds such as jatropha and karanja.
China has also intensified its push toward green energy, integrating soybean and rapeseed oils into its national biodiesel strategy
These regulatory initiatives are encouraging investment in oilseed crushing facilities, especially those capable of producing high-quality methyl esters suitable for biodiesel applications.
MARKET DRIVERS
Volatility in Raw Material Supply and Pricing
A significant restraint affecting the Asia Pacific Oilseed Processing Market is the persistent volatility in raw material supply and pricing, largely influenced by climatic conditions, geopolitical tensions, and trade disruptions. Oilseed crops such as soybeans, rapeseed, and palm are highly sensitive to weather fluctuations, which can drastically impact yield levels and export availability.
For example, in 2023, prolonged droughts in Brazil and Argentina—major soybean exporters to China—led to a 12% drop in expected shipments, according to the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA). This disruption forced Chinese processors to seek alternative suppliers or reduce operational capacity temporarily, leading to price spikes in domestically processed oils.
In India, erratic monsoon patterns affected mustard and sesame yields, pushing local oilseed prices up by 17% during the 2023 fiscal year, as reported by the Directorate of Economics & Statistics under the Ministry of Agriculture. Small-scale processors, who often lack hedging capabilities, were disproportionately impacted, resulting in reduced profitability and limited expansion opportunities.
Moreover, trade restrictions imposed by exporting nations further exacerbate supply instability. In 2023, Argentina introduced new export taxes on soybean oil to conserve domestic supplies, while Russia temporarily halted sunflower oil exports due to internal shortages. Such measures disrupt established supply chains and increase input costs for Asia Pacific-based processors.
Stringent Environmental Regulations and Land Use Conflicts
Another major constraint facing the Asia Pacific Oilseed Processing Market is the imposition of stringent environmental regulations and increasing land use conflicts, particularly concerning palm oil production. Countries like Indonesia and Malaysia, which dominate palm oil cultivation, have faced mounting pressure from international buyers and environmental groups over deforestation and biodiversity loss linked to plantation expansion.
As per the Center for International Forestry Research (CIFOR), Indonesia enforced stricter moratoriums on new palm oil plantation permits in 2023, citing the need to preserve peatlands and endangered species habitats. These restrictions have slowed down the rate of fresh fruit bunch supply, forcing processors to either source from certified sustainable plantations at higher costs or reduce operational throughput.
In parallel, India and China have introduced labeling requirements mandating disclosure of sustainability certifications for imported oils. The European Union's Renewable Energy Directive II (RED II) has further complicated matters by restricting the import of palm-based biofuels deemed unsustainable, thereby impacting downstream demand for oilseed derivatives.
Land-use conflicts have also intensified in rural areas where smallholder farmers compete with large agribusinesses for arable land. In Thailand and Vietnam, protests against land acquisition for oilseed plantations have led to project delays and increased scrutiny from regulatory bodies.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Rise of Plant-Based Diets and Alternative Protein Demand
A major opportunity emerging in the Asia Pacific Oilseed Processing Market is the growing popularity of plant-based diets and the expanding demand for alternative proteins. Consumers across the region are increasingly adopting vegetarian and flexitarian lifestyles, driven by health consciousness, ethical considerations, and environmental awareness. This shift is creating strong demand for protein-rich oilseed by-products such as soybean meal, canola meal, and sunflower meal, which serve as essential ingredients in meat substitutes, dairy alternatives, and nutritional supplements.
Companies such as Beyond Meat and Nestlé have expanded their presence in the region, launching locally tailored plant-based products that rely heavily on oilseed-derived proteins.
In India, the government-backed initiative "Protein Innovation Consortium" was launched to encourage domestic production of plant-based protein sources, including oilseed meals.
Oilseed processors that integrate downstream protein separation technologies stand to benefit from this growing market. By leveraging existing infrastructure and expertise, they can diversify revenue streams and capture a larger share of the expanding plant-based food industry in the Asia Pacific region.
Integration with Circular Economy and Waste Valorization Initiatives
Another promising opportunity in the Asia Pacific Oilseed Processing Market lies in the integration of circular economy principles and waste valorization initiatives. Traditionally, oilseed processing generated large volumes of by-products such as husks, cakes, and glycerin, often treated as low-value residues. However, advancements in biorefining and fermentation technologies now allow processors to convert these co-products into high-value inputs for various industries, including livestock feed, biochemicals, and organic fertilizers.
According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), a significant portion of soybean meal produced in China in 2023 was repurposed for aquaculture feed formulations, reflecting a growing emphasis on resource efficiency. In India, the National Institute of Abiotic Stress Management conducted pilot projects converting mustard cake into biopesticides and soil enhancers, reducing agricultural dependency on chemical fertilizers.
Indonesian and Malaysian palm oil processors have also adopted similar strategies, extracting residual fibers and empty fruit bunches for bioenergy generation and compost production. Wilmar International and IOI Corporation have invested in biogas plants that utilize oil mill effluent to generate renewable electricity, reducing operational costs and carbon footprints.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Fragmented Supply Chains and Logistics Inefficiencies
One of the foremost challenges confronting the Asia Pacific Oilseed Processing Market is the fragmentation of supply chains and logistical inefficiencies that hinder seamless movement of raw materials and finished products. Unlike North America and Europe, where integrated agricultural networks support streamlined procurement and distribution, many Asia Pacific countries face infrastructural limitations, inconsistent transportation systems, and bureaucratic hurdles that delay deliveries and inflate costs.
According to the World Bank’s Logistics Performance Index (LPI) 2023, several countries in the region, including Indonesia, the Philippines, and parts of India, scored below the global average in terms of customs efficiency, infrastructure quality, and shipment reliability. This inconsistency affects oilseed processors reliant on timely imports of soybeans and palm kernels, particularly in countries with high import dependency such as China and Japan.
Apart from these, the lack of standardized storage and handling protocols across rural collection centers leads to post-harvest losses and quality degradation of oilseeds before reaching processing units. In India, as per the estimation by the Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA), over 10% of domestically grown oilseeds were lost due to poor logistics and inadequate cold storage facilities in 2023.
Technological Disparity and Lack of Skilled Workforce
Another critical challenge impeding the growth of the Asia Pacific Oilseed Processing Market is the technological disparity between large multinational corporations and small-to-medium enterprises (SMEs), compounded by a shortage of skilled labor in the sector. While major players such as Wilmar International, Cargill, and Adani Wilmar operate highly automated, energy-efficient refineries equipped with AI-driven process optimization tools, many regional and independent processors continue to rely on outdated machinery and manual operations.
The situation is exacerbated by insufficient vocational training programs focused on modern oilseed processing techniques, leaving a skills gap that limits productivity and innovation.
In China, despite government efforts to promote smart agriculture and automation, according to a survey conducted by the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences found that nearly 45% of oilseed mill operators lacked proficiency in digital control systems and predictive maintenance tools. A similar scenario exists in India, where the Directorate General of Training reported that only a small percentage of agricultural engineering graduates pursued careers in oilseed processing due to perceived job insecurity and lower wages compared to other industries.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
8.14% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Type, Process, Application, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
India, China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, New Zealand, Thailand, Malaysia, Vietnam, Philippines, Indonesia, Singapore, and the Rest of Asia-Pacific |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Archer Daniels Midland Company, Bunge Limited, Cargill, Wilmar International Ltd., Richardson International Limited, Louis Dreyfus Company B.V., CHS Inc., Ag Processing Inc., ITOCHU Corporation, EFKO GROUP, and others |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Type Insights
Soybean continued to be the largest segment in the Asia Pacific Oilseed Processing Market, accounting for 58.1% of total processed oilseeds by volume in 2024. China remains the dominant player in this category, processing a substantial quantity of soybeans annually, primarily sourced from imports due to domestic production limitations.
According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), China imported nearly 95 million metric tons of soybeans in 2023, making it the world’s largest importer. The country's crushing industry operates at near-full capacity, with major processors such as Cofco International and Yihai Kerry driving large-scale refining operations.
The dominance of soybean is largely attributed to its widespread use in edible oil production. In India, as per the Solvent Extractors’ Association of India, soybean oil accounted for more than 20% of total vegetable oil consumption in 2023, driven by urbanization and rising middle-class purchasing power.
Additionally, the livestock feed sector heavily relies on soybean meal as a primary protein source.
Sunflower seed is emerging as the fastest-growing oilseed segment in the Asia Pacific region, projected to expand at a CAGR of 7.4%. While currently smaller in volume compared to soybean or palm, sunflower oil is gaining traction due to shifting consumer preferences toward healthier alternatives with lower saturated fat content. This shift is supported by government initiatives promoting nutrition labeling and trans-fat reduction in food products.
India has also played a pivotal role in this growth trajectory. Also, Indian refiners have responded by increasing sunflower oil imports from Ukraine and Argentina to meet growing domestic demand.
Moreover, the renewable energy sector is leveraging sunflower oil for biodiesel applications. In Malaysia, state-backed biofuel programs incorporated sunflower-based methyl esters into blending mandates, enhancing feedstock diversification efforts.
With continued emphasis on health benefits, sustainability, and import diversification, the sunflower oil segment is poised for sustained growth across the Asia Pacific region.
By Process Insights
Chemical processing commanded the Asia Pacific Oilseed Processing Market, capturing an estimated 64.1% of total processing volume in 2024. This method involves solvent extraction using hexane to maximize oil yield, followed by refining, bleaching, and deodorization steps to produce high-purity oils suitable for commercial food and industrial applications.
One key driver of this dominance is efficiency. As per the American Oil Chemists’ Society (AOCS), chemical extraction achieves oil recovery rates above 98%, significantly higher yields compared to mechanical methods alone. This ensures cost-effectiveness and scalability, which is critical for meeting the region’s vast demand for edible oils and biofuels.
Apart from these, regulatory support for refined oils in packaged food manufacturing has reinforced the preference for chemically extracted products. In India, the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) mandates strict quality controls for commercially sold oils, favoring standardized chemical refining processes over artisanal mechanical pressing.
Furthermore, advancements in solvent recovery systems and environmental controls have mitigated earlier concerns about emissions.
Mechanical processing is the fastest-growing segment in the Asia Pacific Oilseed Processing Market, expanding at a CAGR of 6.2% through 2033. This method, which includes expeller pressing and cold-pressing techniques, is increasingly favored in niche markets that prioritize natural, unrefined, and organic oils.
As per the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), mechanically extracted oils saw a 15% rise in premium retail sales in 2023, particularly in India and Southeast Asia, where clean-label trends are influencing consumer choices. Countries like Japan and South Korea have also witnessed a surge in demand for cold-pressed sesame and mustard oils, which are marketed for their purported health benefits and minimal processing.
A primary factor behind its rapid growth is the rising popularity of organic and specialty oils among health-conscious consumers. According to the Organic Trade Association (OTA), organic oil sales in Asia grew in 2023, with mechanical extraction being the preferred method for certification compliance.
Also, small-scale rural enterprises are adopting decentralized mechanical oil mills to enhance local value addition and reduce dependency on large refineries. In India, the Ministry of Food Processing Industries launched a program in 2023 to promote decentralized oilseed processing units in oil-deficit states, supporting livelihoods and improving supply chain resilience.
By Application Insights
Food application led the segment in the Asia Pacific Oilseed Processing Market, accounting for 55.1% of total processed output in 2024. The demand for edible oils derived from soybean, palm, rapeseed, and sunflower remains robust across both household and commercial cooking sectors.
In India alone, as per the Solvent Extractors’ Association of India, edible oil consumption reached 24 million metric tons in 2023, driven by population growth, urbanization, and changing dietary habits.
One key driver of this dominance is the widespread reliance on refined vegetable oils for frying, baking, and food preparation. Moreover, the expansion of the packaged food and restaurant industries has further intensified demand. Government policies also play a role. In Indonesia, the mandatory fortification of palm oil with vitamin A has increased its adoption in mass-produced foods, reinforcing its position in the food application segment. These combined factors ensure the continued supremacy of food-grade oilseed derivatives in the regional market.
Industrial applications are the fastest-growing segment in the Asia Pacific Oilseed Processing Market, expanding at a CAGR of 8.3%. This category encompasses uses such as bio-lubricants, surfactants, coatings, and biodegradable polymers derived from oilseed-based triglycerides and fatty acids.
Companies like BASF, Croda International, and Sime Darby are increasingly incorporating oilseed derivatives into green chemistry solutions to replace petroleum-based compounds.
A key driver of this growth is the tightening of environmental regulations aimed at reducing carbon footprints and hazardous waste.
Additionally, the rise of sustainable aviation fuels (SAFs) and renewable diesel has spurred interest in oilseed-derived feedstocks. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), over 25 new SAF and renewable diesel projects were launched in Asia in 2023, many of which incorporate oilseed esters in their feedstock mix, ensuring sustained demand from the industrial sector. With growing corporate ESG commitments and regulatory incentives, industrial applications of oilseed derivatives are expected to maintain their rapid growth trajectory across the Asia Pacific region.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
China
China led the Asia Pacific Oilseed Processing Market with a dominant share of 38.5% in 2025. As the world’s largest importer and processor of soybeans, the country plays a central role in shaping regional and global oilseed dynamics.
According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), China imported nearly 95 million metric tons of soybeans in 2023, primarily from Brazil and the United States, with over 90% of this volume undergoing crushing and refining. Major domestic processors such as Cofco International, Yihai Kerry, and Sinograin Oil operate extensive facilities that supply both domestic and international markets with edible oils, protein meals, and biodiesel feedstocks.
Government policies, including strategic stockpiling and trade agreements, have ensured a stable supply chain despite geopolitical tensions affecting imports. Additionally, according to the Chinese Ministry of Agriculture, domestic oilseed production, particularly of rapeseed, reached record levels in 2023, helping to marginally reduce import dependency.
The expansion of plant-based protein markets and the push for renewable fuels have further reinforced demand for soybean oil and meal.
India
India is a lucrative market. The country is one of the top consumers and processors of edible oils, with a diverse portfolio that includes soybean, mustard, cottonseed, and palm oil.
Despite this, the country remains heavily reliant on imports, sourcing a large share of its edible oil needs from foreign suppliers, particularly Malaysia and Indonesia for palm oil.
A key driver of growth is the expanding middle class and rising disposable incomes, which have led to increased consumption of packaged foods and ready-to-eat meals. Government initiatives such as the "Edible Oil – Mission Abundance" program aim to boost domestic production and reduce import dependence. Additionally, the introduction of stricter food safety regulations has encouraged processors to adopt advanced refining technologies, enhancing product quality and market competitiveness.
Indonesia
Indonesia holds a significant share of the Asia Pacific Oilseed Processing Market, primarily driven by its dominance in palm oil production and processing. As the world’s largest producer and exporter of palm oil, Indonesia plays a crucial role in supplying both domestic and international markets with refined oils and biofuel feedstocks.
Domestic consumption has also surged due to government-mandated biodiesel blending programs such as B30, which requires a 30% palm methyl ester blend in diesel fuel.
In response to international pressure regarding sustainability, Indonesia introduced the Indonesian Sustainable Palm Oil (ISPO) certification, mandating compliance with environmental and social standards. Additionally, the government has promoted downstream investment by offering tax incentives for new refineries and oleochemical plants.
Japan
Japan is distinguished by its focus on high-quality edible oils and specialty fats. Unlike other major players in the region, Japan does not cultivate significant volumes of oilseeds but instead relies heavily on imports of soybean and rapeseed oil from the United States, Canada, and China.
The country's stringent food safety regulations and preference for non-GMO ingredients have shaped processing practices, encouraging domestic refiners to invest in premium filtration and refining technologies.
A key trend driving the market is the growing demand for imported oils in the foodservice and convenience food sectors. Additionally, Japan’s renewable energy strategy includes limited biodiesel production using imported rapeseed oil.
Malaysia
Malaysia is another key player in the Asia Pacific Oilseed Processing Market, primarily driven by its leadership in palm oil production and refining. As the world’s second-largest palm oil producer after Indonesia, Malaysia plays a vital role in supplying both domestic and global markets with refined palm oil and related derivatives.
Malaysia's strong logistics network and deep-sea ports facilitate efficient exports to China, India, and Europe.
Environmental sustainability remains a key challenge and opportunity. The Malaysian government has strengthened its commitment to the Malaysian Sustainable Palm Oil (MSPO) certification, requiring all plantations to comply by 2025. Additionally, Malaysia is expanding into downstream oleochemicals and bio-based materials. Petronas and IOI Corporation have invested in biorefinery projects that convert palm oil into industrial lubricants, cosmetics ingredients, and bio-plastics, adding value beyond raw commodity exports.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS AND COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
Archer Daniels Midland Company, Bunge Limited, Cargill, Wilmar International Ltd., Richardson International Limited, Louis Dreyfus Company B.V., CHS Inc., Ag Processing Inc., ITOCHU Corporation, EFKO GROUP are some of the notable companies in the Asia Pacific Oilseed Processing market.
The competition in the Asia Pacific Oilseed Processing Market is marked by a blend of multinational corporations, national agribusiness giants, and numerous regional players vying for market share across a highly fragmented yet rapidly evolving industry. Large-scale processors dominate the landscape, leveraging economies of scale, advanced technologies, and vertically integrated operations to maintain operational efficiency and cost competitiveness. These firms benefit from strong supply chain networks, access to capital, and established relationships with global trading partners, giving them an edge over smaller competitors.
However, mid-sized and independent processors continue to play a significant role, particularly in niche segments such as organic oils, cold-pressed varieties, and specialty proteins that cater to specific consumer preferences and regional tastes. In response to shifting dietary habits and increasing health awareness, many companies are innovating their product portfolios to include fortified oils, low-saturated-fat alternatives, and plant-based protein derivatives.
Strategic acquisitions, joint ventures, and investments in digital transformation are frequently used tools to expand capabilities and geographic reach. Additionally, companies are aligning their operations with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) goals to appeal to conscious consumers and institutional investors alike. The interplay between these factors creates a dynamic yet fiercely competitive environment, where technological advancement and supply chain resilience are key differentiators among market participants.
TOP PLAYERS IN THE MARKET
Wilmar International
Wilmar International is a leading agribusiness and food processing company headquartered in Singapore, with a dominant presence across the Asia Pacific Oilseed Processing Market. The company operates one of the largest integrated palm oil and soybean processing networks in the region, supplying refined oils, biodiesel feedstocks, and value-added food ingredients. Wilmar plays a crucial role in shaping supply chain dynamics through its extensive logistics and distribution infrastructure. The firm is also actively involved in sustainable sourcing initiatives, influencing global standards for responsible oilseed production. Its diversified product portfolio and strategic partnerships with major food and energy firms make it a key player in both regional and international markets.
Cofco International
Cofco International, a subsidiary of China National Cereals, Oils, and Foodstuffs Corporation (COFCO), is a major force in the Asia Pacific Oilseed Processing Market. With a strong foothold in China’s soybean crushing industry, the company ensures a steady supply of edible oils and protein meals to meet domestic demand. Cofco International has expanded its operations into Southeast Asia and Africa, securing raw material sources and strengthening its global trade position. The company integrates upstream farming, logistics, refining, and retail to optimize efficiency and sustainability. Its strategic alignment with Chinese government policies on food security further reinforces its influence in regional and global agri-commodity markets.
Adani Wilmar
Adani Wilmar is one of India’s largest edible oil companies and a key participant in the Asia Pacific Oilseed Processing Market. Through its extensive refining and packaging network, the company serves millions of consumers across India and exports to neighboring countries. Adani Wilmar processes a wide range of oilseeds including soybean, mustard, sunflower, and palm, offering diverse products under well-known consumer brands. The company focuses on vertical integration, from import logistics to retail distribution, ensuring competitive pricing and quality control. It also invests in innovation and sustainability to align with evolving consumer preferences and regulatory expectations, making it a formidable player in South Asia’s rapidly growing oilseed sector.
TOP STRATEGIES USED BY KEY MARKET PLAYERS
One of the primary strategies adopted by key players in the Asia Pacific Oilseed Processing Market is vertical integration , allowing companies to control multiple stages of the supply chain—from raw material sourcing and processing to logistics and end-user distribution. This approach enhances cost efficiency, ensures consistent supply, and mitigates risks associated with fluctuating commodity prices.
Another critical strategy is investment in sustainable and traceable sourcing practices , as companies aim to meet growing consumer and regulatory demands for environmentally responsible production. Leading firms are increasingly adopting certified sustainable oilseed programs and investing in regenerative agriculture to secure long-term market access and enhance brand reputation.
Lastly, expansion into high-growth regional markets and downstream diversification is a key focus area. Companies are forming strategic alliances, acquiring local processors, and launching specialty oil and protein-based products tailored to emerging dietary trends, thereby reinforcing their competitive edge in the dynamic Asia Pacific landscape.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THE MARKET
- In February 2023, Wilmar International announced the expansion of its biorefinery complex in Indonesia to increase production capacity for sustainable palm-based oleochemicals and biofuels.
- In July 2023, Cofco International signed a long-term supply agreement with Brazilian soybean exporters to ensure a stable raw material source for its crushing plants in northern China.
- In November 2023, Adani Wilmar launched a new line of fortified edible oils in India, emphasizing improved nutrition and compliance with national health initiatives.
- In March 2024, Wilmar International acquired a stake in a Singapore-based startup developing AI-driven solutions for optimizing oilseed refining processes.
- In August 2024, Cofco International partnered with a European renewable fuels company to co-develop advanced biodiesel blends using soybean oil sourced from its Chinese refineries.
- In April 2024, DynaTouch, a kiosk solutions provider, acquired KioWare, a kiosk management software company. This acquisition is anticipated to allow DynaTouch to offer more comprehensive kiosk solutions and strengthen their market presence.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the Asia Pacific oilseed processing market has been segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Type
- Soybean
- Rapeseed
- Sunflower
- Cottonseed
By Process
- Mechanical
- Chemical
By Application
- Food
- Feed
- Industrial
By Country
- India
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Thailand
- Malaysia
- Vietnam
- Philippines
- Indonesia
- Singapore
- Rest of Asia-Pacific
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the projected market size and CAGR of the Asia Pacific oilseed processing market?
The market is expected to reach USD 221.13 million by 2033 from USD 122.25 million in 2025, growing at a CAGR of 7.69%.
2. What factors are driving growth in the Asia Pacific oilseed processing market?
Rising demand for edible oils, increased health awareness, and the expanding food processing sector are key growth drivers.
3. Which countries are contributing the most to market growth in the region?
China, India, Indonesia, Japan, and Australia are major contributors due to high oilseed production and consumption rates.
4. What are the primary oilseeds processed in this market?
Soybean, sunflower, rapeseed, and palm kernel are the most commonly processed oilseeds in the region.
5. What trends are shaping the Asia Pacific oilseed processing industry?
Sustainable sourcing, organic oil demand, and technological upgrades in extraction and refining processes are major trends.
6. What are the major applications of processed oilseeds in the region?
They are widely used in food manufacturing, animal feed, biodiesel production, and personal care products.
7. What challenges are impacting market expansion?
Fluctuating raw material prices, environmental concerns, and high capital investment requirements are key challenges.
8. How is technology enhancing oilseed processing operations?
Innovations like cold pressing, enzyme-assisted extraction, and automation are increasing yield and efficiency.
9. Are there any sustainability initiatives in the oilseed sector?
Yes, several companies are adopting eco-friendly processes and sourcing certified sustainable oilseeds.
10. What are the emerging opportunities in this market?
Opportunities lie in specialty oils, value-added products, and the rising demand for plant-based ingredients.
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from
$ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: sales@marketdataforecast.com