Asia Pacific Air Quality Control Systems Market Size, Share, Growth, Trends, And Forecasts Report, Segmented By Technology, Pollutant, And By Country (India, China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, New Zealand, Thailand, Malaysia, Vietnam, Philippines, Indonesia, Singapore and Rest of APAC), Industry Analysis From 2025 to 2033
Asia Pacific Air Quality Control Systems Market Size
The Asia Pacific air quality control systems market Size was valued at USD 25.19 billion in 2025, from USD 27.18 billion in 202,5, from USD 49.84 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 7.87% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2033.
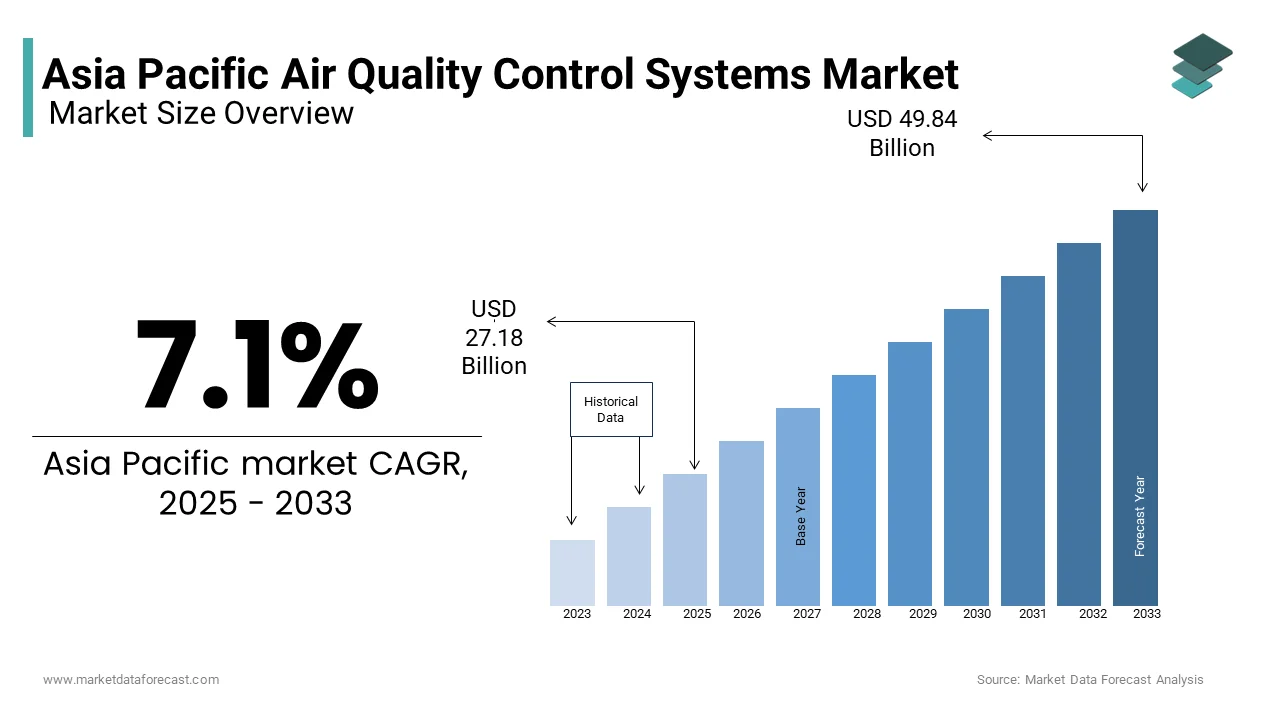
The Asia Pacific air quality control systems market is driven by growing environmental concerns and the urgent need to address rising atmospheric pollution across the region, forming a dynamic ecosystem dedicated to pollution mitigation and sustainable development. This market encompasses a range of technologies including dust collectors, scrubbers, electrostatic precipitators, and catalytic converters designed to curb emissions from industrial, commercial, and urban sources. The region's rapid urbanization, industrial expansion, and growing vehicular density have elevated concerns about ambient air quality, which makes these systems indispensable. Nine out of ten people globally breathe polluted air, with the Asia Pacific region bearing a disproportionate burden due to its dense population centers like Delhi, Beijing, and Jakarta. Over 60% of global energy consumption occurs in the Asia Pacific, contributing significantly to air pollution through fossil fuel combustion. The socio-economic implications are profound, with air pollution causing millions of premature deaths annually.
MARKET DRIVERS
Industrial Expansion and Stringent Environmental Regulations
Industrial expansion and environmental regulations in the Asia Pacific serve as a pivotal driver for the adoption of air quality control systems. Countries like China, India, and Indonesia are witnessing unprecedented growth in manufacturing sectors such as steel, cement, power generation, and petrochemicals. The Asia Pacific accounts for nearly 45% of global industrial output, with heavy industries being significant contributors to particulate matter and greenhouse gas emissions. In response, governments have introduced stringent environmental regulations to curb industrial pollution. China's Ministry of Ecology and Environment mandates the installation of advanced emission control technologies in coal-fired power plants, reducing sulfur dioxide emissions by over 80% since 2010. Similarly, India’s Central Pollution Control Board requires industries in critically polluted areas to adopt Best Available Techniques (BAT) for emission reduction. The increasing number of industrial clusters and special economic zones further amplifies this demand and ensures a steady pipeline of projects requiring pollution abatement solutions.
Rising Urbanization and Public Health Awareness
Urbanization in the Asia Pacific is accelerating at an unprecedented pace, with the region housing over half of the world's megacities. The increasing urbanization, with nearly 60% of the population residing in urban areas, is a major driver of air quality concerns, particularly in densely populated cities. South Korea's Air Quality Management Roadmap aims to reduce fine particulate matter (PM2.5) levels by 30% by 2024. Such initiatives drive the adoption of residential and commercial air purifiers, which are integral components of air quality control systems. Additionally, investments in smart city infrastructure valued at $3 trillion across the region emphasize the integration of air quality monitoring and mitigation technologies.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Capital and Operational Costs
High capital and operational costs are one of the primary barriers to the widespread adoption of air quality control systems in the Asia Pacific. Advanced technologies such as flue gas desulfurization (FGD), selective catalytic reduction (SCR), and fabric filters require significant upfront investments. The cost of installing FGD systems in coal-fired power plants can exceed $100 million per facility and deter smaller enterprises and emerging economies from adopting these solutions. Furthermore, operational expenses related to maintenance, energy consumption, and replacement of consumables add to the financial burden. For instance, electrostatic precipitators commonly used in the cement and steel industries consume up to 2% of a plant's total energy output. This economic strain is particularly pronounced in low-income countries like Bangladesh and Vietnam, where industrial players often prioritize short-term profitability over long-term sustainability.
Lack of Skilled Workforce and Technical Expertise
Shortage of skilled professionals capable of designing, implementing, and maintaining air quality control systems is aneyey restraint in the Asia Pacific. Improper calibration of SCR systems can lead to ammonia slip, resulting in secondary pollution and inefficiencies. Moreover, the lack of standardized training programs exacerbates the issue, leaving many operators ill-equipped to handle advanced technologies. In rural and semi-urban areas, where industrial activities are expanding and the problem is more acute due to limited access to technical education. This shortfall not only hampers the effective deployment of air quality control systems but also increases operational risks, undermining the overall reliability and efficacy of pollution abatement efforts in the region.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Green Financing and Government Subsidies
The proliferation of green financing mechanisms presents a transformative opportunity for the Asia Pacific air quality control systems market. Financial institutions and multilateral organizations are increasingly channeling funds into sustainable projects. Additionally, governments are offering subsidies to incentivize the adoption of pollution control systems. Initiatives like China’s Green Credit Policy encourage banks to offer preferential loans for environmentally friendly projects, which drive demand for air quality solutions.
Advancements in IoT and Smart Monitoring Technologies
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) and smart monitoring technologies offers another significant growth avenue for the Asia Pacific air quality control systems market. Real-time air quality monitoring systems powered by IoT sensors enable industries and municipalities to track emissions with unprecedented precision. For example, Singapore’s Smart Nation initiative uses IoT-enabled devices to monitor PM2.5 levels across the city-state, facilitating data-driven decision-making. Similarly, Japan’s NTT Data has developed predictive analytics platforms that optimize the performance of air filtration systems and reduce downtime, and enhance efficiency. These innovations not only improve regulatory compliance but also enhance operational transparency, attracting environmentally conscious stakeholders. Furthermore, the advent of 5G networks in the region accelerates IoT adoption, enabling seamless connectivity and scalability.
MARKET CHALLENGES Frameworks fragmented nature of regulatory frameworks across the region is a significant challenge facing the Asia Pacific air quality control systems market. Some countries like Japan and South Korea have established comprehensive environmental policies, whereas Myanmar and Cambodia lag due to limited institutional capacity and enforcement mechanisms. Regulatory inconsistencies hinder cross-border collaboration and create uneven playing fields for multinational corporations operating in the region. For instance, varying emission standards between neighboring countries often result in regulatory arbitrage where industries relocate to jurisdictions with laxer norms to avoid compliance costs. This fragmentation complicates the harmonization of air quality control technologies as manufacturers must tailor their products to meet diverse requirements.
Resistance from Traditional Industries
Resistance from traditional industries poses another formidable challenge to the adoption of air quality control systems in the Asia Pacific. Many small-scale enterprises, particularly in sectors like textiles, ceramics, and food processing, ng view pollution control technologies as an unnecessary expense that erodes profit margins. Over 90% of informal industries in the region operate without adequate emission control measures, citing affordability and operational disruptions as primary concerns. For example, brick kilns in India, which contribute significantly to black carbon emissions, often resist transitioning to cleaner technologies due to perceived economic risks. Similarly, artisanal mining operations in Indonesia frequently bypass environmental safeguards to maintain low production costs. This resistance is exacerbated by a lack of awareness about the long-term benefits of air quality control systems. Without targeted interventions to address these misconceptions, traditional industries remain a significant obstacle to market expansion and perpetuating unsustainable practices, and hindering regional efforts to combat air pollution.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2032 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
7.87% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Technology, Pollutant Type, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
India, China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, New Zealand, Thailand, Malaysia, Vietnam, Philippines, Indonesia, Singapore, and the Rest of APAC |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
MITSUBISHI HEAVY INDUSTRIES, LTD (Japan), Babcock & Wilcox Enterprises, Inc (US), Duconenv (US), Thermax Limited (India), Testo SE & Co. KGaA (Germany), Air Spectrum Environmental Ltd (UK), Yokogawa Electric Corporation (Japan), GE Vernova (US), Doosan Power Systems India (India), Rajdeep Engineering Systems Pvt Ltd (India), GEA Group Aktiengesellschaft (Germany), ELEX AG (Schwerzenbach), Tri-Mer Corporation (US), CompAir (US), Donaldson Company, Inc. (US), Essar Enviro Air Systems (India), APZEM Inc (India), ENVIROPOL ENGINEERS PVT. LTD. (India), Beltran Technologies, Inc. (US), Calgon Carbon Corporation (US), Daikin (), FLSmidth Cement A/S (Denmark), and EnviroAir, Inc. c.c (US). |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Technology Insights
The Flue Gas Desulfurization (FGD) segment was the largest and held 40.3% of the Asia Pacific air quality control systems market in 20,24, with the reliance on coal-fired power plants, which are significant contributors to sulfur dioxide emissions. China alone accounts for over 50% of global coal consumption. The technology's ability to reduce SO₂ emissions by up to 95% makes it indispensable for heavy industries like power generation, steel, and cement. A key driving factor is the regulatory push for cleaner energy production. For instance, India’s Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change has introduced the Central Sector Scheme for Installation of FGD Systems, allocating an investment of $8 billion. In Japan, the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) is actively promoting the adoption of flue gas desulfurization (FGD) systems by offering subsidies to help industries meet the country’s ambitious goal of achieving carbon neutrality by 2050. Another key driver is the rising awareness of the harmful effects of acid rain caused by sulfur dioxide (SO₂) emissions, which severely damage crops and ecosystems.
NOx control systems segment is projected to grow at a CAGR of 12.5% during the forecast period. This rapid growth is fueled by increasing vehicular emissions and industrial activities, which are primary sources of nitrogen oxides. The Asia Pacific region houses over 60% of the world’s population, with urban areas like Delhi and Beijing recording NO₂ concentrations exceeding WHO guidelines by fivefold. One major factor propelling this segment is the shift toward Euro VI-equivalent emission standards. South Korea implemented these standards in 2021, mandating selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems in diesel vehicles. Similarly, China’s Blue Sky Protection Campaign emphasizes reducing NOx emissions from transportation and industrial sectors by 30% by 2025. Another critical driver is the rise of smart cities, particularly in countries like Singapore and Australia, where IoT-enabled NOx monitoring systems are being deployed.
By Pollutant Type Insights
The dust pollution segment dominated the Asia Pacific air quality control systems market by capturing 45% of the share in 2,024 with heavy reliance on construction, mining, and manufacturing industries, which generate significant particulate matter emissions. For instance, India’s construction sector contributes to 25% of the country’s GDP but emits over 30 million tons of dust annually.
A primary driver is the alarming health impact of dust pollution. Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) causes respiratory diseases, leading to 1.6 million premature deaths annually in the region. Governments are responding with stringent regulations. For example, Australia’s National Clean Air Agreement mandates dust suppression technologies in mining operations, while Thailand’s Pollution Control Department enforces strict PM10 limits in urban areas. Another factor is the expansion of industrial clusters such as those in Vietnam and IIndonesiahich necessitate advanced dust collection systems like baghouses and cyclones.
The multi-pollutant systems segment is projected to witness a CAGR of 15.2% during the forecast period. This growth is driven by the increasing complexity of pollution sources and the need for integrated solutions capable of addressing multiple contaminants simultaneously. For instance, China’s dual-carbon goals peaking by 2030 and carbon neutrality by 2060 require industries to adopt multi-pollutant systems to tackle SO₂, NOx, and particulate matter emissions concurrently.
A key factor is the rising adoption of circular economy principles. South Korea’s Green Growth Strategy promotes multi-pollutant technologies that recover valuable byproducts from industrial emissions, such as sulfuric acid from FGD systems. Another driver is the proliferation of ultra-low emission zones (ULEZs) in urban centers like Singapore and Tokyo, yo which demand comprehensive air quality solutions. Advancements in artificial intelligence enable predictive maintenance of these systems, enhancing operational efficiency.
COUNTRY ANALYSIS
Top Leading Countries in the Market
China was the top performer in the Asia Pacific air quality control systems market and accounted for 50.7% of the share with its status as the world’s largest emitter of greenhouse gases and its aggressive efforts to combat air pollution. The "Blue Sky Defense" initiative, launched in 201,8, has mandated the installation of advanced air quality systems in over 10,000 industrial facilities and reduced PM2.5 levels by 25% in major cities. A key driver is the sheer scale of industrial activity. The government’s $1.4 trillion investment in renewable energy projects shows its commitment to sustainable development. Another factor is public pressure, where 80% of citizens prioritize air quality improvements, compelling policymakers to accelerate the adoption of cutting-edge technologies.

India was positioned second in holding the dominant share of the Asia Pacific air quality control systems market. The country’s rapid industrialization and urbanization have exacerbated air pollution, making air quality control systems indispensable. Delhi is ranked as the world’s most polluted capital and experiences PM2.5 levels 15 times higher than WHO guidelines. The National Clean Air Programme (NCAP), launched in 201,9, aims to reduce particulate matter concentrations by 20-30% by 2024, driving demand for technologies like FGD and dust collectors. Investments in green infrastructure valued at $1.2 trillion by NITI Aayog further bolster market growth.
Japan's air quality control systems market growth is due to its technological prowess in addressing air quality challenges. The country’s aging industrial base, coupled with natural resource constraints, has spurred innovation in air quality control systems. Japan invests over $500 million annually in R&D for emission reduction technologies.
A key driver is the focus on achieving carbon neutrality by 2050. The Green Growth Strategy outlines plans to retrofit existing plants with advanced scrubbers and electrostatic precipitators, reducing emissions by 46% by 2030. Another factor is the prevalence of urban air pollution, with Tokyo recording NO₂ levels 20% above WHO standards. The Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers notes that over 80% of commercial buildings now incorporate air purification systems, reflecting growing consumer awareness.
South Korea's air quality control systems market growth is driven by its proactive environmental policies and smart city initiatives. The country’s Air Quality Management Roadmap aims to reduce fine particulate matter (PM2.5) levels by 30% by 2024 . A key driver is the rise of smart cities like Seoul, which uses IoT-enabled air quality monitoring systems to regulate emissions. Investments in smart city infrastructure exceed $10 billion annually, creating a robust demand for multi-pollutant systems. Hyundai Motor Group has integrated NOx control technologies into its entire fleet, setting a benchmark for the industry.
Australia and New Zealand are to showcase lucrative growth opportunities for the Asia Pacific air quality control systems market, with the stringent environmental regulations and a focus on sustainable development. The Australian government allocates $2 billion annually to combat air pollution. A key driver is the mining sector, which generates significant dust emissions. The Minerals Council of Australia reports that over 70% of mining operations now employ advanced dust suppression systems. Another factor is the tourism industry, which relies on pristine air quality to attract visitors. These efforts position Australia and New Zealand as leaders in sustainable air quality management within the region.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
MITSUBISHI HEAVY INDUSTRIES, LTD (Japan), Babcock & Wilcox Enterprises, Inc (US), Duconenv (US), Thermax Limited (India), Testo SE & Co. KGaA (Germany), Air Spectrum Environmental Ltd (UK), Yokogawa Electric Corporation (Japan), GE Vernova (US), Doosan Power Systems India (India), Rajdeep Engineering Systems Pvt Ltd (India), GEA Group Aktiengesellschaft (Germany), ELEX AG (Schwerzenbach), Tri-Mer Corporation (U), CompAir (US), Donaldson Company, Inc. (US), Essar Enviro Air Systems (India), APZEM Inc (India), ENVIROPOL ENGINEERS PVT. LTD. (India), Beltran Technologies, Inc. (US), Calgon Carbon Corporation (US), Daikin (), FLSmidth Cement A/S (Denmark), and EnviroAir IncNCc (S) are the market players that are dominating the Asia-Pacific air.Qualityy control systems market
Top Players in the Market
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI)
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries is a global leader in air quality control systems, renowned for its cutting-edge flue gas desulfurization (FGD) and selective catalytic reduction (SCR) technologies. The company has made significant contributions to reducing industrial emissions in the Asia Pacific region by providing scalable solutions tailored to heavy industries like power generation and steel manufacturing. MHI’s emphasis on innovation and sustainability has positioned it as a key player in advancing cleaner energy production globally.
Siemens Energy
Siemens Energy plays a pivotal role in addressing air pollution challenges through its advanced air quality control system, particularly in NOx and multi-pollutant abatement technologies. The company’s focus on integrating digital solutions with traditional pollution control methods has set new benchmarks in operational efficiency.
Thermax Limited
Thermax Limited is a prominent player in the Asia Pacific market, offering innovative solutions for dust collection, scrubbing, and emission control. The company’s strong foothold in emerging economies like India and Southeast Asia has enabled it to address diverse air quality challenges effectively. Thermax’s emphasis on developing cost-effective and energy-efficient technologies has made its products accessible to small and medium-sized enterprises. Thermax continues to drive innovation in the global air quality control systems market.
Top Strategies Used By Key Market Participants
Strategic Collaborations and Partnerships
Strategic collaborations with local government, along with research institutions and industry stakeholders, are on the rise among key players in the Asia Pacific air quality control systems market, et driving advancements and strengthening market presence. These partnerships facilitate the development of customized solutions that cater to specific regional needs, such as urban air pollution or industrial emissions. By leveraging local expertise and resources, these companies can enhance their product offerings and expand their market reach while ensuring compliance with regional regulations.
Focus on Research and Development
Investment in R&D is a cornerstone strategy for leading companies aiming to strengthen their position in the market. By innovating advanced technologies like IoT-enabled monitoring systems and multi-pollutant abatement solutions, these players are addressing the evolving demands of industries and consumers. Continuous innovation not only enhances product performance but also positions companies as pioneers in sustainable air quality management.
Expansion into Emerging Markets
Expansion into emerging economies within the Asia Pacific region, such as Vietnam, Indonesia, and Thailand, nd where rapid industrialization is driving demand for air quality control systems. By establishing local manufacturing units and service centers, these players are reducing costs and improving accessibility for clients. This expansion strategy enables them to capitalize on untapped opportunities and build long-term relationships with regional stakeholders.
COMPETITION OVERVIEW
The Asia Pacific air quality control systems market is characterized by intense competition and is driven by the presence of both global giants and regional players striving to capture market share. Global leaders like Mitsubishi Heavy Industries and Siemens Energy leverage their technological expertise and extensive networks to dominate the market, while regional players such as Thermax Limited focus on affordability and localized solutions to cater to smaller enterprises. The competitive landscape is further shaped by increasing regulatory pressures and growing public awareness of air pollution, which compel companies to innovate continuously. Strategic initiatives such as mergers, acquisitions, and partnerships are common as firms seek to consolidate their positions. Additionally, the rise of smart city projects and green financing mechanisms has intensified competition with companies vying to provide integrated and sustainable solutions. This dynamic environment fosters both collaboration and rivalry, which pushes the industry toward greater advancements in air quality management.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THE MARKET
- In April 2023, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries launched a joint venture with a Chinese environmental technology firm to develop advanced FGD systems tailored for coal-fired power plants in East Asia.
- In June 2023, Siemens Energy partnered with the Indian government to implement NOx control systems in over 50 industrial clusters across the country.
- In August 2023, Thermax Limited introduced a state-of-the-art dust collection system designed specifically for small-scale industries in Southeast Asia.
- In October 2023, Babcock & Wilcox acquired a Singapore-based startup specializing in IoT-enabled air quality monitoring systems.
- In December 2023, Hitachi Zosen Corporation signed a memorandum of understanding with the Indonesian Ministry of Environment to deploy multi-pollutant systems in major urban centers.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the Asia Pacific air quality control systems market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Technology
- FGD, Electrostatic Precipitators
- NOx Control Systems
- Scrubber & Mercury Control Systems
By Pollutant Type
- Gas
- Dust
- Multi-Pollutant
By Country
- India
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Thailand
- Malaysia
- Vietnam
- Philippines
- Indonesia
- Singapore
- Rest of APAC
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary industrial and urban drivers behind the rising demand for air quality control systems in Asia Pacific?
This question investigates the core economic and environmental triggers—like urbanization, manufacturing growth, or public health crises—that are fueling demand.
How are regional air quality regulations and emissions standards influencing technology adoption in the AQCS market across different Asia Pacific countries?
Focuses on the regulatory landscape and how varying compliance thresholds in countries like China, India, Japan, and ASEAN nations shape system designs and upgrades.
What types of AQCS technologies (e.g., flue gas desulfurization, electrostatic precipitators) are gaining traction in Asia Pacific, and why?
Encourages analysis of technical trends and the shift toward advanced or hybrid systems suited to local environmental challenges and energy infrastructure.
How does infrastructure development and energy generation mix (coal, gas, renewables) impact AQCS deployment strategies in Asia Pacific?
Explores how differing levels of power generation and industrialization influence the scope, scale, and urgency of AQCS investments.
What are the major barriers to adoption of advanced air quality control systems in the Asia Pacific region, especially among small to mid-sized enterprises?
Targets the real-world implementation challenges—cost, awareness, technical expertise, and access to capital—that slow down market penetration in emerging economies.
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]