Asia Pacific Autonomous Cars Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report By Autonomy (Level 2 Autonomous Vehicles, Level 4 Autonomous Vehicles), Fuel, End User, And Country (India, China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, New Zealand, Thailand, Malaysia, Vietnam, Philippines, Indonesia, Singapore And Rest Of Asia-Pacific), Industry Analysis From 2025 To 2033
Asia Pacific Autonomous Cars Market Size
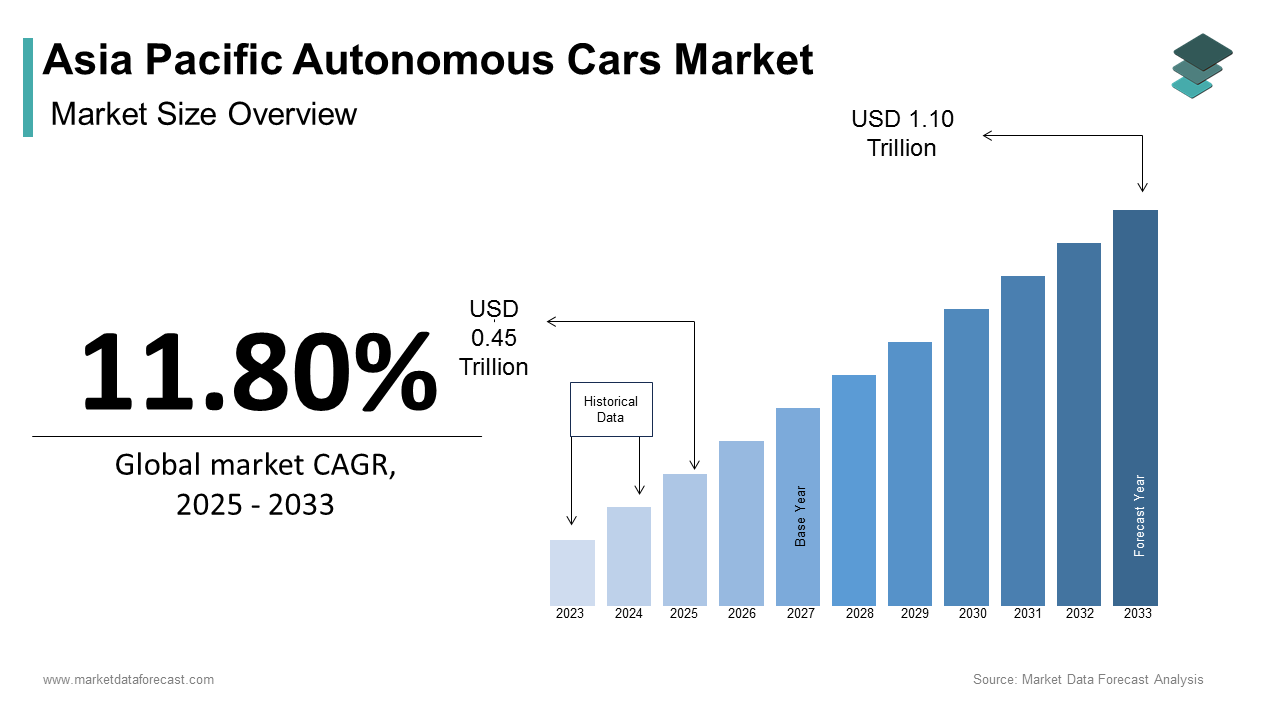
The Asia Pacific autonomous cars market size was calculated to be USD 0.40 trillion in 2024 and is anticipated to be worth USD 1.10 trillion by 2033, from USD 0.45 trillion in 2025, growing at a CAGR of 11.80% during the forecast period.
Autonomous vehicles (AVs) are reshaping transportation paradigms across countries like Japan, China, South Korea, and India, where urbanization and population density necessitate innovative mobility solutions. These cars, equipped with advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), aim to reduce traffic congestion, lower emissions, and enhance road safety.
MARKET DRIVERS
Government Initiatives and Policy Support
Government-led initiatives play a crucial role in propelling the adoption of autonomous cars in the Asia Pacific region. Countries such as China, Singapore, and South Korea have implemented comprehensive regulatory frameworks to foster innovation and testing of autonomous vehicles. By 2023, over 30 pilot zones for autonomous vehicle testing were established across Chinese cities like Beijing and Shanghai. Similarly, Singapore’s Land Transport Authority has collaborated with private companies to deploy autonomous shuttle services in designated districts, aiming to reduce reliance on private vehicles. These efforts align with broader sustainability goals. Autonomous vehicles, when integrated with electric powertrains, offer a dual solution to reducing emissions and enhancing energy efficiency. Furthermore, governments are incentivizing research and development through tax breaks and subsidies
Rising Demand for Enhanced Road Safety
Road safety remains a pressing concern in the Asia Pacific region, where accidents result in significant economic and human costs. According to the World Health Organization, road traffic injuries are the leading cause of death among individuals aged 5–29 years in the region. Autonomous vehicles, equipped with advanced sensors and AI algorithms, hold the potential to mitigate these risks by eliminating human error. Countries like India and Indonesia, characterized by high traffic congestion and insufficient infrastructure, stand to benefit immensely from autonomous technologies. Moreover, consumer awareness about safety is increasing which is further adding to the market growth.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Costs of Development and Implementation
One of the primary barriers to the widespread adoption of autonomous cars in the Asia Pacific region is the exorbitant cost associated with their development and deployment. Autonomous vehicles rely on cutting-edge technologies such as lidar sensors, radar systems, and high-performance computing units, all of which contribute significantly to manufacturing expenses. These costs are further exacerbated by the need for extensive testing and validation processes, which require substantial financial resources. For emerging economies like India and Vietnam, affordability remains a critical challenge. While urban centers may exhibit interest in autonomous mobility, rural areas often lack the economic capacity to support such innovations. This disparity shows the difficulty in achieving mass-market penetration without addressing affordability concerns. In addition, the high costs deter small and medium-sized enterprises from entering the market, limiting competition and innovation.
Technological Limitations and Infrastructure Gaps
Technological limitations and inadequate infrastructure pose another major restraint for the Asia Pacific autonomous cars market. Autonomous vehicles require robust digital infrastructure, including reliable 5G networks and smart road systems, to function optimally. Furthermore, existing road conditions in many countries remain unsuitable for autonomous driving due to poorly maintained surfaces and inconsistent signage. Another challenge lies in the complexity of urban environments. Dense metropolitan areas like Jakarta and Manila present unique obstacles such as erratic pedestrian behavior and unpredictable traffic patterns.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Expansion of Shared Mobility Services
The rise of shared mobility platforms presents a lucrative opportunity for the Asia Pacific autonomous cars market. Ride-hailing services like Grab in Southeast Asia and Didi Chuxing in China already dominate urban transportation landscapes, offering scalable frameworks for integrating autonomous vehicles. Autonomous taxis and shuttles can capitalize on this trend by providing cost-effective, on-demand transportation solutions that cater to densely populated cities. Shared autonomous fleets eliminate the need for personal ownership, aligning with shifting consumer preferences toward convenience and sustainability. Also, businesses operating logistics and delivery services stand to benefit from autonomous vehicles, particularly amid the surge in e-commerce activities.
Integration with Smart City Initiatives
Autonomous vehicles are poised to play a pivotal role in the development of smart cities across the Asia Pacific region. Governments and municipalities are increasingly investing in smart infrastructure projects designed to enhance urban living standards. For example, South Korea’s Songdo International Business District incorporates intelligent transportation systems that seamlessly integrate with autonomous mobility solutions. This convergence of autonomous vehicles and smart city ecosystems offers multifaceted benefits, including reduced traffic congestion, improved air quality, and enhanced public safety. Autonomous buses and shuttles can operate on dedicated lanes equipped with IoT sensors, ensuring efficient navigation and minimizing delays. Moreover, partnerships between automakers and tech giants like Huawei and Tencent are accelerating the deployment of Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication systems, enabling real-time interaction between vehicles and urban infrastructure.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Regulatory Uncertainty and Standardization Issues
Regulatory uncertainty remains a significant challenge for the Asia Pacific autonomous cars market, as differing national policies create fragmented legal frameworks. Each country adopts its own approach to regulating autonomous vehicles, complicating cross-border operations and standardization efforts. For instance, while Japan permits Level 3 autonomous driving under specific conditions, neighboring countries like Thailand have yet to establish clear guidelines. This lack of uniformity hinders collaboration among automakers and technology providers, who must navigate complex compliance requirements across jurisdictions. Moreover, liability issues in the event of accidents involving autonomous vehicles remain unresolved. Traditional insurance models are ill-equipped to handle scenarios where machines replace human drivers, leaving insurers and policymakers grappling with questions of accountability. Autonomous systems are vulnerable to hacking attempts, necessitating stringent security protocols.
Public Perception and Trust Deficit
Public perception and trust deficits represent another formidable challenge for the Asia Pacific autonomous cars market. Despite technological advancements, skepticism persists regarding the reliability and safety of autonomous systems. This apprehension stems from incidents involving semi-autonomous cars, such as Tesla’s Autopilot-related crashes, which have garnered widespread media attention. Cultural factors further influence public attitudes. In collectivist societies like those prevalent in East Asia, there is a strong preference for human oversight in critical tasks, including driving.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
11.80% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Autonomy, Fuel, End User, And Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis; Segment-Level Analysis; DROC, PESTLE Analysis; Porter’s Five Forces Analysis; Competitive Landscape; Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
India, China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, New Zealand, Thailand, Malaysia, Vietnam, Philippines, Indonesia, Singapore, Rest of Asia-Pacific |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Toyota, Honda, Nissan, Hyundai, Baidu, Pony.ai, Didi Chuxing, AutoX, Mitsubishi, SAIC Motor, BYD, Tata Motors, Mahindra & Mahindra, Nuro, Xpeng Motors |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Autonomy Insights

The segment of Level 2 autonomous vehicles dominated the Asia Pacific market by accounting for 60.2% of the total market share in 2024. This segment includes vehicles equipped with advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), such as adaptive cruise control and lane-keeping assistance, which provide partial automation. The widespread adoption of Level 2 autonomy is primarily driven by its affordability and practicality compared to higher levels of autonomy. One key factor fueling this dominance is the growing emphasis on road safety. In addition, government mandates have played a pivotal role. Another contributing factor is consumer acceptance.
The Level 4 segment is projected to grow at a remarkable CAGR of 35.1%. This rapid surge can be attributed to advancements in artificial intelligence and the increasing investment in smart city infrastructure across the region. Level 4 autonomy refers to vehicles capable of performing all driving functions without human intervention in specific conditions, such as urban environments or designated zones. A primary driver of this growth is the expansion of autonomous ride-hailing services. Companies like Baidu Apollo and Pony.ai have launched Level 4 robotaxis in cities like Beijing and Guangzhou, offering commuters a glimpse into the future of urban mobility. Furthermore, governments in countries like Singapore are actively supporting pilot projects, allocating substantial amount for autonomous vehicle research and development. Technological maturity also plays a critical role. Innovations in lidar sensors and high-definition mapping have significantly reduced costs, making Level 4 systems more viable.
By Fuel Insights
The Internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles segment remained the largest category in the Asia Pacific autonomous cars market. Despite the global push toward electrification, ICE vehicles continue to dominate due to their established manufacturing infrastructure and lower production costs. One major factor sustaining this dominance is the widespread availability of fueling stations. This disparity ensures that ICE-powered autonomous vehicles remain a practical choice for consumers, particularly in rural areas where charging infrastructure is sparse. Also, the cost-effectiveness of ICE technology allows automakers to integrate autonomous features without inflating prices excessively, appealing to price-sensitive markets like India and Indonesia. Another key driver is the retrofitting trend. Many existing ICE vehicles are being upgraded with autonomous capabilities, extending their lifecycle and relevance.
The electric vehicles (EVs) segment represents the rapidly advancing category in the Asia Pacific autonomous cars market, with a projected CAGR of 42%. This exponential growth is influenced by the convergence of environmental policies, technological advancements, and shifting consumer preferences. Government incentives are a primary catalyst. In China, subsidies and tax exemptions for EV purchases have led to an increase in sales over the past two years. Consumer awareness about sustainability is also rising.
By End Use Insights
The personal autonomous vehicles segment accounted for 65.8% of the market share in the Asia Pacific region in 2024. This segment’s dominance is credited to the growing demand for convenience and luxury among affluent consumers, particularly in urban centers like Tokyo, Seoul, and Sydney. A key factor driving this trend is the rise of dual-income households. Autonomous vehicles offer a seamless commuting experience, allowing users to multitask during travel. Also, the integration of AI-driven infotainment systems enhances user engagement, making personal AVs highly desirable. Urban congestion is another contributing factor. Autonomous vehicles mitigate these inefficiencies by optimizing routes and reducing travel time.
The shared mobility is emerging as the fastest-growing segment, with a CAGR of 38.4%. This expansion is fueled by the proliferation of ride-hailing platforms and the increasing popularity of shared autonomous fleets in densely populated areas. One major driver is cost efficiency. Furthermore, the rise of micro-mobility solutions, such as autonomous shuttles, addresses first-mile and last-mile connectivity challenges. Technological advancements also play a crucial role.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
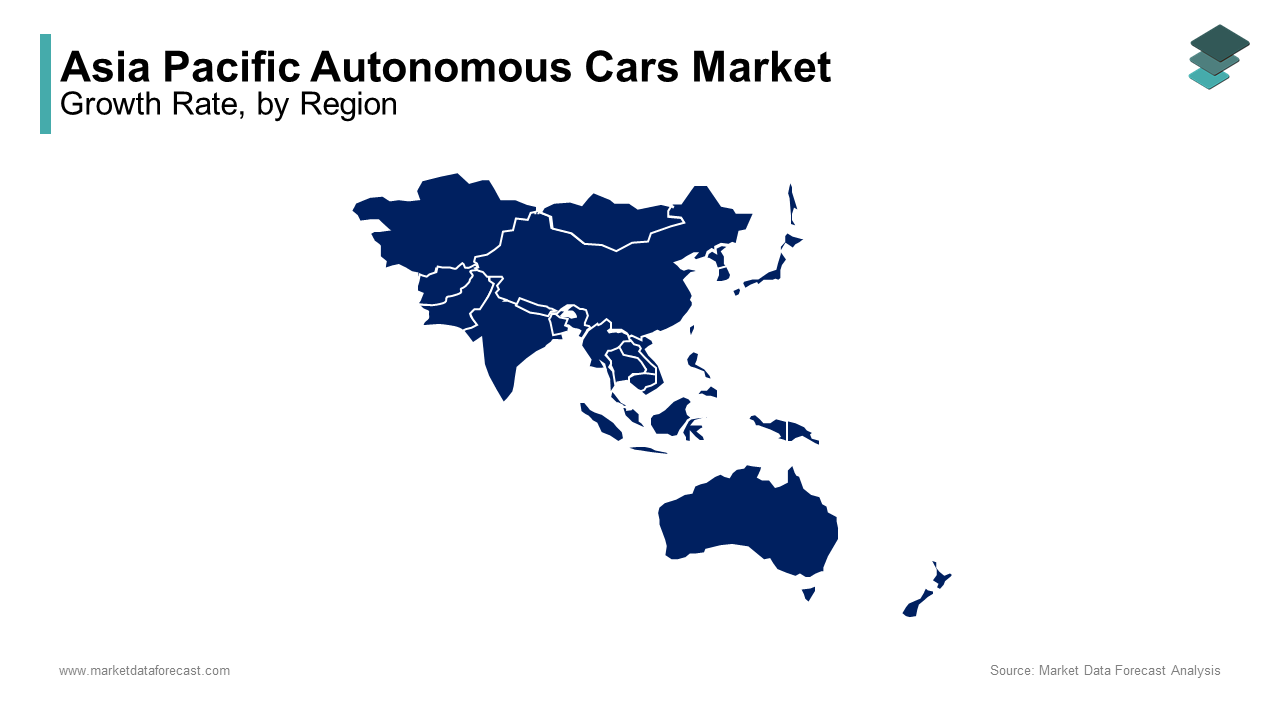
China leads the Asia Pacific autonomous cars market, commanding a 35% share, as per McKinsey & Company. The country’s dominance is driven by its robust manufacturing capabilities, extensive R&D investments, and supportive government policies. Beijing’s “Made in China 2025” initiative allocates $150 billion for autonomous vehicle development, fostering innovation and collaboration. Additionally, the presence of tech giants like Baidu and Tencent accelerates advancements in AI and sensor technologies, positioning China at the forefront of the industry.
Japan holds the second-largest share, accounting for 20% of the market , according to the Japan Automobile Manufacturers Association. The country’s leadership is rooted in its expertise in robotics and precision engineering. Toyota and Honda have pioneered Level 3 autonomous systems, which are widely adopted in domestic markets. Furthermore, Japan’s aging population fuels demand for autonomous mobility solutions, with the Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry reporting a 25% increase in elderly-focused AV projects since 2020.
South Korea ranks third, with a 15% market share, as highlighted by the Korea Automotive Technology Institute. The nation’s success is attributed to its advanced 5G infrastructure, which supports real-time data exchange for autonomous vehicles. Hyundai Motor Group’s investment of $7 billion in autonomous and electric technologies underscores the country’s commitment to innovation. Moreover, Seoul’s Smart City initiatives integrate AVs into public transportation networks, enhancing urban mobility.
India represents a burgeoning market, capturing 10% of the regional share , according to NITI Aayog. The country’s growth is fueled by its young demographic and rapid urbanization. Tata Motors’ partnership with NVIDIA to develop AI-powered AVs highlights the potential for localized solutions. Additionally, government initiatives like the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles (FAME) scheme promote sustainable mobility, driving adoption.
Australia and New Zealand collectively hold a 7% market share, as per the Australasian Railway Association. Their leadership stems from stringent safety regulations and a focus on sustainable transport. Companies like Zoox have launched pilot programs in Sydney, while Auckland’s Smart Transport initiatives leverage autonomous shuttles to reduce congestion. These efforts demonstrate the region’s proactive approach to embracing autonomous technologies.
LEADING PLAYERS IN THE ASIA PACIFIC AUTONOMOUS CARS MARKET
Toyota Motor Corporation
Toyota has emerged as a key player in the Asia Pacific autonomous cars market, leveraging its expertise in hybrid technology and robotics. The company’s focus on developing Level 3 autonomous systems, such as its Guardian and Chauffeur platforms, positions it as a leader in safety and innovation. Globally, Toyota’s contributions extend to partnerships with tech giants like NVIDIA and Uber, fostering advancements in AI-driven mobility solutions. Its commitment to sustainability aligns with global trends, ensuring its relevance in both regional and international markets.
Hyundai Motor Group
Hyundai has made significant strides in autonomous vehicle development through its subsidiary, Motional. The company’s emphasis on integrating advanced sensors and AI technologies has set new benchmarks for autonomous driving. On a global scale, Hyundai collaborates with industry leaders like Aptiv to enhance self-driving capabilities, while also investing heavily in hydrogen fuel cell technology to complement its AV initiatives. These efforts underscore Hyundai’s vision for a sustainable and connected future.
Baidu Inc.
Baidu’s Apollo platform has revolutionized autonomous mobility in China and beyond. As a pioneer in AI and machine learning, Baidu has developed cutting-edge solutions for urban transportation, including robotaxis and autonomous shuttles. Globally, Baidu partners with automakers like BMW and Ford, enabling the integration of its software into diverse vehicle models. By focusing on shared mobility and smart city ecosystems, Baidu continues to shape the trajectory of autonomous vehicle adoption worldwide.
TOP STRATEGIES USED BY KEY PLAYERS IN THE ASIA PACIFIC AUTONOMOUS CARS MARKET
Strategic Partnerships and Collaborations
Key players in the Asia Pacific autonomous cars market have prioritized forming alliances with tech companies, governments, and academic institutions. These collaborations facilitate knowledge sharing and accelerate R&D efforts. For instance, partnerships between automakers and AI firms enable the development of robust autonomous systems tailored to regional needs, enhancing innovation and scalability.
Investment in R&D and Innovation
Companies are heavily investing in research and development to overcome technological barriers and improve system reliability. By focusing on areas like sensor fusion, real-time mapping, and cybersecurity, players aim to create safer and more efficient autonomous vehicles. This strategy ensures they remain competitive while addressing consumer concerns about trust and performance.
Expansion into Shared Mobility Services
To capitalize on urbanization trends, key players are launching autonomous ride-hailing and shuttle services in major cities. By targeting shared mobility, companies can reduce costs for consumers and demonstrate the practicality of autonomous solutions. This approach not only strengthens brand presence but also fosters public acceptance of self-driving technologies.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS AND COMPETITION OVERVIEW
Major Players in the Asia Pacific autonomous cars market include Toyota, Honda, Nissan, Hyundai, Baidu, Pony.ai, Didi Chuxing, AutoX, Mitsubishi, SAIC Motor, BYD, Tata Motors, Mahindra & Mahindra, Nuro, Xpeng Motors
The Asia Pacific autonomous cars market is characterized by intense competition driven by technological innovation, regulatory support, and evolving consumer preferences. Leading automakers like Toyota, Hyundai, and Nissan are racing to develop advanced autonomous systems, while tech giants such as Baidu and Huawei leverage their expertise in AI and connectivity to disrupt traditional mobility paradigms. Startups like Pony.ai and WeRide are also gaining traction by focusing on niche applications like robotaxis and logistics. Governments across the region play a pivotal role by establishing pilot zones and funding R&D initiatives, creating a fertile ground for experimentation. However, challenges such as high development costs and infrastructure gaps persist, forcing players to adopt innovative strategies. The competitive landscape is further shaped by collaborations between incumbents and disruptors, ensuring rapid progress toward a fully autonomous future.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THE MARKET
- In March 2023, Toyota Motor Corporation partnered with Japan’s National Police Agency to test Level 4 autonomous vehicles in Tokyo. This initiative aimed to enhance road safety and demonstrate the feasibility of self-driving technologies in urban environments.
- In June 2023, Hyundai Motor Group launched its IONIQ 5 Robotaxi service in partnership with Motional in South Korea. The service marked a significant step toward commercializing autonomous ride-hailing solutions in the region.
- In September 2023, Baidu Inc. expanded its Apollo Go robotaxi operations to ten cities across China, including Shanghai and Shenzhen. This move reinforced Baidu’s leadership in shared autonomous mobility and increased public exposure to self-driving technologies.
- In November 2023, Nissan Motor Co. collaborated with DeNA to introduce autonomous delivery vehicles in Yokohama. This project targeted last-mile logistics, addressing growing e-commerce demands and showcasing the versatility of AVs.
- In January 2024, Honda Motor Co. unveiled its Level 3 autonomous Legend sedan in Australia, marking the first deployment of such technology in the country. The launch highlighted Honda’s commitment to advancing autonomous driving standards in the Asia Pacific region.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the Asia Pacific autonomous cars market has been segmented and sub-segmented based on autonomy, fuel, end user, and region.
By Autonomy
- Level 2 Autonomous Vehicles
- Level 4 Autonomous Vehicles
By Fuel
- Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) Vehicles
- Electric Vehicles (EVs)
By End Use
- Personal Autonomous Vehicles
- Shared Mobility
By Region
- India
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Thailand
- Malaysia
- Vietnam
- Philippines
- Indonesia
- Singapore
- Rest of Asia-Pacific
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the major factors driving the growth of autonomous cars in the Asia Pacific region?
Key drivers include technological advancements, government support, increasing traffic congestion, demand for safer transportation, and rising investments in smart infrastructure.
2. Which countries are leading in the adoption of autonomous vehicles in Asia Pacific?
China, Japan, and South Korea are the front-runners in terms of adoption and investment in autonomous vehicle technologies.
3. Who are the key players in the Asia Pacific Autonomous Cars Market?
Some major players include Toyota, Honda, Nissan, Hyundai, Baidu, Pony.ai, Didi Chuxing, AutoX, SAIC Motor, and Xpeng Motors.
4. How is government regulation impacting the market?
Government initiatives and policies across countries like China, Japan, and South Korea are supporting R&D and testing of autonomous vehicles, though regulatory frameworks are still evolving.
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]