Asia Pacific Dry Eye Syndrome Market Size, Share, Growth, Trends, And Forecasts Report, Segmented Product, Distribution, And By Country (India, China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, New Zealand, Thailand, Malaysia, Vietnam, Philippines, Indonesia, Singapore and Rest of APAC), Industry Analysis From 2025 to 2033
Asia Pacific Dry Eye Syndrome Market Size
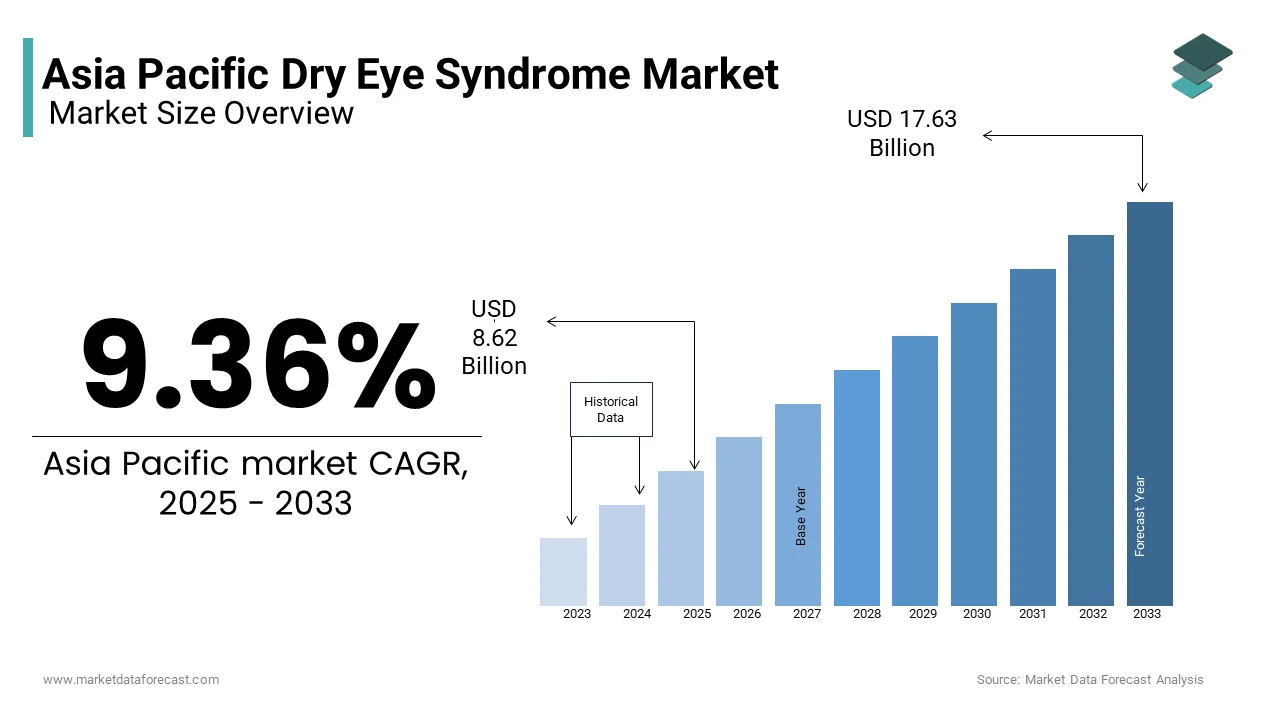
The Asia Pacific dry eye syndrome market was valued at USD 7.88 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 8.62 billion in 2025 from USD 17.63 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 9.36% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2033.
The Asia Pacific dry eye syndrome market is witnessing significant traction due to the rising prevalence of ocular disorders, coupled with growing awareness about eye health. As per a study published by the Asia Pacific Academy of Ophthalmology, over 30% of adults above the age of 50 in the region experience symptoms associated with dry eye syndrome. Countries like Japan, China, and South Korea are at the forefront of this trend, driven by their aging populations and advanced healthcare infrastructure. According to a report by the World Health Organization, approximately 65% of individuals in urban areas of the Asia Pacific region spend more than six hours daily on digital devices, contributing to dry eye symptoms.
MARKET DRIVERS
Growing Aging Population
One of the primary drivers of the Asia Pacific dry eye syndrome market is the rapidly aging population in the region. According to the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, the number of individuals aged 65 and above in the Asia Pacific region is expected to reach 535 million by 2030. This demographic shift is critical because dry eye syndrome predominantly affects older adults, with studies indicating that nearly 70% of people over the age of 65 exhibit symptoms of the condition. Age-related factors such as reduced tear production and hormonal changes contribute significantly to the prevalence of dry eye syndrome. Furthermore, countries like Japan, which has one of the oldest populations globally, are witnessing heightened demand for effective treatments. The Japanese Ministry of Health estimates that approximately 22 million people in the country suffer from dry eye syndrome, creating a robust market for innovative therapies and products. The increasing geriatric population not only amplifies the patient pool but also drives investments in research and development by ensuring the availability of advanced treatment options.
Urbanization and Digital Device Usage
Urbanization and the widespread use of digital devices are other major drivers shaping the dry eye syndrome market. Prolonged screen exposure reduces blink rates and increases tear evaporation, which leads to dry eye symptoms. A study conducted by the Singapore National Eye Centre found that 40% of office workers in metropolitan areas reported experiencing dry eye discomfort. This trend is particularly pronounced in tech-savvy nations like South Korea and India, where digital device penetration is exceptionally high. Moreover, urban environments often have higher levels of air pollution, which exacerbates ocular irritation. The convergence of these factors has spurred demand for preventive measures, such as blue light-blocking glasses, and therapeutic solutions, including lubricating eye drops and prescription medications.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Cost of Advanced Treatments
A significant restraint in the Asia Pacific dry eye syndrome market is the high cost associated with advanced diagnostic tools and treatments. For instance, procedures like punctal plug insertion or laser-assisted therapies can cost upwards of $1,000 per session, which is making them inaccessible to a large segment of the population. According to a survey conducted by the Asian Healthcare Foundation, less than 30% of patients in rural areas of Southeast Asia can afford premium treatments for chronic dry eye. Even in urban centers, where income levels are higher, out-of-pocket expenses remain a deterrent. The lack of comprehensive insurance coverage for ophthalmic conditions further compounds the issue. In countries like India and Indonesia, where healthcare spending is heavily reliant on personal savings, the affordability gap limits market expansion. Consequently, many patients resort to over-the-counter remedies, which may provide temporary relief but fail to address underlying causes. This economic barrier not only restricts access to cutting-edge therapies but also slows the adoption of emerging technologies in the region.
Limited Awareness and Misdiagnosis
Another key restraint is the limited awareness and frequent misdiagnosis of dry eye syndrome, particularly in rural and semi-urban areas. According to a study published in the Journal of Ophthalmology Asia-Pacific, over 50% of dry eye cases go undiagnosed due to a lack of understanding among both patients and healthcare providers. Many individuals attribute symptoms like redness and irritation to fatigue or allergies, which delays proper medical intervention. Additionally, primary care physicians in remote regions often lack specialized training in diagnosing ocular conditions, which leads to incorrect prescriptions or ineffective treatments. The situation is exacerbated by cultural beliefs in some communities, where eye discomfort is dismissed as a minor issue. For example, in parts of rural China, traditional remedies are preferred over clinical consultations, reducing the likelihood of accurate diagnosis.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Rising Adoption of Telemedicine for Eye Care
The integration of telemedicine into eye care presents a substantial opportunity for the Asia Pacific dry eye syndrome market. Telemedicine bridges this gap by enabling virtual consultations, remote monitoring, and personalized treatment plans. For instance, platforms like Practo and Ping An Good Doctor in India and China, respectively, have seen a surge in users seeking advice for dry eye symptoms. This trend creates opportunities for pharmaceutical companies and device manufacturers to collaborate with telemedicine providers by offering bundled solutions such as online prescriptions for lubricants or home-delivered diagnostic kits.
Development of Biologic Therapies
Another promising opportunity lies in the development and commercialization of biologic therapies tailored for dry eye syndrome. Unlike conventional treatments, biologics target the root causes of inflammation and immune dysregulation, which is offering long-term relief. According to a report by the Biotechnology Innovation Organization, the global pipeline for biologic-based dry eye treatments includes over 20 candidates in various stages of clinical trials, with several being pioneered in the Asia Pacific region. South Korea’s Samsung Bioepis and Japan’s Santen Pharmaceuticals are at the forefront of this innovation, which is investing heavily in recombinant proteins and monoclonal antibodies. Clinical data from Phase III trials indicate that biologics can reduce symptom severity by up to 60% within three months of initiation by surpassing the efficacy of traditional therapies. The growing emphasis on precision medicine, coupled with supportive regulatory frameworks in countries like Australia and Singapore, positions the region as a hub for biotech advancements.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Regulatory Hurdles in Emerging Markets
Navigating complex regulatory landscapes poses a significant challenge for the Asia Pacific dry eye syndrome market in emerging economies. Each country has its own set of approval processes, clinical trial requirements, and quality standards by creating barriers for multinational companies seeking to introduce innovative products. For example, in India, the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization mandates extensive local clinical trials even for treatments approved elsewhere, delaying market entry by an average of two years, according to Deloitte Insights. Similarly, in Indonesia, bureaucratic inefficiencies often prolong the registration process for ophthalmic drugs and devices. These delays stifle innovation and limit patient access to cutting-edge therapies. Furthermore, inconsistent enforcement of intellectual property laws in some regions discourages investment in research and development. Companies must allocate additional resources to comply with diverse regulations, increasing operational costs and complicating market strategies. This fragmented regulatory environment remains a persistent obstacle to achieving widespread adoption of novel treatments.
Environmental Factors Worsening Symptoms
Environmental degradation across the Asia Pacific region exacerbates dry eye syndrome, which presents a unique challenge for market stakeholders. According to data from the Air Quality Life Index, air pollution levels in major cities like Delhi, Beijing, and Jakarta exceed World Health Organization guidelines by over 10 times, which is leading to increased cases of ocular irritation. Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) disrupt the tear film stability, worsening symptoms for millions of patients. A study by the Chinese Academy of Sciences revealed that urban residents exposed to high pollution levels were 2.5 times more likely to develop chronic dry eye compared to those in cleaner environments. Climate change further compounds the issue, with rising temperatures and humidity fluctuations altering tear evaporation rates. While environmental factors drive demand for treatments, they also complicate prevention efforts, as mitigating external triggers requires systemic policy changes beyond the control of healthcare providers.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2032 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
9.36% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Product, Distribution, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
India, China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, New Zealand, Thailand, Malaysia, Vietnam, Philippines, Indonesia, Singapore, and the Rest of APAC |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
AbbVie Inc. (Ireland), Alcon (Switzerland), Novartis AG (Switzerland), Santen Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Japan), OASIS Medical (U.S.), Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. (India), Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Otsuka Holdings, Co., Ltd) (Japan), Sentiss Pharma Pvt. Ltd. (India), Johnson & Johnson Vision Care, Inc. (Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc.) (U.S.), VISUfarma (Netherlands). |
SEGMENT ANALYSIS
By Product Insights
The artificial tears and lubricants segment accounted in holding 45.3% of the Asia Pacific dry eye syndrome market share in 2024. This segment's prominence is driven by its widespread availability, affordability, and ease of use by making it the first line of treatment for mild to moderate dry eye symptoms. A key factor fueling this dominance is the increasing prevalence of screen-related ocular fatigue. According to the International Telecommunication Union, over 70% of urban dwellers in the region spend more than five hours daily on digital devices, which is leading to heightened demand for over-the-counter solutions like artificial tears. Additionally, the growing geriatric population plays a pivotal role. Data from the United Nations indicates that nearly 30% of adults aged 60 and above experience chronic dry eye, with many relying on lubricants for symptomatic relief.

The Anti-inflammatory products are projected to grow at the fastest compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.3% during the forecast period. This rapid expansion is attributed to the rising awareness of inflammation as a root cause of severe dry eye syndrome among patients with underlying conditions like Sjögren’s syndrome or rheumatoid arthritis. According to the Asia Pacific Rheumatology Association, autoimmune disorders affect over 5% of the adult population in the region, with dry eye being a common comorbidity. The increasing adoption of targeted therapies, such as cyclosporine and lifitegrast, is another factor boosting the growth of the segment.
By Distribution Channel
The retail pharmacies segment was the largest and held 49.1% of the Asia Pacific dry eye syndrome market share in 2024. This dominance is primarily due to their widespread presence and accessibility, especially in rural and semi-urban areas where hospital pharmacies are scarce. According to the World Health Organization, 70% of the region's population resides in areas served by retail pharmacies by ensuring easy access to over-the-counter treatments like artificial tears. Another contributing factor is the strategic partnerships between manufacturers and retailers, which facilitate promotional campaigns and product discounts. For instance, in India, retail pharmacies collaborated with multinational brands to launch awareness drives about dry eye syndrome.
The online pharmacies segment is swiftly emerging with a CAGR of 15.8% in the coming years. This exponential growth is fueled by the rapid digital transformation across the region and the increasing preference for e-commerce platforms. The rise of telemedicine has further accelerated this trend, with patients seeking end-to-end solutions for their healthcare needs. Additionally, competitive pricing and subscription models offered by platforms like PharmEasy in India and JD Health in China attract cost-conscious consumers. Furthermore, regulatory reforms in countries like Australia and South Korea have streamlined the approval process for online pharmacies by encouraging investments in logistics and customer service.
COUNTRY ANALYSIS
Top Leading Countries in The Market
Japan was the top performer in the Asia Pacific dry eye syndrome market with a 28.3% share in 2024. The country's aging population, with over 28% of citizens aged 65 or older, is escalating the demand for advanced treatments. According to the National Institute of Population and Social Security Research, Japan has one of the highest prevalences of dry eye globally, which is affecting nearly 22 million individuals. Government initiatives, such as subsidies for ophthalmic research and public awareness campaigns that bolster the growth of the market.

China was positioned second by holding 22.4% of the Asia Pacific dry eye syndrome market share in 2024. The country's massive urban population, coupled with high air pollution levels, exacerbates dry eye symptoms. Beijing’s Air Quality Monitoring Agency reports that PM2.5 concentrations exceed WHO guidelines by 12 times, which is impacting ocular health. Additionally, the proliferation of digital devices fuels demand for preventive measures. Tencent Research estimates that over 900 million Chinese citizens use smartphones daily, contributing to increased screen-related ocular fatigue. The government’s push for universal healthcare coverage has also expanded access to affordable treatments, with domestic manufacturers capitalizing on low-cost production capabilities.
South Korea's dry eye syndrome market growth is driven by its technologically advanced healthcare system and high awareness levels. The country’s emphasis on aesthetics and eye health has spurred innovation in dry eye treatments. According to the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety, South Korea approved six new ophthalmic drugs in 2022 alone, which reflects its commitment to addressing unmet medical needs. Moreover, the popularity of K-beauty trends has led to increased interest in eye care products, with exports of premium lubricants growing by 30% annually. Partnerships between hospitals and tech firms have also enabled the development of AI-driven diagnostic tools, enhancing patient outcomes.
Australia’s dry eye syndrome market growth is due to the robust healthcare infrastructure and stringent regulatory standards, as noted by the Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration. The country’s arid climate, particularly in regions like Western Australia, contributes to dry eye prevalence.
India's dry eye syndrome market is rapidly growing with the rapidly;y increasing population, combined with increasing urbanization, creating a substantial patient pool. Over 60% of urban Indians suffer from screen-induced dry eye, according to a study by the All India Institute of Medical Sciences. Rising disposable incomes and expanding insurance coverage have also fueled demand for premium treatments.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
AbbVie Inc. (Ireland), Alcon (Switzerland), Novartis AG (Switzerland), Santen Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Japan), OASIS Medical (U.S.), Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd. (India), Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Otsuka Holdings, Co., Ltd) (Japan), Sentiss Pharma Pvt. Ltd. (India), Johnson & Johnson Vision Care, Inc. (Johnson & Johnson Services, Inc.) (U.S.), VISUfarma (Netherlands). are the market players that are dominating the Asia Pacific dry eye syndrome market.
Top Players in The Market
Santen Pharmaceuticals
Santen Pharmaceuticals, a Japan-based leader in ophthalmology, has established itself as a cornerstone of innovation in the dry eye syndrome market. The company’s contributions extend beyond the Asia Pacific region, shaping global standards for ocular care. Santen’s focus on research and development has led to groundbreaking therapies, such as cyclosporine ophthalmic solutions, which address inflammation-related dry eye. Its presence in over 60 countries amplifies its influence, making it a key driver of advancements in the global dry eye treatment landscape.
Novartis AG
Novartis AG, a Swiss multinational, has made significant strides in the Asia Pacific dry eye syndrome market through its commitment to precision medicine. The company’s portfolio includes innovative biologic therapies designed to target the underlying causes of chronic dry eye. Novartis leverages its expertise in biotechnology to introduce treatments that offer long-term relief, setting new benchmarks in therapeutic efficacy.
Allergan (AbbVie)
Allergan, now part of AbbVie, has been instrumental in advancing the dry eye syndrome market with its flagship product, Restasis. Known for its pioneering work in anti-inflammatory treatments, Allergan has consistently addressed unmet medical needs across the Asia Pacific region. The company’s emphasis on patient-centric approaches has led to the development of user-friendly formulations and educational campaigns.
Top Strategies Used By Key Players In The Market
Strategic Collaborations
Key players in the market have increasingly embraced strategic collaborations to enhance their competitive edge. By partnering with local healthcare providers, research institutions, and technology firms, companies can leverage shared expertise to develop innovative solutions tailored to regional needs. For instance, alliances with telemedicine platforms enable seamless integration of diagnostic tools and treatments, improving patient access to care. These partnerships also facilitate knowledge exchange, driving advancements in areas like biologics and personalized medicine, while ensuring compliance with regional regulatory frameworks.
Product Diversification
Product diversification is another critical strategy employed by industry leaders to cater to varying patient needs. Companies are expanding their portfolios to include advanced formulations, such as preservative-free lubricants and biologic therapies, alongside traditional treatments. This approach not only addresses specific symptoms but also appeals to a broader demographic, including tech-savvy urban professionals and aging populations.
Digital Transformation
Digital transformation has become a cornerstone for strengthening market presence. Leading companies are investing in AI-driven diagnostic tools, mobile applications, and online pharmacies to streamline patient care. These innovations not only enhance diagnostic accuracy but also provide real-time monitoring and personalized treatment plans.
COMPETITION OVERVIEW
The Asia Pacific dry eye syndrome market is characterized by intense competition, driven by the presence of both global giants and regional players striving to establish dominance. Multinational corporations like Santen Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, and Allergan bring technological prowess and extensive R&D capabilities, enabling them to introduce breakthrough therapies that set industry benchmarks. Simultaneously, domestic players leverage their understanding of local preferences and cost-effective manufacturing to carve out significant market shares. This dynamic creates a dual-layered competitive landscape where innovation and affordability coexist. The market is further fueled by rising patient awareness and the growing prevalence of ocular disorders, which is prompting companies to adopt aggressive marketing strategies and expand their distribution networks. Additionally, the emergence of telemedicine and e-commerce platforms has intensified competition, as players vie to capitalize on digital trends. Regulatory challenges and environmental factors add complexity, requiring firms to balance compliance with innovation.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THE MARKET
- In March 2023, Santen Pharmaceuticals launched a new preservative-free artificial tear formulation in Japan and South Korea. This move was aimed at addressing the growing demand for safer and more comfortable dry eye solutions among aging populations.
- In June 2023, Novartis AG partnered with a leading telemedicine provider in India to offer virtual consultations for dry eye syndrome. This collaboration enabled the company to reach remote areas and enhance patient access to its biologic therapies.
- In September 2023, Allergan introduced an AI-powered diagnostic tool in Australia to improve the accuracy of dry eye diagnoses. The tool was integrated into hospital pharmacies by streamlining the patient journey from diagnosis to treatment.
- In November 2023, Pfizer acquired a South Korean startup specializing in biologic treatments for ocular inflammation. This acquisition strengthened Pfizer’s pipeline and expanded its footprint in the Asia Pacific dry eye market.
- In January 2024, Johnson & Johnson collaborated with a Singapore-based e-commerce platform to launch a subscription service for its lubricating eye drops. This initiative targeted young professionals experiencing screen-induced dry eye, enhancing customer retention through convenience.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the Asia Pacific dry eye syndrome market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Product
- Anti-inflammatory Products
- Cyclosporin
- Corticosteroids
- Others
- Artificial Tears and Lubricants
- Others
By Distribution Channel
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Retail Pharmacies
- Online Pharmacies
- Others
By Country
- India
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Thailand
- Malaysia
- Vietnam
- Philippines
- Indonesia
- Singapore
- Rest of APAC
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the core growth driver of the dry eye syndrome market in Asia Pacific?
The primary engine of growth is digital strain. In Asia Pacific, screen exposure among the population under 40 has increased by over 40% in the last five years. This has resulted in a sharp rise in lifestyle-induced dry eye cases, especially in tech-centric urban hubs like Seoul, Bengaluru, and Singapore.
Which demographic is becoming a major contributor to market demand?
A unique shift is occurring: millennials and Gen Z (ages 20–40) are increasingly driving demand. Unlike traditional age-related dry eye markets, Asia Pacific sees early-onset symptoms caused by overuse of screens, cosmetic lens usage, and polluted urban environments.
How are local innovation and R&D shaping the treatment landscape?
Asian countries like Japan and South Korea are pioneering biomimetic eye drop technologies and natural tear film stabilizers. Japan, in particular, is focusing on enzyme-based treatments derived from traditional herbal sources, tapping into a market that values natural and hybrid therapies.
What’s the most overlooked segment of growth in this market?
Veterinary ophthalmology is a niche but rapidly emerging segment. With rising pet ownership in urban centers and increasing awareness of animal health, treatments for dry eye in dogs and cats (especially brachycephalic breeds) are creating a parallel demand for animal-grade formulations.
How is distribution evolving in rural vs. urban markets?
Urban areas are shifting to e-commerce-based distribution, especially via mobile pharmacy apps and tele-optometry. In contrast, rural markets in countries like India and Indonesia are seeing growth through public health campaigns, where dry eye treatment is bundled with general vision care kits in outreach programs.
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]
