Asia Pacific Electric Fuse Market Research Report – Segmented By Voltage ( Low Voltage Fuse, High Voltage Fuses) Current Rating, Application, End-User, Country (India, China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, New Zealand, Thailand, Malaysia, Vietnam, Philippines, Indonesia, Singapore and Rest of APAC) - Industry Analysis From 2025 to 2033
Asia Pacific Electric Fuse Market Size
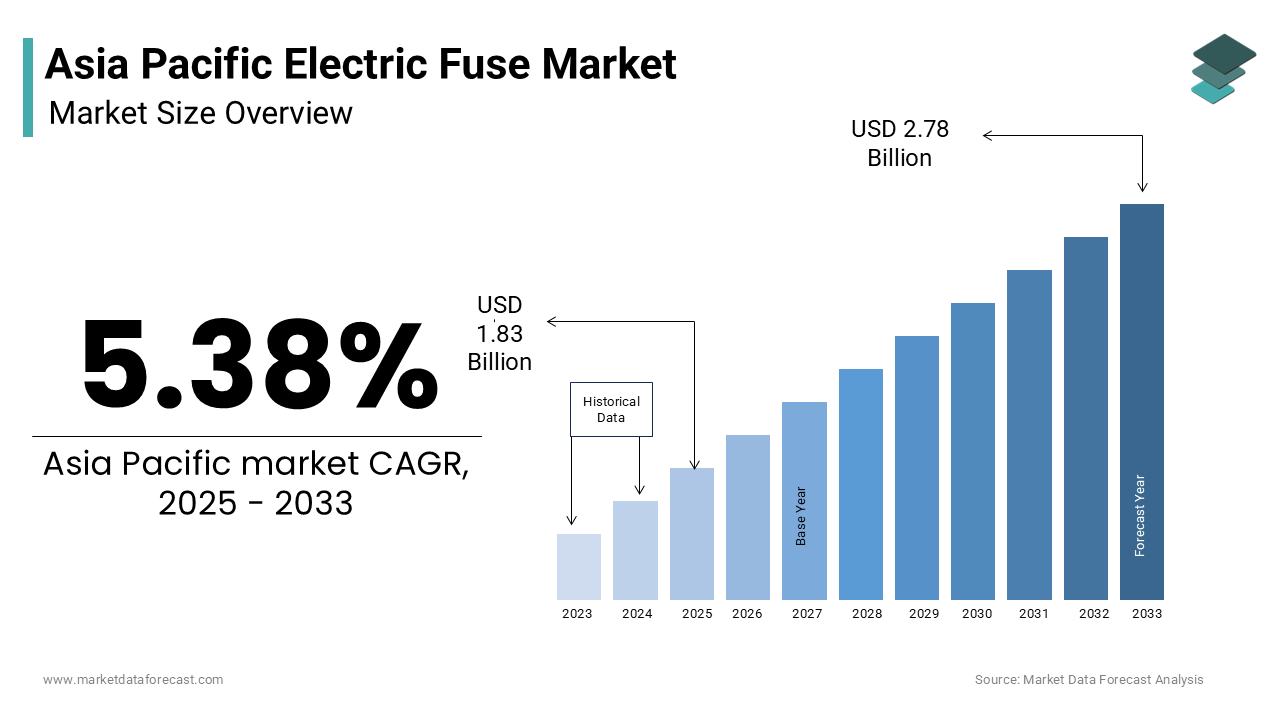
The Asia Pacific electric fuse market was worth USD 1.74 billion in 2024. The Asia Pacific market is expected to reach USD 2.78 billion by 2033 from USD 1.83 billion in 2025, rising at a CAGR of 5.38% from 2025 to 2033.
An electric fuse is a safety device designed to protect electrical circuits from overcurrent by interrupting the flow of electricity when abnormal conditions occur. In the Asia Pacific region, fuses are widely used across residential, commercial, industrial, and utility applications to safeguard equipment, wiring systems, and electronic devices. These components play a crucial role in ensuring operational safety, minimizing electrical hazards, and preventing costly system failures.
Also, the demand for electric fuses in Asia Pacific is being driven by rapid urbanization, infrastructure modernization, and the increasing deployment of automated and energy-efficient systems. As countries like India, China, and Indonesia invest heavily in smart grid development and electrification programs, the need for reliable circuit protection solutions has grown significantly.
In addition, expanding manufacturing sectors and rising investments in renewable energy installations are reinforcing the need for high-performance fuses that can handle fluctuating loads and variable voltage levels.
MARKET DRIVERS
Expansion of Industrial Automation and Manufacturing Infrastructure
One of the primary drivers of the Asia Pacific electric fuse market is the rapid expansion of industrial automation and manufacturing infrastructure. As countries in the region pursue industrial modernization strategies particularly in China, India, Thailand, and Vietnam the reliance on automated machinery, robotics, and precision electronics has surged, necessitating robust electrical protection systems. Electric fuses serve as essential components in control panels, motor drives, and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) used in production lines and factory automation. Like, manufacturing output in Asia Pacific increased notably between 2021 and 2023, reflecting heightened demand for secure and efficient electrical systems. In China, where industrial robot installations accounted for a major share of global deployments in recent years, the integration of high-speed, low-voltage fuses has become critical to prevent damage from short circuits and equipment malfunctions. Moreover, the proliferation of small-to-medium enterprises (SMEs) adopting automated production techniques has further expanded the application base for electric fuses.
Rising Demand for Electrical Safety in Residential and Commercial Sectors
Another major driver of the Asia Pacific electric fuse market is the growing emphasis on electrical safety in residential and commercial buildings. With rapid urbanization and a surge in construction activities, especially in emerging economies like Indonesia, the Philippines, and Vietnam, there is an increasing need for standardized electrical protection measures to mitigate fire risks and ensure occupant safety. Electric fuses are integral to electrical distribution boards used in homes, offices, shopping malls, and healthcare facilities, where they prevent overloads and short circuits that could lead to hazardous incidents. According to the World Bank, Asia Pacific is experiencing one of the fastest rates of urban population growth globally, with cities expected to accommodate an additional 1.2 billion people by 2050. This demographic shift translates into heightened demand for safe and code-compliant electrical installations in new constructions. Governments across the region have responded by implementing stricter building codes and electrical safety regulations. For instance, in Australia, the Australian Standard AS/NZS 3000 mandates the use of appropriate fusing devices in all new residential developments.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
Availability of Alternative Circuit Protection Technologies
One of the key restraints affecting the Asia Pacific electric fuse market is the increasing availability and adoption of alternative circuit protection technologies such as circuit breakers and residual current devices (RCDs). Unlike traditional fuses, which require replacement after tripping, these alternatives offer reusable, resettable, and often remotely controllable protection mechanisms, making them more attractive in certain applications. This trend is particularly evident in Japan, South Korea, and Singapore, where building codes favor circuit breakers for their adaptability to smart home and energy management systems. Also, the integration of digital monitoring capabilities in advanced circuit breakers allows for real-time diagnostics and predictive maintenance an advantage that conventional fuses do not offer. As a result, electrical engineers and system designers in multinational corporations operating in Asia Pacific are increasingly specifying circuit breakers over fuses in new infrastructure projects.
Fluctuations in Raw Material Prices Affecting Production Costs
Fluctuations in raw material prices pose a significant challenge to the stability and profitability of the Asia Pacific electric fuse market. The production of electric fuses relies heavily on metals such as copper, silver, aluminum, and zinc, all of which have experienced considerable price volatility in recent years due to geopolitical tensions, supply chain disruptions, and trade policy changes. Companies in China, India, and Malaysia are key production hubs for fuses and have had to absorb or pass on these higher costs, affecting both pricing competitiveness and profit margins. In addition, rare materials such as quartz sand, used in high-voltage fuse elements, have also seen supply constraints, particularly from China, which is a dominant supplier. Logistics bottlenecks at major ports and inflationary pressures in transportation have further exacerbated cost uncertainties.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Growth of Renewable Energy Installations Requiring Reliable Circuit Protection
A significant opportunity for the Asia Pacific electric fuse market lies in the ongoing expansion of renewable energy generation systems, including solar photovoltaic (PV) farms, wind turbines, and battery storage installations. These clean energy sources introduce unique electrical protection challenges due to variable load generation, frequent switching, and potential fault currents that require specialized fuse solutions. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), Asia Pacific accounted for over 60% of global renewable energy capacity additions in 2023, led by China, India, and Japan. Each of these installations requires fuses at multiple points—from inverters and charge controllers to DC combiner boxes—to ensure safe and efficient operation. Solar PV systems, in particular, rely heavily on high-voltage DC fuses to protect against reverse currents and module faults. Wind farms, on the other hand, utilize time-delay and semiconductor fuses to safeguard converters and turbine generators from electrical surges.
Increasing Adoption of Electric Vehicles and Charging Infrastructure
The rising adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and the parallel build-out of EV charging networks present a compelling opportunity for the Asia Pacific electric fuse market. As EV sales accelerate in countries like China, South Korea, and Thailand, so does the need for robust electrical protection components in onboard systems, battery packs, and charging stations. Electric fuses play a critical role in protecting vehicle traction inverters, onboard chargers, and high-voltage battery systems from overcurrent situations that could compromise performance or safety. According to BloombergNEF, EV sales in Asia Pacific surpassed 12 million units in 2023, representing more than half of the global market, thereby amplifying the demand for automotive-grade fuses. Beyond vehicles, the expansion of public and private EV charging infrastructure further boosts fuse requirements. Fast-charging stations, especially those using high-power direct current (DC) configurations, require high-capacity fuses to manage extreme electrical loads safely. In response, manufacturers are developing compact, high-breaking capacity fuses specifically for EV applications, ensuring compliance with international standards such as ISO 8820.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Counterfeit Products and Quality Compliance Issues
A pressing challenge confronting the Asia Pacific electric fuse market is the prevalence of counterfeit and substandard products infiltrating the supply chain. The presence of low-quality fuses that fail to meet safety and performance standards poses serious risks, including electrical fires, equipment failure, and personal injury. According to the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), non-compliant electrical components account for a significant portion of electrical accidents in the region, with fuses frequently cited as contributing factors. Many counterfeit products mimic branded items but lack proper testing, certification, and quality assurance procedures required by national and international standards. These inferior products often bypass regulatory checks and are sold at lower prices, misleading buyers who prioritize cost savings over safety.
Rapid Technological Evolution Threatening Conventional Fuse Designs
The electric fuse market in Asia Pacific faces a fundamental challenge due to the rapid pace of technological evolution in circuit protection systems. As digitalization, smart grid infrastructure, and advanced monitoring tools gain traction, traditional passive fuse designs are increasingly viewed as outdated compared to intelligent, digitally integrated alternatives. Modern circuit breaker technologies now incorporate features such as remote diagnostics, self-resetting capabilities, and real-time data analytics—capabilities that standard fuses lack. According to a report by the International Council on Large Electric Systems (CIGRE), power utilities and industrial operators are gradually shifting toward adaptive protection systems that offer greater flexibility and responsiveness. This transition is particularly pronounced in developed markets such as Japan and South Korea, where smart city initiatives and Industry 4.0 frameworks prioritize interconnected and self-regulating electrical networks. Even in emerging economies like Malaysia and Vietnam, large-scale infrastructure projects are incorporating programmable logic controllers and smart relays that reduce dependency on manual fuse interventions.
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Voltage Insights
The low voltage fuses segment dominated the Asia Pacific electric fuse market in 2024. This dominance is due to their widespread use in residential and commercial electrical systems, small industrial applications, and consumer electronic devices that operate below 1,000 volts. According to the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), a large majority of household appliances and lighting circuits rely on low-voltage protection mechanisms, making these fuses indispensable across all urban and rural electrification initiatives. The rapid expansion of housing projects in countries like India, Indonesia, and Vietnam has further intensified the demand for standard cartridge and blade-type fuses used in residential distribution boards. In addition, the growth of the electronics manufacturing sector in China, South Korea, and Malaysia has increased the incorporation of miniature fuses in printed circuit boards (PCBs) and power supplies. Furthermore, government-led rural electrification programs such as India’s Saubhagya Scheme have significantly boosted deployment of low-voltage fuse units in new grid connections.
The High voltage fuses are emerging as the fastest-growing segment in the Asia Pacific electric fuse market, projected to expand at a CAGR of 6.8% between 2025 and 2033. This is primarily driven by increasing investments in utility-scale renewable energy projects, high-voltage transmission infrastructure, and industrial automation systems that require robust circuit protection at elevated voltage levels. In China alone, state-backed green energy policies have led to the commissioning of over 100 gigawatts of new solar and wind capacity annually, each requiring dedicated high-voltage protection components. Japan has also seen a surge in high-voltage fuse adoption due to its efforts to modernize aging power infrastructure and integrate hydrogen-based energy systems. Similarly, Australia’s renewable energy zones (REZs) are being equipped with advanced fuse technologies to manage large-scale power injections into the national grid.
By Current Rating Insights
The 500 A to 2,000 A current rating segment held the largest share of the Asia Pacific electric fuse market by capturing 40.6% of total demand in 2024. This range caters to a broad spectrum of applications including HVAC systems, motor drives, industrial control panels, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), and medium-capacity transformers, making it highly versatile across end-use sectors. These fuses are particularly crucial in manufacturing plants where machinery demands stable power flow while ensuring safety against sudden surges. India’s Make in India initiative has spurred significant demand for this category, especially in textile mills, food processing units, and automotive assembly lines where load management is critical. Moreover, rising investments in commercial real estate developments across cities like Jakarta, Ho Chi Minh City, and Manila have increased the demand for circuit protection in elevators, escalators, and building automation systems.
The > 4,000 A fuse segment is currently experiencing the highest growth in the Asia Pacific market, projected to expand at a CAGR of 7.2% through 2033. This surge is mainly attributed to the increasing deployment of heavy-duty industrial equipment, high-power traction systems, and large-scale renewable energy installations that require extreme current protection capabilities. According to a study by the International Council on Large Electric Systems (CIGRE), high-current fuses are essential in protecting main power transformers, converter stations, and substation busbars in ultra-high voltage (UHV) transmission systems—many of which are being rolled out across China and India to support nationwide electrification goals. China leads the deployment of UHV direct current (UHVDC) transmission lines. In parallel, Japan’s push toward hydrogen-powered rail networks has resulted in increased usage of high-current fuses in train propulsion systems.
By Application Insights
The industrial usage accounted for the largest segment in the Asia Pacific electric fuse market by contributing 35.1% of total demand in 2024. This dominance is driven by the extensive reliance on fuses in manufacturing plants, process industries, and automation systems, where electrical integrity is critical to continuous operations. According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), Asia Pacific remains the world’s leading manufacturing hub, producing over 55% of global industrial output in 2023. From textile mills in Bangladesh to semiconductor fabrication units in South Korea, the demand for standardized and high-performance fuses continues to rise. Similarly, India is witnessing growing deployment of fuses in steel plants, cement factories, and chemical refineries, where short-circuit protection is vital for worker safety and equipment longevity.
The utility applications are emerging as the fastest-growing segment in the Asia Pacific electric fuse market, expected to expand at a CAGR of 7.5%. This progress is fueled by the ongoing modernization of power grids, integration of distributed energy resources, and expansion of rural electrification programs across the region. Australia’s grid operators, such as TransGrid and Powerlink Queensland, are incorporating high-voltage fuses into new renewable energy zones (REZs) to enhance network stability. India’s Rural Electrification Corporation (REC) has mandated the installation of protective fuse units in newly established feeder lines serving remote villages, contributing to the segment's strong momentum.
By End Use Insights
The electrical appliances represent the largest end-use segment in the Asia Pacific electric fuse market by commanding 25.4% of total demand in 2024. This dominance is attributed to the massive production and consumption of home and kitchen appliances such as refrigerators, washing machines, air conditioners, water heaters, and microwave ovens across the region. Each of these appliances incorporates internal fuses to prevent overheating, short circuits, and component damage. Like India’s Bureau of Energy Efficiency mandates minimum safety standards, including fuse integration, for all appliances sold under its Star Labeling Program. South Korea and Japan, known for their advanced consumer electronics sectors, continue to drive demand for miniature and surface-mount fuses used in compact and high-efficiency appliances.
Automotive applications are witnessing the highest growth in the Asia Pacific electric fuse market, projected to expand at a CAGR of 8.1% through 2033. This growth is primarily fueled by the rapid electrification of transportation, increasing vehicle complexity, and the proliferation of onboard electronics requiring circuit protection. Each EV contains numerous fuses to protect battery management systems, traction inverters, and charging circuits—a stark increase compared to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. Japanese automakers such as Toyota and Honda are integrating higher numbers of semiconductor fuses in hybrid and fuel cell vehicles to enhance electrical safety. Additionally, advancements in autonomous driving and connected car technologies have led to increased fuse requirements for sensors, cameras, and control modules.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
China led the Asia Pacific electric fuse market by contributing 30.2% of total demand in 2024. As the world’s largest manufacturer of electrical equipment and electronics, China’s vast industrial base, booming consumer goods sector, and aggressive infrastructure modernization program create substantial demand for circuit protection components. The country’s State Grid Corporation continues to invest in high-voltage transmission upgrades, requiring protective fuses for transformers and substations. Also, China's automotive industry, particularly its electric vehicle boom, has significantly boosted the demand for specialized fuses used in battery packs and onboard chargers. Local manufacturers such as Chint Electric and Delixi Electric play a major role in supplying cost-effective fuse solutions tailored to domestic needs, while international brands like Siemens and ABB cater to premium segments.
India is a rapidly expanding market with strong domestic demand. The country’s expanding electrification initiatives, industrialization drive, and rising consumer electronics penetration have fueled consistent demand for fuses across residential, commercial, and utility sectors. The Government of India’s Saubhagya Scheme and Deendayal Upadhyaya Gram Jyoti Yojana have facilitated widespread rural grid connectivity, resulting in increased fuse deployment in new electrical installations. Moreover, the automotive industry’s shift toward electric mobility has created a surge in demand for automotive-grade fuses, particularly in the two-wheeler and three-wheeler segments. Indian manufacturers such as Polycab India, Finolex, and Havells have ramped up production to meet growing domestic needs. At the same time, multinational companies are expanding their presence through local partnerships and R&D centers focused on next-generation fuse technologies.
Japan is a technologically advanced and quality-focused market and is distinguished by its emphasis on precision engineering, innovation, and high-quality product standards. As a mature economy with a well-established electrical infrastructure, Japan’s fuse demand is primarily driven by replacement cycles, industrial automation, and advanced electronics manufacturing. Leading Japanese companies such as Panasonic, Toshiba, and Mitsubishi Electric develop specialized fuses for robotics, semiconductors, and high-speed rail systems. The country’s commitment to clean energy transitions has also spurred the use of high-voltage fuses in hydrogen refueling stations and renewable energy inverters. Regulatory agencies like the Japanese Industrial Standards Committee (JISC) enforce strict compliance norms, ensuring only certified products enter the market.
South Korea contributes a major share of the Asia Pacific electric fuse market, with growth propelled by its advanced smart infrastructure and burgeoning electric mobility ecosystem. The country’s Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy has prioritized industrial digitization, leading to increased deployment of automated production lines that rely on precise fuse-based protection systems. South Korea’s automotive sector, led by companies like Hyundai and Kia, is rapidly transitioning to electric vehicles, significantly increasing the need for high-reliability fuses in battery packs and charging systems. Additionally, the government’s push for smart grid modernization has encouraged the adoption of intelligent fuse monitoring solutions.
Australia is growing a focus on renewable integration and grid modernization. Also, renewable sources now contribute a major share of the country’s electricity mix, necessitating robust fuse protection in solar farms, wind turbines, and battery storage systems. Additionally, the rise in home solar installations has increased demand for DC-rated fuses used in photovoltaic arrays. Both domestic and international fuse manufacturers are capitalizing on this trend by introducing high-performance, weather-resistant fuse solutions suited for Australia’s diverse climate conditions.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS AND COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
ABB Ltd., Schneider Electric SE, Siemens AG, Littelfuse Inc., Eaton Corporation, Mersen S.A., Bel Fuse Inc., Legrand S.A., SCHURTER Holding AG, and Fuji Electric Co., Ltd are some of the key market players.
The competition in the Asia Pacific electric fuse market is shaped by a mix of global leaders and regionally strong brands striving to maintain or expand their market position through differentiation and innovation. Established multinational corporations such as Siemens, ABB, and Eaton leverage their global expertise, advanced R&D capabilities, and brand recognition to dominate premium segments. These firms focus on delivering technologically superior products that integrate seamlessly with digital power management systems and renewable energy setups.
At the same time, a growing number of regional players from China, India, and South Korea are gaining traction by offering cost-effective, standardized fuses tailored to local infrastructure needs. These manufacturers are increasingly investing in improving product quality and certification processes to compete on both price and performance. The competitive landscape is further intensified by the influx of counterfeit and substandard products, which challenge legitimate suppliers by distorting pricing structures and eroding consumer trust.
Top Players in the Asia Pacific Electric Fuse Market
Siemens Energy
Siemens Energy is a global leader in electrical infrastructure and plays a pivotal role in the Asia Pacific electric fuse market. The company offers a comprehensive portfolio of low and medium voltage fuses tailored for industrial, utility, and commercial applications. Siemens integrates advanced protection technologies with digital capabilities to enhance system reliability and safety. In the Asia Pacific region, Siemens collaborates closely with governments and private enterprises on smart grid development and electrification projects. Its focus on innovation and compliance with international standards positions it as a key contributor to both regional and global market advancements.
Eaton Corporation
Eaton Corporation is a major participant in the Asia Pacific electric fuse market, known for its high-quality circuit protection solutions that span residential, industrial, and transportation sectors. The company provides a diverse range of fuse types designed for durability and precision in demanding environments. Eaton’s regional operations emphasize localized product development and customer support, ensuring adaptability to varying regulatory landscapes. Its commitment to sustainable energy solutions has led to increased adoption of renewable energy systems across the region. Through strategic partnerships and a strong distribution network, Eaton continues to expand its influence in the global fuse market.
ABB Ltd.
ABB is a globally recognized innovator in power technologies and maintains a dominant presence in the Asia Pacific electric fuse landscape. The company delivers customized fuse solutions for industrial automation, utility networks, and electric mobility applications. ABB emphasizes environmental sustainability by developing eco-friendly alternatives that align with evolving industry demands. With a strong R&D base and collaborations with local utilities, ABB enhances grid resilience and operational efficiency across Asia Pacific countries. Its integration of smart technologies into fuse-based protection systems supports the region’s transition toward intelligent and reliable electrical networks.
Top Strategies Used by Key Market Participants
One of the primary strategies utilized by leading players in the Asia Pacific electric fuse market is product innovation and technological differentiation. Companies are continuously enhancing fuse designs to improve performance, safety, and compatibility with modern electrical systems such as smart grids and renewable energy inverters. This includes introducing compact, fast-acting, and environmentally friendly fuse options that cater to specialized applications in automotive, industrial automation, and consumer electronics.
Another important strategy involves expanding regional manufacturing and supply chain capabilities. Major manufacturers are setting up or expanding production facilities within the Asia Pacific region to reduce lead times, lower costs, and meet local regulatory requirements. This localized approach enables companies to serve emerging markets more efficiently while also adapting product specifications to regional needs and preferences.
A third critical strategy is forming strategic alliances and participating in government-led infrastructure initiatives. Leading firms are actively engaging with public sector stakeholders involved in rural electrification, urban modernization, and green energy programs.
RECENT MARKET DEVELOPMENTS
- In March 2024, Siemens Energy launched a new line of ultra-compact, high-interrupting capacity fuses specifically designed for industrial automation applications in Southeast Asia, aiming to meet rising demand for space-efficient and reliable circuit protection solutions.
- In June 2024, Eaton Corporation expanded its manufacturing facility in Pune, India, to increase local production capacity of automotive-grade fuses, supporting the country’s rapid shift towards electric vehicles and onboard electronic systems.
- In August 2024, ABB formed a strategic partnership with a Japanese energy systems integrator to co-develop next-generation fuses optimized for hydrogen-based energy storage projects currently being deployed across Japan’s industrial zones.
- In October 2024, LS Electric entered the Vietnamese market by acquiring a local fuse manufacturer, strengthening its presence in Indochina and enabling faster deployment of customized fuse solutions for smart city and factory automation projects.
- In December 2024, Hyundai Electric introduced an IoT-enabled fuse monitoring system in South Korea, designed to integrate with smart grid platforms and enable predictive maintenance for industrial and utility applications.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the Asia Pacific electric fuse market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Voltage
- Low Voltage Fuse
- High Voltage Fuses
By Current Rating
- 500 A – 2,000 A Fuses
- 4,000 A Fuses
By Application
- Industrial Application
- Utility Application
By End Use
- Electrical Appliances
- Automotive Applications
By Country
- India
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Thailand
- Malaysia
- Vietnam
- Philippines
- Indonesia
- Singapore
- Rest of APAC
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors are driving the Asia Pacific Electric Fuse Market?
Key growth drivers include rising power demand, increased infrastructure and industrial development, rapid urbanization, and the growing adoption of renewable energy sources and electric vehicles.
How is the Asia Pacific Electric Fuse Market expected to grow in the near future?
The Asia Pacific Electric Fuse Market is projected to witness steady growth over the forecast period due to increased electrification, expansion of smart grids, and a surge in demand for safety and reliability in electrical systems.
What are the challenges faced by the Asia Pacific Electric Fuse Market?
Challenges include the growing use of alternative circuit protection devices (like MCBs and RCCBs), high competition among key players, and fluctuating prices of raw materials.
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: sales@marketdataforecast.com