Asia Pacific Electric Insulator Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report By Type (Ceramic, Glass, Composite), Voltage, End User, Application, And Country (India, China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, New Zealand, Thailand, Malaysia, Vietnam, Philippines, Indonesia, Singapore And Rest Of Asia-Pacific), Industry Analysis From 2025 To 2033
Asia Pacific Electric Insulator Market Size
The Asia Pacific electric insulator market size was calculated to be USD 3.26 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to be worth USD 5.64 billion by 2033, from USD 3.47 billion in 2025, growing at a CAGR of 6.28% during the forecast period.
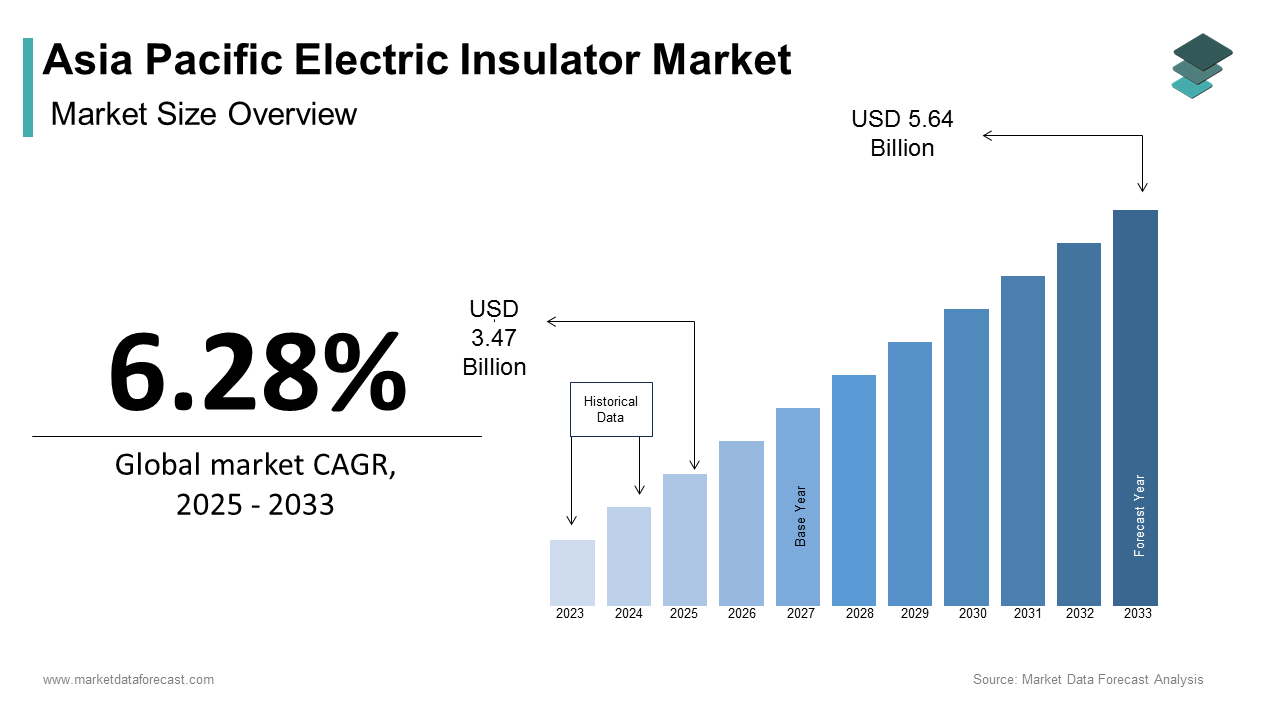
Electric insulators, which are designed to prevent the flow of current between conductors, are essential components in overhead power lines, substations, and distribution systems. The growth of the market is driven by the need for reliable energy transmission as urbanization, industrialization, and electrification efforts intensify across the region. Furthermore, the region's population growth has been significant, with the United Nations projecting that the Asia Pacific will remain home to over half of the world’s population through 2030. This demographic trend places immense pressure on existing power infrastructure with robust investments in high-performance insulators. Additionally, the increasing frequency of extreme weather events, as documented by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, highlights the growing importance of durable insulators capable of withstanding environmental stressors.
MARKET DRIVERS
Expanding Urbanization and Infrastructure Development
Urbanization in the Asia Pacific region has reached unprecedented levels, which is creating a surge in electricity demand and driving the need for advanced electric insulators. As per the World Bank, more than 50% of the region's population now resides in urban areas, with cities like Tokyo, Shanghai, and Delhi emerging as megacities with populations exceeding 10 million. This urban shift has led to increased investments in power infrastructure, including transmission and distribution networks that rely heavily on high-quality insulators. Such investments are often directed toward upgrading existing systems and integrating renewable energy sources, both of which require specialized insulators to handle higher voltages and varying environmental conditions. Furthermore, India’s Smart Cities Mission, aimed at developing 100 smart cities, is expected to significantly boost demand for insulators as these projects prioritize modernized power systems. The integration of smart grid technologies, which require insulators to support digital monitoring and control systems, further amplifies this demand.
Rising Adoption of Renewable Energy Sources
The transition toward renewable energy sources is another major driver propelling the Asia Pacific electric insulator market forward. Countries like China, India, and Australia are leading the charge in renewable energy capacity additions, with solar and wind energy installations witnessing exponential growth. This rapid expansion necessitates the deployment of specialized insulators capable of withstanding the unique challenges posed by renewable energy systems, such as fluctuating voltages and harsh environmental conditions. For example, offshore wind farms, which are gaining traction in countries like Japan and South Korea, which require insulators with enhanced resistance to saltwater corrosion and high humidity levels. Similarly, large-scale solar farms in desert regions of Australia and India demand insulators that can endure extreme temperatures and dust exposure. Additionally, the decentralized nature of renewable energy systems, which often involve long-distance power transmission, increases the reliance on high-performance insulators to minimize energy losses. The commitment to achieving net-zero emissions, as outlined in the Paris Agreement, which will further accelerates this trend, with governments pledging substantial funding for renewable projects.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Initial Costs and Budget Constraints
One of the primary restraints affecting the Asia Pacific electric insulator market is the high initial cost associated with advanced insulator technologies. Modern insulators are those made from composite materials or designed for high-voltage applications that often come with a premium price tag due to their complex manufacturing processes and stringent quality requirements. For instance, composite insulators, which offer superior performance in terms of durability and resistance to environmental stressors, can cost up to 30% more than traditional ceramic or glass insulators, as per a study by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). This cost differential poses a significant challenge for developing nations within the region, where budget constraints often limit the adoption of cutting-edge technologies. Countries like Bangladesh and Indonesia, which are still in the early stages of electrification, prioritize cost-effective solutions over high-performance alternatives. Furthermore, utility companies operating in rural or remote areas face additional financial burdens due to the logistical challenges of transporting and installing these insulators
Stringent Regulatory Standards and Compliance Challenges
Another significant restraint impacting the Asia Pacific electric insulator market is the complexity of adhering to stringent regulatory standards and compliance requirements. Governments across the region have implemented rigorous quality and safety regulations to ensure the reliability of power transmission systems, particularly in light of increasing environmental concerns and technological advancements. For example, the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) mandates specific performance benchmarks for insulators used in high-voltage applications, including resistance to pollution, mechanical strength, and thermal stability. Meeting these standards often requires manufacturers to invest heavily in research and development, as well as advanced testing facilities. According to a report by the Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce & Industry (FICCI), small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) account for over 60% of the insulator manufacturing base in India, yet many struggle to comply with international standards due to limited resources and technical expertise. Additionally, the lack of harmonization in regulatory frameworks across the region creates operational inefficiencies for multinational companies. For instance, an insulator certified for use in Japan may not meet the specifications required in Australia, necessitating costly modifications. These compliance challenges not only increase production costs but also extend time-to-market, thereby acting as a significant barrier to the widespread adoption of innovative insulator technologies in the Asia Pacific region.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Technological Advancements in Material Science
Technological advancements in material science present a transformative opportunity for the Asia Pacific electric insulator market. Innovations in nanotechnology and polymer composites are enabling the development of next-generation insulators with unparalleled performance characteristics. For instance, researchers at the National University of Singapore have pioneered the use of graphene-enhanced polymers in insulator manufacturing, which results in products that exhibit superior electrical insulation properties and mechanical strength. These advanced materials are not only lightweight but also highly resistant to environmental degradation by making them ideal for deployment in challenging terrains such as coastal regions and mountainous areas. Moreover, the integration of smart technologies, such as sensors embedded within insulators allows for real-time monitoring of performance metrics like temperature and voltage fluctuations. This capability aligns with the region’s push toward smart grid infrastructure, as per the Global Smart Grid Federation.
Expansion into Emerging Markets
The expansion into emerging markets represents another lucrative opportunity for the Asia Pacific electric insulator market. Countries like Vietnam, Myanmar, and Cambodia are experiencing rapid economic growth, which accompanied by a surge in electricity demand. This trend is mirrored across other Southeast Asian nations, where governments are prioritizing energy access and infrastructure development as part of their national agendas. For instance, Myanmar’s National Electrification Plan aims to achieve universal electricity access by 2030, requiring substantial investments in transmission and distribution networks. These initiatives create a fertile ground for insulator manufacturers to establish a foothold in untapped markets. Additionally, regional trade agreements such as the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) facilitate cross-border collaborations and reduce trade barriers by enabling companies to expand their reach more efficiently.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Environmental Degradation and Weather Extremes
Environmental degradation and increasingly frequent weather extremes pose a formidable challenge to the Asia Pacific electric insulator market. The region is highly susceptible to natural disasters such as typhoons, floods, and earthquakes, which can severely damage power infrastructure, including insulators. For instance, Typhoon Haiyan, which struck the Philippines in 2013, caused widespread destruction of power lines and insulators, leaving millions without electricity for weeks, as reported by the United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction. Furthermore, rising pollution levels, particularly in densely populated urban areas, exacerbate the risk of insulator flashovers, a phenomenon where contaminants on the surface of insulators cause unintended electrical discharge. According to the World Health Organization, air pollution in cities like Delhi and Beijing frequently exceeds safe limits by increasing the likelihood of such failures. Addressing these challenges requires continuous innovation in material science and design, which many manufacturers find difficult to achieve without compromising profitability.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Raw Material Scarcity
Supply chain disruptions and raw material scarcity represent another critical challenge for the Asia Pacific electric insulator market. The production of high-quality insulators relies heavily on specialized raw materials such as silica, alumina, and epoxy resins, which are often sourced from geographically concentrated regions. For example, China dominates the global supply of rare earth elements, which are integral to the manufacture of certain types of insulators. However, geopolitical tensions and trade restrictions have occasionally disrupted the availability of these materials, as noted by the International Monetary Fund. Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic exposed vulnerabilities in global supply chains, with lockdowns and transportation bottlenecks causing delays in the procurement of raw materials. According to a report by the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development, global shipping costs surged by over 200% during the pandemic by significantly impacting manufacturing timelines and costs. These disruptions are further compounded by the increasing demand for raw materials driven by other industries, such as automotive and electronics, leading to heightened competition and price volatility. Such fluctuations create uncertainty for manufacturers, who must navigate these challenges while maintaining product quality and meeting customer expectations.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
6.28% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Type, Voltage, End User, Application, And Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis; Segment-Level Analysis; DROC, PESTLE Analysis; Porter’s Five Forces Analysis; Competitive Landscape; Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
India, China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, New Zealand, Thailand, Malaysia, Vietnam, Philippines, Indonesia, Singapore, Rest of Asia-Pacific |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
NGK Insulators, ABB Ltd, General Electric, Siemens AG, Toshiba Corporation, Aditya Birla Insulators, Seves Group, Lapp Insulators, Zhejiang Jinlihua Electric Co. Ltd, Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL) |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Type Insights
The ceramic insulators segment dominated the Asia Pacific electric insulator market with a share of 45.4% in 2024. This dominance is driven primarily by their widespread use in high-voltage applications and their proven reliability over decades of deployment. One key factor fueling this dominance is the extensive infrastructure investments in countries like India and China, where ceramic insulators are preferred for overhead power lines due to their cost-effectiveness and durability. Additionally, the robust mechanical strength of ceramic insulators makes them suitable for regions prone to extreme weather conditions, such as typhoons in Japan and monsoons in Southeast Asia. According to the World Meteorological Organization, these climatic challenges necessitate materials that can withstand environmental stressors without compromising performance. Another driving factor is the established manufacturing base for ceramics in the region. Countries like India and Vietnam have a long history of producing high-quality ceramic products, supported by abundant raw material availability.
The composite insulators segment is swiftly emerging with an estimated CAGR of 8.5% throughout the forecast period owing to their superior performance characteristics, including lightweight design, resistance to pollution flashovers, and enhanced durability. A pivotal driver of this growth is the increasing adoption of renewable energy systems, particularly solar and wind farms, which require specialized insulators capable of handling fluctuating voltages and harsh environments. Moreover, advancements in polymer technology have significantly improved the electrical and mechanical properties of composite insulators, which is making them more competitive against traditional materials. Another contributing factor is the push toward smart grid infrastructure, which relies on advanced insulators equipped with embedded sensors for real-time monitoring.
By Voltage Insights
The high-voltage insulators segment accounted in holding 50.4% of the Asia Pacific electric insulator market share in 2024 with the focus on expanding and modernizing its high-voltage transmission networks to support growing electricity demand. One critical driver is the rise of cross-border power trade initiatives, such as the ASEAN Power Grid, which aims to integrate national grids across Southeast Asia. These projects require high-performance insulators capable of transmitting electricity over long distances with minimal losses. According to the Asian Development Bank, over $15 billion has been allocated to regional grid interconnections by 2030 with the growing importance of high voltage insulators. Additionally, the proliferation of ultra-high voltage (UHV) transmission lines in countries like China and India further bolsters demand. Another factor is the increasing urbanization rate, which necessitates efficient power distribution systems capable of handling heavy loads. The United Nations estimates that urban populations in the Asia Pacific will grow by 25% by 2030, driving investments in high-voltage infrastructure.
The medium voltage insulators segment is likely to register a CAGR of 7.8% in the next coming years with the rapid expansion of industrial and commercial sectors, which rely heavily on medium voltage systems for efficient power distribution. A key driver is the booming manufacturing sector in countries like Vietnam and Thailand, where industrial parks and special economic zones are being developed at an unprecedented pace. Furthermore, the electrification of rural areas is another significant factor. Governments across the region are prioritizing rural electrification programs, such as India’s Saubhagya Scheme, which aims to provide electricity access to all households. These initiatives often involve medium voltage distribution networks, as they strike a balance between cost and efficiency. According to the Rural Electrification Corporation of India, over 25 million rural connections were established under the scheme, which requires millions of medium voltage insulators.
By End-User Insights
The utility segment was the largest and held 60.5% of the Asia Pacific electric insulator market share in 2024 with the massive scale of utility operations, which encompass power generation, transmission, and distribution across the region. A primary driver is the ongoing modernization of aging power infrastructure, particularly in developed nations like Japan and Australia.
The industrial segment is poised to register a CAGR of 9.2% in the next coming years with the rapid industrialization occurring across the region in emerging economies like Vietnam, Malaysia, and Bangladesh. A key driver is the expansion of manufacturing hubs, which require reliable power supply systems supported by high-performance insulators. Another contributing factor is the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies, which emphasize automation and digitalization. These technologies often operate at specific voltage levels with specialized insulators to ensure optimal performance. Additionally, the rise of renewable energy-powered industrial complexes, such as green hydrogen plants, is creating new opportunities. Australia’s Green Hydrogen Strategy aims to establish large-scale hydrogen production facilities, which will rely on advanced insulators for safe and efficient operation.
By Application Insights
The transformers segment was the largest by capturing 35.4% of the Asia Pacific electric insulator market share in 2024 with the widespread deployment of transformers in power distribution systems, which are essential for stepping down voltage levels for end-user consumption. One major factor is the escalating demand for electricity in urban areas, where transformer installations are concentrated to meet residential and commercial needs. According to the United Nations, urban populations in the Asia Pacific are projected to grow by 25% by 2030 with significant investments in transformer infrastructure. Another driver is the replacement of outdated transformers in developed nations like Japan and South Korea, where aging equipment poses reliability risks. The Japanese Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry estimates that over 30% of transformers in the country are nearing the end of their operational life by creating a steady demand for new units equipped with advanced insulators. Additionally, the integration of renewable energy sources into the grid requires specialized transformers capable of handling variable inputs, further boosting demand.
The cables segment is likely to register a CAGR of 8.9% in the next coming years with the increasing complexity of power distribution networks, which rely on insulated cables to transmit electricity efficiently. A key driver is the expansion of underground cabling systems in densely populated urban areas where space constraints limit the use of overhead lines. For example, Singapore’s Underground Cable Network Expansion Project aims to replace existing overhead lines with underground alternatives, requiring millions of cable insulators. Another factor is the rising adoption of high-voltage direct current (HVDC) cables for long-distance power transmission, especially in offshore wind farms. The Global Wind Energy Council reports that offshore wind capacity in the region is expected to reach 50 gigawatts by 2030, which is creating a surge in demand for HVDC cable insulators. Additionally, the electrification of transportation networks, such as railways and electric vehicle charging stations, is driving demand for specialized cables.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
China was the largest contributor to the Asia Pacific electric insulator market with a share of 35.4% in 2024. The market’s growth is propelled by the country’s status as the world’s largest electricity consumer and producer. A key driver is the massive scale of infrastructure development in high-voltage transmission networks. China’s State Grid Corporation has invested over $100 billion annually in grid modernization projects, with a focus on ultra-high voltage (UHV) lines. Another factor is the country’s dominance in renewable energy integration, with solar and wind farms driving demand for specialized insulators. The International Renewable Energy Agency reports that China accounted for 50% of global renewable energy capacity additions in 2022.
India was positioned second in holding 20.3% of the Asia Pacific electric insulator market share in 2024. A primary factor is the government’s commitment to universal electricity access, exemplified by programs like the Saubhagya Scheme, which successfully provided connections to over 25 million households. According to the Rural Electrification Corporation of India, these efforts have created a massive demand for insulators in rural electrification projects. Another driver is the modernization of urban power grids, with cities like Delhi and Mumbai investing heavily in smart grid technologies. According to the Indian Ministry of Power, over $50 billion has been allocated to smart grid initiatives by 2030, which require advanced insulators for seamless integration. Additionally, India’s renewable energy targets, which aim to achieve 500 gigawatts of installed capacity by 2030, are spurring demand for specialized insulators.
Japan was ranked second by accounting for 15.3% of the share in the Asia Pacific electric insulator market in 2024 with a focus on technological innovation and resilience against natural disasters. A key factor is the country’s vulnerability to earthquakes and typhoons, which necessitates the use of high-performance insulators. The Japanese Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry reports that over $20 billion is invested annually in disaster-resilient infrastructure, including advanced insulators. Another driver is the replacement of aging power infrastructure, with many transformers and substations nearing the end of their operational life.
South Korea's electric insulator market growth is driven by its advanced industrial base and focus on sustainable energy solutions. Another driver is the expansion of renewable energy projects in solar and wind sectors. Additionally, the country’s smart city initiatives, such as the Sejong Smart City project, are driving demand for advanced insulators to support digitalized power systems.
Australia and New Zealand are likely to showcase huge growth opportunities for the Asia pacific electric insulator market in next coming years. A key factor is the rise of renewable energy projects, particularly in solar and wind sectors. The Australian Energy Market Operator reports that renewable energy capacity in the country is expected to double by 2030 by creating a surge in demand for insulators. Another driver is the electrification of remote areas, which often rely on specialized insulators for efficient power distribution. The Australian Government estimates that over $10 billion will be invested in rural electrification projects by 2030. Additionally, New Zealand’s commitment to achieving net-zero emissions by 2050 is driving demand for advanced insulators to support renewable energy integration.
LEADING PLAYERS IN THE ASIA PACIFIC ELECTRIC INSULATOR MARKET
NGK Insulators Ltd.
NGK Insulators Ltd. is a global leader in the electric insulator market, renowned for its innovative solutions and high-quality products. The company has established a strong presence in the Asia Pacific region by leveraging its expertise in ceramic and composite insulators. NGK’s contribution to the global market lies in its ability to cater to diverse applications, from high-voltage transmission lines to specialized industrial uses. Its focus on research and development has enabled the creation of advanced insulators that meet the stringent demands of modern power systems.
Hitachi Energy Ltd.
Hitachi Energy Ltd. plays a pivotal role in shaping the Asia Pacific electric insulator market through its cutting-edge technologies and sustainable solutions. The company’s emphasis on smart grid infrastructure and renewable energy integration has positioned it as a key contributor to the global market. Hitachi Energy’s insulators are designed to address the unique challenges of the region, such as extreme weather conditions and growing urbanization.
Hubbell Incorporated
Hubbell Incorporated is a prominent player in the Asia Pacific electric insulator market, known for its robust product portfolio and customer-centric approach. The company’s contributions to the global market stem from its ability to provide tailored solutions for utilities, industries, and renewable energy projects. Hubbell’s focus on enhancing product durability and performance has earned it a reputation for reliability.
TOP STRATEGIES USED BY KEY MARKET PARTICIPANTS
Strategic Partnerships and Collaborations
Key players in the Asia Pacific electric insulator market have increasingly relied on strategic partnerships to expand their reach and enhance their product offerings. By collaborating with local utilities, governments, and renewable energy developers, these companies ensure their solutions align with regional requirements. Such alliances enable them to tap into emerging markets and address specific challenges, such as rural electrification and grid modernization. These partnerships also facilitate knowledge sharing and resource optimization by allowing companies to deliver innovative and cost-effective solutions.
Investment in Research and Development
Investment in research and development remains a cornerstone strategy for strengthening market positions. Companies are focusing on developing advanced materials and technologies to improve the performance and durability of insulators. Innovations such as graphene-enhanced composites and pollution-resistant designs are being prioritized to meet the demands of harsh environments and renewable energy integration.
Expansion of Manufacturing Facilities
To meet the growing demand in the Asia Pacific region, key players are expanding their manufacturing facilities and localizing production. Establishing production hubs closer to end-users reduces logistical costs and ensures faster delivery. This strategy also helps companies comply with regional regulations and cater to localized preferences.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS AND COMPETITION OVERVIEW
Major Players in the Asia Pacific electric insulator market include NGK Insulators, ABB Ltd, General Electric, Siemens AG, Toshiba Corporation, Aditya Birla Insulators, Seves Group, Lapp Insulators, Zhejiang Jinlihua Electric Co. Ltd, Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL)
The Asia Pacific electric insulator market is characterized by intense competition, driven by the presence of both global giants and regional players striving to capture market share. Leading companies leverage their technological expertise and extensive distribution networks to maintain dominance, while smaller firms focus on niche segments to carve out their positions. The competitive landscape is shaped by the rapid adoption of advanced materials, such as composites, and the increasing demand for renewable energy-compatible solutions. Innovation plays a central role, with companies investing heavily in R&D to differentiate their offerings. Additionally, collaborations with utilities and governments are becoming increasingly common, enabling players to align with regional electrification goals. As environmental concerns and regulatory standards grow stricter, manufacturers are compelled to adopt sustainable practices, further intensifying competition.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THE MARKET
- In April 2023, NGK Insulators Ltd. launched a new line of composite insulators designed for offshore wind farms. This move was aimed at addressing the unique challenges posed by marine environments and supporting the region’s renewable energy transition.
- In June 2023, Hitachi Energy Ltd. partnered with a leading utility company in Australia to supply advanced insulators for a major smart grid project. This collaboration strengthened Hitachi’s foothold in the Australian market and reinforced its commitment to sustainable energy solutions.
- In August 2023, Hubbell Incorporated expanded its manufacturing facility in India to cater to the growing demand for medium-voltage insulators. This expansion enabled the company to localize production and reduce delivery times for its South Asian customers.
- In October 2023, NGK Insulators Ltd. signed a memorandum of understanding with a Southeast Asian government agency to support rural electrification initiatives. This agreement highlighted NGK’s focus on contributing to regional development while expanding its customer base.
- In December 2023, Hitachi Energy Ltd. unveiled a next-generation ceramic insulator with enhanced thermal stability. This innovation was targeted at high-voltage applications in challenging terrains, showcasing the company’s dedication to pushing technological boundaries.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the Asia Pacific Electric Insulator Market has been segmented and sub-segmented based on type, voltage, end user, application, and region.
By Type
- Ceramic
- Glass
- Composite
By Voltage
- Low
- Medium
- High
By End User
- Utilities
- Industries
By Application
- Transformer
- Cables
- Busbar
By Region
- India
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Thailand
- Malaysia
- Vietnam
- Philippines
- Indonesia
- Singapore
- Rest of Asia-Pacific
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the major drivers of the market?
Key drivers include rapid urbanization, rising electricity demand, grid modernization projects, and growing investments in renewable energy infrastructure.
2. Which countries are the main contributors to this market in Asia Pacific?
China, India, Japan, South Korea, and Australia are major contributors due to their extensive power transmission networks and infrastructure development.
3. How does this market benefit from renewable energy expansion?
As countries expand their solar and wind energy capacities, the need for efficient and durable insulators in new high-voltage transmission lines increases significantly.
4. Who are the key market players?
Leading players include NGK Insulators, ABB Ltd, General Electric, Siemens AG, Toshiba Corporation, Aditya Birla Insulators, Seves Group, and Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL).
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]