Asia Pacific Fuel Cell Market Size, Share, Growth, Trends, And Forecasts Report, Product, Application, And By Country (India, China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, New Zealand, Thailand, Malaysia, Vietnam, Philippines, Indonesia, Singapore and Rest of APAC), Industry Analysis From 2025 to 2033
Asia Pacific Fuel Cell Market Size
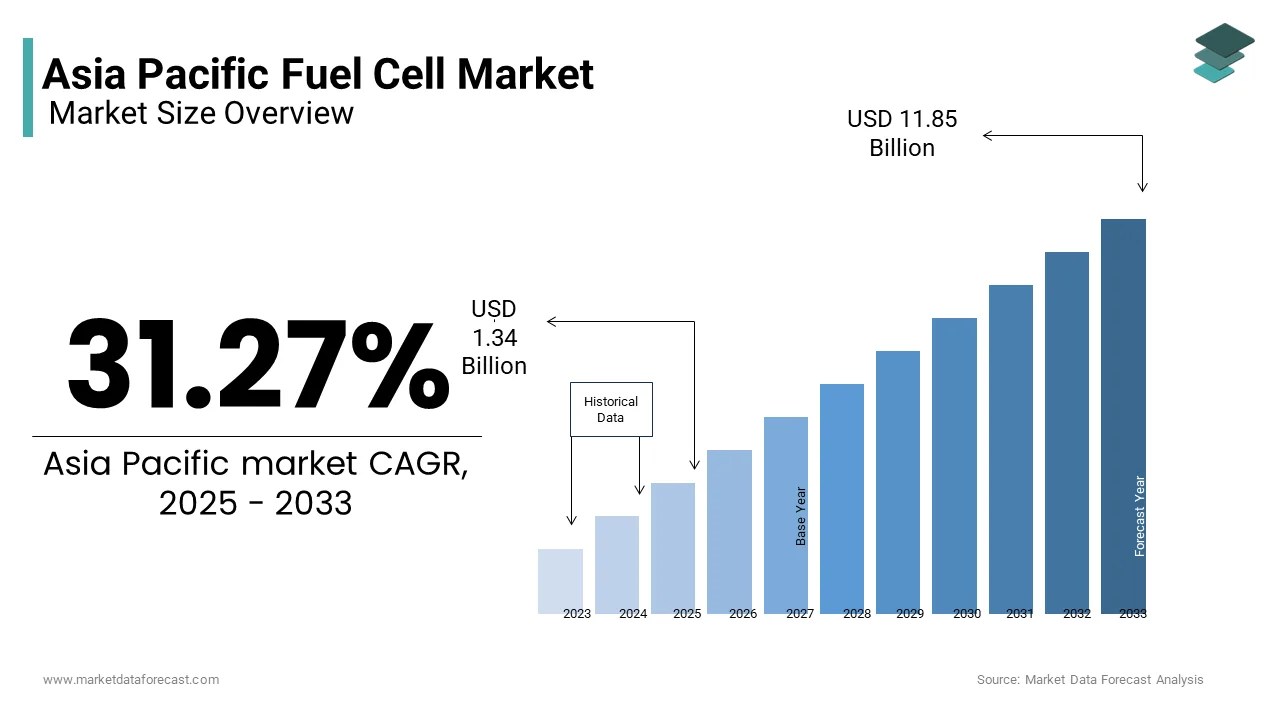
The Asia Pacific fuel cell market was valued at USD 1.02 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 1.34 billion in 2025 from USD 11.85 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 31.27% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2033.
MARKET DRIVERS
Government Policies and Incentives
Government policies and incentives form a cornerstone of the Asia Pacific fuel cell market's growth trajectory. Japan’s Strategic Road Map for Hydrogen and Fuel Cells, introduced in 2019, allocates significant funding for research and development, alongside subsidies for hydrogen refueling stations. These policies not only lower barriers to entry but also stimulate private sector participation. Additionally, China’s Five-Year Plan emphasizes hydrogen as a key pillar of its energy strategy, offering tax breaks and grants to manufacturers. This regulatory push ensures sustained demand for fuel cells across industries like automotive, power generation, and residential heating.
Rising Industrial Adoption
Industrial sectors are increasingly adopting fuel cells due to their efficiency and environmental benefits. The logistics industry in South Korea, for example, is transitioning to hydrogen-powered forklifts. In China, heavy-duty trucks powered by fuel cells are gaining traction, supported by partnerships between manufacturers like Weichai Power and Ballard Power Systems. This industrial shift underscores how operational needs and sustainability goals converge to propel fuel cell adoption.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Initial Costs
One of the primary restraints hindering the Asia Pacific fuel cell market is the high initial investment required for deployment. Fuel cell systems involve complex manufacturing processes and expensive materials like platinum, which significantly elevate costs. While economies of scale are gradually reducing these costs, progress remains slow. For instance, the Asian Development Bank reports that small-scale fuel cell projects in Southeast Asia often face financial bottlenecks, with only 15% securing full funding due to perceived risks. High upfront expenses also deter smaller enterprises from adopting fuel cell technology, particularly in emerging markets like Vietnam and Indonesia.
Lack of Skilled Workforce
Another critical restraint is the shortage of skilled professionals equipped to handle fuel cell technologies. For example, a survey conducted by the Federation of ASEAN Engineering Organizations revealed that less than 10% of engineering graduates in Southeast Asia possess expertise in hydrogen technologies. This skills gap impedes the efficient operation and maintenance of fuel cell systems, leading to higher downtime and operational inefficiencies.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Expansion of Green Hydrogen Production
The expansion of green hydrogen production presents a transformative opportunity for the Asia Pacific fuel cell market. With renewable energy capacity surging across the region, green hydrogen offers a sustainable pathway to fuel cell adoption. This aligns seamlessly with Japan and South Korea’s import needs, creating a lucrative export-import dynamic. Furthermore, China’s State Council estimates that green hydrogen production costs will drop by 30% by 2025, thanks to advancements in electrolyzer technology. Such developments position green hydrogen as a catalyst for scaling fuel cell applications across mobility, power generation, and industrial sectors.
Urbanization and Smart City Initiatives
Urbanization trends coupled with smart city initiatives offer immense potential for fuel cell integration. By 2050, the United Nations projects that 68% of Asia’s population will reside in urban areas, driving demand for clean energy solutions. Singapore’s Smart Nation initiative, for example, includes deploying hydrogen fuel cells for grid stabilization and powering public transport hubs.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Infrastructure Development Bottlenecks
A significant challenge facing the Asia Pacific fuel cell market is the inadequate infrastructure to support widespread adoption. Hydrogen production, storage, and distribution networks remain underdeveloped, creating logistical hurdles. According to the Hydrogen Council, building a comprehensive hydrogen refueling network in Japan alone would require substantial amount in investments over the next decade. In rural areas of Southeast Asia, where energy access is already limited, establishing fuel cell infrastructure poses even greater challenges.
Public Perception and Awareness Gaps
Another pressing challenge is the lack of public awareness and trust in fuel cell technologies. Misconceptions about hydrogen safety persist, deterring consumer acceptance despite evidence of its safe use in industrial applications. As per a survey by Ipsos, only 35% of respondents in key Asia Pacific markets view hydrogen as a viable alternative to fossil fuels. This perception gap is particularly pronounced in countries like India and Indonesia, where educational campaigns are minimal. Additionally, misinformation about the environmental benefits of fuel cells undermines their appeal among eco-conscious consumers. The International Association for Hydrogen Energy notes that addressing these misconceptions requires targeted outreach programs, yet governments and private entities have been slow to act. For instance, South Korea’s Ministry of Environment reports that less than 5% of its annual budget is allocated to hydrogen awareness initiatives.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2032 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
31.27% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Product, Application, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Ballard Power Systems, Bloom Energy, Plug Power, FuelCell Energy, AFC Energy, Ceres Power Holdings, Hydrogenics Corporation (Now part of Cummins Inc.), Nuvera Fuel Cells (A Plug Power Company), PowerCell Sweden AB, Horizon Fuel Cell Technologies, and Others. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Application Insights
The stationary fuel cells dominated the Asia Pacific fuel cell market by capturing a 45.5% of the total market share in 2022. This segment’s prominence is attributed to its widespread adoption in power generation for residential, commercial, and industrial applications. Japan leads this trend, with over 300,000 ENE-FARM units installed as of 2021, which are residential fuel cell systems providing combined heat and power (CHP). These systems achieve energy efficiencies, making them highly attractive for urban areas facing grid constraints. A key driver is the growing demand for decentralized energy solutions. Additionally, China’s National Development and Reform Commission highlights that stationary fuel cells are integral to achieving carbon neutrality by 2060, with plans to install 5 GW of capacity by 2025. Another factor is government incentives. For instance, Australia’s Renewable Energy Agency offers subsidies for deploying stationary fuel cells in remote mining operations, where reliability is critical.
The emerging segment is transportation fuel cells which is projected to grow at a CAGR of 38%. This swift development is fueled by stringent emissions regulations and the rising adoption of hydrogen-powered vehicles. South Korea exemplifies this trend, with Hyundai’s Nexo fuel cell vehicle sales reaching 27,000 units globally by 2022, supported by the government’s Hydrogen Economy Roadmap. Urban mobility is another significant factor. Collaborative efforts also play a role.
By Type Insights
The polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) held the largest share of the Asia Pacific fuel cell market i.e. 55.4% of the total portion in 2024. Their dominance is attributed to their versatility and efficiency in low-temperature applications. In Japan, PEMFCs are extensively used in residential ENE-FARM systems, with Toshiba reporting a increase in shipments in 2022. The automotive sector further amplifies PEMFC adoption. Hyundai’s partnership with Ballard Power Systems has resulted in producing over 10,000 PEMFC stacks annually for fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs), as per Automotive World. Additionally, China’s aggressive push toward green hydrogen aligns with PEMFC technology, given its compatibility with renewable energy sources.
The solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) segment is poised to grow at a remarkable CAGR of 42% from 2025 to 2033. This surge is driven by their superior efficiency in high-temperature applications, particularly for stationary power generation. Mitsubishi Heavy Industries reports that SOFC systems achieve electrical efficiencies, making them attractive for industrial use. In South Korea, SK Group’s investment in SOFC technology underscores its potential, with plans to deploy 1 GW of capacity by 2025. Another catalyst is the integration of biogas as a feedstock; a study reveals that using biogas in SOFCs can reduce lifecycle emissions by 70%. Moreover, Japan’s Strategic Road Map for Hydrogen emphasizes SOFCs for large-scale cogeneration projects, targeting 10% of industrial energy needs by 2030.
COUNTRY ANALYSIS
Japan is a dominant force in the Asia-Pacific fuel cell market. The leading position is rooted in decades of investment in hydrogen technologies, exemplified by initiatives like the Fukushima Hydrogen Energy Research Field. Residential fuel cells, or ENE-FARM units, have seen widespread adoption, with Panasonic reporting sales exceeding 400,000 units since inception. Government backing plays a pivotal role. The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry outlines plans to establish 900 hydrogen refueling stations by 2030, supporting FCEV deployment. A study by Nomura Research Institute projects that Japan’s hydrogen economy could reach $30 billion by 2030, underscoring its continued dominance.
is projected to be the leading market in the region. Its rapid industrialization and urbanization drive demand for clean energy solutions. The Five-Year Plan prioritizes hydrogen, with Weichai Power announcing plans to produce 20,000 fuel cell systems annually by 2025. Public transportation is a major focus. Industrial applications also thrive. These initiatives highlight China’s strategic positioning in the fuel cell landscape.
South Korea holds an notable market share and is propelled by its Hydrogen Economy Roadmap. Stationary applications also gain traction. South Korea’s proactive approach ensures its prominence in the regional market.
Australia is a significant participant in the Asia-Pacific fuel cell market. This leverages its renewable energy resources for green hydrogen production. The Australian Renewable Energy Agency outlines plans to produce 11 TWh of green hydrogen annually by 2030. Export opportunities abound, with Japan and South Korea identified as key markets. Mining companies like Fortescue Metals Group invest heavily in hydrogen-powered equipment, reducing emissions. These developments position Australia as a vital player in the fuel cell ecosystem.
India is projected to experience significant growth. It is driven by its National Hydrogen Mission. Urban centers like Delhi and Mumbai pilot hydrogen refueling stations, fostering infrastructure growth.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
Companies playing a prominent role in the Asia Pacific fuel cell market include Ballard Power Systems, Bloom Energy, Plug Power, FuelCell Energy, AFC Energy, Ceres Power Holdings, Hydrogenics Corporation (Now part of Cummins Inc.), Nuvera Fuel Cells (A Plug Power Company), PowerCell Sweden AB, Horizon Fuel Cell Technologies, and Others.
Top Players in the Market
Hyundai Motor Group
Hyundai Motor Group has emerged as a global leader in fuel cell technology, particularly through its flagship Nexo fuel cell electric vehicle (FCEV). The company’s commitment to hydrogen extends beyond mobility, as it actively collaborates with governments and industries to build hydrogen ecosystems. Hyundai’s establishment of the HTWO brand focuses on advancing hydrogen fuel cell systems for diverse applications, including power generation and marine transport. By fostering partnerships across Asia Pacific, Hyundai is driving innovation while promoting the adoption of sustainable energy solutions globally.
Toyota Motor Corporation
Toyota’s Mirai FCEV exemplifies its dedication to fuel cell technology, positioning the company as a key player in the Asia Pacific market. Through initiatives like the Hydrogen Council, Toyota collaborates with stakeholders to accelerate hydrogen infrastructure development. Beyond automotive applications, Toyota explores stationary fuel cells for industrial and residential use, reinforcing its role in shaping the global hydrogen economy. Its emphasis on research and development ensures cutting-edge advancements, bolstering its leadership in clean energy transitions.
Ballard Power Systems
Ballard Power Systems specializes in proton exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cell technology, serving diverse sectors such as transportation, marine, and stationary power. In Asia Pacific, Ballard partners with local manufacturers to deliver scalable solutions tailored to regional needs. Its focus on commercializing heavy-duty fuel cell applications, including buses and trucks, underscores its strategic vision.
Top Strategies Used by Key Players
Strategic Partnerships and Collaborations
Key players in the Asia Pacific fuel cell market leverage strategic partnerships to enhance their technological capabilities and expand their reach. For instance, partnerships facilitate the integration of fuel cells into public transportation networks, accelerating adoption rates. These alliances also help align with national hydrogen strategies, ensuring compliance with regulatory frameworks while fostering mutual growth.
Investment in R&D and Innovation
Research and development form the backbone of competitive strategies in the fuel cell market. Leading companies allocate significant resources to innovate materials, improve system efficiencies, and reduce costs. By focusing on next-generation technologies, firms aim to differentiate themselves and capture emerging opportunities.
Expansion of Production Facilities
To meet rising demand, key players are expanding their manufacturing capacities within the Asia Pacific region. Establishing localized production facilities not only reduces logistical costs but also strengthens supply chain resilience. Companies invest in state-of-the-art plants capable of producing high-quality fuel cell components at scale. This strategy ensures timely delivery of products while catering to specific regional requirements, thereby solidifying their market presence and customer loyalty.
COMPETITION OVERVIEW
The Asia Pacific fuel cell market is characterized by intense competition driven by rapid technological advancements and increasing demand for clean energy solutions. Key players vie for dominance through innovation, strategic collaborations, and aggressive market penetration tactics. Established automakers like Hyundai and Toyota compete alongside specialized firms such as Ballard Power Systems, each leveraging unique strengths to capture market share. The race to develop cost-effective and efficient fuel cell systems fuels continuous R&D efforts, resulting in a dynamic landscape marked by frequent product launches and technological breakthroughs. Governments play a pivotal role by offering subsidies and creating favorable policies, intensifying competition among participants striving to capitalize on these incentives. Emerging startups further disrupt the status quo by introducing niche applications, challenging incumbents to adapt quickly. Additionally, collaborations between international and regional players blur traditional boundaries, fostering an ecosystem where innovation thrives.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THE MARKET
- In January 2023, Hyundai Motor Group announced the construction of a new hydrogen fuel cell plant in Guangzhou, China, aimed at supporting the production of fuel cell systems for commercial vehicles and contributing to China's hydrogen economy goals.
- In March 2023, Toyota Motor Corporation partnered with seven Japanese energy companies to establish the Japan Hydrogen Association, focusing on developing hydrogen infrastructure and promoting widespread adoption of fuel cell technologies in Asia Pacific markets.
- In June 2023, Ballard Power Systems launched a joint venture with Weichai Power in Shandong, China, to manufacture proton exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cell modules for buses and trucks, enhancing local supply chains and meeting growing demand.
- In September 2023, Panasonic unveiled plans to expand its ENE-FARM residential fuel cell business into Southeast Asia, targeting urban households seeking reliable and sustainable energy solutions amid increasing electricity costs.
- In December 2023, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries completed the acquisition of a majority stake in a South Korean solid oxide fuel cell (SOFC) manufacturer, enabling the company to strengthen its portfolio of high-temperature fuel cell systems for industrial applications.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the Asia-Pacific fuel cell market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Type
- PEMFC
- PAFC
- SOFC
- MCFC
- Others
By Application
- Portable
- Stationary
- Transport
By End-User
- Residential
- Commercial and Industrial
- Utilities
- Automotive
- Military and Defense
- Aerospace
By Country
- India
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Thailand
- Malaysia
- Vietnam
- Philippines
- Indonesia
- Singapore
- Rest of APAC
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a fuel cell, and how is it being used in the Asia Pacific region?
A fuel cell is a clean energy device that generates electricity through an electrochemical reaction, typically using hydrogen. In Asia Pacific, it's increasingly used in transportation, backup power, and stationary energy systems, especially in Japan, South Korea, and China
What factors are driving the growth of the Asia Pacific fuel cell market?
Key growth drivers include government decarbonization policies, investments in hydrogen infrastructure, automotive industry innovation, and the region’s commitment to net-zero emission targets by 2050 or sooner.
Which sectors are seeing the fastest fuel cell adoption in Asia Pacific?
Fuel cells are gaining traction in automobiles (especially buses and trucks), industrial backup power, portable electronics, and distributed energy systems for smart buildings and off-grid applications.
What are the main challenges limiting fuel cell expansion in this region?
Barriers include high production and storage costs for hydrogen, limited refueling infrastructure, technology complexity, and inconsistent regulatory frameworks across countries.
What trends are shaping the future of fuel cells in Asia Pacific?
Emerging trends include green hydrogen production, fuel cell integration in hybrid energy systems, localized manufacturing, and cross-border collaboration to develop a sustainable hydrogen economy.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from
$ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: sales@marketdataforecast.com