Asia Pacific Membrane Bioreactor Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report By Membrane Type (Hollow Fiber, Flat Sheet, Multi Tubular), System Configuration, Application, And Country (India, China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, New Zealand, Thailand, Malaysia, Vietnam, Philippines, Indonesia, Singapore And Rest Of Asia-Pacific), Industry Analysis From 2025 To 2033
Asia Pacific Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) Market Size
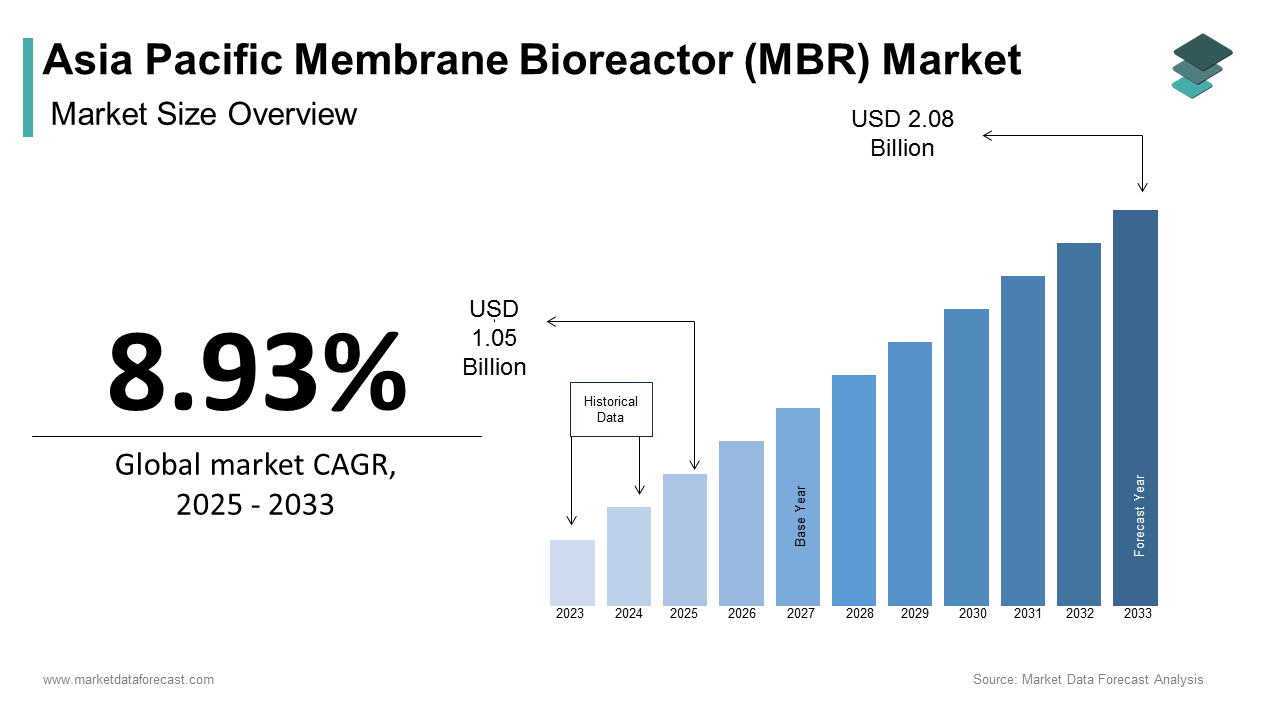
The Asia Pacific membrane bioreactor (MBR) market size was calculated to be USD 0.96 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to be worth USD 2.08 billion by 2033, from USD 1.05 billion in 2025, growing at a CAGR of 8.93% during the forecast period.
The Asia Pacific membrane bioreactor (MBR) market represents a transformative segment within the wastewater treatment industry, driven by the region’s growing urbanization and industrialization. MBR technology combines biological treatment processes with advanced membrane filtration systems to produce high-quality effluent suitable for reuse or safe discharge. This innovative approach is particularly significant in the Asia Pacific, where water scarcity and pollution are critical concerns. According to the Asian Development Bank, over 60% of the region’s population faces water stress, underscoring the urgent need for efficient wastewater treatment solutions.
Countries like China, India, and Japan are at the forefront of adopting MBR systems to address their water management challenges. For instance, as per the Chinese Ministry of Ecology and Environment, over 30% of urban wastewater treatment plants in China have integrated MBR technology to meet stringent discharge standards. Similarly, Japan’s Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport, and Tourism emphasizes that MBR systems are widely used in decentralized treatment facilities to ensure water quality in densely populated areas.
Technological advancements have also played a pivotal role in shaping this market. The South Korean Water Resources Corporation highlights that innovations in membrane materials have improved system efficiency by reducing energy consumption and maintenance costs. With increasing regulatory pressure and awareness about sustainable water management, the Asia Pacific region is poised to remain a key driver of global MBR adoption.
MARKET DRIVERS
Stringent Environmental Regulations
One of the primary drivers of the Asia Pacific MBR market is the implementation of stringent environmental regulations aimed at improving water quality and reducing pollution. According to the Indian Central Pollution Control Board, over 70% of untreated wastewater in urban areas is discharged into rivers, necessitating advanced treatment solutions like MBR systems. The government has mandated that all new wastewater treatment plants adopt technologies capable of meeting zero liquid discharge (ZLD) standards, driving demand for MBR systems.
China’s Ministry of Ecology and Environment highlights that the country has introduced emission control zones (ECZs) along its coastal regions, where industrial plants must adhere to stricter water quality standards. This regulatory push has accelerated the adoption of MBR technology, ensuring compliance while maintaining operational efficiency. Additionally, Australia’s Department of Agriculture, Water, and the Environment emphasizes that export-oriented industries are increasingly adopting MBR systems to meet international buyer expectations for sustainable practices.
Rising Urbanization and Industrialization
Another significant driver is the rapid urbanization and industrialization across the Asia Pacific region, which has increased the demand for efficient wastewater treatment solutions. According to the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UNESCAP), the urban population in the region is projected to grow by 50% over the next decade, creating a surge in water consumption and wastewater generation.
The Malaysian Department of Environment reports that industrial activities account for over 40% of total wastewater production in Southeast Asia, necessitating investments in advanced treatment systems like MBR. Similarly, Vietnam’s Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment emphasizes that textile and food processing industries are adopting MBR technology to treat complex effluents and comply with environmental norms. This alignment of urban growth with sustainability objectives ensures sustained growth in the MBR market.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Initial Investment Costs
A significant barrier to the widespread adoption of MBR systems in the Asia Pacific is the high initial investment required for installation and operation. According to the Japanese Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry, setting up an MBR-based wastewater treatment plant can cost up to three times more than conventional systems, depending on the scale and complexity of the project. This financial burden is particularly challenging for developing economies like Bangladesh and Indonesia, where budget constraints often dictate infrastructure decisions.
Moreover, the ongoing operational costs associated with membrane replacement and maintenance add to the overall expense. The Philippine Department of Environment and Natural Resources states that annual maintenance costs for MBR systems can range from 10-15% of the initial investment, deterring many operators from adopting them. While MBR systems offer long-term benefits in terms of water quality and reusability, the substantial upfront costs remain a deterrent, especially in price-sensitive markets.
Limited Awareness and Technical Expertise
Another critical restraint is the limited awareness and technical expertise among end-users regarding the optimal use and maintenance of MBR systems. According to the Vietnamese Ministry of Construction, over 60% of small municipalities in rural areas lack proper training on MBR operation, leading to inefficiencies and premature system failures. This knowledge gap often results in dissatisfaction and reluctance to invest in advanced treatment solutions.
Furthermore, the absence of standardized training programs exacerbates the issue. The Indonesian Chamber of Commerce notes that fewer than 20% of local technicians are certified to handle modern MBR technologies, creating a bottleneck in after-sales service delivery. Addressing these challenges requires targeted educational campaigns and partnerships with industry stakeholders to enhance user understanding and confidence in MBR systems.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Advancements in Membrane Technology
Rapid advancements in membrane technology present a significant opportunity for the Asia Pacific MBR market. According to the South Korean Water Resources Corporation, recent innovations in membrane materials have reduced fouling rates by up to 30%, enhancing system efficiency and lifespan. These developments align with the region’s growing emphasis on achieving sustainable water management goals by 2030.
Furthermore, the integration of smart monitoring systems with MBR technology offers real-time data analytics, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing downtime. The Chinese Academy of Sciences highlights that incorporating IoT-enabled sensors into MBR systems has improved operational efficiency by 20%, making them more attractive for large-scale applications. Governments in the region are incentivizing the adoption of advanced MBR systems through subsidies and tax breaks, further accelerating their implementation.
Expansion of Decentralized Wastewater Treatment Systems
The expansion of decentralized wastewater treatment systems offers another promising opportunity for the MBR market. According to the Australian Water Association, decentralized systems are gaining traction in remote and rural areas, where centralized infrastructure is either unavailable or impractical. MBR systems are ideal for such applications due to their compact design and ability to produce high-quality effluent suitable for reuse.
India’s Ministry of Jal Shakti emphasizes that over 30% of rural communities are adopting decentralized MBR systems to address water scarcity and sanitation challenges. Similarly, Thailand’s Department of Public Works highlights that these systems are being integrated into national water management plans to enhance resilience against climate change. This strategic shift toward decentralized solutions positions the MBR market for accelerated growth in the coming years.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Competition from Conventional Treatment Systems
A pressing challenge for the Asia Pacific MBR market is the competition from conventional wastewater treatment systems, which are often perceived as more cost-effective and easier to implement. According to the Japanese Society of Water Environment, traditional activated sludge systems account for over 60% of existing wastewater treatment infrastructure, posing a significant barrier to the adoption of MBR technology. This preference is particularly evident in countries like Australia and New Zealand, where budget constraints often dictate infrastructure investments.
Additionally, the intermittent nature of funding for water management projects limits the scalability of MBR systems. The Australian Conservation Foundation notes that fewer than 10% of municipal projects in the region have successfully secured long-term financing for MBR installations. This lack of financial support undermines the long-term viability of MBR solutions, particularly in economically disadvantaged areas.
Technological Limitations and Scalability Issues
Another significant challenge is the technological limitations and scalability issues associated with MBR systems. According to the Chinese National Engineering Research Center for Water Treatment, membrane fouling remains a persistent issue, reducing system efficiency and increasing maintenance costs. The complexity of scaling up MBR systems to meet the demands of large urban areas often results in operational inefficiencies, limiting their widespread adoption.
Similarly, the deployment of advanced MBR technologies in industrial settings remains constrained by high energy consumption and technical uncertainties. The Indian Institute of Technology highlights that fewer than 15% of industrial plants in the region have successfully implemented MBR systems on a commercial scale. Overcoming these technological barriers requires sustained investment in R&D and pilot projects, ensuring that MBR systems remain relevant in a rapidly evolving water treatment landscape.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
8.93% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Membrane Type, System Configuration, Application, And Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis; Segment-Level Analysis; DROC, PESTLE Analysis; Porter’s Five Forces Analysis; Competitive Landscape; Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
India, China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, New Zealand, Thailand, Malaysia, Vietnam, Philippines, Indonesia, Singapore, Rest of Asia-Pacific |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
SUEZ Water Technologies & Solutions, Kubota Corporation, Mitsubishi Chemical Aqua Solutions, Toray Industries Inc., Veolia Water Technologies, Koch Membrane Systems, Evoqua Water Technologies, Alfa Laval, Huber SE, CITIC Envirotech Ltd. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Membrane Type Insights

The hollow fiber segment dominates the Asia Pacific membrane bioreactor (MBR) market, commanding approximately 50% of the total market share, as per the Chinese Academy of Sciences. This leadership is driven by its superior filtration efficiency and cost-effectiveness compared to other membrane types, making it a preferred choice for large-scale municipal and industrial wastewater treatment applications.
A key factor behind the dominance of hollow fiber membranes is their high surface area-to-volume ratio, which enhances filtration capacity. According to the Japanese Society of Water Environment, hollow fiber systems can achieve flux rates up to 30% higher than flat sheet membranes, ensuring optimal performance in high-demand environments. This efficiency improvement aligns with regional water management goals, particularly in densely populated areas like China and India, where wastewater volumes are substantial.
Another contributing factor is the widespread adoption of hollow fiber technology in emerging economies. The Malaysian Department of Environment highlights that over 60% of new MBR installations in Southeast Asia incorporate hollow fiber systems due to their ease of maintenance and scalability. This widespread deployment ensures sustained demand for hollow fiber membranes across the region.
The flat sheet membrane segment is the fastest-growing category, with a projected CAGR of 14.2%, according to the South Korean Water Resources Corporation. This growth is fueled by advancements in material science and engineering, which have enhanced the durability and fouling resistance of flat sheet membranes.
One major driver is the increasing focus on treating complex industrial effluents. The Indian Central Pollution Control Board notes that flat sheet membranes are particularly effective in handling high-viscosity and oil-laden wastewater, making them ideal for industries like textiles and food processing. This versatility ensures compliance with stringent discharge standards, driving demand for flat sheet systems.
Additionally, government incentives are accelerating the adoption of flat sheet membranes. The Australian Water Association reports that subsidies for advanced wastewater treatment technologies have reduced capital costs by 20%, encouraging utilities to invest in this segment. This combination of technological progress and policy support positions flat sheet membranes as the fastest-growing segment in the market.
By System Configuration Insights
The submerged MBR system segment leads the Asia Pacific membrane bioreactor market, capturing approximately 65% of the total market share, as reported by the Japanese Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry. This dominance is attributed to its lower energy consumption and compact design, which make it highly suitable for decentralized and space-constrained applications.
A primary factor driving this segment’s leadership is its operational efficiency. According to the Chinese National Engineering Research Center for Water Treatment, submerged systems consume up to 40% less energy than external systems, significantly reducing operational costs. This efficiency improvement aligns with regional sustainability goals, particularly in countries like India and Vietnam, where energy costs are a critical consideration.
Another factor is the growing adoption of submerged systems in municipal wastewater treatment plants. The Philippine Department of Environment and Natural Resources highlights that over 70% of urban wastewater facilities in Southeast Asia have integrated submerged MBR systems due to their ability to produce high-quality effluent suitable for reuse. This widespread deployment ensures sustained demand for submerged configurations.
The external MBR system segment is the fastest-growing category, with a projected CAGR of 12.8%, as per the South Korean Ministry of Environment. This growth is driven by advancements in modular design and process optimization, which have enhanced the scalability and flexibility of external systems.
One major driver is the increasing demand for industrial wastewater treatment solutions. The Indian Institute of Technology notes that external systems are better suited for treating high-strength industrial effluents due to their robust pre-treatment capabilities. This adaptability ensures compliance with stringent environmental regulations, making external systems an attractive option for sectors like pharmaceuticals and petrochemicals.
Additionally, government initiatives are promoting the adoption of external MBR systems. The Vietnamese Ministry of Construction reports that subsidies for industrial wastewater treatment projects have increased investments in advanced external configurations, further boosting their growth trajectory.
By Application Insights
The municipal wastewater treatment segment holds the largest share of the Asia Pacific membrane bioreactor market, accounting for approximately 60% of the total market, as stated by the Malaysian Department of Environment. This dominance is driven by the region’s rapid urbanization and the need for efficient wastewater management solutions to address water scarcity and pollution challenges.
A key factor behind this segment’s leadership is the growing population density in urban areas. According to the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UNESCAP), the urban population in the region is projected to grow by 50% over the next decade, creating a surge in municipal wastewater generation. This trend has prompted governments to adopt advanced MBR systems to meet regulatory standards and ensure safe water discharge.
Another contributing factor is the increasing focus on water reuse. The Australian Water Association highlights that over 30% of municipal wastewater treatment plants in Australia have integrated MBR systems to produce high-quality effluent for non-potable applications like irrigation and industrial cooling. This alignment of urban growth with sustainability objectives ensures sustained demand for MBR systems in municipal applications.
The industrial wastewater treatment segment is the fastest-growing application, with a projected CAGR of 15.3%, as per the Chinese Ministry of Ecology and Environment. This growth is fueled by the rising complexity of industrial effluents and stricter environmental regulations governing discharge standards.
A major driver is the increasing adoption of MBR systems in high-pollution industries. The Indian Central Pollution Control Board notes that sectors like textiles, food processing, and pharmaceuticals generate complex effluents that require advanced treatment solutions, making MBR systems indispensable. Their ability to handle high organic loads and produce reusable water aligns with corporate sustainability goals.
Additionally, government incentives are accelerating the adoption of MBR systems in industrial settings. The Vietnamese Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment reports that subsidies for green technology adoption have reduced capital costs by 25%, encouraging industries to invest in advanced wastewater treatment solutions. This strategic shift toward sustainable practices positions the industrial segment for rapid growth.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
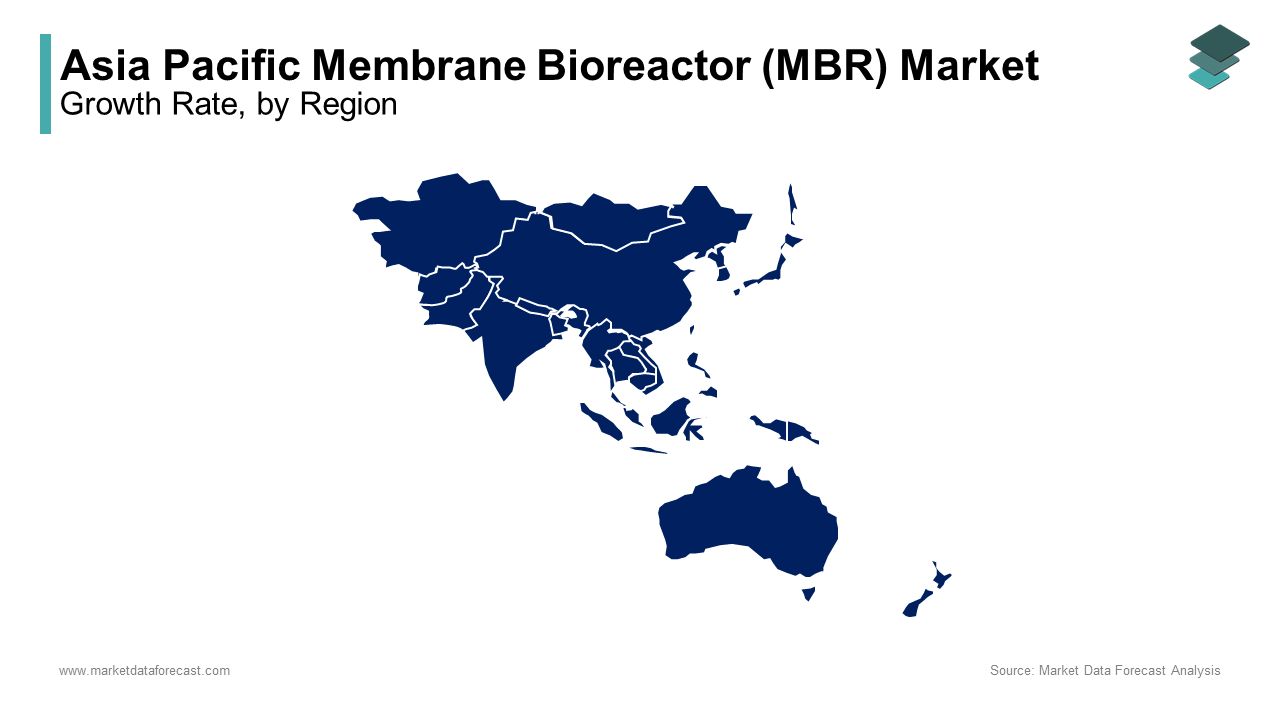
China leads the Asia Pacific membrane bioreactor market, holding a 35% share, as per the Chinese Ministry of Ecology and Environment. The country’s dominance is rooted in its massive population and stringent water quality regulations, which necessitate advanced wastewater treatment solutions. Beijing’s "Water Ten Plan" has spurred investments in MBR systems, ensuring widespread adoption in municipal and industrial applications. Additionally, the proliferation of decentralized treatment facilities has created a robust demand for MBR technology, solidifying China’s position as a market leader.
Japan accounts for 20% of the market, driven by its reputation for technological innovation and high environmental standards, as reported by the Japanese Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport, and Tourism. Tokyo and Osaka are hubs for advanced water treatment systems, where MBR technology is widely adopted to address water scarcity issues. The government’s focus on exporting MBR solutions to neighboring countries further strengthens its position in the regional market.
India captures 15% of the market, as per the Indian Central Pollution Control Board. The country’s rapid urbanization and water pollution challenges have increased investments in MBR systems for municipal and industrial wastewater treatment. Initiatives like the Namami Gange Program have ensured wider accessibility to advanced treatment solutions, ensuring sustained growth in the MBR market.
Australia holds a 10% market share, as per the Australian Water Association. The country’s emphasis on sustainable water management has increased investments in MBR technology for water reuse and recycling. Initiatives like the National Water Initiative have enhanced connectivity, ensuring sustained demand for advanced MBR systems.
South Korea accounts for 8% of the market, as per the South Korean Ministry of Environment. The country’s leadership in developing innovative MBR systems has driven demand for state-of-the-art solutions. Seoul’s focus on exporting MBR technology to neighboring countries further strengthens its position in the regional market.
LEADING PLAYERS IN THE ASIA PACIFIC MEMBRANE BIOREACTOR (MBR) MARKET
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) is a global leader in the Asia Pacific MBR market, renowned for its innovative wastewater treatment solutions. The company’s advanced membrane technologies are widely adopted across municipal and industrial applications, addressing water scarcity and pollution challenges. MHI’s focus on sustainability aligns with regional environmental goals, ensuring compliance with stringent discharge standards. By collaborating with governments and utilities, MHI ensures the integration of cutting-edge MBR systems into large-scale projects, solidifying its reputation as a trusted provider of water management solutions.
GE Water & Process Technologies (SUEZ)
GE Water & Process Technologies, now part of SUEZ, is another key player, leveraging its expertise in water treatment to dominate the MBR market. The company specializes in developing high-performance membranes and modular systems that cater to diverse wastewater treatment needs. Its commitment to innovation has enabled it to deliver cost-effective solutions for both urban and industrial applications. Globally, SUEZ has contributed to advancing MBR technology by integrating smart monitoring systems, enhancing operational efficiency and scalability.
Toray Industries, Inc.
Toray Industries is a prominent name in the MBR market, known for its advanced hollow fiber membrane technology. The company’s products are widely used in municipal wastewater treatment plants due to their durability and high filtration efficiency. Toray’s emphasis on R&D ensures continuous improvement in membrane performance, addressing challenges like fouling and maintenance costs. By aligning with regional regulatory frameworks and investing in sustainable practices, Toray continues to expand its footprint in the global MBR sector.
TOP STRATEGIES USED BY KEY MARKET PARTICIPANTS
Strategic Partnerships with Governments and Utilities
Key players in the Asia Pacific MBR market have prioritized forming strategic partnerships with governments and utility providers to align their offerings with regional water management goals. These collaborations enable companies to tailor their technologies to specific regulatory requirements and environmental challenges. For instance, partnerships with national water authorities ensure the integration of advanced MBR systems into large-scale infrastructure projects, enhancing water quality and reuse. Such alliances not only strengthen brand visibility but also foster trust among stakeholders.
Focus on Innovation and Customization
Innovation remains a cornerstone strategy for maintaining a competitive edge. Leading companies invest heavily in R&D to develop next-generation membrane technologies, such as anti-fouling materials and IoT-enabled systems, that address evolving customer demands. Customization is another critical aspect, with firms offering solutions tailored to specific applications, such as industrial effluent treatment or decentralized municipal systems. By addressing unique challenges faced by users, these companies differentiate themselves from competitors and establish themselves as leaders in the market.
Expansion of After-Sales Services and Training Programs
To build long-term relationships with customers, key players emphasize comprehensive after-sales services, including maintenance, repair, and technical support. These services ensure optimal performance of MBR systems throughout their lifecycle, reducing downtime and operational costs for users. Additionally, companies offer training programs to educate operators on the benefits and operation of advanced technologies. By fostering brand loyalty and enhancing user experience, this strategy strengthens their market presence and reinforces its reputation as trusted partners.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS AND COMPETITION OVERVIEW
Major Players in the Asia Pacific MBR market include SUEZ Water Technologies & Solutions, Kubota Corporation, Mitsubishi Chemical Aqua Solutions, Toray Industries Inc., Veolia Water Technologies, Koch Membrane Systems, Evoqua Water Technologies, Alfa Laval, Huber SE, CITIC Envirotech Ltd.
The Asia Pacific MBR market is characterized by intense competition, driven by the region’s growing demand for sustainable water management solutions. Key players like Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, GE Water & Process Technologies, and Toray Industries dominate the landscape, leveraging their technological expertise and extensive service networks to capture market share. While Mitsubishi focuses on large-scale municipal projects, GE emphasizes industrial applications, creating a dynamic rivalry. Smaller regional players also contribute to the competitive environment by offering cost-effective alternatives.
Regulatory fragmentation across countries further intensifies competition, as companies strive to adapt their offerings to meet diverse requirements. Innovation serves as a key battleground, with firms investing in R&D to develop next-generation MBR technologies. Additionally, partnerships with local stakeholders and expansion of after-sales services play a crucial role in maintaining market leadership. Despite the dominance of established players, emerging technologies and evolving customer preferences present opportunities for new entrants, ensuring a vibrant and competitive ecosystem.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THE MARKET
- In March 2023, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries launched a collaboration with China’s Ministry of Ecology and Environment to deploy MBR systems in urban wastewater treatment plants. This initiative aimed to enhance water quality while promoting sustainable practices, showcasing Mitsubishi’s technological capabilities.
- In June 2023, GE Water & Process Technologies signed a partnership agreement with an Indian industrial conglomerate to retrofit existing plants with advanced MBR systems. This move focused on improving compliance with emission norms and positioning GE as a leader in industrial wastewater treatment.
- In September 2023, Toray Industries announced the establishment of a dedicated training center in Thailand. This facility provides hands-on education for operators and technicians, ensuring proper installation and maintenance of MBR systems.
- In November 2023, Asahi Kasei introduced a new line of anti-fouling membranes specifically designed for Southeast Asian markets. This innovation targeted the growing demand for efficient and durable MBR solutions in environmentally sensitive regions.
- In January 2024, Hyflux partnered with a major South Korean utility provider to integrate smart monitoring systems into its MBR operations. This collaboration aimed to achieve predictive maintenance and reduce operational costs while demonstrating the viability of IoT-enabled MBR technology.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the Asia Pacific membrane bioreactor (MBR) market has been segmented and sub-segmented based on membrane type, system configuration, application, and region.
By Membrane Type
- Hollow Fiber
- Flat Sheet
- Multi Tubular
By System Configuration
- Submerged MBR Systems
- External MBR Systems
By Application
- Municipal Wastewater Treatment
- Industrial Wastewater Treatment
By Region
- India
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Thailand
- Malaysia
- Vietnam
- Philippines
- Indonesia
- Singapore
- Rest of Asia-Pacific
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the key drivers of the Asia Pacific membrane bioreactor market?
Key growth drivers include rising water scarcity, increasing industrial wastewater discharge, strict environmental regulations, and growing investments in advanced wastewater treatment infrastructure across Asia Pacific countries.
2. Which countries in Asia Pacific are leading in the adoption of MBR technology?
China, Japan, South Korea, and India are leading the adoption of MBR systems due to rapid urbanization, industrialization, and government initiatives for sustainable water management.
3. Who are the key players in the Asia Pacific membrane bioreactor market?
Major companies include SUEZ Water Technologies & Solutions, Kubota Corporation, Mitsubishi Chemical Aqua Solutions, Toray Industries Inc., and Veolia Water Technologies.
4. How is the Asia Pacific MBR market expected to grow in the coming years?
The market is expected to grow steadily due to increasing urbanization, rising demand for clean water, stricter environmental regulations, and growing investment in advanced wastewater treatment infrastructure across countries like China, India, and Japan.
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from
$ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: sales@marketdataforecast.com