Asia Pacific Microgrid Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report By Power Source (Natural Gas, Fuel Cells), Product, Application, And Country (India, China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, New Zealand, Thailand, Malaysia, Vietnam, Philippines, Indonesia, Singapore And Rest of Asia-Pacific), Industry Analysis From 2025 To 2033
Asia Pacific Microgrid Market Size
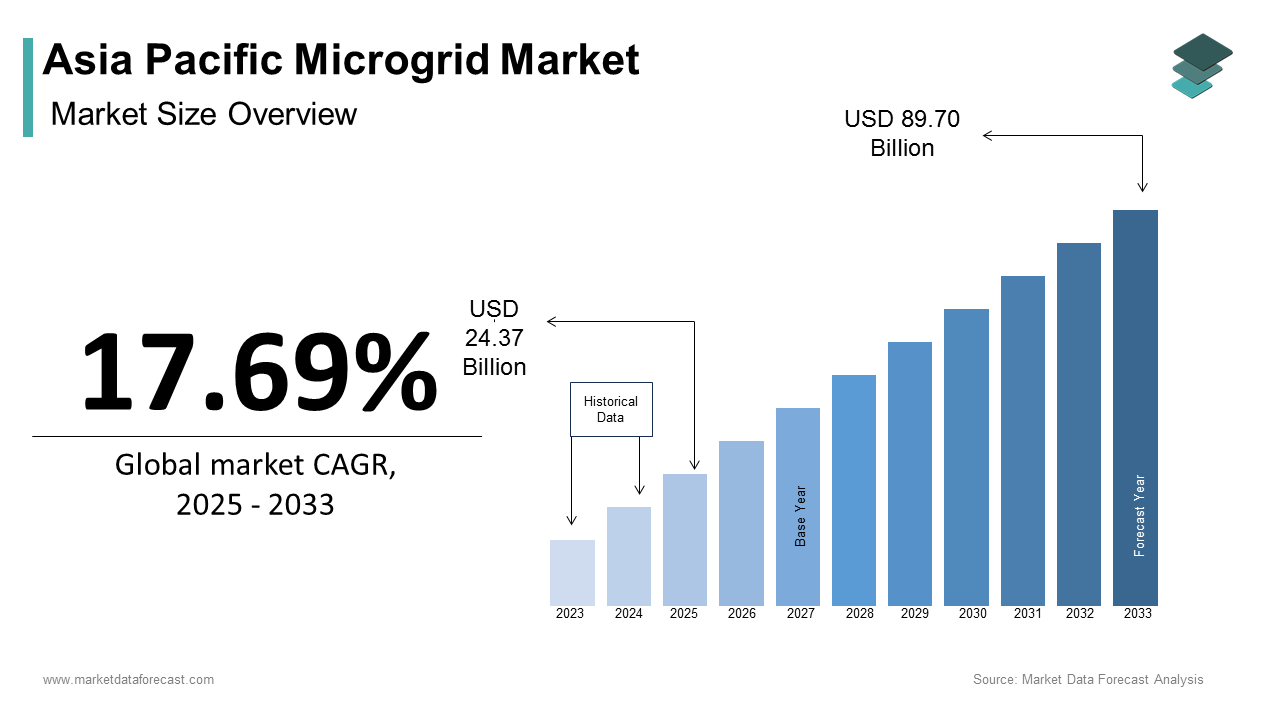
The Asia Pacific microgrid market size was calculated to be USD 20.70 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to be worth USD 89.70 billion by 2033, from USD 24.37 billion in 2025, growing at a CAGR of 17.69% during the forecast period.
MARKET DRIVERS
Energy Access in Remote Areas
A key driver of the Asia Pacific microgrid market is the urgent need to provide energy access in remote and underserved regions. Microgrids offer a cost-effective way to deliver power to these areas, leveraging renewable energy sources like solar and wind. For instance, India’s Ministry of New and Renewable Energy reports that a large number of solar microgrids have been installed in rural villages, providing electricity to more than 10 million households. Additionally, governments are incentivizing microgrid deployment. The Government of Indonesia has allocated $1 billion to develop renewable energy microgrids in remote islands, aiming to achieve universal electrification by 2030. Similarly, Papua New Guinea’s Electrification Partnership seeks to deploy microgrids to connect 70% of its population to electricity by 2030.
Integration of Renewable Energy Sources
The increasing adoption of renewable energy sources is another major driver propelling the Asia Pacific microgrid market forward. Microgrids enable seamless integration of intermittent energy sources like solar and wind, ensuring stable and reliable power supply. E.g., China’s State Grid Corporation has implemented over 1,000 renewable energy microgrids in urban areas, reducing carbon emissions significantly. In Australia, the Australian Renewable Energy Agency supports pilot projects combining solar microgrids with battery storage, achieving energy savings. Furthermore, South Korea’s Green New Deal emphasizes microgrids as part of its strategy to transition to a low-carbon economy.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Initial Costs and Financing Challenges
One of the primary restraints hindering the Asia Pacific microgrid market is the high initial investment required for deployment. Microgrid systems involve complex technologies such as energy storage, inverters, and control systems, which significantly elevate costs. In emerging economies like Vietnam and the Philippines, securing financing remains a significant barrier. Additionally, the lack of standardized regulatory frameworks complicates project approvals, further delaying implementation.
Regulatory and Policy Uncertainty
Another critical restraint is the lack of clear regulatory frameworks governing microgrid operations. For instance, in India, state-level regulations often conflict with national policies, leading to delays in project execution. Furthermore, tariff structures for microgrid-generated electricity are often unclear, discouraging private sector participation. A study by the Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce and Industry shows that ambiguous policies hinder the integration of microgrids with main grids, limiting their potential.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Decentralized Energy Solutions in Urban Areas
Urban areas in the Asia Pacific region present immense opportunities for microgrid adoption, driven by the need for resilient and sustainable energy systems. According to the United Nations, 68% of Asia’s population will reside in cities by 2050, increasing energy demand and straining existing grids. Microgrids offer a decentralized solution, enabling localized power generation and distribution. Singapore’s Smart Nation initiative, for example, includes deploying microgrids in industrial parks to enhance energy efficiency and reduce reliance on centralized grids. In Japan, Tokyo Electric Power Company has piloted microgrid projects in commercial districts, achieving energy savings of 15%.
Cross-Border Energy Trade and Export Potential
Microgrids also present opportunities for cross-border energy trade and export, particularly in Southeast Asia. According to the ASEAN Centre for Energy, regional collaboration on microgrid projects can enhance energy security and promote renewable energy exports. For instance, Laos and Thailand have partnered to develop solar microgrids, exporting surplus energy to neighboring countries. Similarly, Australia’s National Hydrogen Strategy outlines plans to integrate microgrids with green hydrogen production, positioning the country as a global exporter of clean energy. A report estimates that cross-border microgrid initiatives could generate $20 billion in economic value by 2030. Furthermore, India’s International Solar Alliance encourages member countries to adopt microgrids, fostering regional cooperation.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Technical Integration with Existing Grids
A significant challenge facing the Asia Pacific microgrid market is the technical integration of microgrids with existing centralized grids. According to the International Energy Agency, many traditional grids in the region lack the infrastructure to accommodate decentralized energy systems, leading to operational inefficiencies. For example, in rural India, frequent voltage fluctuations and grid instability hinder seamless integration, resulting in higher maintenance costs. Additionally, outdated grid management systems pose compatibility issues. Furthermore, the absence of real-time monitoring tools limits the ability to optimize energy flows between microgrids and main grids.
Public Awareness and Acceptance
Another pressing challenge is the lack of public awareness and acceptance of microgrid technologies. Misconceptions about the reliability and safety of decentralized energy systems persist, deterring consumer adoption despite proven benefits. This perception gap is particularly pronounced in rural areas, where educational campaigns are minimal. Moreover, misinformation about the environmental benefits of microgrids undermines their appeal among eco-conscious consumers. For instance, South Korea’s Ministry of Environment reports that less than 5% of its annual budget is allocated to microgrid awareness initiatives.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
17.69% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Power Source, Product, Application, And Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis; Segment-Level Analysis; DROC, PESTLE Analysis; Porter’s Five Forces Analysis; Competitive Landscape; Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
India, China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, New Zealand, Thailand, Malaysia, Vietnam, Philippines, Indonesia, Singapore, Rest of Asia-Pacific |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
ABB; Siemens AG; General Electric; Eaton Corp.; Exelon; Honeywell International; NRG International; Anarbic; Pareto; Spirae; Northern Power; Viridity |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Power Source Insights
The natural gas segment dominated the Asia Pacific microgrid market by capturing a 45.6% of the total share in 2024. This prominence is driven by its reliability and cost-effectiveness as a primary energy source. Natural gas-powered microgrids are particularly favored in urban areas where grid stability is critical. For instance, Japan’s Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry noted that natural gas microgrids account for over 60% of installations in commercial districts, ensuring uninterrupted power supply during peak demand periods. Government policies also amplify its dominance. Additionally, Australia’s National Energy Market supports natural gas microgrids as a transitional solution toward renewable energy adoption.
The fuel cells segment is projected to rise at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 38% from 2025 to 2033. This rapid expansion is fueled by advancements in hydrogen technology and increasing investments in clean energy solutions. Urban mobility also plays a role. Furthermore, Japan’s Strategic Road Map for Hydrogen emphasizes fuel cell applications in residential complexes, targeting 10% adoption by 2030.
By Product Insights
The remote microgrids segment held the largest market share at 50.5% in 2024. This dominance is due to their ability to provide reliable electricity in off-grid and underserved regions. India’s Ministry of New and Renewable Energy reports that over 70% of rural electrification projects rely on remote microgrids, with more than 5,000 systems installed as of 2022. Government initiatives further bolster their adoption. Similarly, Papua New Guinea’s Electrification Partnership seeks to connect 70% of its population using remote microgrids by 2030.
The hybrid microgrids segment is poised to grow at a CAGR of 42.7%. This surge is driven by their ability to integrate multiple energy sources, such as solar, wind, and battery storage, ensuring optimal performance. Additionally, Australia’s Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation emphasizes hybrid microgrids as a solution for remote mining operations, achieving energy savings. South Korea’s Green New Deal also prioritizes hybrid microgrids for industrial applications, targeting a 40% reduction in emissions by 2030.
By Application Insights
The commercial sector accounted for 40.4% of the Asia Pacific microgrid market in 2024. This dominance is driven by the need for reliable and cost-effective energy solutions in industries like retail, hospitality, and manufacturing. For instance, China’s Five-Year Plan mandates the deployment of microgrids in commercial zones to enhance energy efficiency and reduce reliance on centralized grids. Technological advancements also play a role. Furthermore, Japan’s Tokyo Electric Power Company has piloted microgrid projects in commercial districts, ensuring uninterrupted power supply during peak demand periods.
The education sector is predicted to advance at a CAGR of 35%. This quick development is caused by the increasing adoption of microgrids in educational institutions to ensure energy resilience and sustainability. Government incentives further accelerate adoption. India’s Ministry of Education highlights that over 100 universities have adopted microgrids under the National Solar Mission, supported by subsidies worth $50 million annually.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
China led the Asia Pacific microgrid market by holding a 30.3% share in 2024. This dominance is driven by aggressive investments in renewable energy and smart city initiatives. Government backing plays a pivotal role. China’s State Grid Corporation reports that microgrid deployments have reduced carbon emissions by 20%, aligning with national decarbonization targets. Additionally, the government’s substantial investment in microgrid infrastructure ensures steady growth, positioning China as a leader in sustainable energy transitions.
India commands a significant market share which is driven by its focus on rural electrification and renewable energy integration. Government initiatives further amplify adoption. The International Solar Alliance encourages member countries to adopt microgrids, fostering regional cooperation. Also, India’s National Hydrogen Mission integrates microgrids with green hydrogen solutions, ensuring long-term sustainability.
Australia is accelerating in the market by leveraging its abundant renewable energy resources for microgrid deployment. The Australian Renewable Energy Agency outlines plans to integrate microgrids with green hydrogen production, positioning the country as a global exporter of clean energy. Mining companies like Fortescue Metals Group invest heavily in microgrid solutions, achieving energy savings.
Japan is a major player in the market and that is propelled by its focus on urban energy resilience and hydrogen integration. Residential complexes increasingly adopt fuel cell microgrids, supported by the Strategic Road Map for Hydrogen. Public-private partnerships further drive adoption. Tokyo Electric Power Company has implemented a large number of microgrid projects in commercial districts, ensuring uninterrupted power supply during peak demand periods.
South Korea holds a notable market share. It is driven by its Green New Deal and hydrogen economy initiatives. Hyundai Motor Group collaborates with local governments to deploy hybrid microgrids in industrial zones, achieving a reduction in emissions by 2030. Educational institutions also embrace microgrids. The Green Campus Initiative promotes solar microgrid installations in schools, targeting a 10% reduction in energy costs.
LEADING PLAYERS IN THE ASIA PACIFIC MICROGRID MARKET
Schneider Electric
Schneider Electric is a global leader in energy management and automation, playing a pivotal role in advancing microgrid solutions across the Asia Pacific region. The company focuses on integrating renewable energy sources with advanced control systems to create resilient and sustainable microgrids. Its emphasis on innovation and scalability positions it as a key contributor to the global microgrid market.
ABB Ltd
ABB Ltd is renowned for its expertise in electrification and digital technologies, making it a dominant player in the microgrid space. The company’s Ability™ e-mesh platform provides end-to-end solutions for managing distributed energy resources, ensuring seamless integration of renewables. ABB’s focus extends beyond urban areas, as it actively deploys microgrids in remote regions to address energy access challenges. Through strategic partnerships with utilities and research institutions, ABB drives advancements in grid resilience and energy efficiency. Its commitment to sustainability underscores its leadership in shaping the future of decentralized energy systems globally.
Siemens AG
Siemens AG leverages its extensive experience in power systems to deliver cutting-edge microgrid solutions tailored to the Asia Pacific market. The company’s Sinalytics platform enables predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring, ensuring optimal performance of microgrid systems. Its focus on smart city initiatives and renewable energy integration shows its contribution to global energy transitions. Siemens’ innovative approach ensures its prominence in the rapidly evolving microgrid landscape.
TOP STRATEGIES USED BY KEY PLAYERS
Expansion of Product Portfolios
Key players in the Asia Pacific microgrid market are diversifying their product offerings to cater to varying customer needs. Companies like Schneider Electric and ABB are introducing modular and scalable solutions that can be customized for different applications, from rural electrification to urban energy management. This strategy also enables them to capture emerging opportunities in sectors such as education and government infrastructure.
Investment in R&D and Innovation
Research and development form the cornerstone of competitive strategies in the microgrid market. Leading companies allocate significant resources to enhance system efficiencies, improve energy storage capabilities, and reduce costs. Innovations in artificial intelligence and IoT-based platforms enable real-time monitoring and optimization of microgrid operations. Collaborations with universities and research institutions drive breakthroughs in renewable energy integration, ensuring these companies stay ahead of technological trends and meet evolving customer demands.
Strategic Partnerships and Collaborations
Collaborations with governments, utilities, and private entities are critical for strengthening market presence. Companies like Siemens and ABB partner with local stakeholders to develop pilot projects and demonstrate the feasibility of microgrid solutions. These alliances help align with national energy policies while fostering mutual growth. Additionally, joint ventures with technology providers ensure access to cutting-edge innovations, enabling companies to deliver comprehensive solutions that address regional challenges effectively.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS AND COMPETITION OVERVIEW
Major Players of the Asia Pacific Microgrid Market include ABB, Siemens AG, General Electric, Eaton Corp, Exelon, Honeywell International, NRG International, Anarbic, Pareto, Spirae, Northern Power and Viridity
The Asia Pacific microgrid market is characterized by intense competition, driven by rapid technological advancements and increasing demand for sustainable energy solutions. Key players vie for dominance through innovation, strategic collaborations, and aggressive market penetration tactics. Established giants like Schneider Electric and Siemens compete alongside specialized firms like ABB, each leveraging unique strengths to capture market share. The race to develop cost-effective and efficient microgrid systems fuels continuous R&D efforts, resulting in a dynamic landscape marked by frequent product launches and technological breakthroughs. Governments play a pivotal role by offering subsidies and creating favorable policies, intensifying competition among participants striving to capitalize on these incentives. Emerging startups further disrupt the status quo by introducing niche applications, challenging incumbents to adapt quickly. Additionally, collaborations between international and regional players blur traditional boundaries, fostering an ecosystem where innovation thrives.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THE MARKET
- In January 2023, Schneider Electric launched a new AI-driven microgrid management platform in Australia, enabling real-time optimization of renewable energy integration and enhancing grid resilience for industrial clients.
- In March 2023, ABB partnered with the Indian government to deploy solar-powered microgrids in rural villages, supporting the nation’s goal of achieving universal electrification by 2030.
- In June 2023, Siemens completed the acquisition of a renewable energy startup in South Korea, strengthening its capabilities in hybrid microgrid solutions and expanding its footprint in the Asia Pacific region.
- In September 2023, Schneider Electric announced a collaboration with Thailand’s Ministry of Energy to pilot microgrid projects in educational institutions, promoting energy efficiency and sustainability in the education sector.
- In December 2023, ABB signed a memorandum of understanding with Vietnam’s largest utility provider to develop smart microgrid systems for urban areas, aiming to reduce reliance on centralized grids and improve energy reliability.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the Asia Pacific microgrid market has been segmented and sub-segmented based on power source, product, application, and region.
By Power Source
- Natural Gas
- Fuel Cells
By Product
- Remote Microgrids
- Hybrid Microgrids
By Application
- Commercial
- Education
By Region
- India
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Thailand
- Malaysia
- Vietnam
- Philippines
- Indonesia
- Singapore
- Rest of Asia-Pacific
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is driving the growth of the microgrid market in Asia Pacific?
Key drivers include increasing energy demand, rural electrification programs, integration of renewable energy, government incentives, and a need for energy security and resilience.
2. Which countries are leading in microgrid adoption in Asia Pacific?
China, India, Japan, Australia, and South Korea are at the forefront, supported by policy initiatives, investments in smart grids, and renewable energy targets.
3. Who are the key players in the Asia Pacific microgrid market?
ABB, Schneider Electric, Siemens AG, Hitachi Energy, GE, Tesla, Toshiba, Eaton, Honeywell, and Caterpillar are among the major companies.
4. How is digital technology transforming microgrid operations?
Digital tools like IoT, AI, and smart meters optimize energy use, enable real-time monitoring, and improve microgrid efficiency and automation.
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from
$ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: sales@marketdataforecast.com