Asia Pacific Power Rental Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report By Power Rating (Below 75 kVA, 75–375 kVA, 375–750 kVA, Above 750 kVA), Fuel Type (Diesel, Gas, Others), Application (Continuous Load, Standby Load, Peak Load), End-user (Mining, Construction, Manufacturing, Utility, Events, Oil & Gas, Others), and Country (India, China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, New Zealand, Thailand, Malaysia, Vietnam, Philippines, Indonesia, Singapore, Rest of APAC) – Industry Analysis From 2025 to 2033.
Asia Pacific Power Rental Market Size
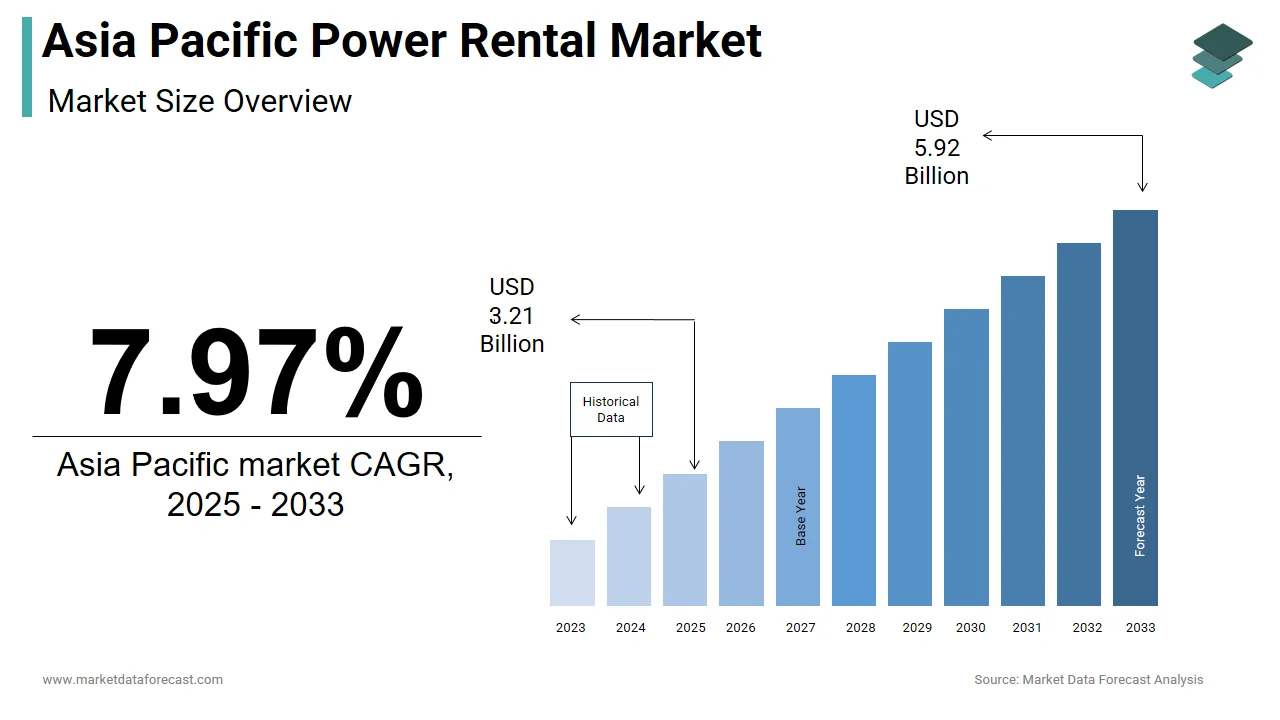
The size of the Asia Pacific power rental market was worth USD 2.97 billion in 2024. The Asia Pacific market is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 7.97% from 2025 to 2033 and be worth USD 5.92 billion by 2033 from USD 3.21 billion in 2025.
MARKET DRIVERS
Rising Industrialization and Urbanization
The rapid pace of industrialization and urbanization in the Asia Pacific region is a major driver of the power rental market. Industrial hubs like Japan’s automotive sector and South Korea’s electronics manufacturing rely heavily on an uninterrupted power supply. A study notes that industries facing grid instability often opt for rental generators, ensuring minimal disruptions. Furthermore, India’s push for "Make in India" initiatives has spurred demand for temporary power in manufacturing zones, supported by government subsidies. These trends demonstrate how industrial and urban growth propels the adoption of power rental services across the region.
Frequent Power Outages and Grid Instability
Frequent power outages and grid instability are significant drivers of the Asia Pacific power rental market. According to the World Bank, a significant portion of rural areas in Southeast Asia experience daily power interruptions, creating a strong demand for reliable backup solutions. Natural disasters further exacerbate grid vulnerabilities. The Philippines, prone to typhoons, relies on rental generators to restore electricity in disaster-affected areas. Similarly, Vietnam’s industrial zones frequently deploy rental power systems to mitigate grid failures, reducing downtime.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Operational Costs and Fuel Dependency
One of the primary restraints hindering the Asia Pacific power rental market is the high operational costs associated with fuel dependency. Diesel-powered generators, which dominate the market, require significant fuel expenses, making them less cost-effective for long-term use. Like, the cost of diesel fuel accounts for a notable share of the total operational expenses of rental generators, posing financial challenges for end-users. In emerging economies like Bangladesh and Myanmar, securing affordable fuel supplies remains a barrier, limiting the scalability of power rental services. Additionally, fluctuating oil prices further amplify operational uncertainties. Without innovative alternatives or government subsidies, the affordability of power rental services will remain constrained, impeding broader adoption.
Environmental Concerns and Regulatory Pressures
Another critical restraint is the growing environmental concerns and regulatory pressures surrounding diesel-powered generators. Like, governments across the region are implementing stricter emissions standards to combat air pollution, which disproportionately affects urban areas. For instance, China’s Ministry of Ecology and Environment mandates that rental generators meet Euro VI emission norms, increasing compliance costs for manufacturers. Similarly, India’s National Green Tribunal has imposed penalties on industries using high-emission generators, discouraging their adoption. These regulatory and environmental challenges create barriers to entry, slowing down the expansion of the power rental market while pushing companies to explore sustainable alternatives.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Integration of Renewable Energy Solutions
The integration of renewable energy solutions presents a transformative opportunity for the Asia Pacific power rental market. According to Wood Mackenzie, solar and wind-powered temporary solutions are gaining traction, particularly in remote areas with abundant renewable resources. Government incentives further accelerate adoption. India’s Ministry of New and Renewable Energy offers subsidies worth substantial amounts for deploying renewable-based rental systems in rural electrification projects. Additionally, Japan’s Strategic Road Map for Hydrogen emphasizes hydrogen fuel cell generators as a clean alternative, targeting 10% adoption by 2030.
Expansion into Emerging Markets
Emerging markets in Southeast Asia offer immense potential for the power rental industry, driven by rapid economic growth and infrastructure development. According to the Asian Development Bank, countries like Vietnam, Indonesia, and the Philippines are investing significantly in industrial and commercial projects, creating a robust demand for temporary power solutions. Furthermore, cross-border collaborations enhance market penetration. Singapore’s partnership with neighboring countries promotes the deployment of advanced rental systems, fostering regional energy resilience. These opportunities underscore how expanding into underserved markets can drive revenue growth while addressing critical energy needs.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Limited Awareness and Adoption in Rural Areas
A significant challenge facing the Asia Pacific power rental market is the limited awareness and adoption of rental solutions in rural and underserved regions. Misconceptions about the reliability and cost-effectiveness of rental generators persist, particularly in areas with low literacy rates and minimal outreach programs. For instance, Papua New Guinea’s rural communities rely heavily on traditional energy sources, with a small fraction of utilizing rental power systems. Bridging this awareness gap is essential to fostering confidence and driving adoption among underserved populations.
Competition from Permanent Grid Expansion
Another pressing challenge is the competition posed by permanent grid expansion initiatives across the region. According to the International Energy Agency, governments are investing heavily in upgrading and expanding centralized grids to provide reliable electricity, reducing the reliance on temporary power solutions. Similarly, China’s State Grid Corporation plans to extend its network to rural areas, achieving 99% electrification by 2030. Overcoming this challenge requires companies to differentiate their offerings by focusing on niche applications, such as disaster recovery and industrial peak shaving, to maintain market relevance.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
Segments Covered |
By Power Rating, Fuel Type, Application, End-user, and Region. |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional and Country-Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, Drivers, Restraints, Opportunities, Challenges; PESTLE Analysis; Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Countries Covered |
India, China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, New Zealand, Thailand, Malaysia, Vietnam, Philippines, Indonesia, Singapore, Rest of APAC |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Caterpillar Inc. (United States), Cummins Inc. (United States), Aggreko (United Kingdom), Atlas Copco (Sweden), Kohler-SDMO (France), Shenton Group (United Kingdom), NIDS GROUP (India), Jassim Transport & Stevedoring Co. K.S.C.C. (Kuwait), Pump Power Rental (United Kingdom), United Rentals (United States), Sudhir Power Ltd. (India), Modern Hiring Service (India), Newburn Power Rental Ltd (United Kingdom), Global Power Supply (United States), FG Wilson (United Kingdom), ProPower Rental (United States), APR Energy (United States), and others. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Power Rating Insights
The 75-375 kVA segment dominated the Asia Pacific power rental market by capturing a 40.8% of the total share in 2024. This dominance is driven by its versatility and suitability for a wide range of applications, from construction sites to small-scale industrial operations. For instance, India’s Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs highlights that a significant share of urban infrastructure projects rely on this power rating due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of deployment. Government initiatives further amplify adoption. The Asian Development Bank reports that countries like Indonesia and Vietnam are investing in temporary power solutions within this range to address energy shortages in rural areas. Additionally, Japan’s manufacturing sector frequently deploys 75-375 kVA generators to ensure uninterrupted operations during peak demand periods. These factors underscore how this segment balances affordability and performance, maintaining its leadership in the region.
The above 750 kVA segment is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12% from 2025 to 2033. This rapid expansion is fueled by increasing demand for high-capacity generators in large-scale industrial and utility projects. For example, China’s State Grid Corporation has deployed a large number of high-capacity generators in grid stabilization projects, achieving energy savings. Urbanization also plays a role. Furthermore, South Korea’s Green New Deal emphasizes high-capacity generators for renewable energy integration, targeting a 20% reduction in emissions by 2030.
By Fuel Type Insights
The segment of Diesel-powered generators commanded the Asia Pacific power rental market by accounting for 60.5% of the total share in 2024. This is because of their reliability and widespread availability, making them ideal for both emergency backup and continuous power supply. For instance, India’s Ministry of Power reports that diesel generators account for a significant majority of temporary power solutions during peak load periods. Industrial demand amplifies their dominance. The Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce and Industry notes that industries facing grid instability often opt for diesel generators, ensuring minimal disruptions. Similarly, Indonesia’s reliance on diesel-powered systems in disaster-prone areas underscores their critical role in addressing energy gaps while fostering resilience.
The gas-powered generators segment is poised to grow at a CAGR of 15%. This surge is propelled by increasing investments in cleaner energy solutions and stricter emissions regulations. For example, Japan’s Strategic Road Map for Hydrogen emphasizes natural gas generators as a transitional solution toward renewable energy adoption. Urban mobility also plays a role.
By Application Insights
The standby load applications held the largest market share at 45.5%. This influence is credited to frequent power outages and grid instability, particularly in emerging economies. For instance, standby generators account for a considerable share of temporary power solutions during typhoon seasons, ensuring uninterrupted electricity supply. Plus, government support further bolsters adoption. Similarly, India’s National Green Tribunal mandates the use of low-emission standby systems, aligning with national decarbonization goals. These efforts demonstrate how standby load applications address critical energy gaps while fostering sustainability.
The Peak load applications are estimated to grow at a CAGR of 10%. This rapid expansion is fueled by increasing industrial and commercial activities during peak demand periods. For example, China’s manufacturing hubs frequently deploy peak load generators to ensure uninterrupted operations, supported by government subsidies. South Korea’s Green New Deal also prioritizes peak load generators for renewable energy integration, targeting a notable reduction in emissions by 2030.
By End-User Insights
The construction sector segment accounted for 35.5% of the Asia Pacific power rental market in 2024. This is propelled by rapid urbanization and infrastructure development across the region. For instance, a substantial share of urban projects rely on temporary power solutions to meet energy demands during construction phases. Government initiatives further amplify adoption. Similarly, Indonesia’s reliance on rental power in disaster-prone areas underscores its critical role in addressing energy gaps while fostering economic growth.
The oil and gas sector is predicted to advance at a CAGR of 12%. This surge is supported by increasing exploration and production activities in remote areas. Government incentives further accelerate adoption. India offers subsidies worth substantial amount for deploying rental systems in oil and gas projects. Additionally, Malaysia’s focus on renewable energy integration highlights the potential of hybrid solutions in this sector, targeting a notable reduction in emissions by 2030.
COUNTRY LEVEL ANALYSIS
China was at the forefront of the Asia Pacific power rental market, holding a 30.5% share. It is driven by rapid industrialization and urbanization, creating a robust demand for temporary power solutions. The Five-Year Plan emphasizes grid modernization, with a significant number of high-capacity generators deployed in urban areas to address peak load demands. Government backing plays a pivotal role. Additionally, investments in renewable energy integration ensure steady growth, positioning China as a leader in sustainable energy transitions.
India commands a notable market share, and is driven by its focus on rural electrification and industrial development. The Ministry of Power highlights that over 200 million people still face intermittent power supply, creating a strong demand for rental generators. Government initiatives further amplify adoption. Additionally, India’s "Make in India" initiative spurs demand for temporary power in manufacturing zones, ensuring minimal disruptions during peak periods.
Australia is steadily moving ahead by leveraging its abundant renewable energy resources for remote operations. Mining companies like Fortescue Metals Group invest heavily in rental generators, ensuring reliable power supply in remote areas. These efforts shows Australia’s commitment to energy resilience and sustainability.
Japan continues to be a key player in the market which is propelled by its focus on urban energy resilience and hydrogen integration. Residential complexes increasingly adopt rental generators, supported by the Strategic Road Map for Hydrogen. Public-private partnerships further drive adoption. Tokyo Electric Power Company has implemented a large number of rental systems in commercial districts, ensuring uninterrupted power supply during peak demand periods.
South Korea holds a small market share. It is driven by its Green New Deal and renewable energy initiatives. Hyundai Motor Group collaborates with local governments to deploy rental generators in industrial zones, achieving a reduction in emissions by 2030.
Educational institutions also embrace rental solutions. The Green Campus Initiative promotes solar-powered systems in schools, targeting a reduction in energy costs.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
Some of the noteworthy companies in the APAC power rental market profiled in this report are Caterpillar Inc. (United States), Cummins Inc. (United States), Aggreko (United Kingdom), Atlas Copco (Sweden), Kohler-SDMO (France), Shenton Group (United Kingdom), NIDS GROUP (India), Jassim Transport & Stevedoring Co. K.S.C.C. (Kuwait), Pump Power Rental (United Kingdom), United Rentals (United States), Sudhir Power Ltd. (India), Modern Hiring Service (India), Newburn Power Rental Ltd (United Kingdom), Global Power Supply (United States), FG Wilson (United Kingdom), ProPower Rental (United States), APR Energy (United States), and others.
TOP LEADING PLAYERS IN THE MARKET
Aggreko
Aggreko is a global leader in temporary power solutions, playing a pivotal role in advancing the Asia Pacific power rental market. The company specializes in providing scalable and reliable generators for industries such as mining, construction, and utilities. Aggreko’s innovative hybrid systems integrate renewable energy with traditional fuel-based generators, addressing sustainability goals while ensuring uninterrupted power supply. Its emphasis on technological innovation positions it as a key contributor to the global power rental landscape.
Caterpillar Inc.
Caterpillar Inc. leverages its expertise in heavy machinery and power systems to deliver robust rental solutions tailored to the Asia Pacific region. The company’s advanced generator sets are widely used in remote mining operations and disaster recovery efforts, ensuring resilience and reliability. Its focus on sustainability and emissions reduction underscores its leadership in shaping the future of decentralized energy systems globally.
Atlas Copco
Atlas Copco is renowned for its energy-efficient and portable power solutions, making it a dominant player in the power rental space. The company’s compact and modular generators cater to diverse applications, from urban infrastructure projects to rural electrification initiatives. Atlas Copco actively invests in research and development to enhance fuel efficiency and reduce environmental impact. Through strategic partnerships with utilities and governments, Atlas Copco drives advancements in grid resilience and energy accessibility. Its commitment to innovation ensures its prominence in the rapidly evolving power rental market.
TOP STRATEGIES USED BY KEY PLAYERS
Expansion into Emerging Markets
Key players in the Asia Pacific power rental market are aggressively expanding their presence in emerging economies to tap into untapped opportunities. Companies like Aggreko and Caterpillar are establishing localized distribution networks and service centers in countries like Vietnam, Indonesia, and the Philippines. By tailoring their offerings to address specific regional challenges, such as frequent power outages and grid instability, these firms ensure they remain competitive while fostering long-term customer relationships. This strategy enables them to capture a larger share of the growing demand for temporary power solutions.
Focus on Sustainable Solutions
Sustainability is a cornerstone of competitive strategies in the power rental market. Leading companies allocate significant resources to develop cleaner technologies, such as hybrid and gas-powered generators, to align with stricter emissions regulations. Innovations in renewable energy integration, including solar-hybrid systems, enhance the appeal of rental solutions among eco-conscious customers. Collaborations with research institutions drive breakthroughs in energy efficiency, ensuring these companies stay ahead of technological trends and meet evolving customer demands while contributing to global decarbonization efforts.
Strategic Partnerships and Collaborations
Collaborations with governments, utilities, and private entities are critical for strengthening market presence. Companies like Atlas Copco partner with local stakeholders to develop pilot projects and demonstrate the feasibility of advanced rental systems. These alliances help align with national energy policies while fostering mutual growth. Additionally, joint ventures with technology providers ensure access to cutting-edge innovations, enabling companies to deliver comprehensive solutions that address regional challenges effectively, such as disaster recovery and industrial peak shaving.
COMPETITION OVERVIEW
The Asia Pacific power rental market is characterized by intense competition, driven by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and the increasing demand for reliable energy solutions. Key players vie for dominance through innovation, strategic collaborations, and aggressive market penetration tactics. Established giants like Aggreko and Caterpillar compete alongside specialized firms like Atlas Copco, each leveraging unique strengths to capture market share. The race to develop cost-effective and efficient power rental systems fuels continuous R&D efforts, resulting in a dynamic landscape marked by frequent product launches and technological breakthroughs. Governments play a pivotal role by offering subsidies and creating favorable policies, intensifying competition among participants striving to capitalize on these incentives. Emerging startups further disrupt the status quo by introducing niche applications, challenging incumbents to adapt quickly. Additionally, collaborations between international and regional players blur traditional boundaries, fostering an ecosystem where innovation thrives. As the market evolves, competition will likely intensify, pushing companies to refine strategies and explore untapped opportunities to maintain their edge.
TOP 5 MAJOR ACTIONS TAKEN BY COMPANIES
- In January 2023, Aggreko launched a new line of hybrid solar-diesel generators in Australia, enabling mining operations to reduce fuel consumption and carbon emissions while ensuring uninterrupted power supply.
- In March 2023, Caterpillar announced a partnership with the Indian government to deploy high-capacity rental generators in rural areas, supporting the nation’s rural electrification initiatives under the Saubhagya Scheme.
- In June 2023, Atlas Copco completed the acquisition of a renewable energy startup in South Korea, strengthening its capabilities in solar-powered rental solutions and expanding its footprint in the Asia Pacific region.
- In September 2023, Aggreko signed a memorandum of understanding with Thailand’s Ministry of Energy to provide temporary power solutions for large-scale infrastructure projects, ensuring timely completion despite grid constraints.
- In December 2023, Caterpillar introduced a new range of low-emission gas-powered generators in Japan, aligning with the country’s Strategic Road Map for Hydrogen and promoting cleaner energy alternatives in urban areas.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This Asia Pacific power rental market research report is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Power Rating
- Below 75 kVA
- 75-375 kVA
- 375-750 kVA
- Above 750 Kva
By Fuel Type
- Diesel
- Gas
- Others
By Application
- Continuous Load
- Standby Load
- Peak Load
By End-user
- Mining
- Construction
- Manufacturing
- Utility
- Events
- Oil & Gas
- Others
By Country
- India
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Thailand
- Malaysia
- Vietnam
- Philippines
- Indonesia
- Singapore
- Rest Of APAC
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What drives the Asia Pacific power rental market?
Rapid industrialization, urbanization, frequent power outages, and infrastructure projects drive the Asia Pacific power rental market’s growth
2. What challenges does the Asia Pacific power rental market face?
High operational costs, fuel price volatility, strict emissions regulations, and limited awareness in rural areas challenge the Asia Pacific power rental market
3. What opportunities exist in the Asia Pacific power rental market?
Integration of renewables, expansion in emerging markets, and adoption of hybrid and smart rental solutions offer growth opportunities in the Asia Pacific power rental market
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from
$ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: sales@marketdataforecast.com