Asia Pacific Steam Turbine Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report By Design (Reaction, Impulse), Fuel (Fossil Fuel, Biomass, Geothermal), End Use (Industrial, Utility), Capacity (≤ 3 MW, >3 MW – 100 MW, >100 MW), and Country (India, China, Japan, South Korea, Australia) – Industry Analysis From 2025 to 2033.
Asia Pacific Steam Turbine Market Size
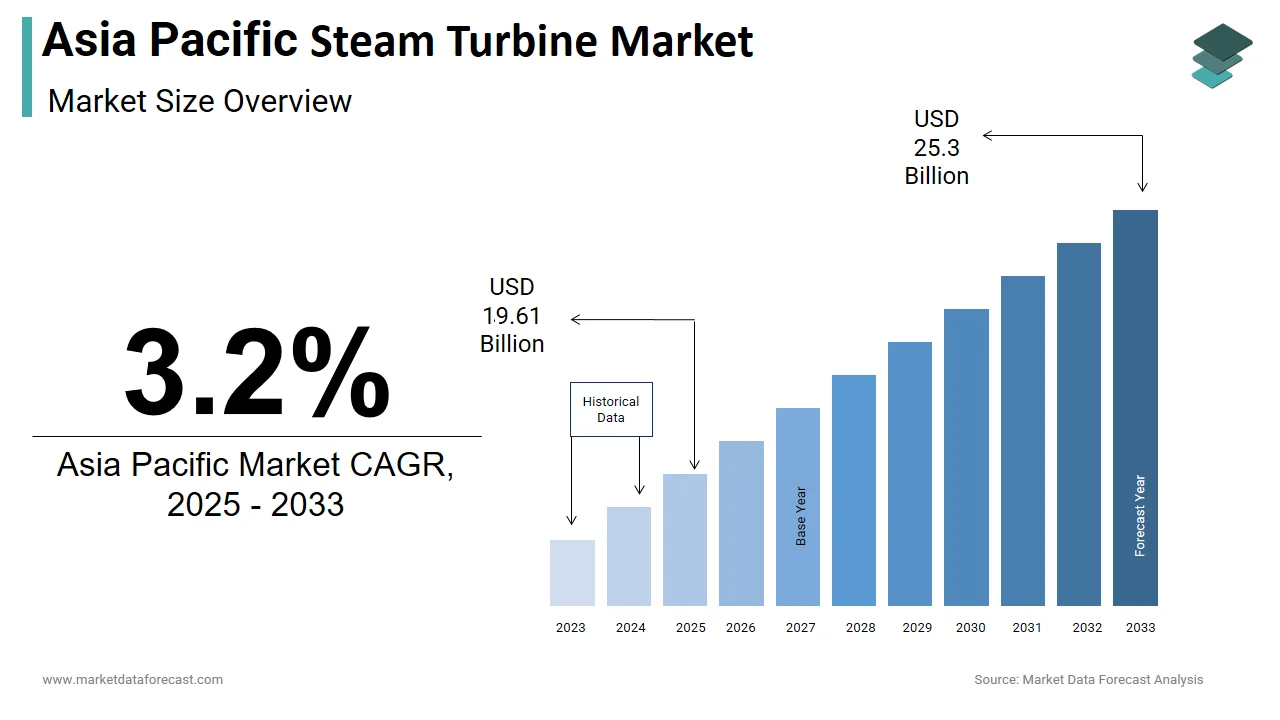
The size of the Asia Pacific steam turbine market was worth USD 19 billion in 2024. The Asia Pacific market is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 3.2% from 2025 to 2033 and be worth USD 25.23 billion by 2033 from USD 19.61 billion in 2025.
Steam turbines are pivotal in power generation, functioning as the backbone of thermal and combined-cycle power plants by converting steam energy into mechanical energy to drive generators. These systems are indispensable in coal-fired, natural gas, and nuclear power plants, as well as in renewable energy applications like concentrated solar power (CSP) and biomass. The region’s energy infrastructure is also evolving to address environmental concerns. Steam turbines play a dual role in this transition—supporting traditional fossil fuel plants while enabling hybrid systems that integrate renewable energy sources.
MARKET DRIVERS
Rising Demand for Electricity
The escalating demand for electricity across the Asia Pacific region is a primary driver of the steam turbine market. According to the Asian Development Bank, urbanization in the region is projected to grow at a high rate through 2030, leading to increased energy consumption in residential, commercial, and industrial sectors. This surge in demand necessitates the expansion of power generation capacity, with steam turbines playing a crucial role in both fossil fuel-based and renewable energy plants. For example, India’s Central Electricity Authority estimates that coal-fired power plants will continue to account for major share of the country’s energy mix until 2030, ensuring sustained demand for steam turbines. Moreover, industrial activities are intensifying energy needs. The World Bank reports that manufacturing output in Southeast Asia grew between 2015 and 2022, creating a robust demand for reliable power sources. Steam turbines are integral to industries such as steel, cement, and petrochemicals, where they provide stable and efficient energy solutions. For instance, Vietnam’s steel industry has adopted steam turbines to optimize energy usage in production processes, reducing operational costs while maintaining output levels.
Integration of Renewable Energy Sources
The integration of renewable energy sources, particularly concentrated solar power (CSP) and biomass, is another significant driver propelling the steam turbine market. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency, renewable energy capacity in the Asia Pacific region exceeded 1,000 gigawatts in 2022, with CSP and biomass projects gaining traction. Steam turbines are essential components of CSP plants, converting thermal energy from solar concentrators into electricity. For example, Australia’s Solar Dawn project utilizes advanced steam turbines to achieve higher efficiency in solar thermal energy conversion. In addition, biomass power plants leverage steam turbines to generate electricity from organic waste materials. Thailand’s Alternative Energy Development Plan aims to increase biomass energy usage to 5,000 megawatts by 2036, creating opportunities for steam turbine manufacturers. According to the Thai Ministry of Energy, these plants not only reduce reliance on fossil fuels but also contribute to waste management efforts.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
Environmental Regulations and Carbon Emission Concerns
Stringent environmental regulations targeting carbon emissions pose a significant restraint to the steam turbine market, particularly in fossil fuel-dependent regions. According to the United Nations Environment Programme, coal-fired power plants are responsible for a notable share of global CO2 emissions, prompting governments to impose stricter emission limits. In Australia, the National Greenhouse and Energy Reporting Act mandates reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, compelling utilities to reconsider their reliance on traditional steam turbine systems powered by coal. This regulatory pressure is further compounded by public opposition to fossil fuel projects. For instance, Japan reported that over 60% of citizens support phasing out coal-fired plants, creating challenges for new installations. While advanced steam turbines with carbon capture and storage (CCS) capabilities exist, their high costs deter widespread adoption.
High Maintenance Costs and Aging Infrastructure
Another major restraint is the high maintenance costs associated with aging steam turbine infrastructure. Many power plants in the Asia Pacific region, particularly in countries like Indonesia and the Philippines, operate legacy systems that require frequent repairs and upgrades. Like, a large share of steam turbines in Southeast Asia are more than 20 years old, leading to inefficiencies and increased operational expenses. Additionally, the complexity of retrofitting these systems with modern components further escalates costs.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Modernization of Aging Power Plants
The modernization of aging power plants presents a significant opportunity for the steam turbine market in the Asia Pacific region. According to the Asian Development Bank, over 50% of coal-fired power plants in the region are nearing the end of their operational lifespan, necessitating upgrades or replacements. Retrofitting these plants with advanced steam turbines offers a cost-effective solution to improve efficiency and reduce emissions. For instance, South Korea’s KEPCO plans to upgrade 30% of its existing fleet by 2030, creating a robust demand for high-performance turbines. Modern steam turbines equipped with digital monitoring systems can enhance operational reliability and extend plant lifespans. In addition, upgrading older systems aligns with regional sustainability goals, as newer turbines consume less fuel and emit fewer pollutants.
Growth of Combined-Cycle Power Plants
The expansion of combined-cycle power plants (CCPPs) offers another promising opportunity for steam turbine manufacturers. According to the International Energy Agency, CCPPs are among the most efficient power generation technologies, achieving thermal efficiencies. These plants combine gas turbines with steam turbines to maximize energy output, making them ideal for meeting the region’s growing electricity demands. For example, China’s State Grid Corporation has invested $100 billion in CCPP projects to support its clean energy transition. Similarly, India’s Ministry of Power aims to add 50 gigawatts of CCPP capacity by 2030, driving demand for steam turbines. According to the Gas Turbine Association, steam turbines in CCPPs can recover significant share of waste heat, significantly improving overall plant efficiency.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Competition from Alternative Technologies
One of the primary challenges facing the steam turbine market is increasing competition from alternative power generation technologies, such as wind and solar photovoltaics. These technologies offer lower installation costs and shorter deployment timelines compared to steam turbine-based systems, making them attractive to investors and utilities. This rapid expansion of renewables has reduced reliance on traditional thermal power plants, limiting opportunities for steam turbines. Besides, advancements in energy storage systems are addressing intermittency issues, further eroding the competitive advantage of steam turbines.
Economic Uncertainty and Budget Constraints
Economic uncertainty and budget constraints in developing economies present another challenge to the steam turbine market. Fluctuations in global commodity prices, particularly coal and natural gas, directly impact the feasibility of new power plant projects. Also, inflationary pressures in economies like India and the Philippines have increased operational expenses for utilities, limiting their ability to invest in advanced steam turbines. These economic challenges hinder the adoption of new technologies and impede market expansion.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
Segments Covered |
By Design, Exhaust, Fuel, End Use, Capacity, Technology, and Region. |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional and Country-Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, Drivers, Restraints, Opportunities, Challenges; PESTLE Analysis; Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Countries Covered |
India, China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, New Zealand, Thailand, Malaysia, Vietnam, Philippines, Indonesia, Singapore, Rest of APAC |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Bharat Heavy Electricals, CTMI - Steam Turbines, Dongfang Turbine, Doosan Skoda Power, Elliott Group, Fuji Electric, General Electric, Hangzhou Steam Turbine Power Group, Howden Group, Kawasaki Heavy Industries, MAN Energy Solutions, Mitsui E&S, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Shin Nippon Machinery, Siemens Energy, Toshiba Corporation, Triveni Turbine, and Turbotech Precision Engineering. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Design Insights
The reaction steam turbines segment dominated the Asia Pacific market by accounting for a 65.4% of the total market share in 2024. This performance is driven by their superior efficiency and adaptability to a wide range of applications, particularly in fossil fuel-based power plants. Like, coal-fired power plants remain a dominant energy source in the region, with over 1,000 gigawatts of installed capacity in recent years. Reaction turbines excel in these environments due to their ability to handle high-pressure steam, making them ideal for large-scale utility projects. Another critical factor is their compatibility with combined-cycle power plants (CCPPs).
The segment of impulse steam turbines segment is the fastest-growing, with a projected CAGR of 8.5%. This is fueled by their suitability for renewable energy applications, such as concentrated solar power (CSP) and geothermal projects. One more contributing factor is their compact design, which makes them ideal for small-scale industrial applications. Additionally, Indonesia’s Ministry of Energy reports that geothermal projects in the country have adopted impulse turbines due to their reliability in handling variable steam conditions.
By Type Insights
The condensing steam turbines segment held the largest share of the Asia Pacific market in 2024. This dominance is attributed to their higher efficiency in power generation, particularly in utility-scale applications. A different factor is their role in reducing water consumption. Like, condensing turbines minimize water usage by recycling steam through cooling towers, aligning with regional sustainability goals. In South Korea, KEPCO has retrofitted several plants with advanced condensing turbines to improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
The non-condensing steam turbines segment is emerging as the quickest category, with a CAGR of 9.2%. This progress is supported by their suitability for industrial applications, such as process heating and cogeneration systems. For instance, Vietnam’s steel industry has adopted non-condensing turbines to optimize energy usage in production processes. Further driving point is the rise of district heating networks. According to the Japanese District Heating Corporation, these systems can supply thermal energy to over 10,000 households per unit, enhancing scalability.
By Fuel Insights
The fossil fuel-based steam turbines segment commanded the market by accounting for a 60.8% of the total market share in 2024. This is associated to the region’s reliance on coal and natural gas for power generation. A critical factor is their cost-effectiveness. In addition, advancements in turbine technology have improved efficiency, reducing emissions and operational costs.
The biomass-fueled steam turbines segment is swiftest one to accelerate, with a CAGR of 10.3%. This development is caused by the increasing adoption of bioenergy projects across the region. Also, further contributing factor is waste management initiatives. The Philippine Department of Energy reports that biomass plants utilizing agricultural waste have reduced landfill usage, addressing environmental concerns. In addition, Malaysia’s Ministry of Energy highlights the role of biomass turbines in achieving renewable energy targets, further boosting adoption.
By End Use Insights
The utility applications segment accounted for a substantial share of the market business in 2024. This is driven by the region’s growing electricity demands, necessitating large-scale power generation systems. For example, China’s State Grid Corporation plans to add 50 gigawatts of coal-fired capacity by 2030, ensuring robust demand for utility-grade steam turbines. Another factor is the expansion of renewable energy projects. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency, utility-scale CSP and geothermal projects in the region rely heavily on steam turbines for electricity generation.
The Industrial applications segment is the rapidly advancing, with a CAGR of 9.8%. This expansion is due to the increasing need for process heating in industries like steel, cement, and petrochemicals. For instance, Vietnam’s steel industry has adopted steam turbines to optimize energy usage in production processes. A different driving aspect is the rise of cogeneration systems. These developments position industrial applications as a key growth driver.
COUNTRY LEVEL ANALYSIS
China led the Asia Pacific steam turbine market by commanding a 40.6% share in 2024. The country’s rise is propelled by its aggressive investments in power infrastructure, including coal-fired and combined-cycle power plants. With over 1,000 gigawatts of installed capacity, as stated by the National Energy Administration, China has integrated advanced steam turbines to meet its growing energy demands. Another factor is the push for cleaner technologies. The Made in China 2025 initiative allocates $300 billion for advanced manufacturing, including high-efficiency turbines.
India holds a key market share. The country’s growth is due to its reliance on coal-fired power plants, which account for over 50% of its energy mix. India’s focus on modernizing aging infrastructure has created opportunities for advanced steam turbines. Besides, the government’s emphasis on renewable energy integration supports growth.
Japan had a significant position in the market. The country’s development is fueled by its focus on sustainability and technological innovation. Japan’s Green Growth Strategy aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 2030, driving the adoption of steam turbines in geothermal and CSP projects. Moreover, Japan’s aging infrastructure is being upgraded with energy-efficient systems, reinforcing its market position.
South Korea is advancing in this market. The country’s progress is driven by its commitment to renewable energy and smart city initiatives. South Korea’s Green New Deal allocates substantial amount for sustainable urban development, including the integration of steam turbines in district heating systems. Additionally, the chemical and petrochemical industries leverage steam turbines for process heating, ensuring consistent demand.
Australia and New Zealand contribute majorly in the market. Their growth is driven by renewable energy integration and environmental regulations. Australia’s mining sector adopts steam turbines for ore processing, while New Zealand’s dairy industry uses them for milk pasteurization. Also, both countries emphasize sustainability, aligning with global trends.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
Some of the noteworthy companies in the APAC steam turbine market profiled in this report are Bharat Heavy Electricals, CTMI - Steam Turbines, Dongfang Turbine, Doosan Skoda Power, Elliott Group, Fuji Electric, General Electric, Hangzhou Steam Turbine Power Group, Howden Group, Kawasaki Heavy Industries, MAN Energy Solutions, Mitsui E&S, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Shin Nippon Machinery, Siemens Energy, Toshiba Corporation, Triveni Turbine, and Turbotech Precision Engineering.
TOP LEADING PLAYERS IN THE MARKET
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI)
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries is a dominant player in the Asia Pacific steam turbine market, renowned for its cutting-edge technology and reliability. The company’s steam turbines are integral to both fossil fuel-based and renewable energy projects, including concentrated solar power (CSP) and geothermal plants. MHI contributes to the global market by integrating digital solutions like IoT and AI into its systems, enabling predictive maintenance and operational optimization. Its focus on sustainability aligns with global decarbonization goals, as it develops high-efficiency turbines that minimize emissions.
General Electric (GE) Power
General Electric (GE) Power is another key player, known for its innovative and versatile steam turbine solutions. GE’s turbines cater to utility-scale power plants as well as industrial applications, offering flexibility in design and operation. The company’s contribution to the global market lies in its ability to provide scalable systems that meet the unique needs of emerging markets in Asia Pacific. GE emphasizes research and development, focusing on improving efficiency and reducing environmental impact.
Siemens Energy
Siemens Energy stands out for its advanced steam turbines designed for high-efficiency power generation and industrial use. The company’s global presence is bolstered by its commitment to innovation and customer-centric solutions. Siemens contributes to the market by promoting renewable energy integration, particularly through biomass and geothermal applications. Its emphasis on reducing carbon footprints resonates with environmentally conscious industries.
TOP STRATEGIES USED BY KEY MARKET PARTICIPANTS
Focus on Sustainability and Decarbonization
Key players in the Asia Pacific steam turbine market prioritize sustainability to align with global decarbonization goals. Companies are developing advanced turbines with carbon capture and storage (CCS) capabilities to reduce emissions from fossil fuel-based plants. For instance, integrating renewable energy sources like biomass and geothermal into steam turbine systems demonstrates a commitment to cleaner energy solutions.
Strategic Collaborations and Partnerships
Collaborations with regional utilities, governments, and renewable energy providers are a cornerstone of market strategies. These partnerships enable companies to gain insights into local requirements and develop tailored solutions. For example, joint ventures with geothermal energy projects allow for the deployment of specialized steam turbines. Such alliances also facilitate knowledge sharing and enhance brand credibility, creating long-term value for all parties involved. By leveraging these relationships, companies strengthen their foothold in the dynamic Asia Pacific market.
Investment in Research and Development
Investment in R&D is critical for staying ahead in the steam turbine market. Companies focus on developing next-generation turbines capable of achieving higher efficiencies and adaptability to renewable energy applications. Innovations such as digitally enabled turbines with predictive maintenance capabilities improve operational reliability. Additionally, advancements in materials and design enhance performance while reducing costs.
COMPETITION OVERVIEW
The Asia Pacific steam turbine market is characterized by intense competition, driven by the presence of global giants and regional players vying for market share. Established companies leverage their technological expertise and extensive distribution networks to maintain leadership, while smaller firms focus on niche segments like renewable energy integration or industrial applications. The market’s competitive landscape is shaped by rapid industrialization, urbanization, and the growing emphasis on sustainability, all of which create opportunities for innovation. Companies strive to differentiate themselves through product quality, pricing strategies, and sustainability initiatives. Regulatory pressures further intensify competition, as players race to develop compliant solutions. Additionally, the rise of smart manufacturing and district heating projects has heightened demand for advanced steam turbines, prompting companies to invest in research and development.
RECENT MARKET DEVELOPMENTS
- In March 2024, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (MHI) launched a new line of IoT-enabled steam turbines designed for utility-scale applications in Southeast Asia. This move aimed to enhance operational efficiency and provide real-time performance analytics to customers.
- In June 2023, General Electric (GE) Power partnered with a leading Indian utility provider to integrate its advanced steam turbines into a large-scale coal-fired power plant modernization project. This collaboration reinforced GE’s presence in South Asia while showcasing its expertise in retrofitting legacy systems.
- In August 2023, Siemens Energy expanded its production facility in Thailand to meet rising demand for high-efficiency steam turbines in the renewable energy sector. This expansion underscored the company’s commitment to serving the Asia Pacific region.
- In November 2023, Doosan Heavy Industries introduced a next-generation geothermal steam turbine tailored for the Indonesian market. This product launch highlighted the company’s focus on addressing specific regional needs while promoting renewable energy adoption.
- In January 2024, Toshiba Energy Systems & Solutions acquired a stake in a Japanese biomass energy initiative to promote circular economy practices. This investment aligned with Toshiba’s broader sustainability goals and strengthened its position in the domestic market.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This Asia Pacific steam turbine market research report is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Design
- Reaction
- Impulse
By Exhaust
- Condensing
- Non-Condensing
By Fuel
- Fossil Fuel
- Biomass
- Geothermal
By End Use
- Industrial
- Refinery
- Chemical Plant
- Sugar Plant
- Pulp & Paper
- Others
- Utility
By Capacity
- ≤ 3 MW
- >3 MW - 100 MW
- >100 MW
By Technology
- Steam Cycle
- Combined Cycle
- Cogeneration
By Country
- India
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Thailand
- Malaysia
- Vietnam
- Philippines
- Indonesia
- Singapore
- Rest Of APAC
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What drives the Asia Pacific steam turbine market?
The Asia Pacific steam turbine market is driven by surging electricity demand, rapid urbanization, industrial growth, and power sector expansion, along with increased integration of renewables like CSP and biomass.
2. What challenges affect the Asia Pacific steam turbine market?
The Asia Pacific steam turbine market faces challenges from stringent environmental regulations, high maintenance costs for aging infrastructure, and rising competition from alternative technologies like wind and solar.
3. What opportunities exist in the Asia Pacific steam turbine market?
The Asia Pacific steam turbine market offers opportunities in modernizing aging power plants, expanding combined-cycle projects, integrating digital monitoring, and supporting clean energy transitions with advanced turbine technologies.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]