Asia Pacific Wound Care Biologics Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report By Product (Biological Skin Substitutes, Topical Agents), Wound Type (Ulcers – Diabetic Foot Ulcers, Venous Ulcers, Pressure Ulcers, Other Ulcers; Surgical and Traumatic Wounds; Burns), End User (Hospitals/Clinics, Ambulatory Surgical Centers, Other End Users), and Country (India, China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, New Zealand, Thailand, Malaysia, Vietnam, Philippines, Indonesia, Singapore, Rest of APAC) – Industry Analysis From 2025 to 2033.
Asia Pacific Wound Care Biologics Market Size
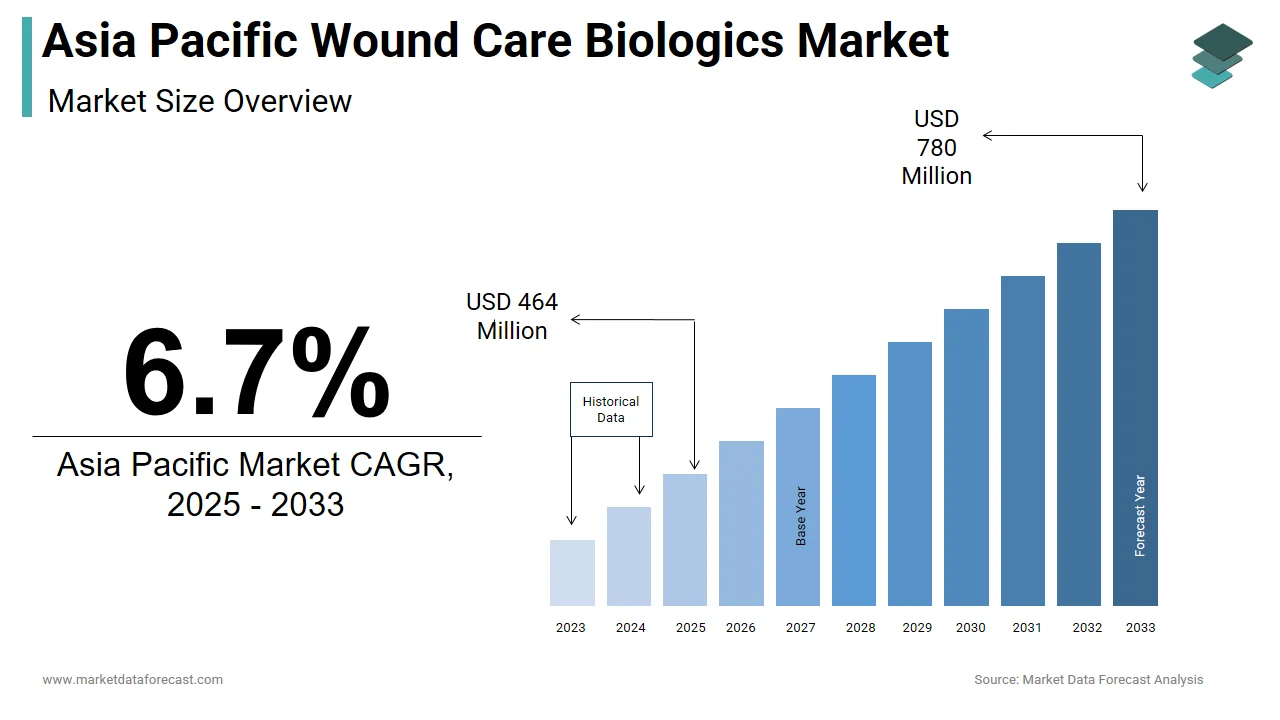
The size of the Asia Pacific wound care biologics market was worth USD 435 million in 2024. The Asia Pacific market is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 6.7% from 2025 to 2033 and be worth USD 780 million by 2033 from USD 464 million in 2025.
The Asia Pacific wound care biologics market growth is driven by the growing demand for advanced therapeutic products derived from biological sources such as skin substitutes, growth factors, platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and cellular and tissue-based therapies. These products are increasingly being used in the management of chronic wounds such as diabetic foot ulcers, pressure ulcers and venous leg ulcers where conventional wound care solutions demonstrate limited efficacy. The region has witnessed a surge in demand for these biologics due to rising prevalence of diabetes along with an aging population and growing awareness about regenerative medicine. China alone accounts for over 140 million cases of diabetes while India reports more than 74 million individuals living with the condition. This massive disease burden has led to a corresponding rise in complications such as non-healing ulcers which require advanced interventions. Healthcare systems across the region are gradually adopting novel wound healing technologies to reduce hospitalization durations and lower the risk of amputations. Governments in countries like Australia and South Korea are investing in regenerative medicine research thereby further fostering innovation.
MARKET DRIVERS
Rising Prevalence of Chronic Wounds Due to Diabetic Complications
Rising prevalence of chronic wounds due to diabetic complications is one of the primary drivers of growth in the Asia Pacific wound care biologics market. Countries such as China, India and Thailand have witnessed a significant increase in diabetes rates over the past two decades while contributing to a surge in related conditions like diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs). Diabetes affects more than 190 million people across the Asia-Pacific region with nearly 15.06% developing DFUs at some stage. These chronic wounds often do not respond well to traditional dressings or topical treatments thereby necessitating the use of advanced biologics such as skin substitutes and bioengineered tissues. In Singapore, over 20.77% of hospitalized diabetic patients had foot ulcers with many requiring advanced wound healing interventions. In Japan, the Japanese Society of Wound Healing reported increasing adoption of epidermal cell grafts and collagen-based matrices for managing hard-to-heal ulcers in elderly patients. The urgency to prevent limb amputations and reduce long-term morbidity has prompted both public hospitals and private clinics to incorporate biologic therapies into standard wound care protocols.
Increasing Geriatric Population and Associated Post-Surgical Complications
Increasing geriatric population and associated post-surgical complications are significant drivers of growth in the Asia Pacific wound care biologics market particularly in developed economies such as Japan, South Korea and Australia. Older adults are more susceptible to slow-healing wounds due to diminished cellular regeneration, reduced circulation and higher incidences of comorbidities like hypertension and cardiovascular diseases. The number of people aged 65 and older in the Asia Pacific region is expected to surpass 1 billion by 2050.This demographic transition has triggered a surge in surgical procedures including joint replacements and cardiovascular surgeries which carry a high risk of delayed wound healing. In response, healthcare providers are increasingly adopting biologic wound healing products such as amniotic membrane allografts and growth factor therapies. In South Korea, the use of cellular and tissue-based products has increased by 25% in post-operative wound management between 2020 and 2023. Hospitals in Australia are also integrating wound care biologics into geriatric rehabilitation programs to shorten recovery times and improve patient outcomes.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Cost of Advanced Wound Biologics and Limited Reimbursement Coverage
The high cost of advanced wound biologics and limited reimbursement coverage remain major restraints to their widespread adoption in the Asia Pacific region. Biologics like dermal substitutes and cellular therapies involve complex manufacturing, cold-chain logistics and specialized application techniques resulting in significantly higher costs, unlike conventional wound care products such as gauzes, hydrocolloids or foam dressings. The average cost of a single application of a bioengineered skin substitute can exceed USD 1,000 thereby placing it beyond the reach of many patients in low and middle-income markets. Moreover, reimbursement coverage for these products remains inconsistent across the region. Countries like Australia and Japan offer partial or full reimbursement under national health schemes, in contrast with most Southeast Asian nations that lack structured insurance frameworks for advanced wound care therapies. In addition, out-of-pocket expenditures dominate healthcare spending in several APAC countries thereby discouraging patients from opting for costly biologics.
Regulatory Complexity and Fragmented Approval Pathways Across the Region
Regulatory challenges present another formidable obstacle to the growth of the Asia Pacific wound care biologics market. The region comprises a diverse set of regulatory environments ranging from highly stringent systems in Japan and Australia to more fragmented and evolving frameworks in countries like Indonesia, Vietnam and the Philippines. Differences in product classification as well as approval timelines and clinical trial requirements, create operational inefficiencies for manufacturers seeking multi-country registration. In China, the National Medical Products Administration mandates extensive local clinical trials even for products already approved abroad thereby delaying market entry by several months. In Malaysia, evolving guidelines around tissue-engineered products have created uncertainty among stakeholders. The time required for regulatory clearance of a wound care biologic in Southeast Asia is nearly 18–24 months unlike 12 months in Japan. Such disparities force companies to invest heavily in country-specific compliance strategies thereby increasing development costs and reducing agility.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Expansion of Regenerative Medicine Policy Frameworks in Key APAC Countries
Expansion of regenerative medicine policy frameworks in key APAC countries presents a significant opportunity for the Asia Pacific wound care biologics market. Several countries in the region have introduced dedicated regulations and financial incentives to accelerate the development and commercialization of advanced wound healing therapies. For instance, in Japan, the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Act of 2014 established a conditional early approval system for regenerative products, enabling faster market access. Five wound care biologics received conditional approval under this framework between 2018 and 2023 thereby enhancing treatment availability. In South Korea, a regenerative medicine roadmap is launched in 2022 that includes streamlined pathways for stem cell-based wound treatments. The Asia Pacific region is well-positioned to emerge as a global hub for wound care biologics development and deployment with supportive legislation and increased investment in biotech innovation.
Growth of Telemedicine and Digital Platforms Supporting Remote Wound Monitoring
The rapid proliferation of telehealth services and digital wound monitoring tools presents a transformative opportunity for the Asia Pacific wound care biologics market. With chronic wound management becoming increasingly decentralized particularly in rural and underserved areas many clinicians are turning to remote diagnostics and AI-assisted image analysis to track healing progress and deliver targeted interventions. The digital wound management market in the Asia Pacific is projected to grow at a CAGR of over 18.87% from 2025 to 2033 and is driven by smartphone penetration and cloud-based electronic health records. In India, startups such as Niramai and Tricog are partnering with wound care clinics to deploy AI-powered thermal imaging platforms that enable early detection of infection risks in diabetic foot ulcers. These insights allow physicians to initiate biologic therapy before complications escalate. In Singapore, the Ministry of Health collaborated with tech firms to integrate robotic-assisted dressing systems into home healthcare settings and improve adherence to advanced treatment protocols. Additionally, teleconsultation platforms like Apollo Telehealth and MyDoc facilitate real-time specialist input thereby ensuring optimal utilization of wound biologics even in remote locations.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Lack of Standardized Clinical Guidelines for Wound Biologics Application
Lack of standardized clinical guidelines for wound care biologics remains one of the key challenges facing the Asia Pacific market resulting in limiting the consistent and appropriate use of these advanced therapies. Antibiotics or analgesics follow well-established prescribing norms whereas wound biologics are often employed based on subjective physician judgment, regional practices and institutional preferences. Less than 40.95% of hospitals in Southeast Asia follow consistent protocols for selecting and applying wound biologics which leads to variability in treatment outcomes. In countries such as Malaysia and the Philippines clinical decision-making regarding biologics is largely influenced by anecdotal evidence rather than robust clinical trials. Only 20.72% of general practitioners were trained in the proper application of cellular therapies resulting in underutilization or misuse of available products. This lack of uniformity hampers the scalability of wound care biologics and complicates efforts to train new users.
Limited Awareness Among Primary Care Providers About Advanced Wound Biologics
Limited awareness among primary care providers about advanced wound biologics remains a significant challenge impeding their uptake in the Asia Pacific region despite ongoing technological advancements. Many general practitioners, nurses and community health workers continue to rely on traditional wound management techniques and remain unaware of the potential of biologics to accelerate healing and reduce amputation risks. Nearly 60.86% of primary care physicians in rural India were unfamiliar with growth factor-based therapies for chronic ulcers. In Indonesia, only 10.05% of surveyed doctors had exposure to wound biologics during medical training thereby emphasizing gaps in continuing education and professional development. Efforts by industry stakeholders to conduct workshops, webinars and hospital demonstrations are gaining traction but broader systemic interventions such as inclusion in medical curricula and national wound care protocols are needed to drive awareness at scale.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
Segments Covered |
By Product, Wound Type, End User, and Region. |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional and Country-Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, Drivers, Restraints, Opportunities, Challenges; PESTLE Analysis; Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Countries Covered |
India, China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, New Zealand, Thailand, Malaysia, Vietnam, Philippines, Indonesia, Singapore, Rest of APAC |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Smith+Nephew, Integra LifeSciences, Convatec Inc., Mölnlycke Health Care AB, and 3M. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Product Type Insights

The biologic skin substitutes segment dominated the Asia Pacific wound care biologics market by capturing 62.09% of the total value in 2024. This dominance is primarily driven by their increasing use in treating chronic wounds such as diabetic foot ulcers and venous leg ulcers where conventional dressings offer limited efficacy. These substitutes derived from human or animal tissues are designed to mimic natural skin structures which in turn promotes cellular regeneration and faster healing. More than 70.83% of tertiary hospitals in Japan now incorporate bioengineered skin grafts into standard wound management protocols particularly for elderly patients with impaired healing capabilities. In South Korea, the adoption of allogeneic skin substitutes increased by 35.79% between 2019 and 2023, especially in post-surgical and burn care settings. China’s demand for amniotic membrane-based products has surged due to their anti-inflammatory properties as a result making them a preferred option among clinicians managing complex wounds. The growth of this segment is further supported by ongoing research into decellularized matrices and stem cell-infused skin grafts which are being explored for improved integration and long-term outcomes.
Topical agents segment is on the rise and is expected to be the fastest growing segment in the global market by witnessing a CAGR of 14.8% from 2025 to 2033. This includes advanced formulations such as growth factor gels, antimicrobial peptides and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) solutions which offer non-invasive alternatives to grafting procedures. Their ease of application, cost-effectiveness and suitability for outpatient settings make them particularly attractive in both urban and rural healthcare environments. In India, the prescription rate for PRP-based topical treatments for ulcer management rose by nearly 40.57% between 2020 and 2023 particularly in government hospitals aiming to reduce amputation rates among diabetic patients. In Australia, the Therapeutic Goods Administration approved several new biological gel formulations in 2022 which have since been integrated into home care programs under national health insurance schemes. Moreover, the rise of compounding pharmacies and point-of-care PRP preparation kits is enabling physicians to customize treatments based on patient-specific needs.
By Wound Type Insights
The ulcers segment was the largest in the Asia Pacific wound care biologics market by capturing 58.88% of the total market share in 2024. This is largely attributed to the high prevalence of diabetes and associated complications such as diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs), pressure ulcers and vascular ulcers across both developed and developing economies in the region. In Japan, ulcer-related hospitalizations increased by 22.08% between 2018 and 2023 thus prompting greater utilization of biologics such as dermal substitutes and recombinant growth factors. In Australia, non-healing ulcers contributed to more than 10,000 lower-limb amputations annually showcasing the urgent need for effective biologic therapies. Furthermore, the rising geriatric population across the region exacerbates the incidence of pressure ulcers particularly in long-term care facilities. The Singapore General Hospital documented a 30.63% increase in the use of cellular and tissue-based products for treating bedsores among nursing home residents thereby reflecting broader clinical adoption trends.
The surgical and traumatic wounds segment is estimated to register a fastest CAGR of 15.3% during 2025 to 2033. This surge is driven by the increasing number of surgical procedures, trauma cases and post-injury wound complexities that require rapid tissue repair and infection prevention. Southeast Asia records over 1.5 million road traffic injuries annually where many of which result in deep lacerations and burns requiring regenerative interventions. In response, hospitals are adopting biologic dressings and autologous cell therapies to enhance wound closure and minimize scarring. Additionally, the rise in cosmetic and reconstructive surgeries throughout the region has led to higher demand for advanced healing solutions. In South Korea, the Korean Society of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgeons observed a 30.95% rise in the use of growth factor-based topical agents for post-operative wound healing and aimed at accelerating recovery and improving aesthetic outcomes.
By End User Insights
The hospitals and clinics segment held the leading share of 71.6% of the Asia Pacific wound care biologics market in 2024. This growth is primarily attributable to the high prevalence of chronic and acute wounds managed in inpatient and specialized outpatient wound care units. These settings provide access to trained medical professionals, diagnostic tools and controlled environments necessary for applying advanced biologics such as skin substitutes and cellular therapies. In Japan, over 65.11% of all wound care biologics applications occur within hospital settings and particularly in departments dealing with diabetes, orthopedics and plastic surgery. In Australia, a significant increase in the use of amniotic membrane grafts in its wound healing clinic as a result indicates strong institutional adoption. In India, under the Ayushman Bharat scheme a network of dedicated wound care clinics was established in public hospitals thus facilitating greater access to biologics for low-income patients. Moreover, regulatory frameworks often require certain biologics to be administered only in certified healthcare facilities thereby further consolidating hospital usage.
The ambulatory surgical centers segment is anticipated to witness a fastest CAGR of 16.2% from 2025 to 2033. These centers are increasingly being utilized for minor surgical procedures, wound debridement and post-trauma dressing applications thereby offering cost-effective and efficient alternatives to hospital-based care. The rapid proliferation of ASCs in countries like South Korea and Singapore has created new opportunities for biologic wound care adoption. The number of accredited ambulatory care centers grew by 25.84% between 2020 and 2023 many of which incorporated advanced wound healing technologies. ASCs are playing a larger role in post-operative wound monitoring and regenerative interventions as healthcare systems seek to reduce hospital readmissions and optimize resource allocation. ASCs are set to become a critical channel for biologic wound care delivery with growing investments in infrastructure and service diversification.
COUNTRY LEVEL ANALYSIS
Japan was the top performer in the Asia Pacific wound care biologics market and accounted for 24.07% of regional market share in 2024. Its well-developed healthcare infrastructure, aging population and progressive regulatory environment for regenerative medicine have positioned it as a pioneer in advanced wound healing solutions. In Japan over 30.76% of the population is aged 65 years or older resulting in a high incidence of chronic wounds such as pressure ulcers and diabetic foot ulcers. The country’s proactive approach to fostering innovation in biologics is evident through policies like the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Act of 2014 which allows conditional approval for regenerative products based on early-phase evidence. Additionally, collaborations between academic institutions and pharmaceutical companies have resulted in cutting-edge developments along with including stem cell-derived skin substitutes and autologous platelet therapies.
China was positioned second in holding the dominant share of the Asia Pacific wound care biologics market in 2024. The country's vast population base coupled with a surging prevalence of diabetes and cardiovascular diseases has significantly increased the demand for advanced wound healing solutions. Diabetes affects over 140 million individuals nationwide many of whom suffer from related foot ulcers requiring intensive care. In response to the growing disease burden, regulatory authorities have streamlined approval pathways for biologic products thereby encouraging both domestic and international firms to enter the market. Public hospitals in Tier-1 cities across China have adopted dermal substitutes in over 50.76% of chronic wound cases which reflects a significant increase compared to previous years. Moreover, rising investments in regenerative medicine research and manufacturing capabilities have enabled local companies to produce cost-effective alternatives to imported biologics.
Australia’s wound care biologics market growth is likely to have fastest growth opportunities in the next coming years.The country benefits from a well-established healthcare system, high per capita healthcare expenditure and supportive reimbursement mechanisms for advanced wound care therapies. Over 400,000 people suffer from chronic wounds with diabetic foot ulcers being a major contributor. Australia serves as a regional hub for clinical trials and product launches with multinational companies testing new wound care biologics in the country before expanding to other APAC markets. The presence of world-class research institutions such as the Wound Management Innovation Cooperative Research Centre (CRC) also supports continuous advancements in wound healing science.
South Korea’s wound care biologics market growth is driven by rapid adoption of regenerative medicine coupled with a tech-savvy healthcare ecosystem. The number of registered chronic wound cases has grown by 30.87% over the past five years and thus necessitating more advanced treatment options. Government-backed initiatives including the Regenerative Medicine Act of 2018 have provided a clear legal framework for the development and commercialization of biologics. Leading pharmaceutical companies such as GC Cell and Medipost have introduced autologous cell therapies for diabetic ulcers and burn injuries thereby gaining traction in both domestic and international markets. The country’s emphasis on digital health integration and remote wound monitoring further enhances the effectiveness of biologic interventions.
India’s wound care biologics market is likely to grow with a healthy CAGR in the next coming years. The country’s market growth is primarily fueled by the escalating burden of diabetes and circulatory disorders which drive the need for cost-effective and scalable wound healing solutions. Over 74 million people live with diabetes and a significant proportion develop foot ulcers requiring advanced care. Companies like BioMeTushya and Stempeutics have launched locally produced stem cell-based wound healing products thereby aligning with national health priorities. The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare reported that Ayushman Bharat-funded hospitals incorporated biologic wound care into their treatment protocols for lower-income groups resulting in enhancing access.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
Some of the noteworthy companies in the APAC wound care biologics market profiled in this report are Smith+Nephew, Integra LifeSciences, Convatec Inc., Mölnlycke Health Care AB, and 3M.
TOP LEADING PLAYERS IN THE MARKET
Vericel Corporation
Vericel is a leading player in the Asia Pacific wound care biologics market and known for its innovative autologous cell therapies designed to treat chronic wounds. The company has been instrumental in advancing regenerative medicine through products that utilize a patient’s own cells to promote healing. Vericel has expanded its influence in the APAC region through licensing agreements and collaborative research initiatives with academic institutions. Its focus on high-quality and patient-specific solutions aligns with the growing demand for personalized medicine in Asia.
MiMedx Group, Inc.
MiMedx plays a vital role in the Asia Pacific wound care biologics landscape by developing and commercializing placental tissue-based biologics for wound healing applications. The company’s amniotic-derived products are widely recognized for their anti-inflammatory and regenerative properties thereby making them highly effective in treating diabetic foot ulcers and surgical wounds. MiMedx has established a strong distribution network across Australia and Japan which are two major markets in the region.
GC Cell Corporation
GC Cell is a South Korean biotechnology firm that has emerged as a dominant force in the Asia Pacific wound care biologics market. GC Cell offers regenerative treatments tailored for chronic wound conditions such as diabetic ulcers and burn injuries because of its specializing in stem cell-based therapies. The company’s commitment to innovation is evident in its continuous R&D investments and product approvals from regional regulatory bodies. GC Cell supports the advancement of biologics in Asia while contributing to the global expansion of regenerative medicine by leveraging its expertise in cellular therapy manufacturing and clinical application.
TOP STRATEGIES USED BY KEY MARKET PARTICIPANTS
Expanding into emerging markets through localized partnerships is one major strategy employed by key players in the Asia Pacific wound care biologics market. Companies are forming alliances with domestic distributors, hospitals and government agencies to enhance product accessibility and navigate complex regulatory landscapes. These collaborations help firms tailor their offerings to specific regional needs and accelerate commercialization.
Another crucial approach is investing heavily in research and development to drive innovation. Market participants are focusing on developing next-generation biologics while including stem cell therapies, growth factor formulations and bioengineered skin substitutes. Firms are increasingly adopting strategic pricing and reimbursement support models to improve affordability and adoption rates. Given the high cost of biologics where more companies are working with insurance providers and public health systems to design flexible payment plans and subsidy programs thereby ensuring broader access to advanced wound care treatments across both urban and rural populations.
COMPETITION OVERVIEW
The competition in the Asia Pacific wound care biologics market is intensifying as both global and regional players strive to capture a larger share of this rapidly evolving sector. In countries with mature healthcare infrastructures like Japan and Australia many multinational corporations leverage their extensive R&D capabilities, brand strength and global supply chains to establish a foothold. Meanwhile, regional biotech firms are gaining traction by offering cost-effective alternatives and tailoring products to meet local clinical preferences and regulatory requirements. Intense rivalry exists not only in product innovation but also in market access strategies as stakeholders seek to overcome challenges related to reimbursement, awareness and affordability. The market is witnessing increased collaboration between industry leaders and academic institutions to accelerate the development of novel therapies and expand clinical evidence supporting biologic interventions. Additionally, companies are investing in education programs for healthcare professionals to improve understanding and adoption of advanced wound care solutions. The competitive landscape is expected to become even more dynamic as demand for regenerative therapies continues to rise and is driven by firms seeking differentiation through advanced technology, localization strategies and strategic partnerships.
RECENT MARKET DEVELOPMENTS
- In March 2024, Vericel Corporation entered into a strategic partnership with a Japanese regenerative medicine institute to conduct joint clinical trials on autologous cell therapies for diabetic foot ulcers.
- In August 2023, MiMedx announced the launch of a dedicated distributorship network in Australia to improve the availability of its placental-based wound healing products in both hospital and outpatient settings.
- In November 2024, GC Cell Corporation obtained regulatory approval from South Korea’s Ministry of Food and Drug Safety for an updated formulation of its stem cell-based wound healing product.
- In May 2023, Organogenesis collaborated with a Singaporean healthcare provider to pilot an integrated chronic wound management program that includes biologic therapies.
- In January 2025, Apyx Medical formed a licensing agreement with a Chinese biotech firm to co-develop and commercialize a minimally invasive plasma-based wound healing solution.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This Asia Pacific wound care biologics market research report is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Product
- Biological Skin Substitutes
- Topical Agents
By Wound Type
- Ulcers
- Diabetic Foot Ulcers
- Venous Ulcers
- Pressure Ulcers
- Other Ulcers
- Surgical and Traumatic Wounds
- Burns
By End User
- Hospitals/Clinics
- Ambulatory Surgical Centers
- Other End Users
By Country
- India
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Thailand
- Malaysia
- Vietnam
- Philippines
- Indonesia
- Singapore
- Rest Of APAC
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What factors are driving the Asia Pacific wound care biologics market?
The Asia Pacific wound care biologics market is driven by rising diabetes rates, an aging population, increased chronic wounds, and growing adoption of advanced biologics like skin substitutes and growth factors for better healing.
2. What challenges does the Asia Pacific wound care biologics market face?
The Asia Pacific wound care biologics market faces high product costs, limited reimbursement, fragmented regulatory pathways, lack of standardized clinical guidelines, and low awareness among primary care providers about advanced therapies.
3. What opportunities exist in the Asia Pacific wound care biologics market?
Opportunities in the Asia Pacific wound care biologics market include supportive government policies, digital wound monitoring, expansion of ambulatory surgical centers, and increased investment in regenerative medicine and biotech innovation.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: sales@marketdataforecast.com
