Global Edible Films and Coatings for Fruits and Vegetables Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report - Segmented By Ingredient Type (Protein, Polysaccharides, Lipids, and Composites), Region (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, And Middle East & Africa) - Industry Analysis (2025 to 2033)
Global Edible Films and Coatings for Fruits and Vegetables Market Size
The global edible films and coatings for fruits and vegetables market size was valued at USD 3.27 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 6.32 billion by 2033 from USD 3.52 billion in 2025. The market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.58% during the forecast period.
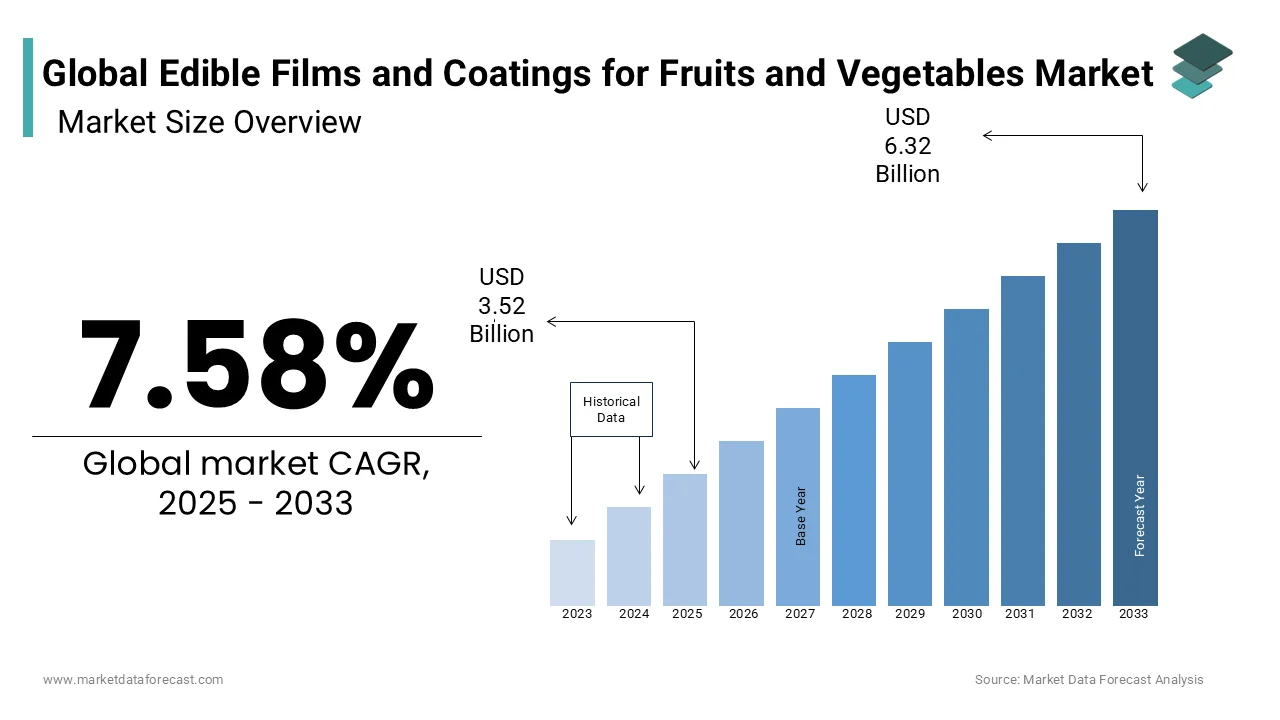
The strong consumer awareness around food waste reduction and sustainable packaging solutions, rising demand for ready-to-eat produce, and supportive regulatory frameworks that encourage biodegradable food contact materials are propelling the demand for edible films and coatings in the food and beverages sector. According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture, over 30% of all food produced in the U.S. goes to waste, prompting both government agencies and private companies to invest in technologies that extend shelf life. Innovations such as Apeel Sciences’ plant-based coating have demonstrated the ability to double the freshness duration of avocados and citrus fruits, leading to increased adoption across major retailers like Costco and Kroger. Moreover, the growing popularity of clean-label products has prompted food processors to replace synthetic preservatives with natural, edible barriers.
MARKET DRIVERS
Rising Consumer Demand for Extended Shelf Life and Reduced Food Waste
The rising need to extend the shelf life of perishable fruits and vegetables, particularly in urban markets where supply chains are long and complex is one of the significant factors driving the growth of the edible films and coatings in the food and beverages market. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), approximately one-third of all food produced globally is lost or wasted, amounting to 1.3 billion tons annually. Fresh produce accounts for a significant portion of this waste due to spoilage during transportation and storage. Edible coatings made from natural polymers such as cellulose, chitosan, and pectin act as moisture barriers and oxygen scavengers, effectively reducing microbial growth and delaying ripening. Apeel Sciences, a leading player in this space, reported that its plant-derived coating can increase the shelf life of strawberries by up to five days and avocados by nearly ten days. Retailers such as Marks & Spencer and Carrefour have integrated these technologies into their supply chains, resulting in measurable reductions in shrinkage and improved inventory management. The demand for edible coatings is expected to grow significantly through 2030, largely attributed to the urgent need for sustainable food preservation methods. This trend is being reinforced by consumers who are increasingly seeking out products that align with environmental values while maintaining freshness and quality.
Growing Preference for Clean-Label and Natural Ingredients
The shift toward clean-label and minimally processed foods is significantly boosting the adoption of edible films and coatings derived from natural ingredients. Consumers today are more informed and cautious about what they consume, favoring products free from synthetic additives and preservatives. According to a 2024 survey by NielsenIQ, 72% of global shoppers prefer food items with recognizable, simple ingredient lists, and are willing to pay a premium for them. This consumer behavior has prompted manufacturers to develop edible coatings using substances like whey protein, alginate, starch, and beeswax, all of which are perceived as safe and environmentally friendly. For instance, Japan-based Kewpie Corporation launched an edible coating made from lemon extract and natural oils to preserve cut fruits without altering taste or texture. Similarly, Italian startup Grìn has introduced a citrus-based protective layer that extends the freshness of leafy greens and berries. In addition, regulatory bodies such as the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) have approved several bio-based edible coatings as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS), facilitating their incorporation into mainstream food processing. The demand for clean-label foods is projected to increase tremendously, indicating strong tailwinds for the edible films and coatings sector.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
Limited Barrier Properties Compared to Synthetic Packaging
Despite their sustainability benefits, edible films and coatings often exhibit inferior barrier properties compared to conventional plastic packaging, particularly in terms of moisture vapor transmission and gas permeability. According to a 2024 study published in the Journal of Food Engineering, most edible coatings demonstrate higher water vapor permeability than synthetic films, making them less effective under high-humidity conditions commonly encountered in tropical climates and extended transport scenarios. This limitation restricts their application primarily to short-shelf-life products and controlled environments. In contrast, synthetic materials like polyethylene terephthalate (PET) offer superior protection against oxygen, moisture, and microbial ingress, ensuring longer preservation of delicate produce. For instance, traditional plastic films still account for over 70% of the global fresh produce packaging market, highlighting the entrenched preference for performance-driven solutions. Additionally, the variability in formulation and functionality among different types of edible coatings makes it difficult to establish standardized applications across diverse fruit and vegetable categories. Without advancements in composite material engineering and nanotechnology integration, the effectiveness gap between edible and synthetic barriers will continue to hinder widespread adoption.
High Production Costs and Scalability Challenges
The relatively high cost of production and limited scalability associated with natural raw materials is further impeding the growth of the edible films and coatings in the food and beverages market. Unlike petroleum-based plastics, which benefit from mature manufacturing ecosystems and economies of scale, edible coatings often rely on agricultural inputs such as starches, proteins, and lipids, which can be subject to seasonal price fluctuations and supply chain disruptions. For instance, the average cost of producing edible coatings ranges from USD 3 to USD 6 per kilogram, compared to less than USD 1 per kilogram for standard plastic wraps. This cost disparity discourages mass adoption, especially in price-sensitive emerging markets where affordability is a critical purchasing factor. Moreover, small-scale producers often lack the technical expertise required to integrate coating technologies into existing packing lines efficiently. Startups and academic institutions are actively exploring ways to reduce costs through process optimization and feedstock diversification. However, until large-scale commercial viability is achieved, economic constraints will remain a substantial barrier to market expansion.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Expansion into Emerging Markets with Rapid Urbanization and Cold Chain Development
Emerging markets in Asia Pacific, Latin America, and Africa is a major growth opportunity for edible films and coatings due to rapid urbanization, increasing disposable incomes, and improving cold chain infrastructure. Countries like India, Brazil, and Nigeria are witnessing a surge in demand for packaged and convenience foods, driven by shifting lifestyles and greater access to organized retail formats. According to the World Bank, urban populations in developing economies are expected to grow by 2.5 billion by 2050, creating new demand centers for fresh produce with extended shelf life. In India, for example, the Ministry of Food Processing Industries estimates that post-harvest losses of fruits and vegetables exceed 30%, largely due to inadequate storage and packaging facilities. Edible coatings offer a viable solution to reduce spoilage while aligning with national sustainability goals. Furthermore, governments in countries such as Thailand and Mexico are promoting eco-friendly packaging alternatives through policy incentives and public-private partnerships. For instance, investment in cold chain logistics in Southeast Asia grew by 14% in 2024, enhancing the feasibility of deploying edible coatings across regional supply chains. These developments signal a promising future for market expansion beyond traditional Western hubs.
Integration with Smart and Active Packaging Technologies
The convergence of edible films with smart and active packaging technologies is unlocking new avenues for product differentiation and functional enhancement. Unlike passive packaging, smart packaging includes sensors and indicators that monitor freshness, temperature, and microbial activity, while active packaging interacts with the food environment to prolong shelf life. Companies such as TIPA Corp and Notpla are pioneering hybrid models that combine edible barriers with biosensors capable of detecting ethylene levels in real time, offering consumers visibility into produce freshness. For instance, active and intelligent packaging accounted for 15% of total food packaging innovations, with a strong emphasis on natural and biodegradable substrates. Moreover, startups like Mori and Cambridge Crops are leveraging silk fibroin and chitosan-based edible films embedded with antimicrobial agents to create multifunctional coatings that not only preserve but also protect against pathogens. With global investments in smart packaging increasing exponentially, the integration of edible materials into this evolving landscape presents a compelling growth pathway.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Regulatory Hurdles and Standardization Gaps Across Regions
The lack of harmonized regulatory standards across different geographies is a major challenge to the edible films and coatings in food and beverages market. While many natural ingredients used in edible coatings are classified as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) by the FDA, other regions impose stricter approval processes that delay commercialization and increase compliance costs. For example, the European Union’s Novel Foods Regulation requires extensive safety assessments for any ingredient not consumed significantly before May 1997, even if it is naturally derived. According to the European Commission, approval timelines for novel edible materials can extend beyond two years, deterring smaller players from entering the EU market. In contrast, regulatory clarity and faster approvals in the U.S. have enabled quicker scaling of innovative products. Additionally, inconsistencies in labeling requirements and permissible use levels complicate cross-border trade and marketing strategies. For instance, a few of edible film manufacturers operate in multiple continents cited regulatory fragmentation as a key obstacle. Until international guidelines converge, the market will face ongoing difficulties in achieving global uniformity and scalability.
Consumer Perception and Acceptance Barriers
Despite technological advancements, consumer perception remains a significant challenge for the widespread adoption of edible films and coatings. Many consumers are unfamiliar with the concept and may perceive coated produce as "chemically treated" or "artificial," even though the materials used are entirely natural and edible. For instance, only 42% of surveyed shoppers were aware of edible coatings, and less than 30% understood how they functioned. Misconceptions about altered taste, texture, or nutritional content can deter trial and repeat purchases. Furthermore, cultural preferences vary widely in some Asian countries, for instance, consumers associate glossy surfaces on fruits with waxing, which is often viewed negatively due to health concerns. Educational campaigns and transparent labeling are essential to build trust. Companies like Apeel and It’s Fresh! have invested in in-store demonstrations and digital storytelling to improve awareness. However, until consumer understanding catches up with technological progress, acceptance will remain a limiting factor in market penetration.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
7.58% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Ingredient Type, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional, & Country Level Analysis; Segment-Level Analysis; DROC; PESTLE Analysis; Porter’s Five Forces Analysis; Competitive Landscape; Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
SUFRESCA, Flo Chemical Corporation (FloZein), RPM International Inc. (Mantrose-Haeuser Co. Inc.), Hazel Technologies, and Sumitomo Chemical Co. Ltd., and others. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Ingredient Type Insights
The polysaccharides segment captured the major share of 38.8% of the global market in 2024. The dominance of polysaccharides segment in the global market is primarily attributed to the widespread availability, biodegradability, and functional versatility of polysaccharide-based materials such as cellulose, starch, pectin, and chitosan. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), polysaccharides are increasingly favored due to their excellent film-forming properties and compatibility with food-grade applications, making them ideal for preserving moisture-sensitive produce like berries, leafy greens, and citrus fruits. Apeel Sciences, one of the leading innovators in this space, utilizes plant-derived polysaccharides to create invisible barriers that significantly extend shelf life without altering taste or texture. Moreover, regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and the European Food Safety Authority have approved several polysaccharide-based formulations as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS), facilitating their integration into mainstream food supply chains. For instance, over 60% of commercial edible coating products currently on the market utilize polysaccharides as primary ingredients, underlining their central role in driving the market growth.
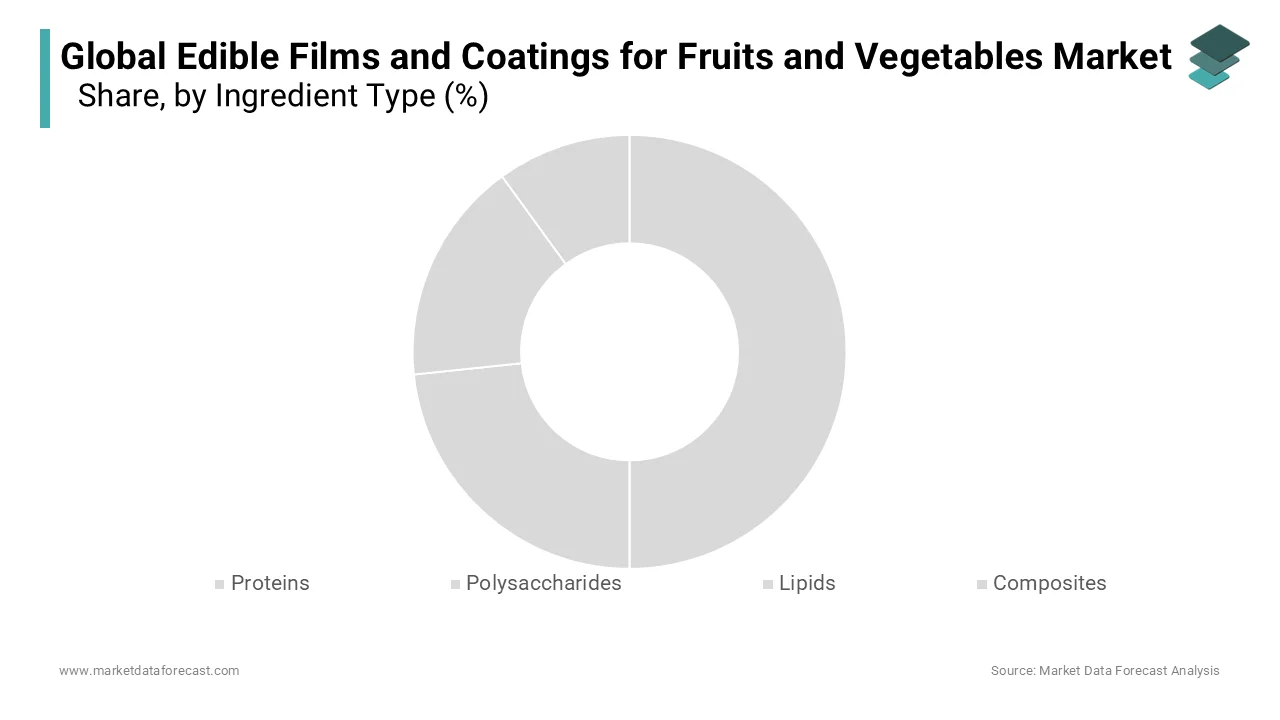
The composites segment is anticipated to register a CAGR of 12.2% over the forecast period in the global edible films and coatings in the food and beverages market. Composite films combine multiple natural polymers often blending proteins, lipids, and polysaccharides to enhance mechanical strength, barrier properties, and antimicrobial functionality beyond what single-component films can achieve. The demand for composite-based edible coatings is rising rapidly due to their ability to mimic synthetic packaging performance while maintaining eco-friendliness. Innovations such as nano-enhanced composite films developed by startups like Cambridge Crops and Notpla are gaining traction among major retailers seeking sustainable alternatives to plastic wrap. Additionally, academic institutions and research labs are actively exploring ways to integrate bioactive compounds like essential oils and antioxidants into composite matrices, further improving preservation capabilities. For instance, over 50% of new product launches in the edible packaging space in 2024 featured composite technologies, indicating strong momentum in both R&D and commercial deployment.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
North America continues to be the leading regional market by holding 29.9% of the global market share in 2024. The United States dominates this position due to its advanced food technology ecosystem, high consumer awareness regarding sustainability, and supportive government policies promoting food waste reduction. More than 30% of all food produced in the country goes to waste, prompting major investments in solutions that prolong freshness. Companies like Apeel Sciences and It’s Fresh! have gained significant traction with grocery chains including Walmart, Costco, and Kroger, who are adopting edible coatings to reduce spoilage and improve inventory efficiency. Furthermore, regulatory clarity from the FDA has accelerated the approval process for natural preservatives, encouraging innovation and rapid scaling. With increasing partnerships between agritech firms and food processors, North America remains at the forefront of edible packaging adoption.
Europe holds a substantial share of the global market and is primarily attributed to the stringent environmental regulations, strong consumer preference for clean-label products, and a well-established organic food industry. Countries such as Germany, France, and the UK are leading the charge in implementing circular economy principles across the food value chain. According to the European Commission, EU member states have committed to halving food waste by 2030, aligning with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals. This policy environment has spurred investment in edible films made from seaweed extracts, whey protein, and plant-based waxes. In addition, the European Union’s Horizon 2020 program has funded numerous R&D initiatives aimed at developing multifunctional edible coatings with antimicrobial and antioxidant properties. For instance, over 40% of European consumers prefer packaging derived from renewable resources, reinforcing the region's leadership in sustainable food innovations.
Asia Pacific is an emerging hub in the global edible films and coatings for food and beverages market. The rapid urbanization, expanding cold chain infrastructure, and rising concerns over post-harvest losses in perishable crops are propelling the market growth in the Asia-Pacific region. India, China, and Thailand are particularly active in adopting edible coatings to address food security challenges. According to the Indian Ministry of Food Processing Industries, post-harvest losses of fruits and vegetables exceed 30% annually, highlighting the urgent need for scalable preservation technologies. Government-backed initiatives such as India’s Pradhan Mantri Kisan Sampada Yojana and China’s Green Packaging Policy are accelerating the uptake of biodegradable food contact materials. Additionally, local startups like Grìn and Mori are developing region-specific formulations tailored to tropical climates, enhancing applicability and effectiveness.
Latin America accounts for a notable share of the global market, with Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina leading adoption efforts. The region benefits from abundant agricultural output and a growing emphasis on reducing spoilage during export logistics. According to the Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean (ECLAC), nearly 20% of fresh produce exported from the region spoils before reaching international markets, underscoring the economic incentive for edible coating usage. Major fruit exporters such as Chiquita and Dole have started piloting protective coatings on bananas and pineapples to maintain quality during long-distance transport. In addition, local universities and agribusinesses are collaborating on low-cost coating solutions suitable for smallholder farmers. While still in early stages, Latin America presents a promising growth trajectory.
Middle East and Africa is predicted to register a steady CAGR in the global market over the forecast period, with countries like Saudi Arabia, UAE, and South Africa showing early signs of interest in edible packaging solutions. Water scarcity and arid climatic conditions make food preservation a critical concern, especially in regions where refrigeration access is limited. According to the Gulf Research Center, the GCC region imports over 80% of its food, creating a pressing need for technologies that ensure longer shelf life. The UAE’s National Food Security Strategy includes provisions for adopting innovative packaging methods, encouraging startups and multinational firms to enter the market. In Sub-Saharan Africa, NGOs and development agencies are piloting edible coatings to preserve nutrient-rich produce in rural areas. However, high costs and lack of technical expertise remain barriers to large-scale implementation.
KEY MARKET PARTICIPANTS AND COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
SUFRESCA, Flo Chemical Corporation (FloZein), RPM International Inc. (Mantrose-Haeuser Co. Inc.), Hazel Technologies, and Sumitomo Chemical Co. Ltd. are the key players in the global edible films and coatings for fruits and vegetables.
The edible films and coatings for fruits and vegetables market features a diverse and evolving competitive landscape, ranging from established agritech companies to agile startups focused on niche applications. While pioneers like Apeel Sciences and It’s Fresh! dominate in terms of market presence and technological maturity, a growing number of startups and university spin-offs are introducing novel formulations based on proteins, lipids, and nanotechnology-enhanced composites.
Strategic collaborations between food producers, packaging developers, and research institutions are becoming increasingly common, reflecting the interdisciplinary nature of edible film innovation. At the same time, larger food and beverage corporations are entering the space through acquisitions and internal R&D initiatives, aiming to integrate sustainable packaging into their broader ESG strategies.
Despite this dynamism, the market remains fragmented, with no single player holding a dominant global position. This opens opportunities for regional players to scale locally relevant solutions, particularly in emerging economies facing high levels of post-harvest loss.
TOP 3 PLAYERS IN THE MARKET
Apeel Sciences
Apeel Sciences is a pioneer in plant-based edible coatings designed to extend the shelf life of fresh produce. Its proprietary formulation creates an invisible barrier that slows water loss and oxidation, helping retailers reduce food waste. The company collaborates closely with major grocers and growers worldwide, positioning itself as a leader in sustainable food preservation.
It’s Fresh!
It’s Fresh! specializes in ethylene-absorbing packaging and edible film technologies that delay ripening and decay. Widely adopted in the banana and avocado industries, its products help maintain freshness during long transportation cycles. The company works with global supply chains to offer scalable, eco-friendly solutions that align with corporate sustainability goals.
Notpla
Notpla develops biodegradable and edible packaging from seaweed and plant-based materials. Known for its liquid-filled sachets and protective coatings for fruits and vegetables, Notpla blends innovation with environmental responsibility. The company has expanded into retail and event sectors, offering versatile packaging alternatives to conventional plastics.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THE MARKET
- In February 2024, Apeel Sciences announced a strategic partnership with Woolworths Australia, integrating its plant-based coating into the retailer’s avocado supply chain to reduce spoilage and shrinkage, marking a major expansion into the Asia-Pacific region.
- In May 2024, It’s Fresh! launched a new line of edible coatings tailored for tropical fruits, targeting major exporters in Central and South America, with pilot programs in place with Dole and Del Monte to assess real-world performance and scalability.
- In July 2024, Notpla introduced Notpla Fresh, an edible film specifically designed for pre-cut fruits and vegetables sold in convenience stores and airports, expanding its footprint beyond traditional retail into the on-the-go consumption segment.
- In September 2024, Tate & Lyle entered into a joint venture with a French biotech firm, focusing on developing starch-based edible films for use in frozen and chilled produce, combining food science expertise with industrial-scale manufacturing capabilities.
- In November 2024, Mitsubishi Corporation invested in Cambridge Crops’ silk fibroin-based coating technology, aiming to commercialize its application across Japanese and Southeast Asian markets, where extended shelf life and reduced plastic use are top priorities.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the global edible films and coatings for fruits and vegetables market has been segmented and sub-segmented based on ingredient type, and region.
By Ingredient Type
- Proteins
- Polysaccharides
- Lipids
- Composites
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the projected size of the edible films and coatings for fruits and vegetables market by 2033?
The global edible films and coatings for fruits and vegetables market size is expected to reach USD 6.32 billion by 2033.
2. What are the key trends influencing global edible films and coatings for fruits and vegetables market growth?
Key trends include the rising use of natural polymers like proteins and polysaccharides, and increased adoption of edible coatings to extend shelf life and reduce food waste
3. What challenges does the global edible films and coatings for fruits and vegetables market face?
Challenges include high production costs, limited awareness among small-scale producers, and regulatory hurdles for food-grade coatings in certain regions.
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2500
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]