Europe Insurance Market Size, Share, Trends, & Growth Forecast Report by Component (Solution, Services),Insurance Type, Distribution Channel and Country (UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, Czech Republic and Rest of Europe), Industry Analysis From 2025 to 2033
Europe Insurance Market Size
The Europe insurance market was worth USD 121.34 billion in 2024. The Europe market is expected to reach USD 1486.38 billion by 2033 from USD 160.29 billion in 2025, rising at a CAGR of 32.10% from 2025 to 2033.

MARKET DRIVERS
Increasing Demand for Health and Long-Term Care Insurance
One of the most significant drivers shaping the Europe insurance market is the rising demand for health and long-term care insurance, primarily driven by an aging population and growing awareness about personal health security. According to Eurostat, as of 2023, more than 21% of the EU population was aged 65 or older, a proportion expected to rise to 29% by 2050. This demographic shift has increased the prevalence of chronic diseases and age-related health issues, prompting individuals to seek private healthcare coverage beyond public systems. In Germany, where statutory health insurance covers the majority of citizens, supplementary private health insurance has become increasingly popular, covering around 12% of the population but accounting for nearly 25% of total health expenditure. Similarly, in France, complementary health insurance is mandatory for all residents, contributing to a near-universal coverage model. The expansion of private health insurance not only supports the sustainability of public healthcare systems but also enhances revenue streams for insurers.
Growth in Non-Life Insurance Uptake Driven by Climate Risk Exposure
Another key driver fueling the Europe insurance market is the increasing adoption of non-life insurance products, especially property and casualty coverage, due to heightened exposure to climate-related risks. These escalating risks are prompting both individuals and businesses to enhance their insurance coverage against flood, storm, and wildfire damage. Germany and France have witnessed particularly robust growth in home and commercial property insurance. Insurers are adapting by integrating advanced modeling tools and parametric insurance structures to better price climate risk. Additionally, regulatory initiatives such as the EU Taxonomy for Sustainable Activities are pushing insurers toward greener underwriting practices, which aligns risk mitigation with broader environmental goals.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
Persistently Low Interest Rates Impacting Investment Returns
A primary restraint affecting the Europe insurance market is the prolonged period of low interest rates, which has severely compressed investment returns for life insurers. Since the European Central Bank (ECB) introduced negative interest rate policies in 2014, insurers have struggled to generate sufficient yields from their fixed-income portfolios, which typically constitute over 70% of their assets. This decline has made it difficult for insurers to meet guaranteed returns on traditional life insurance products, especially in markets like Germany and Italy, where such guarantees are common. As a result, many insurers have had to reduce new business volumes or restructure product offerings to mitigate margin compression. Additionally, the International Monetary Fund noted that the ECB’s cautious approach to rate hikes despite inflationary pressures has prolonged the low-yield environment, forcing insurers to take on higher credit risk or extend duration in pursuit of better returns.
Regulatory Complexity and Compliance Burdens
Regulatory complexity remains a persistent challenge for insurers operating in Europe, with multiple overlapping frameworks imposing significant compliance costs and operational constraints. The implementation of Solvency II in 2016 marked a milestone in risk-based supervision, but it also introduced stringent capital requirements and reporting obligations that disproportionately affect smaller insurers. Furthermore, divergent national interpretations of EU-wide directives create fragmentation across markets, complicating pan-European operations.
The introduction of the Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR) and the Insurance Distribution Directive (IDD) has added layers of complexity, requiring insurers to overhaul internal processes related to risk assessment, transparency, and product governance. Additionally, the ongoing development of the EU’s Green Deal and its associated financial regulations is compelling insurers to realign investment strategies and underwriting practices, often without clear guidelines. This evolving regulatory landscape not only increases administrative overhead but also delays product launches and market entry strategies, thereby restraining market dynamism and competitive differentiation.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Expansion of Cyber Insurance Amid Rising Digital Threats
A substantial opportunity emerging within the Europe insurance market is the rapid growth of cyber insurance, fueled by the increasing frequency and sophistication of cyberattacks targeting businesses and critical infrastructure. As a result, businesses are seeking comprehensive cyber risk coverage, driving demand for policies that include data breach response, business interruption compensation, and legal liability protection. The European Commission has recognized the urgency of bolstering cyber resilience, mandating stricter incident reporting under the NIS2 Directive, which came into effect in early 2023. This regulatory push has prompted organizations to invest in cyber risk management, including insurance as a key component. Insurers are responding by developing modular policies tailored to specific sectors such as finance, healthcare, and manufacturing, while incorporating AI-driven risk assessment tools to improve underwriting accuracy.
Adoption of Usage-Based and Parametric Insurance Models
The emergence of usage-based and parametric insurance models is opening new avenues for growth in the Europe insurance market, driven by technological advancements and shifting consumer preferences. Traditional indemnity-based insurance models are being supplemented by data-driven alternatives that offer more transparent, flexible, and responsive coverage. According to Accenture, 68% of European consumers expressed willingness to share telematics data if it resulted in fairer premiums, highlighting the potential for growth in usage-based auto insurance.
Parametric insurance, which pays out based on predefined triggers rather than actual loss assessment, is also gaining momentum, particularly in agriculture and catastrophe-prone regions. For example, in Spain, agricultural insurers have started offering index-based drought insurance that provides automatic payouts when rainfall levels fall below a certain threshold, eliminating lengthy claims processing. Insurtech partnerships and open insurance frameworks are further accelerating the adoption of these innovative models, which are enabling insurers to better cater to dynamic risk profiles and improve customer retention through personalized offerings.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Climate Change and Increased Frequency of Natural Catastrophes
Climate change is posing a formidable challenge to the Europe insurance market, as the frequency and severity of natural disasters have surged in recent years, straining underwriting capacity and capital reserves. The European Environment Agency recorded a 60% increase in extreme weather events between 2000 and 2023, including floods, wildfires, and storms, which collectively caused over EUR 200 billion in economic losses. Such trends are making traditional risk modeling insufficient, as historical data becomes less predictive of future losses. Similarly, in southern Europe, wildfires have become increasingly destructive, with Greece experiencing a 70% increase in insured losses from wildfires between 2018 and 2023, as per the Hellenic Insurance Organization. Insurers are grappling with the dual challenge of maintaining affordability while managing solvency ratios under Solvency II requirements. The Swiss Re Institute notes that reinsurers are recalibrating catastrophe models to incorporate forward-looking climate scenarios, which is leading to higher risk loadings and reduced capacity in vulnerable regions.
Talent Shortage and Skills Gap in the Insurance Workforce
A growing challenge for the Europe insurance market is the widening talent shortage and skills gap, particularly in digital, analytical, and technical domains. The rapid pace of digital transformation, coupled with evolving customer expectations, has created a pressing need for professionals skilled in artificial intelligence, data science, cybersecurity, and insurtech development. However, the insurance workforce remains largely composed of experienced professionals trained in traditional underwriting and claims handling, with limited exposure to emerging technologies.
Universities and vocational institutions across Europe have been slow to integrate insurance technology into curricula, exacerbating the mismatch between industry needs and available talent. Germany and France face similar challenges, with insurers competing against fintech and tech firms for scarce digital talent. The inability to attract and develop next-generation talent threatens to slow innovation, impair customer experience enhancements, and hinder competitiveness in an increasingly technology-driven market landscape.
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Component Insights
The solutions segment was the largest and held 60.1% of the Europe insurance market share in 2024 owing to the increasing adoption of digital core systems, analytics platforms, and risk management tools across both life and non-life insurers. A key driver behind this trend is the need for legacy system modernization. Additionally, the implementation of Solvency II and GDPR has necessitated advanced data governance and reporting solutions, further fueling demand. Swiss Re Institute noted that AI-driven underwriting tools have been adopted by more than 40% of large European insurers, improving efficiency and reducing manual intervention. The push toward automation, coupled with growing cybersecurity threats, has made robust software solutions indispensable, reinforcing the segment’s leading position in the regional market.
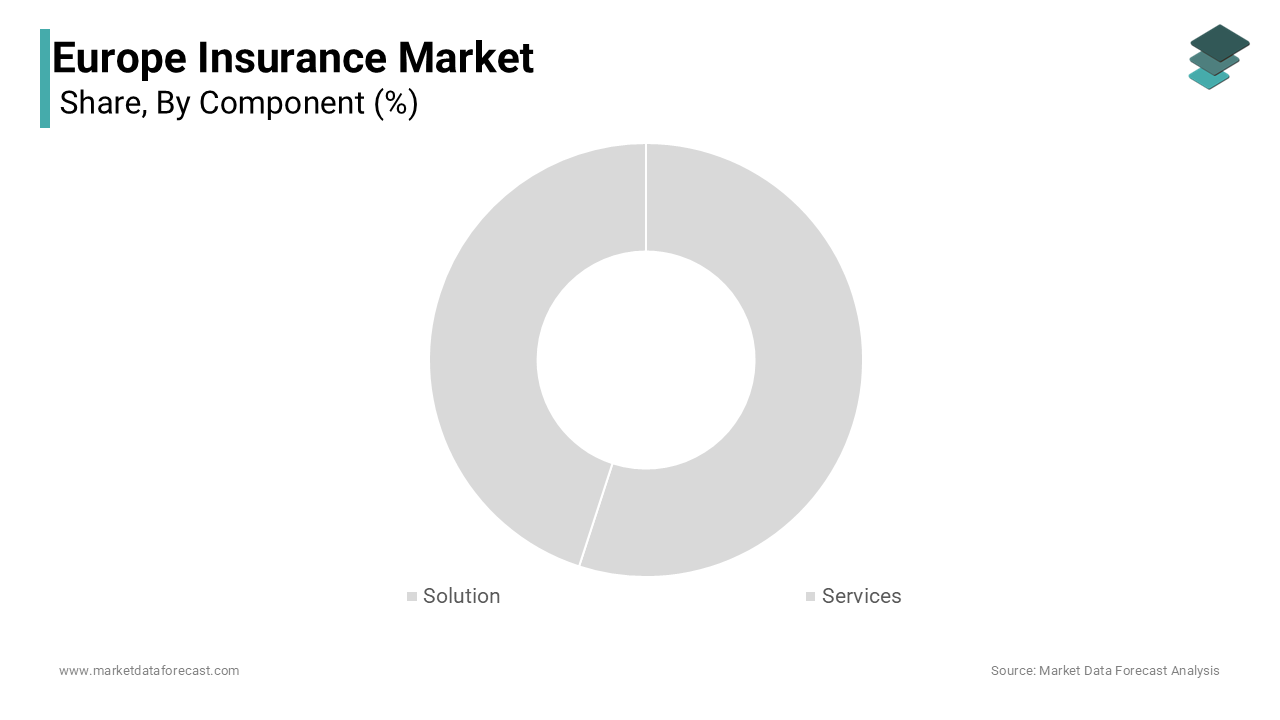
The services segment is projected to grow with a CAGR of 9.8% in the next coming years. This accelerated expansion stems from a rising reliance on managed services, consulting, and cloud-based deployment support as insurers navigate complex transformation initiatives. One major factor driving this shift is the cost-efficiency associated with third-party service providers. Accenture reported that outsourcing IT operations can reduce operational costs by up to 30%, which allows insurers to focus on core business functions. Moreover, the integration of insurtech innovations often requires external expertise, especially in areas like blockchain, IoT, and predictive analytics.
By Insurance Type Insights
The life insurance segment was the top performer in the Europe insurance market with 56.3% of share in 2024. This aging cohort is increasingly opting for guaranteed return life insurance products as part of retirement planning strategies. Additionally, the prevalence of unit-linked policies in the UK and Sweden has reinforced market stability. Deloitte found that 68% of affluent Europeans considered life insurance a core component of wealth preservation in 2023. Regulatory support through solvency frameworks and tax incentives has further strengthened consumer confidence by ensuring sustained demand and promoting life insurance’s dominant position in the regional market.
The health insurance segment is likely to experience a CAGR of 6.4% from 2025 to 2033. This rapid growth is fueled by rising healthcare costs, increasing private health expenditures, and shifting public-private funding dynamics. A primary driver is the growing burden of chronic diseases and an aging population. The World Health Organization estimates that over 86 million Europeans suffer from multiple chronic conditions, which is prompting individuals to seek supplemental coverage beyond public schemes. France mandates complementary health insurance for all residents, contributing to near-universal private coverage. Additionally, post-pandemic awareness has heightened demand for telemedicine and wellness-focused insurance packages.
By Distribution Channel Insights
The brokers segment was the largest and held 41.2% of the Europe insurance market share in 2024 due to their role as independent advisors offering multi-carrier product comparisons, which appeals to both corporate clients and sophisticated retail buyers. One of the key drivers behind the broker segment’s strength is the complexity of commercial insurance needs in sectors such as manufacturing, logistics, and financial services. Marsh Global notes that over 75% of mid-to-large enterprises in Europe rely on brokers for risk assessment and policy structuring. Additionally, regulatory changes like the Insurance Distribution Directive (IDD) have enhanced transparency and professional standards, reinforcing client trust in broker-led transactions.
The tied agents and branches segment is swiftly emerging with a CAGR of 5.7% in the coming years. This growth is primarily driven by the resurgence of personalized customer engagement and localized advisory services, particularly in rural and semi-urban markets. A key catalyst for this trend is the continued preference for face-to-face interactions among older demographics and first-time insurance buyers. Similarly, in Spain and Poland, traditional branch networks serve as critical touchpoints for distributing protection and savings products. Additionally, insurers are enhancing the productivity of tied agents through digital enablement tools, such as mobile CRM applications and e-signature platforms.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
Germany was the top performer in the Europe insurance market by accounting for 21.3% of the share in 2024. As Europe’s largest economy, Germany benefits from high insurance penetration, a mature regulatory framework, and a well-developed network of insurers and reinsurers. Additionally, the country’s aging demographic profile has bolstered demand for life insurance and pension-linked products. The presence of global insurance giants such as Allianz and Munich Re further reinforces the country’s competitive edge.
The United Kingdom insurance market share was next with 16.4% of the share in 2024. Despite economic volatility linked to Brexit and inflationary pressures, the UK maintains a resilient insurance ecosystem anchored by London’s status as a global insurance hub.
A key growth driver is the country’s dynamic cyber insurance market, which has seen exponential expansion due to rising cyber threats. Additionally, the Lloyd’s of London marketplace continues to play a pivotal role in specialty and reinsurance markets, attracting international capital. The Financial Conduct Authority’s push for open insurance and usage-based models has also encouraged innovation.
The French insurance market is likely to grow with a significant CAGR in the coming years. The French insurance sector benefits from a diversified product mix, strong state-backed insurance mechanisms, and high household insurance ownership. Banque de France reports that over 95% of households have supplementary health insurance, making it a cornerstone of the national insurance framework. Additionally, the “catastrophe naturelle” regime provides broad property insurance coverage against natural disasters, which is contributing to resilience in the non-life segment. Climate-related risks have prompted insurers to adopt parametric models, with AXA and CNP Assurances piloting index-based flood insurance in high-risk regions.
Italy insurance market is likely to have lucrative growth opportunities in the coming years. A major driver of Italy’s market strength is the longevity-linked insurance culture, supported by a rapidly aging population. ISTAT reports that 24% of Italians were aged 65 or older in 2023, one of the highest proportions in Europe. This demographic trend has reinforced demand for long-term savings instruments, with life insurance serving as a key vehicle for retirement planning. Additionally, bancassurance remains a dominant distribution model, with banks acting as primary sales channels for insurance products.
The Spanish insurance market is anticipated to have significant growth throughout the forecast period. One of the key drivers behind Spain’s market expansion is the digital transformation of insurance distribution. This shift has been facilitated by the proliferation of insurtech startups and insurer-led digital platforms. Additionally, climate risk exposure has boosted demand for property and catastrophe insurance, particularly in coastal and wildfire-prone regions. The Spanish government’s support for green insurance initiatives, including tax incentives for sustainable building coverage, has further stimulated market activity.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS AND COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
Allianz SE, AXA Group, Generali Group, Zurich Insurance Group, Aviva plc, Munich Re, Swiss Re, Legal & General Group plc, Aegon N.V., and Mapfre S.A. are some of the key market players.
The competition in the Europe insurance market is characterized by a blend of established multinational insurers, regional players, and emerging insurtech firms vying for market share in a mature and highly regulated environment. Incumbents leverage their strong brand recognition, extensive distribution networks, and deep capital reserves to maintain dominance, particularly in life and health insurance segments. However, the rise of digital-first challengers is reshaping the competitive landscape, compelling traditional insurers to accelerate their digital transformation efforts. Customer expectations around speed, transparency, and personalized service are driving innovation in pricing models, claims processing, and risk assessment. At the same time, regulatory pressures such as Solvency II and GDPR necessitate continuous compliance investments, raising barriers for smaller firms. Strategic M&A activity remains a common tactic among top players seeking to diversify portfolios and strengthen regional footholds. As climate risk, cybersecurity threats, and demographic shifts continue to influence demand patterns, insurers must balance profitability with long-term sustainability to remain competitive in this evolving market.
Top Players in the Europe Insurance Market
Allianz SE
Allianz is a leading global insurer and one of the most influential players in the Europe insurance market. Headquartered in Germany, it operates across life, health, property, casualty, and specialty insurance segments. The company has a strong presence in major European markets including France, Italy, Spain, and the UK. Allianz has been at the forefront of digital transformation, investing heavily in insurtech partnerships and AI-driven underwriting tools. Its commitment to sustainability and climate risk management has also positioned it as a responsible leader in the industry.
AXA Group
AXA, based in France, is among the largest insurance groups globally and a dominant force in Europe. It offers a broad range of insurance products, from personal to commercial lines, with a significant focus on health and cyber insurance. AXA has consistently pursued innovation through strategic acquisitions and internal R&D initiatives. The company has been proactive in integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) principles into its investment and underwriting strategies by aligning with evolving regulatory expectations in the European Union.
Zurich Insurance Group
Zurich Insurance, headquartered in Switzerland, plays a crucial role in the European insurance landscape. It specializes in both property and casualty insurance as well as life insurance, catering to individuals, small businesses, and multinational corporations. Zurich has demonstrated resilience through its customer-centric approach and robust risk management framework. The company has actively embraced digitalization by enhancing customer engagement through mobile platforms and data analytics, which is reinforcing its competitive edge in the region.
Top Strategies Used by Key Market Participants
One key strategy employed by leading insurers in the Europe insurance market is the aggressive adoption of digital technologies. Companies are leveraging artificial intelligence, automation, and cloud-based platforms to enhance operational efficiency, improve claims processing, and deliver personalized customer experiences. This digital shift enables faster decision-making and reduces costs while meeting rising consumer expectations for seamless online interactions.
Another critical approach is the expansion of sustainable and green insurance offerings. Insurers are integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors into their underwriting and investment strategies to align with EU regulatory mandates and shifting consumer preferences. By developing climate-resilient products and promoting risk mitigation measures, insurers are positioning themselves as responsible market leaders.
RECENT MARKET DEVELOPMENTS
- In January 2024, Allianz launched a new digital insurance platform tailored for SMEs across Germany, France, and Italy. The initiative aimed to streamline policy issuance and claims processing, offering customized risk coverage through AI-powered analytics and improving accessibility for small business clients.
- In March 2024, AXA entered into a strategic partnership with a leading European insurtech firm to co-develop parametric insurance solutions for climate-related risks. This collaboration focused on creating index-based policies that provide automatic payouts during extreme weather events, enhancing resilience for the agricultural and infrastructure sectors.
- In May 2024, Zurich Insurance expanded its cyber insurance division in the UK by acquiring a boutique cyber risk advisory firm. The move strengthened Zurich’s capabilities in enterprise-level cyber protection and incident response services, positioning it as a key player in the rapidly growing digital risk insurance segment.
- In July 2024, Generali introduced a blockchain-based claims verification system across its Italian and Spanish operations. This initiative aimed to reduce fraud, expedite claim settlements, and improve transparency, marking a significant step toward digitizing core insurance functions.
- In September 2024, Munich Re partnered with a German fintech startup to launch an embedded insurance solution for e-commerce platforms. This integration allowed merchants to offer instant coverage options at checkout, expanding Munich Re’s reach into retail-focused digital insurance ecosystems.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the europe insurance market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Component
- Solution
- Services
By Insurance Type
- Life
- Health
By Distribution Channel
- Brokers
- Tied Agents & Branches
By Country
- UK
- France
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Russia
- Sweden
- Denmark
- Switzerland
- Netherlands
- Turkey
- Czech Republic
- Rest of Europe
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors are driving the growth of the insurance market in Europe?
Key drivers include increasing health awareness, digitalization of insurance services, aging population, regulatory developments, and rising demand for risk protection and financial security.
What challenges does the Europe Insurance Market face?
Challenges include regulatory complexities, pricing pressure, cyber risks, economic uncertainty, and increased competition from insurtech startups.
What is the future outlook of the Europe Insurance Market?
The market is expected to grow steadily due to increased insurance awareness, digital transformation, climate-related risk coverage, and rising demand for health and life insurance products.
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: sales@marketdataforecast.com