Europe Light Commercial vehicles (LCVs) Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report, Segmented By Vehicle Type, Propulsion Type And By Country (UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, Czech Republic and Rest of Europe), Industry Analysis From 2025 to 2033
Europe Light Commercial Vehicles Market Size
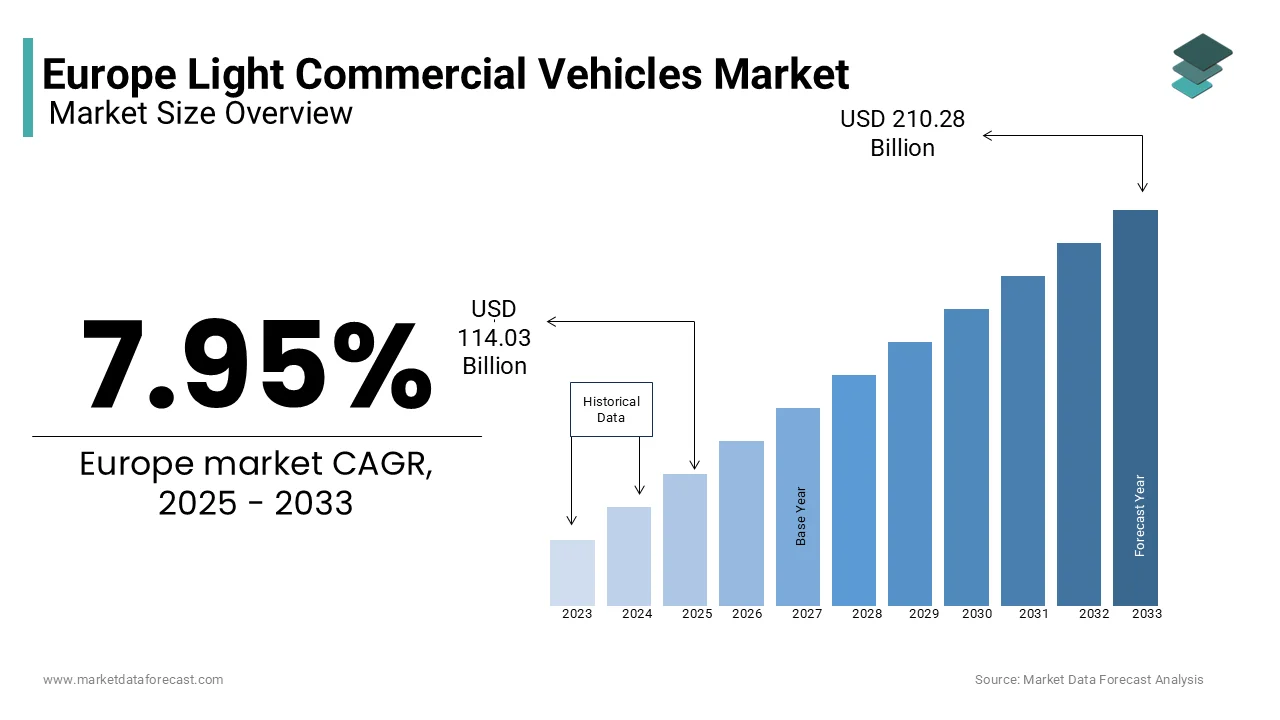
The Europe light commercial vehicle market size was valued at USD 105.63 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 114.03 billion in 2025 from USD 210.28 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 7.95 % during the forecast period from 2025 to 2033.
The Europe light commercial vehicle (LCV) market comprises vehicles with a gross vehicle weight rating (GVWR) of up to 3.5 metric tons, primarily used for urban delivery, logistics, trades, and last-mile transportation services. These include vans, pickups, and minibuses that serve both private and public sector fleets across diverse industries such as e-commerce, construction, healthcare, and municipal services. As the backbone of regional freight movement and service delivery, LCVs play a crucial role in the continent’s evolving mobility ecosystem.
According to ACEA – The European Automobile Manufacturers’ Association, over 1.8 million LCVs were registered across Europe in 2023, reflecting a steady demand despite broader economic uncertainties. Also, the sector has also seen a significant shift toward electrification, with battery electric light commercial vehicles (BEVs) accounting for a significant share of total LCV sales in 2023. This transition aligns with the European Union’s Green Deal objectives, which mandate a 100% reduction in CO₂ emissions from new cars and vans by 2035. Consequently, manufacturers are investing heavily in lightweight materials, advanced powertrains, and smart connectivity features tailored for urban logistics applications.
MARKET DRIVERS
Surge in E-Commerce and Last-Mile Delivery Demand
One of the primary drivers of the Europe light commercial vehicle (LCV) market is the rapid expansion of e-commerce and the corresponding need for efficient last-mile delivery solutions. This growth has been particularly pronounced in countries like Germany, France, and the Netherlands, where logistics companies have scaled their urban delivery networks. Like, last-mile delivery costs account for a major share of total logistics expenditures, prompting companies to invest in cost-effective, high-frequency transport solutions. This has led to a surge in demand for compact, fuel-efficient, and increasingly electric LCVs capable of navigating urban congestion while minimizing emissions. Amazon, DHL, and DB Schenker have all significantly expanded their LCV fleets since 2022 to meet rising parcel volumes, often sourcing directly from European OEMs such as Renault, Volkswagen, and Stellantis. Moreover, city-level policies promoting zero-emission zones have accelerated the adoption of electric LCVs. For instance, London and Paris have implemented low-emission regulations that restrict older diesel models from operating in central areas. As noted by BloombergNEF, electric LCV sales in Europe grew by 67% in 2023 compared to the previous year, underlining how shifting logistics demands are reshaping the commercial vehicle landscape.
Government Incentives and Regulatory Support for Electrified Fleets
Another key driver influencing the Europe light commercial vehicle (LCV) market is the robust policy framework and financial incentives introduced by national governments and the European Union to accelerate fleet electrification. This regulatory push has compelled automakers to prioritize electric LCV development and production. According to Transport & Environment, over €10 billion in combined subsidies and tax exemptions were allocated across European nations in 2023 to encourage businesses to adopt electric commercial vehicles. Countries like Germany and France offer direct purchase incentives, reduced registration fees, and access to dedicated charging infrastructure, making EV ownership more attractive for small and medium enterprises. Also, these initiatives have contributed to a key increase in BEV van registrations in Western Europe over the past two years. Besides, cities are implementing preferential parking and toll exemptions for electric LCVs, further enhancing their operational viability.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Upfront Cost of Electric Light Commercial Vehicles
A major restraint affecting the Europe light commercial vehicle (LCV) market is the elevated upfront cost of electric LCVs compared to their internal combustion engine (ICE) counterparts. Despite long-term savings in fuel and maintenance, the initial investment required for electric vans remains a barrier for many small and mid-sized businesses, especially in price-sensitive markets such as Spain, Poland, and Eastern Europe. This disparity is primarily due to the high cost of lithium-ion batteries, limited economies of scale, and additional expenses related to onboard energy storage systems. As per McKinsey & Company, even with government incentives, the total cost of ownership (TCO) parity for electric LCVs in some segments may not be achieved until the late 2020s. Moreover, uncertainty regarding residual values and second-hand market stability further deters business owners from committing to electric fleet replacements. As reported by BNP Paribas Leasing Solutions, only limited share of fleet managers expressed confidence in the long-term depreciation outlook for electric vans.
Insufficient Charging Infrastructure for Commercial Fleet Operations
An ongoing challenge hindering the growth of the Europe light commercial vehicle (LCV) market is the insufficient availability of fast-charging infrastructure tailored for commercial fleet operations. Unlike passenger car users, LCV operators require reliable, high-capacity charging stations located at depots, logistics hubs, and along urban routes to maintain efficiency and minimize downtime. According to Transport & Environment, as of 2023, only 12% of publicly accessible charging points across Europe were classified as high-power or ultra-fast chargers, limiting the feasibility of full electrification for time-sensitive delivery fleets. Apart from these, the distribution of charging facilities remains uneven, with rural and peripheral regions lagging behind major metropolitan centers. As per McKinsey & Company, a significant percentage of fleet operators cited inadequate charging infrastructure as a primary concern when considering electric LCV adoption.
Furthermore, the lack of standardized charging protocols and interoperability between different charging networks complicates fleet management and route planning. As reported, several logistics firms have delayed large-scale electrification plans due to concerns about reliability and accessibility of charging solutions.
MARKET OPPORTUNITY
Expansion of Urban Mobility and Shared Logistics Networks
A significant opportunity shaping the future of the Europe light commercial vehicle (LCV) market is the growing trend of urban mobility integration and shared logistics networks. Cities across the continent are increasingly adopting collaborative freight strategies to reduce traffic congestion, lower emissions, and optimize delivery efficiency. This shift is creating a demand for compact, flexible, and often electric LCVs designed specifically for micro-distribution centers and multi-tiered delivery systems. According to McKinsey & Company, urban freight demand in Europe is expected to grow notably by 2030, driven by denser city populations and stricter environmental regulations. To accommodate this change, logistics providers such as DB Schenker, UPS, and local cooperatives are deploying smaller electric vans to operate within city-based hub-and-spoke models. These systems rely on centralized warehouses feeding into decentralized last-mile fleets, requiring a higher number of LCVs per delivery volume compared to traditional logistics setups. Besides, municipalities are supporting the development of shared delivery platforms through pilot programs and infrastructure investments. As reported by C40 Cities, over 20 European cities have launched zero-emission delivery zone initiatives that favor electric LCVs with preferential access and reduced permit costs.
Growth of Renewable Energy Integration in Commercial Vehicle Fleets
An emerging opportunity for the Europe light commercial vehicle (LCV) market lies in the increasing integration of renewable energy sources into fleet operations. As businesses strive to achieve net-zero emissions, there is a growing emphasis on not just electrifying vehicles but also ensuring that the electricity used to charge them comes from clean and sustainable sources. According to BloombergNEF, corporate procurement of renewable energy in Europe reached a record 28 gigawatts (GW) in 2023, with logistics and transport companies among the top buyers. Companies such as IKEA Distribution, Hermes, and Deutsche Post DHL are actively investing in solar-powered charging depots and green hydrogen refueling stations to support their electric LCV fleets. This dual strategy—vehicle electrification paired with clean energy sourcing—is becoming a key differentiator in fleet sustainability reporting and corporate responsibility frameworks. Moreover, partnerships between utility providers, charging infrastructure developers, and fleet operators are accelerating the deployment of integrated renewable energy systems. These collaborations enable real-time energy management, grid balancing, and cost optimization, making electric LCVs more viable for long-term operations.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Balancing Operational Efficiency with Decarbonization Goals
One of the most pressing challenges facing the Europe light commercial vehicle (LCV) market is the need to reconcile operational efficiency with aggressive decarbonization targets. While electrification offers a clear path toward reducing emissions, it also introduces complexities related to payload capacity, range limitations, and charging logistics that can impact daily fleet performance. For small businesses and independent contractors, such constraints translate into potential revenue losses unless compensated by optimized routing or multiple trips. Additionally, the current state of battery technology still limits the practicality of electric LCVs for longer-range deliveries, especially in colder climates where energy consumption increases significantly. Fleet operators must therefore navigate trade-offs between environmental compliance and productivity, often leading to hybrid adoption strategies or selective electrification based on route profiles.
Supply Chain Disruptions Affecting Component Availability
Another critical challenge impacting the Europe light commercial vehicle (LCV) market is the ongoing volatility in global supply chains, particularly concerning semiconductor shortages and raw material scarcity. The automotive industry’s reliance on just-in-time manufacturing practices has made it highly susceptible to disruptions, affecting both production schedules and vehicle availability. According to the European Commission, the shortage of microchips and essential components such as wiring harnesses and steel alloys led to a drop in LCV production in 2022 compared to pre-pandemic levels. Furthermore, geopolitical tensions and export restrictions have compounded the problem. As per ACEA, foundries supplying aluminum castings and battery component manufacturers faced increased input costs due to energy price surges and raw material bottlenecks. These factors have forced automakers to delay new model launches and revise production forecasts, creating uncertainty for fleet buyers and leasing companies.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
5.23% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Type, Voltage, Installation, End-Us,er And By Country |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis; Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, Czech Republic & Rest of Europe |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Fiat Chrysler Automobiles N.V., Ford Motor Company, Groupe Renault, Mercedes-Benz, Peugeot S.A., Toyota Motor Corporation, Volkswagen AG. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Vehicle Type Insights
The Panel vans was the strongest vehicle type segment in the Europe light commercial vehicle (LCV) market by grabing a 58.2% of total registrations in 2024. These vehicles are the backbone of urban delivery and logistics operations, widely used by courier services, tradespeople, and last-mile delivery fleets due to their versatility, cargo capacity, and ease of maneuverability in city environments. Germany, France, and the UK collectively account for nearly half of all panel van registrations in Europe. Also, a major share of small and medium enterprises (SMEs) in these countries rely on panel vans for daily business operations, reinforcing their dominance in the LCV landscape. Moreover, fleet renewal programs supported by government incentives have further stimulated demand. This entrenched utility ensures that panel vans remain the most sought-after LCV category across the region.
The electric pickups are emerging as the fastest-growing segment in the Europe light commercial vehicle (LCV) market by expanding at a CAGR of 42.3%. While still a niche category, this rapid growth is being fueled by increasing demand for versatile, high-capacity electric vehicles suitable for construction, agriculture, and rural delivery applications. The introduction of models such as the Rivian R1T, Ford F-150 Lightning Pro, and the upcoming VW Amarok Electric has attracted attention from both private businesses and public sector fleets seeking zero-emission alternatives without compromising load-carrying capability. Additionally, as noted by Transport & Environment, several European municipalities are promoting electric pickups through preferential access policies and reduced toll charges.
By Propulsion Type Insights
The Internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles continued to dominate the Europe light commercial vehicle (LCV) market in 2024. Despite aggressive policy support for electrification, ICE-powered vans and pickups remain the preferred choice for many businesses due to their established infrastructure, lower upfront costs, and proven reliability in long-haul and rural operations. According to study, over 1.5 million ICE-based LCVs were registered across Europe in 2023, with diesel variants making up the vast majority. Diesel engines continue to be favored for their torque efficiency, extended range, and compatibility with existing refueling networks—factors particularly important for SMEs and independent contractors who operate outside major urban centers where charging infrastructure remains limited. Furthermore, While regulatory pressure is gradually shifting the balance, ICE vehicles maintain a strong foothold in the current market structure, especially among cost-conscious operators who prioritize flexibility and operational continuity over immediate environmental benefits.
Battery electric vehicles (BEVs) represent the fastest-growing propulsion type in the Europe light commercial vehicle (LCV) market, recording a CAGR of 55% between 2025 and 2033. This rapid adoption is primarily driven by stringent EU emission regulations, coupled with financial incentives and expanding charging infrastructure in urban areas. According to ACEA, BEV LCV registrations exceeded 190,000 units in 2023, more than tripling since 2020. Leading automakers such as Renault, Volkswagen, and Stellantis have significantly expanded their electric van offerings, including the Kangoo E-Tech, e-Crafter, and e-Expert, which are increasingly integrated into municipal fleets and logistics networks. Moreover, corporate sustainability goals are influencing fleet procurement decisions.
COUNTRY LEVEL ANALYSIS
Germany maintained the top position in the Europe light commercial vehicle (LCV) market by commanding a 23.3% of total regional registrations in 2024. As Europe’s largest economy and automotive manufacturing hub, Germany maintains a robust demand for LCVs across logistics, industrial services, and public administration sectors. The country's well-developed transport infrastructure and dense network of logistics companies drive consistent demand for compact and mid-sized vans. Also, government-backed initiatives such as the "Electromobility Strategy for Commercial Vehicles" have encouraged fleet electrification. With leading manufacturers like Mercedes-Benz and Volkswagen headquartered in the country, Germany remains a key innovator and adopter of next-generation commercial mobility solutions.
France saw strong fleet demand and policy support in the Europe light commercial vehicle (LCV) market in 2024. The country recorded a substantial LCV registrations during the year, driven by strong demand from logistics firms, construction companies, and municipal service providers. As per OICA, France’s LCV market is highly diversified, with a significant presence of both domestic and international brands such as Renault, Citroën, Peugeot, and Fiat. The French government has played a crucial role in shaping market trends through its "Bonus Ecologique" incentive program, which offers financial support for electric and low-emission commercial vehicles. Moreover, Paris and other major cities have introduced low-emission zones that restrict older diesel models, prompting fleet owners to accelerate vehicle replacements.
Italy has a resilient logistics and trade sector in the market. Additionally, the country’s logistics sector has seen steady expansion, particularly in the northern regions where industrial hubs like Milan and Turin serve as critical distribution points for cross-border freight. Government support for sustainable mobility has also gained momentum. With increasing adoption of electric vans in urban centers like Rome and Florence, Italy continues to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of the European LCV market.
The United Kingdom is transitioning commercial fleet landscape. A significant portion of LCV registrations in the UK comes from the logistics and parcel delivery sector, with companies such as Royal Mail, DPD, and Amazon significantly expanding their fleets. Additionally, London’s Ultra Low Emission Zone (ULEZ) expansion has spurred interest in cleaner commercial vehicles. Moreover, electric LCV sales in the UK grew notably in 2023 compared to the previous year, driven by grants under the Plug-in Van Grant scheme. Although the market has faced supply chain disruptions, the push for decarbonization and fleet modernization positions the UK as a key player in the evolving European LCV landscape.
Spain holds a growing urban delivery demand. Also, it’s e-commerce market grew in 2023 compared to the previous year, directly boosting demand for delivery vans in major cities such as Madrid, Barcelona, and Valencia. Like, logistics companies operating in Spain have been actively renewing their fleets with newer, more fuel-efficient models to comply with local emissions regulations. Additionally, the Spanish government has introduced subsidies for electric LCVs under the MOVES III program, encouraging businesses to transition away from older diesel vehicles.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
Fiat Chrysler Automobiles N.V., Ford Motor Company, Groupe Renault, Mercedes-Benz, Peugeot S.A., Toyota Motor Corporation, Volkswagen AG. Are the market players that are dominating the europe commercial vehicle market.
Top Players in the Europe Market
Stellantis is a dominant force in the Europe light commercial vehicle market, offering a comprehensive lineup of LCVs under brands such as Peugeot, Citroën, Fiat, and Opel. The company’s focus on versatility, fuel efficiency, and electrification has made its models like the Peugeot Partner, Fiat Fiorino, and Opel Combo highly popular among small businesses and logistics operators. Stellantis has been at the forefront of introducing electric variants across its LCV portfolio, reinforcing its leadership position in the transition toward sustainable urban mobility. Its strong dealer network and strategic partnerships with fleet management companies further enhance its competitive edge.
Mercedes-Benz Group AG
Mercedes-Benz holds a prestigious position in the European LCV segment, particularly among premium fleet operators and professional users who prioritize durability, performance, and brand reputation. The Sprinter van series remains one of the most sought-after commercial vehicles in Europe due to its adaptability across multiple use cases—from courier services to mobile workshops. Mercedes-Benz combines advanced engineering with digital integration, offering smart connectivity and driver assistance features that appeal to modern fleet managers. Its commitment to developing electric versions of its iconic models positions it strongly in the evolving LCV landscape.
Renault S.A.
Renault is a long-standing leader in the European LCV market, known for its practical and cost-effective commercial vehicles such as the Renault Kangoo and Master. These models are widely adopted by both individual entrepreneurs and large delivery firms due to their reliability, ease of maintenance, and space-efficient designs. Renault was among the first automakers to introduce mass-market electric LCVs with the Kangoo Z.E., later upgraded to the Kangoo E-Tech Electric. The company continues to innovate with new powertrain technologies and digital fleet solutions, ensuring its sustained relevance in a rapidly transforming commercial mobility sector.
Top Strategies Used By Key Market Participants
One of the primary strategies employed by leading players in the Europe light commercial vehicle (LCV) market is accelerated electrification , where manufacturers are rapidly expanding their portfolios of battery electric and hybrid models to meet tightening emissions regulations and shifting customer demand. Automakers are not only redesigning existing platforms but also developing dedicated EV architectures tailored for commercial use.
Another critical approach is strategic partnerships and fleet ecosystem integration , wherein OEMs collaborate with charging infrastructure providers, logistics software developers, and leasing companies to offer holistic mobility solutions. This enables seamless adoption of electric LCVs by businesses through bundled services including financing, maintenance, and route optimization tools.
Lastly, localized production and customization capabilities are being leveraged to better serve regional markets. Companies are adapting vehicle configurations to suit specific national requirements, enhancing user experience while maintaining cost-efficiency. These strategies collectively strengthen market presence and ensure alignment with evolving industry dynamics.
COMPETITION OVERVIEW
The competition in the Europe light commercial vehicle (LCV) market is intense and multifaceted, driven by a blend of traditional automotive giants, emerging electric vehicle specialists, and evolving customer expectations. Established manufacturers such as Stellantis, Mercedes-Benz, and Renault dominate the landscape with extensive product portfolios, robust distribution networks, and deep-rooted relationships with business customers. However, they face growing pressure from newer entrants and tech-driven startups that are leveraging innovation in electrification, connectivity, and fleet digitization to capture market share. The ongoing shift toward zero-emission mobility has intensified R&D efforts, prompting automakers to invest heavily in battery technology, lightweight materials, and intelligent transport systems. Additionally, the need to comply with stringent regulatory standards and consumer demand for smarter, more efficient commercial vehicles has forced companies to rethink their go-to-market strategies. As a result, differentiation is increasingly achieved through service offerings, total cost of ownership, and integrated mobility ecosystems rather than just hardware. This dynamic environment fosters continuous innovation, reshaping the competitive structure and redefining success metrics within the LCV segment.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THE MARKET
- In March 2024, Stellantis announced the launch of its new electric LCV platform, designed specifically for high-volume urban delivery applications. This platform will underpin next-generation versions of the Peugeot e-Partner and Citroën ë-Berlingo, strengthening the company's position in the fast-growing electric commercial vehicle segment.
- In August 2023, Mercedes-Benz unveiled an expanded range of electrified Sprinter models, including plug-in hybrid and fully electric variants equipped with enhanced battery technology and smart fleet management systems aimed at improving operational efficiency for commercial users.
- In October 2023, Renault entered into a strategic partnership with a major European charging network provider to offer integrated charging solutions for its electric LCV customers, simplifying access to public and depot-based charging infrastructure across key European markets.
- In January 2024, Ford Europe introduced the all-electric version of its Transit Custom model, marking a significant step in its electrification roadmap and positioning the company as a stronger contender in the mid-sized LCV category targeted at logistics and delivery fleets.
In May 2024, Volkswagen Commercial Vehicles launched a digital fleet management platform tailored for its electric van customers, enabling real-time monitoring of energy consumption, route optimization, and predictive maintenance to enhance productivity and reduce downtime.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the Europe light commercial vehicles market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Vehicle Type
- Commercial Vehicles
- Light Commercial Pick-up Trucks
- Light Commercial Vans
By Propulsion Type
- Hybrid and Electric Vehicles
- BEV
- FCEV
- HEV
- PHEV
- ICE
- Fuel Categories
- CNG
- Diesel
- Gasoline
- LPG
By Country
- UK
- France
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Russia
- Sweden
- Denmark
- Switzerland
- Netherlands
- Turkey
- Czech Republic
- Rest of Europe
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors are driving the growth of the light commercial vehicle market in Europe?
E-commerce expansion, last-mile delivery demand, and urban logistics needs are accelerating LCV sales, particularly in countries like Germany, the UK, and France.
How is electrification impacting the European LCV segment?
Stricter EU CO₂ emission targets and urban low-emission zones are pushing fleet operators toward electric vans, with major growth seen in BEV models like the Ford E-Transit and Renault Kangoo E-Tech.
What are key challenges for LCV manufacturers in Europe today?
OEMs face pressure from supply chain disruptions, Euro 7 emission regulations, and the need to balance affordability with tech upgrades such as ADAS and connectivity features.
Which end-use sectors dominate LCV adoption in Europe?
Delivery & logistics, construction, and trades (e.g., plumbing, electrical) are the largest consumers, with increasing customization demands for fleet-specific applications.
What trends are shaping the future of LCV design and functionality?
Trends include modular cargo space solutions, integrated telematics, fleet electrification strategies, and the rise of connected vehicle ecosystems for real-time asset tracking and maintenance.
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from
$ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: sales@marketdataforecast.com