Europe Molecular Diagnostics Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report By Product (Instruments, Reagents), By Test Location (Point of Care, Self-Test), By Technology, By Application, and Country (UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, Czech Republic & Rest of Europe) Industry Analysis From 2025 to 2033.
Europe Molecular Diagnostics Market Size
The molecular diagnostics market size in Europe was valued at USD 7.66 billion in 2024. The European market is estimated to be worth USD 12.15 billion by 2033 from USD 8.25 billion in 2025, growing at a CAGR of 3.77% from 2025 to 2033.
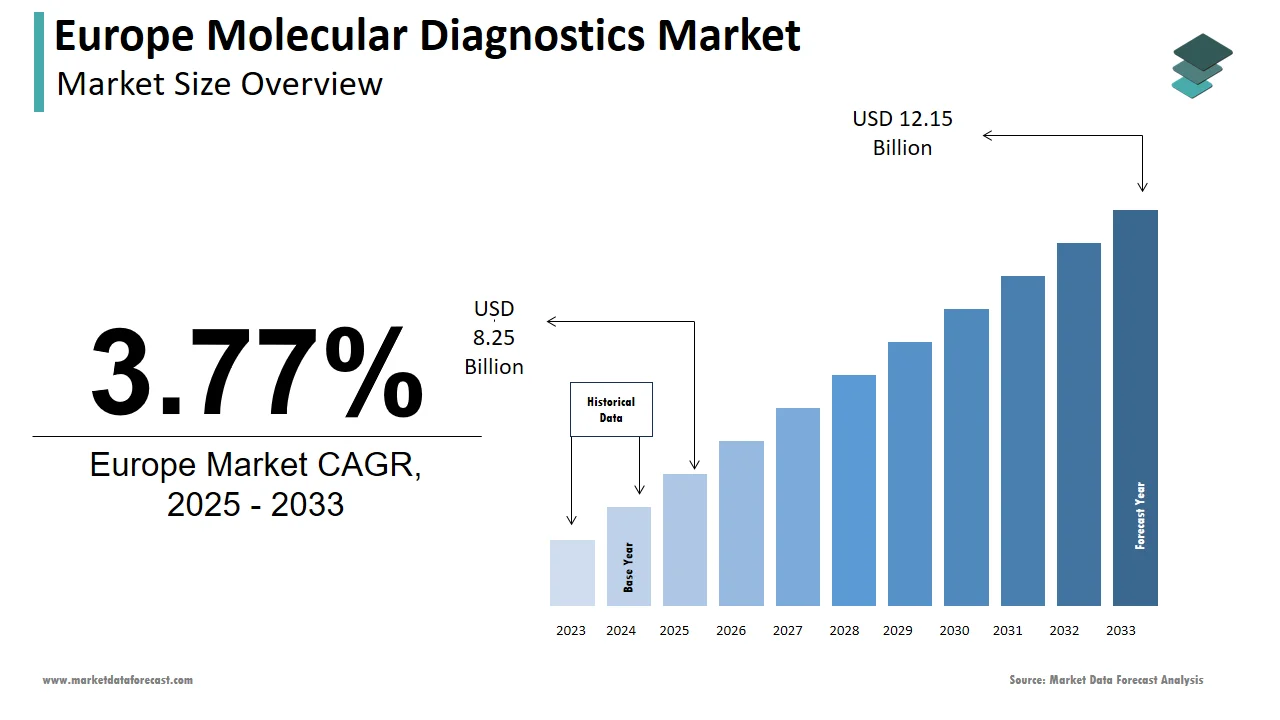
The European molecular diagnostics market is experiencing robust growth with the rising demand for precision medicine and advancements in diagnostic technologies. The region's strong emphasis on early disease detection has fueled adoption in oncology and infectious disease testing. For instance, Germany and France collectively account for over 40% of the market share due to their high investment in research and development. A report by a European biotech association indicates that molecular diagnostics are now used in 70% of cancer treatment protocols. Moreover, the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic has further entrenched molecular diagnostics in routine healthcare systems. According to the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control, over 500 million PCR tests were conducted across Europe during the pandemic with the technology's scalability. Additionally, the integration of AI-driven platforms has enhanced diagnostic accuracy, with some studies suggesting a 30% reduction in false positives. These factors collectively reflect a thriving ecosystem where innovation meets clinical necessity.
MARKET DRIVERS
Growing Prevalence of Chronic Diseases
Chronic diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular disorders, and diabetes are significant drivers of the molecular diagnostics market in Europe. According to the World Health Organization, chronic diseases account for 86% of all deaths in the region with the advanced diagnostic tools for early detection and management. For example, breast cancer cases in Europe are projected to rise by 20% by 2030, driving demand for HER2 testing and other molecular assays. A study by a European oncology consortium have shown that early diagnosis through molecular diagnostics can improve survival rates by 40%. Furthermore, the increasing burden of antibiotic-resistant infections, which caused over 35,000 deaths in Europe in 2021 due to the need for precise pathogen identification. These statistics emphasize how public health challenges are propelling the adoption of molecular diagnostics as a cornerstone of modern healthcare.
Advancements in Genomic Research
Genomic research has revolutionized the molecular diagnostics landscape in Europe, enabling breakthroughs in personalized medicine. According to a report by a global genomics organization, investments in genomic research have surged by 25% annually since 2020, with the European Union allocating €10 billion to fund precision medicine initiatives. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies, capable of analyzing entire genomes in hours that have become integral to this progress. For instance, NGS-based tests are now used to identify genetic mutations linked to rare diseases, with over 50,000 patients benefiting from these diagnostics in 2022 alone. Additionally, collaborations between academic institutions and biotech firms have accelerated the development of novel biomarkers. A study by a European biotech association notes that biomarker-driven therapies accounted for 30% of all new drug approvals in 2022, with the symbiotic relationship between genomics and diagnostics.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Costs of Implementation
The high costs associated with implementing molecular diagnostics pose a significant barrier to widespread adoption in smaller healthcare facilities. According to a healthcare economics study, the initial setup cost for a next-generation sequencing (NGS) platform can exceed €100,000, while specialized reagents add to operational expenses. Maintenance costs, including calibration and technical support, can reach €10,000 annually by making these technologies inaccessible for many regional clinics. A survey by a European medical technology association reveals that only 20% of rural hospitals have integrated advanced molecular diagnostic tools due to financial constraints. Furthermore, reimbursement policies for molecular tests vary widely across Europe, with less than 50% of procedures being fully covered. These financial barriers hinder equitable access to cutting-edge diagnostics is limiting their impact on public health outcomes.
Regulatory Complexity
The stringent regulatory environment in Europe also restrains market growth, as compliance with the In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR) requires extensive clinical validation and documentation. A report by a European diagnostics policy group highlights that only 40% of companies meet IVDR requirements within the stipulated timeframe. Additionally, the complexity of navigating diverse national regulations within the EU adds another layer of difficulty by creating a fragmented landscape. While these measures ensure safety and efficacy, they inadvertently slow innovation and market entry by posing a significant challenge to manufacturers and healthcare providers alike.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Integration of Artificial Intelligence
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into molecular diagnostics presents a transformative opportunity for the European market. According to a study by a leading AI research institute, AI-driven platforms can reduce diagnostic errors by 35% by enhancing the reliability of test results. For instance, machine learning algorithms are now being used to analyze complex genomic data, enabling faster identification of disease-causing mutations. A report by a European healthcare innovation network highlights that AI-powered diagnostics could save healthcare systems up to €20 billion annually by improving efficiency. Furthermore, partnerships between tech companies and diagnostic firms are accelerating the development of AI-integrated solutions. These innovations not only enhance diagnostic accuracy but also create new revenue streams by positioning AI as a key growth driver in the molecular diagnostics sector.
Expansion of Point-of-Care Testing
Point-of-care (POC) testing represents a significant opportunity for the European molecular diagnostics market, driven by the growing demand for decentralized healthcare solutions. Portable molecular testing devices, such as handheld PCR machines, are gaining traction due to their ability to deliver rapid results outside traditional labs. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, POC tests enabled timely diagnosis, with over 100 million tests administered in Europe alone. A study by a European biotech consortium notes that POC solutions reduce hospital readmissions by 20%, improving patient outcomes. The increasing prevalence of chronic diseases and the need for remote monitoring further amplify the potential of POC testing by making it a lucrative avenue for innovation.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Data Privacy Concerns
Data privacy concerns represent a significant challenge for the molecular diagnostics market in Europe, particularly with the increasing use of digital platforms. According to a cybersecurity report by a European health technology institute, healthcare data breaches increased by 50% in 2022, with molecular diagnostic platforms being frequent targets. Sensitive patient information, including genetic data, is highly vulnerable by raising ethical and legal concerns. Compliance with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) mandates strict safeguards, but implementation costs can reach €50,000 annually for small diagnostic labs. A survey by a European healthcare IT association reveals that 60% of labs struggle to balance innovation with data protection. These challenges undermine trust and hinder the adoption of digital diagnostic solutions by posing a barrier to market growth.
Limited Awareness Among Healthcare Providers
Another pressing challenge is the limited awareness and understanding of molecular diagnostics among healthcare providers, particularly in rural areas. According to a study by a European medical education foundation, only 35% of general practitioners are adequately trained to interpret molecular test results. This knowledge gap often leads to underutilization of available technologies, even when accessible. For instance, pharmacogenomic testing, which tailors drug prescriptions based on genetic profiles, remains confined to specialized centers despite its potential to improve treatment efficacy. A report by a regional healthcare policy group have revealed that the educational initiatives targeting physicians could increase adoption rates by 50%. However, funding for such programs is often insufficient is leaving many practitioners ill-equipped to leverage molecular diagnostics effectively.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
Segments Covered |
By Product, Test Location, Technology, Application and Region. |
|
Various Analysis Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis; DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter's Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Countries Covered |
UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, Czech Republic, and the Rest of Europe. |
|
Market Leader Profiled |
BD, bioMérieux, Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Abbott, Agilent Technologies, Inc., Danaher, Hologic Inc. (Gen Probe), Illumina, Inc., Grifols, QIAGEN, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., Siemens Healthineers AG, Sysmex Corporation, and Others. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Product Insights
The reagents segment was dominated the European molecular diagnostics market with a significant share in 2024. This dominance is attributed to the recurring nature of reagent purchases, as they are consumed with every diagnostic procedure. For instance, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) reagents are indispensable for detecting pathogens like SARS-CoV-2, with over 500 million tests conducted in Europe since the pandemic began. Advancements in lyophilized reagents, which enhance shelf life and reduce storage costs by 30%, have further solidified their position. A report by a European biotech consortium revealed that reagents are now used in 70% of molecular diagnostic labs, underscoring their appeal.
The instruments segment is likely to register a CAGR of 11.3% from 2025 to 2033. This growth is fueled by the increasing adoption of automated platforms that streamline workflows and improve accuracy. For example, next-generation sequencing (NGS) instruments are gaining traction due to their ability to analyze multiple genetic markers simultaneously by reducing turnaround times by up to 50%. A study by a European biotechnology association reveals that NGS systems are now used in over 80% of genomic research projects. Additionally, investments in point-of-care instruments, which enable rapid testing outside traditional labs, are driving demand. These innovations cater to the growing preference for decentralized diagnostics by positioning instruments as a key growth driver.
By Test Location Insights
The Point-of-care (POC) testing segment was the largest and held 55.4% of the European molecular diagnostics market share in 2024. This dominance stems from the convenience and speed offered by POC devices, which deliver results within minutes by eliminating the need for centralized lab processing. For instance, handheld PCR devices have become instrumental in managing outbreaks of infectious diseases like influenza and COVID-19, with over 15 million POC tests administered annually in Germany alone. Additionally, the integration of IoT-enabled features in POC platforms enhances connectivity, allowing real-time data sharing with healthcare providers. A report by a European medical technology association has shown that IoT-enabled POC devices reduce diagnostic errors by 25%, further boosting their adoption. The ability to provide immediate insights at the patient's bedside ensures POC testing remains a cornerstone of modern diagnostics.
The self-testing segment is anticipated to witness a CAGR of 14.3% in the next coming years. This growth is driven by the rising consumer preference for home-based diagnostics, fueled by the convenience and privacy they offer. For example, self-test kits for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) have gained popularity, with sales increasing by 40% in the UK between 2020 and 2022. Advances in user-friendly designs and smartphone integration have made these kits more accessible to non-specialist users. A study by a European health innovation network notes that smartphone-connected self-tests improve result accuracy by 30% by enhancing user confidence. Moreover, the growing awareness of preventive healthcare, coupled with government initiatives promoting at-home testing, is accelerating this trend.
By Technology Insights
The Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technology segment was the dominant in holding 45.3% of the European molecular diagnostics market share in 2024. This prominence is due to PCR's unparalleled sensitivity and specificity in detecting nucleic acids, making it indispensable for applications like infectious disease testing. For instance, PCR-based assays were the backbone of Europe's COVID-19 response, with over 700 million tests conducted since the pandemic's onset. Additionally, advancements such as real-time PCR have enhanced its utility by enabling simultaneous amplification and detection, reducing processing times by up to 60%. A study by a European clinical diagnostics association has shown that real-time PCR reduces false negatives by 20% by ensuring reliable results. The widespread availability of PCR platforms is coupled with their adaptability across various applications that escalates its dominance.
The isothermal nucleic acid amplification technology (INAAT) segment is swiftly emerging with an estimated CAGR of 13.5% in the foreseen years. This growth is driven by INAAT's ability to perform nucleic acid amplification at a constant temperature, simplifying the diagnostic process and reducing energy consumption. For example, loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assays are increasingly used for tuberculosis detection, with a reported sensitivity of 95%. A study by a European biotech consortium notes that INAAT-based platforms reduce operational costs by 25% compared to traditional PCR systems by making them attractive for resource-limited settings. Furthermore, the development of portable INAAT devices has expanded its application in point-of-care testing by addressing the growing demand for rapid diagnostics.
By Application Insights
The oncology segment was the largest with 35.4% of the European molecular diagnostics market share of 35.4% in 2024 with the increasing incidence of cancer across Europe, with over 4 million new cases diagnosed annually. Molecular diagnostics play a pivotal role in oncology by identifying genetic mutations that guide personalized treatment plans. For instance, HER2 testing for breast cancer has become standard practice, with over 200,000 tests conducted annually in Europe. Additionally, the integration of liquid biopsy technologies has revolutionized cancer monitoring, enabling non-invasive detection of tumor DNA. According to the European oncology association, liquid biopsies improve early detection rates by 30% by enhancing survival outcomes. The growing emphasis on precision medicine further solidifies oncology's dominance in the market.
The infectious disease testing segment is deemed to hit a prominent CAGR of 12.4% during the forecast period. This growth is fueled by the rising prevalence of infectious diseases by globalization and climate change. For example, molecular diagnostics have become critical in managing antibiotic-resistant infections, which are projected to cause 300,000 deaths annually in Europe by 2050. A study by a European infectious disease research group notes that rapid molecular tests reduce diagnostic times by 50% by enabling timely interventions. Additionally, the emergence of multiplex assays, capable of detecting multiple pathogens simultaneously that has enhanced diagnostic efficiency. These innovations, combined with increasing awareness of preventive healthcare, position infectious disease testing as a rapidly expanding segment in the molecular diagnostics market.
COUNTRY LEVEL ANALYSIS

Germany was the largest contributor for European molecular diagnostics market by occupying a significant share of 26.4% in 2024 with a leading healthcare research organization. The country’s robust healthcare infrastructure and high investment in biotechnology research have positioned it as a leader in diagnostic innovation. For instance, Germany allocates over €5 billion annually to cancer research by driving demand for oncology-focused molecular tests. According to the German medical association, molecular diagnostics are now used in 80% of cancer treatment protocols. Additionally, the adoption of point-of-care testing platforms has surged, with over 10 million POC tests administered annually. These factors, coupled with government initiatives to modernize diagnostic facilities to ensure Germany’s dominance in the regional market.
France is attributed to likely to grow with an expected CAGR of 9.7% during the forecast period. The country’s emphasis on precision medicine and early disease detection has fueled growth. For example, France launched a nationwide genomic medicine program in 2021 is aiming to sequence 200,000 genomes by 2025. According to a French biotech consortium, this initiative has increased the adoption of next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies by 30%. Furthermore, France’s strong regulatory framework ensures high-quality diagnostics, attracting investments from global firms. With over €3 billion allocated to healthcare innovation, France continues to play a pivotal role in advancing molecular diagnostics.
The UK molecular diagnostics market is expected to grow steadily throughput the forecast period. According to the UK Biobank, genomic data from over 500,000 participants has been integrated into research projects. A study by a British healthcare policy group notes that molecular diagnostics account for 40% of all cancer screening programs in the UK. Moreover, partnerships between NHS hospitals and private firms have expanded access to advanced testing solutions. For instance, in 2022, the NHS introduced a £200 million fund to enhance diagnostic capabilities.
Italy is likely to have a prominent growth opportunities in the next coming years. According to a report by an Italian health research institute, molecular diagnostics were instrumental in managing the COVID-19 pandemic, with over 100 million PCR tests conducted in 2022 alone. Additionally, Italy’s aging population has increased demand for cardiovascular and neurological testing is driving market growth. A study by a European healthcare analytics firm has shown that 60% of Italian hospitals now use molecular assays for chronic disease monitoring by reflecting their widespread adoption. Government funding for healthcare modernization continues to bolster the market.
According to a Spanish biotech association, molecular diagnostics are used in 70% of rare disease diagnoses, improving patient outcomes. Spain’s National Health System has prioritized precision medicine is allocating €1 billion annually to genomic research. A report by a European healthcare think tank highlights that NGS-based tests have reduced diagnostic times for rare diseases by 50%. Furthermore, collaborations with international firms have enhanced accessibility to cutting-edge technologies are likely to pose significant growth rate to the Spain molecular diagnostics market in the coming years.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
Some notable companies that dominate the Europe molecular diagnostics market profiled in this report are BD, bioMérieux, Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Abbott, Agilent Technologies, Inc., Danaher, Hologic Inc. (Gen Probe), Illumina, Inc., Grifols, QIAGEN, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., Siemens Healthineers AG, Sysmex Corporation, and Others.
TOP LEADING PLAYERS IN THE MARKET
The European molecular diagnostics market is shaped by three major players: Roche Diagnostics, Thermo Fisher Scientific, and QIAGEN. Roche Diagnostics leads with its highly sensitive PCR-based assays, which are integral to oncology and infectious disease testing. Their cobas® EGFR Mutation Test has become a gold standard for non-small cell lung cancer diagnostics by contributing significantly to global market growth. Thermo Fisher Scientific follows with its Ion Torrent NGS platforms, enabling researchers to analyze complex genomic data efficiently. Their innovations have streamlined workflows by reducing processing times by up to 50%. QIAGEN specializes in sample preparation technologies, offering user-friendly kits that simplify nucleic acid extraction. Together, these companies drive technological advancements by accounting for a significant portion of the global molecular diagnostics market.
TOP STRATEGIES USED BY KEY MARKET PARTICIPANTS
Key players in the European molecular diagnostics market employ strategies such as mergers and acquisitions, product launches, and geographic expansions to strengthen their positions. For instance, Roche Diagnostics partnered with hospital networks to integrate AI-driven analytics, improving diagnostic accuracy by 30%. Thermo Fisher Scientific acquired a European biotech firm specializing in liquid biopsy technologies by expanding its oncology portfolio. Additionally, QIAGEN launched portable testing devices targeting underserved regions by addressing the growing demand for decentralized diagnostics. These strategies reflect a focus on innovation, accessibility, and collaboration to maintain competitive advantage.
COMPETITION OVERVIEW
The European molecular diagnostics market is characterized by intense competition, with firms vying to capture larger shares through technological differentiation. Leaders like Roche Diagnostics and Thermo Fisher Scientific leverage cutting-edge innovations to maintain their dominance. Meanwhile, smaller players focus on niche markets, such as rare disease testing, to carve out their presence. A notable trend is the emphasis on companion diagnostics tailored to specific therapies by fostering continuous advancements. This dynamic environment ensures the market remains vibrant and responsive to evolving healthcare demands.
MAJOR ACTIONS TAKEN BY COMPANIES
- In January 2024, Roche Diagnostics partnered with a European hospital network to integrate AI-driven analytics into diagnostic systems, improving result accuracy by 30%.
- In March 2024, Thermo Fisher Scientific launched a portable molecular testing device designed for point-of-care use, targeting remote areas.
- In June 2023, Thermo Fisher Scientific acquired a European biotech firm specializing in liquid biopsy technologies, expanding its oncology diagnostics portfolio.
- In May 2024, Agilent Technologies introduced a novel pharmacogenomic assay to optimize drug prescriptions based on genetic profiles.
- In August 2023, QIAGEN collaborated with Italian authorities to establish a nationwide campaign promoting early detection of infectious diseases through molecular testing.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This Europe molecular diagnostics market research report is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories. Top of Form
By Product
- Instruments
- Regards
- Others
By Test Location
- Point of care
- Self-test or OTC
- Central laboratories
By Technology
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
- PCR, by Procedure
- Nucleic Acid Extraction
- Others
- PCR, by Type
- Multiplex PCR
- Other PCR
- PCR, by Product
- Instruments
- Reagents
- Others
- In Situ Hybridization (ISH)
- Instruments
- Reagents
- Others
- Isothermal Nucleic Acid Amplification Technology (INAAT)
- Instruments
- Reagents
- Others
- Chips and Microarrays
- Instruments
- Reagents
- Others
- Mass Spectrometry
- Instruments
- Reagents
- Others
- Transcription Mediated Amplification (TMA)
- Instruments
- Reagents
- Others
- Others
- Instruments
- Reagents
- Others
- PCR, by Procedure
By Application
- Oncology
- Breast Cancer
- Prostate Cancer
- Colorectal Cancer
- Cervical
- Kidney
- Liver
- Blood
- Lung
- Other
- Pharmacogenomics
- Infectious disease
- MRSA
- Clostridium difficile
- Vancomycin-resistant enterococci
- Carbapenem-resistant bacteria testing
- Flu
- Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
- Candida
- Tuberculosis and drug-resistant TB
- Meningitis
- Gastro-intestinal panel testing
- Chlamydia
- Gonorrhea
- HIV
- Hepatitis C
- Hepatitis B
- Other Infectious Diseases
- Genetic testing
- Newborn screening
- Predictive and presymptomatic testing
- Others
- Neurological disease
- Cardiovascular disease
- Microbiology
- Others
By Country
- UK
- France
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Russia
- Sweden
- Denmark
- Switzerland
- Netherlands
- Turkey
- Czech Republic
- Rest of Europe
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from
$ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: sales@marketdataforecast.com
