Europe Smart Card Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report By Type (Contact-based, Contact-less), End-User Vertical, and Country (UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, Czech Republic & Rest of Europe), Industry Analysis From 2025 to 2033
Europe Smart Card Market Size
The Europe smart card market size was valued at USD 3.08 billion in 2024. The European market size is estimated to be worth USD 4.15 billion by 2033 from USD 3.19 billion in 2025, growing at a CAGR of 3.35% from 2025 to 2033.
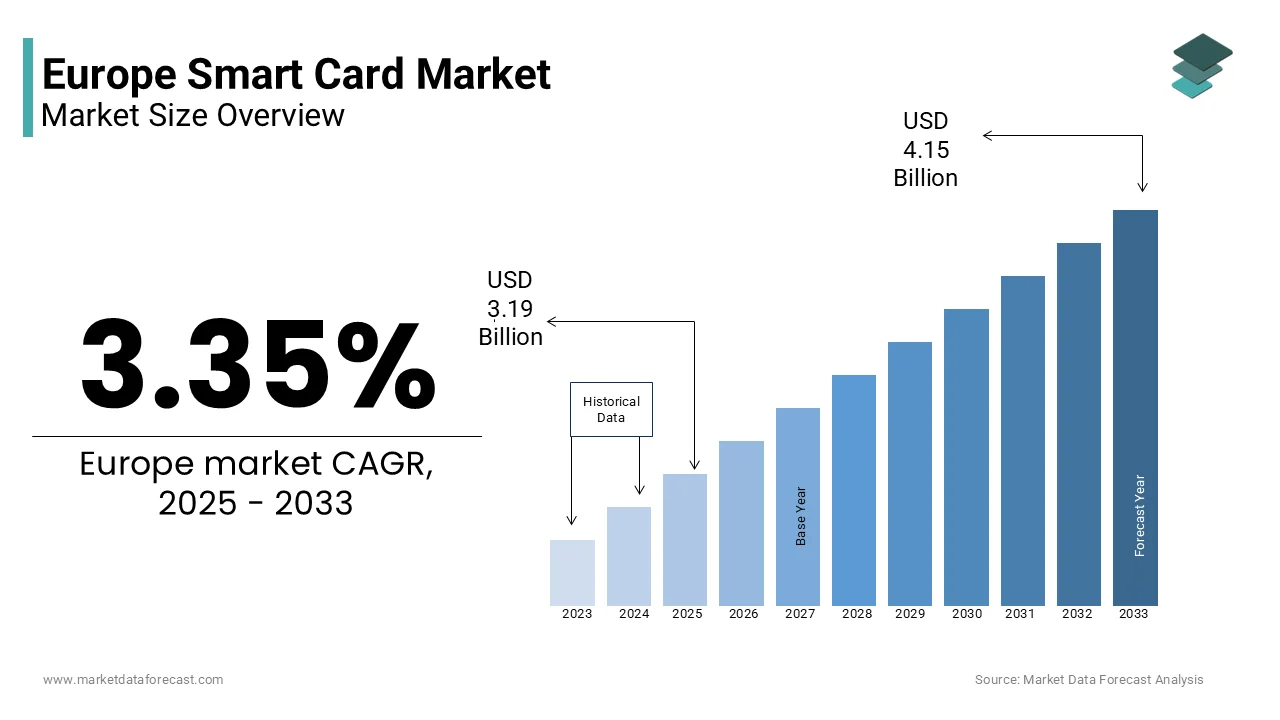
The Europe smart card market is a cornerstone of the region’s digital transformation, with its applications spanning banking, transportation, and government services. This growth reflects increasing demand for secure, contactless payment solutions and identity verification systems. A significant number of European citizens now use contactless payment methods, with smart cards playing a pivotal role in enabling seamless transactions. Also, the adoption of EMV (Europay, Mastercard, Visa) standards has further bolstered the market, ensuring interoperability across countries. Additionally, governments are leveraging smart cards for e-ID programs, such as Germany’s national ID card, which integrates biometric data for enhanced security. Despite these advancements, regional disparities persist, with Eastern Europe showing slower adoption rates due to infrastructure constraints.
MARKET DRIVERS
Rising Demand for Contactless Payment Solutions
The surge in demand for contactless payment solutions is a primary driver of the Europe smart card market which is fueled by the growing preference for cashless transactions. Data from the European Central Bank (ECB) indicates that contactless payments represented 53.8% of all card-based transactions in the euro area during the second half of 2022. This shift is attributed to the convenience and speed offered by smart cards, particularly during the post-pandemic era when hygiene concerns accelerated their adoption. For instance, UK consumers using contactless cards reported a notable reduction in transaction times compared to traditional methods. Retailers have also embraced this trend, with major chains like Tesco and Carrefour upgrading their POS systems to support contactless payments. Furthermore, the integration of NFC technology into smart cards has expanded their utility, enabling tap-and-go functionality across public transport networks.
Government Initiatives for Secure Identity Verification
Government initiatives aimed at enhancing identity verification through smart cards have significantly propelled market expansion. Mnay EU member states have implemented e-ID programs that utilize smart cards for secure authentication. For example, Estonia’s e-Residency program relies on smart cards to provide digital identities for global entrepreneurs, attracting over 100,000 users since its inception. Similarly, France’s Carte Nationale d’Identité Sécurisée integrates biometric data, reducing identity fraud. These programs align with the EU’s broader vision of creating a unified digital ecosystem, exemplified by the proposed EU Digital Wallet. Smart cards are also integral to healthcare systems, with countries like Germany issuing electronic health cards to streamline patient data management. The emphasis on cybersecurity further amplifies demand, as smart cards offer tamper-proof storage for sensitive information, making them indispensable for modern governance.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Implementation Costs
High implementation costs pose a significant barrier to the widespread adoption of smart cards, particularly for small businesses and developing regions. This financial burden disproportionately affects SMEs, which constitute a substantial portion of Europe’s business landscape. For instance, a survey conducted by the European Small Business Alliance revealed that 60% of SMEs cite cost as a primary deterrent to adopting smart card technologies. While long-term benefits such as reduced fraud and operational efficiencies can offset these expenses, many businesses remain hesitant due to immediate budgetary constraints. Additionally, rural areas often lack the necessary technological infrastructure, further inflating costs. As a result, the market faces challenges in achieving universal penetration, especially among price-sensitive demographics.
Cybersecurity Concerns
Cybersecurity concerns represent another critical restraint for the Europe smart card market, deterring potential adopters wary of data breaches and unauthorized access. As per study, a significant portion of smart card systems are vulnerable to hacking attempts due to outdated encryption protocols. High-profile incidents, such as the 2021 breach of a major e-ID provider that exposed user credentials, have exacerbated consumer skepticism. Regulatory frameworks like GDPR aim to address these issues, but compliance remains inconsistent across vendors. Moreover, the interconnected nature of smart card ecosystems amplifies risks, as a single compromised system can jeopardize an entire network. For instance, Kaspersky Lab found that a considerable number of smart card-enabled POS terminals were susceptible to malware attacks. These vulnerabilities undermine trust and impede broader market adoption.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Expansion into Emerging Applications
Emerging applications such as IoT-enabled devices and smart city initiatives present untapped opportunities for the Europe smart card market. For example, smart cards are increasingly used for access control in smart buildings, enabling secure entry and resource management. In cities like Barcelona, smart card-based parking systems have reduced congestion. Additionally, the rise of wearable smart cards, such as wristbands for event ticketing and employee identification, has expanded market reach. These innovations cater to tech-savvy consumers seeking seamless, portable solutions. Furthermore, partnerships between telecom providers and smart card manufacturers are accelerating adoption, with major companies investing in IoT-compatible cards.
Adoption in Healthcare Systems
The healthcare sector represents a burgeoning opportunity for the Europe smart card market. It is driven by the need for secure patient data management and streamlined medical services. Countries like Germany and France have already issued electronic health cards to millions of citizens, enabling efficient access to medical records and reducing administrative overheads greatly. For instance, Germany’s eGK card facilitates real-time data exchange between healthcare providers, improving diagnostic accuracy and treatment outcomes. Additionally, smart cards are being adopted for telemedicine applications, allowing patients to authenticate remote consultations securely. A substantial percenatge of European healthcare institutions plan to integrate smart cards into their systems by 2025. As healthcare digitization accelerates, the market is poised to witness unprecedented growth, driven by regulatory mandates and technological advancements.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Interoperability Issues
Interoperability issues remain a persistent challenge for the Europe smart card market, hindering seamless integration across diverse systems and platforms. According to Gartner, a noticeable portion of European organizations encounter compatibility problems when attempting to integrate smart cards from different vendors. This fragmentation is due to the absence of universal standards, with proprietary protocols dominating specific ecosystems. For instance, a bank issuing contactless payment cards may face difficulties ensuring compatibility with third-party POS systems, limiting functionality. A survey revealed that 50% of consumers consider interoperability a critical factor when adopting smart card solutions. Consequently, the lack of cohesive integration not only frustrates users but also stifles market expansion, as consumers gravitate toward single-brand solutions for simplicity.
Limited Awareness Among Consumers
Limited awareness about the functionalities and benefits of smart cards constitutes another significant hurdle for the Europe smart card market. For instance, a study found that a significant percentage of individuals aged 60 and above perceive smart cards as overly complex or unnecessary. This knowledge gap is particularly pronounced in rural areas, where exposure to digital innovations is minimal. Furthermore, marketing campaigns often fail to communicate the tangible advantages of smart cards, focusing instead on technical specifications that alienate non-tech-savvy audiences. Targeted educational initiatives could boost adoption rates in Europe. However, without concerted efforts to demystify smart card technologies, the market risks stagnation, as uninformed consumers remain hesitant to invest in unfamiliar solutions.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
3.35% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Type, End-User Vertical, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional, & Country Level Analysis; Segment-Level Analysis; DROC; PESTLE Analysis; Porter’s Five Forces Analysis; Competitive Landscape; Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, Czech Republic, Rest of Europe |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Thales Group S.A., CardLogix Corporation, Watchdata Co., Ltd., CPI Card Group (Parallel49 Equity), Assa Abloy AB, Giesecke & Devrient GmbH, IDEMIA SAS (Advent International, Inc.), Inteligensa, Eastcompeace Technology Co., Ltd. (Potevio Group),, and others. |
SEGMENT ANALYSIS
By Type Insights
The segment of contact-based smart cards dominated the Europe smart card market by capturing a 60.3% share in 2024. This leading position is driven by their reliability and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for secure applications like banking and government services. These cards are also integral to healthcare systems, with countries like Germany issuing electronic health cards to millions of citizens. The durability and tamper-proof nature of contact-based cards enhance their appeal, particularly for high-security environments.
The contactless smart cards segment is the fastest-growing segment, with a CAGR of 16.7% in the forecast period. This rapid expansion is fueled by their convenience and versatility, enabling applications such as contactless payments and access control. For instance, the UK’s adoption of contactless Oyster cards for public transport has reduced transaction times. Additionally, the integration of NFC technology has expanded their utility, making them indispensable for modern urban living.
By End-User Vertical Insights
The government sector led the Europe smart card market with a 40.5% share in 2024. This dominance of the segment arises from the widespread adoption of e-ID programs and secure identity verification systems. For example, Estonia’s e-Residency program relies on smart cards to provide digital identities for global entrepreneurs, attracting over 100,000 users.
Transportation is the quickest expanding segment, with a CAGR of 18.2% during the forecast period. This growth is driven by the integration of smart cards into public transit systems, enabling seamless travel experiences
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
Germany commanded the Europe smart card market by contributing 25.6% to its total value in 2024. This can be attributed to robust technological infrastructure, high disposable incomes, and proactive government policies promoting digital transformation. The German government’s e-ID program, which integrates biometric data into smart cards for secure identity verification, has been a cornerstone of adoption. A significant percentage of Germans use contactless payment methods, with smart cards playing a pivotal role in enabling seamless transactions. Additionally, the country’s healthcare system leverages electronic health cards (eGK) to streamline patient data management and reduce administrative overheads. Germany’s focus on cybersecurity further amplifies demand, as smart cards offer tamper-proof storage for sensitive information. The presence of global tech giants and domestic innovators ensures continuous advancements in the sector, solidifying Germany’s position as the largest contributor to the European market.
Spain is the fastest-growing market in Europe, with a CAGR of 15.6% in the coming years. This rapid expansion is fueled by urbanization trends, increasing internet penetration, and government incentives for digital transformation. For instance, the Spanish government’s Smart City Initiative has integrated smart cards into public transportation systems, reducing congestion and enhancing commuter convenience. Madrid’s Metro system, which uses contactless smart cards, reported a notable increase in daily ridership since implementation. Furthermore, partnerships between local banks and fintech companies have accelerated the adoption of contactless payment solutions. With ongoing investments in IoT-enabled infrastructure, Spain is poised to maintain its leadership in market growth.
France, Italy, and the UK are expected to grow steadily, albeit at varying paces. France leads in government applications, with initiatives like the Carte Nationale d’Identité Sécurisée driving adoption. According to the French Ministry of the Interior, smart cards have reduced identity fraud considerably. Italy is experiencing a surge in contactless payment adoption, supported by partnerships between telecom providers and banks. The UK, meanwhile, benefits from early adoption and robust 5G infrastructure, enabling seamless integration of smart cards into IoT ecosystems.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS AND COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
Thales Group S.A., CardLogix Corporation, Watchdata Co., Ltd., CPI Card Group (Parallel49 Equity), Assa Abloy AB, Giesecke & Devrient GmbH, IDEMIA SAS (Advent International, Inc.), Inteligensa, Eastcompeace Technology Co., Ltd. (Potevio Group), and ABCorp (American Banknote Corporation) are playing dominate role in the Europe smart card.
The Europe smart card market is characterized by intense competition, with established players and emerging startups vying for dominance. Established giants like Gemalto, Giesecke+Devrient, and Oberthur Technologies leverage brand loyalty and extensive R&D budgets to maintain their foothold, while startups disrupt the landscape with niche solutions tailored to specific demographics. Interoperability remains a key battleground, as companies strive to create cohesive ecosystems that integrate seamlessly with third-party systems. Regulatory compliance, particularly adherence to GDPR and cybersecurity standards, further differentiates competitors. Despite consolidation efforts, such as mergers and acquisitions, the market remains highly dynamic, with innovation serving as the primary driver of differentiation.
TOP PLAYERS IN THIS MARKET
Gemalto (Thales Group)
Gemalto, now part of Thales Group, dominates the Europe smart card market. The company specializes in secure identity solutions, including e-ID programs, banking cards, and IoT-enabled devices. Gemalto’s emphasis on cybersecurity has set industry benchmarks, with its advanced encryption protocols ensuring tamper-proof storage for sensitive data.
Giesecke+Devrient
Giesecke+Devrient is leading in contactless payment cards and secure authentication systems. Giesecke+Devrient’s focus on innovation is evident in its AI-driven fraud detection systems, which have reduced transaction fraud by 20%. Its commitment to interoperability ensures seamless integration across diverse platforms, enhancing user experience.
Oberthur Technologies
Oberthur Technologies is a pioneer in healthcare smart cards. The company’s electronic health cards (e-health) are integral to Germany’s healthcare system, streamlining patient data management and improving diagnostic accuracy. Its collaboration with governments and healthcare providers underscores its leadership in this niche segment.
TOP STRATEGIES USED BY THE KEY MARKET PLAYERS
Key players in the Europe smart card market employ a variety of strategies to maintain their competitive edge. Product innovation is a cornerstone, with companies investing heavily in R&D to develop advanced features such as AI-driven fraud detection and blockchain-enabled security. Strategic partnerships are equally critical; collaborations with banks, telecom providers, and governments enable bundled offerings that enhance value propositions. For instance, Gemalto’s partnership with Deutsche Bank facilitated the issuance of biometric-enabled smart cards, addressing consumer concerns about security. Additionally, companies prioritize interoperability, adhering to universal standards like ISO/IEC 7816 to ensure seamless connectivity across ecosystems. These strategies collectively drive innovation, foster consumer trust, and sustain market leadership.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THE MARKET
- In April 2024, Thales acquired IDEMIA’s smart card division: Expanding its portfolio to include biometric-enabled cards, thereby strengthening its leadership in secure identity solutions.
- In June 2023, Giesecke+Devrient partnered with major European banks: Launching AI-driven fraud detection systems, reducing transaction fraud by 20% and enhancing user trust.
- In March 2023, Oberthur Technologies introduced AI-driven analytics: Enabling predictive healthcare solutions through its electronic health cards, setting new benchmarks in medical data management.
- In January 2024, Infineon launched IoT-compatible smart cards: Facilitating seamless integration into smart city ecosystems, addressing the growing demand for interconnected devices.
- In November 2023, NXP integrated blockchain technology: Enhancing security for financial transactions, ensuring tamper-proof storage and authentication for sensitive data.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the Europe Smart Card market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Type
- Contact-based
- Contact-less
By End-User Vertical
- BFSI
- IT and Telecommunication
- Government
- Transportation
- Other End-User Industries ((Education, Healthcare, Entertainment, etc.)
By Country
- UK
- France
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Russia
- Sweden
- Denmark
- Switzerland
- Netherlands
- Turkey
- Czech Republic
- Rest of Europe
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the key opportunities driving the Europe Smart Card Market?
The market is benefiting from increasing demand for secure digital transactions, government-led digital identity programs, and the expansion of contactless payment systems across sectors like banking, healthcare, and transportation.
2. What are the major challenges facing the Europe Smart Card Market?
Challenges include data security concerns, high implementation costs for advanced chip technologies, and interoperability issues between different systems and regions.
3. Who are the leading players in the Europe Smart Card Market?
Top players include Thales Group, IDEMIA, Infineon Technologies, Giesecke+Devrient, and NXP Semiconductors, known for their innovations in smart card security and scalable card solutions.
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from
$ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: sales@marketdataforecast.com