Latin America Carbon Black Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report Segmented By Type (Furnace Black, Acetylene Black), Application, Grade, And Country (Brazil, Mexico, Argentina, Chile And Rest Of Latin America), Analysis On Market Size, Share, Trends, And Growth Forecast (2025 To 2033)
Latin America Carbon Black Market Size
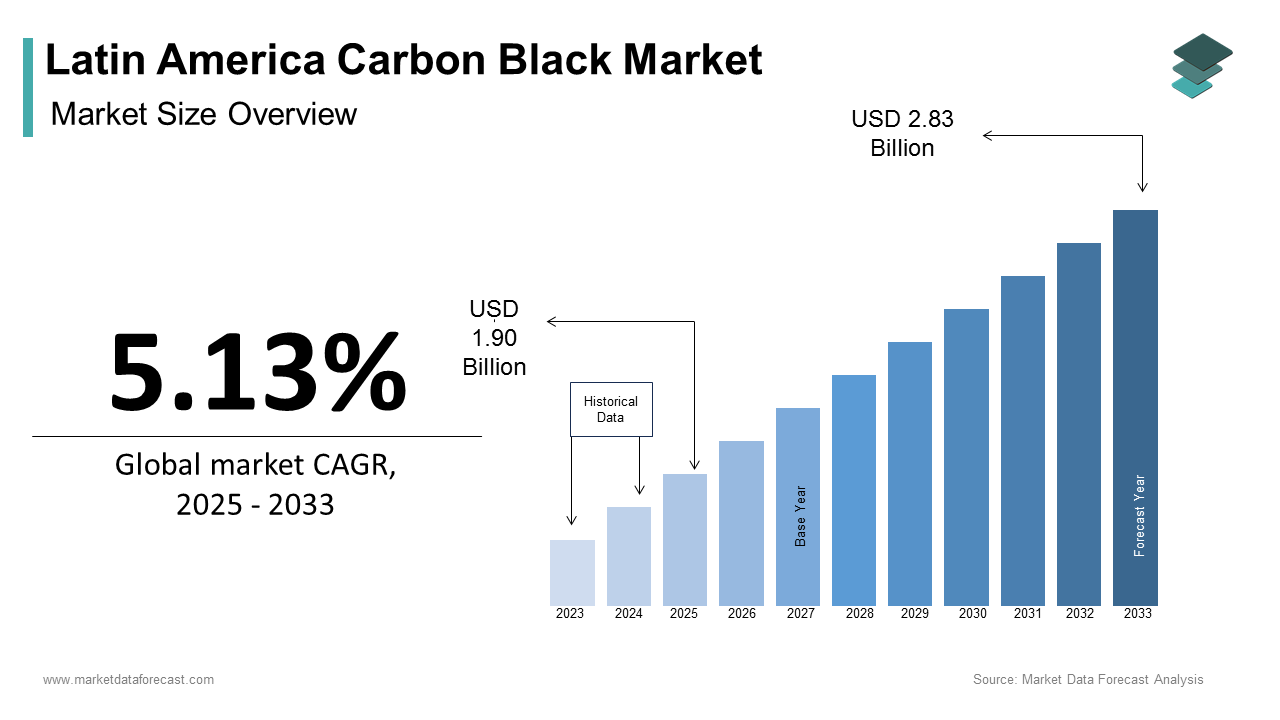
The Latin America Carbon Black Market size was calculated to be USD 1.80 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to be worth USD 2.83 billion by 2033, from USD 1.90 billion in 2025, growing at a CAGR of 5.13% during the forecast period.
Carbon black is a fine, powdery substance primarily produced through the incomplete combustion of hydrocarbons. It is widely used in the manufacturing of tires, rubber products, plastics, and inks due to its reinforcing, conductive, and pigmentation properties. In Latin America, the carbon black market is closely linked with the automotive and tire industries, which are among the largest consumers of the material. The region’s industrial landscape, particularly in Brazil and Mexico, has seen steady growth over the past decade, directly influencing demand for carbon black.
In Brazil, the automotive industry remains a major consumer of carbon black, with tire manufacturers relying heavily on the material for producing durable and high-performance tires suited to tropical climates and rough terrains. Similarly, in Mexico, rising auto production supported by foreign investment has increased domestic consumption of carbon black. Additionally, growing environmental awareness has led to innovations in sustainable carbon black derived from bio-based feedstock, a trend gaining traction across academic and industrial circles in the region.
MARKET DRIVERS
Growth in the Automotive Industry Across Key Economies
One of the primary drivers of the Latin American carbon black market is the sustained expansion of the automotive industry, especially in Brazil and Mexico. As per official reports from Brazil’s National Association of Vehicle Manufacturers (ANFAVEA), the country's automotive production surpassed 2.5 million units in 2023, marking a significant recovery post-pandemic. A large portion of this output includes commercial vehicles such as trucks and buses, which require more tires than passenger cars, thereby increasing the demand for carbon black. Tire manufacturers like Pirelli and Bridgestone, which operate in the region, rely heavily on carbon black to enhance the mechanical strength and longevity of tires. Mexico also plays a critical role in this growth trajectory. According to the Mexican Automotive Industry Association (AMIA), the country remains one of the top ten vehicle producers globally, with over 3 million units manufactured in 2023. With several global automakers including General Motors, Volkswagen, and Nissan maintaining strong production lines in the country, the downstream demand for tires and rubber components continues to rise. Since carbon black is essential for improving abrasion resistance and tensile strength in tire treads, the growth of the automotive sector directly correlates with increased consumption of the material.
Expansion of Industrial Applications Beyond Tires
While the tire industry remains the largest consumer of carbon black in Latin America, the growth of other industrial applications is significantly contributing to the market’s upward trajectory. One notable area is the plastics industry, where carbon black is used as a UV stabilizer and coloring agent. Countries like Colombia and Chile are witnessing a surge in plastic manufacturing, particularly in food packaging and outdoor applications that require UV protection—areas where carbon black plays a vital role. Another expanding application is in the electronics and electrical sectors, where conductive carbon black is used in static dissipative materials and battery components. With the proliferation of electric vehicles and renewable energy systems in Latin America, there is a growing demand for specialty-grade carbon black. Universities and research centers in Brazil and Argentina have been exploring new formulations of conductive carbon black suitable for lithium-ion batteries and printed electronics. In addition, the ink and coatings industry has emerged as a key segment, particularly in countries like Peru and Ecuador, where digital printing and flexible packaging are on the rise. Carbon black’s ability to provide deep black color and durability makes it indispensable in these applications.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
Environmental Regulations and Emission Concerns
Despite its widespread use, the carbon black industry in Latin America faces increasing scrutiny due to environmental concerns associated with its production process. Traditional carbon black manufacturing involves the partial combustion of heavy hydrocarbons, which can release particulate matter, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and greenhouse gases. As per the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), carbon black production ranks among the top industrial sources of black carbon emissions, a potent contributor to air pollution and climate change. Several Latin American countries have begun tightening their environmental regulations in response to global sustainability goals. For example, Brazil’s Ministry of the Environment has introduced stricter emission standards under its National Air Quality Policy, requiring industrial facilities—including carbon black producers—to adopt cleaner technologies. Compliance with these norms often necessitates capital-intensive upgrades, which smaller manufacturers may find difficult to afford. Consequently, some companies have either scaled back operations or opted for alternative raw materials, affecting overall market growth. In addition, public awareness regarding environmental health risks is growing, particularly in urban centers like São Paulo and Mexico City. Consumer pressure and investor focus on green supply chains are prompting downstream industries—such as tire and plastic manufacturers—to explore substitutes or modified formulations that reduce carbon black content.
Volatility in Raw Material Prices and Supply Chain Disruptions
The carbon black industry in Latin America is highly dependent on petroleum-based feedstocks such as furnace oil and aromatic oils, the prices of which are subject to global crude oil market fluctuations. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), crude oil prices experienced significant volatility between 2022 and 2024, influenced by geopolitical tensions and shifts in OPEC+ policies. As Latin American carbon black producers import most of their raw materials, these price swings directly impact production costs and profit margins. Supply chain disruptions have also posed a challenge, particularly in landlocked countries such as Bolivia and Paraguay, where transportation delays and customs bottlenecks increase lead times for raw material imports. These disruptions not only raise operational costs but also discourage long-term investments in new production facilities. Furthermore, the region’s reliance on imported equipment and technology for carbon black processing adds another layer of complexity. Local producers often depend on European and Asian suppliers for advanced reactor systems and filtration equipment. Any geopolitical or trade-related instability can hinder procurement, delaying capacity expansions and technological upgrades.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Rise in Sustainable and Bio-Based Carbon Black Alternatives
A significant opportunity emerging in the Latin America carbon black market is the development and adoption of sustainable and bio-based alternatives to conventional carbon black. As global industries shift toward greener practices, companies in the region are exploring innovative ways to produce carbon black using renewable feedstocks such as waste tires, biomass, and vegetable oils. Brazil has taken a leading role in this transition, with research institutions like the University of São Paulo collaborating with private firms to develop eco-friendly carbon black solutions. Several startups have emerged in recent years, focusing on circular economy models that convert end-of-life tires into valuable carbon materials. These alternatives not only reduce environmental impact but also align with international sustainability certifications, making them attractive to multinational buyers. Similarly, in Argentina and Chile, government-backed initiatives encourage the use of agro-industrial waste for carbon black production. Companies involved in sugar cane processing and biodiesel manufacturing are experimenting with converting by-products into activated carbon and pigment-grade derivatives.
Expansion of Electric Mobility and Specialty Applications
The rapid growth of electric mobility in Latin America is opening new avenues for the carbon black market, particularly in specialty applications beyond traditional tire reinforcement. Conductive carbon black is increasingly being used in lithium-ion batteries, supercapacitors, and conductive polymers, which are integral to electric vehicles (EVs) and energy storage systems. This transition presents a significant opportunity for carbon black producers to diversify their product portfolios. Companies are investing in R&D to develop high-purity, low-residue grades of carbon black suitable for battery electrodes and electronic components. In Mexico, several automotive component suppliers have started incorporating conductive carbon black into EV battery casings and connectors to improve thermal management and electrical conductivity. Beyond the automotive sector, specialty carbon black is gaining traction in niche markets such as medical devices, anti-static packaging, and 3D printing filaments. Educational institutions and research centers in Colombia and Peru are actively testing new formulations tailored for these applications.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Limited Local Production Capacity and Reliance on Imports
One of the most pressing challenges confronting the Latin American carbon black market is the limited local production capacity and heavy dependence on imports to meet industrial demand. Despite the presence of a few established producers, particularly in Brazil and Mexico, the region lacks sufficient domestic manufacturing capabilities to cater to all sectors. As per the Latin American Chemical Industry Council, a significant portion of carbon black consumed in the region is sourced from international suppliers based in Asia and Europe. This reliance on imports exposes the market to logistical complexities and cost volatility. Import duties, fluctuating exchange rates, and geopolitical uncertainties can significantly affect the affordability and availability of carbon black for downstream industries. In countries like Ecuador and Peru, where local refining and petrochemical infrastructure is underdeveloped, sourcing raw materials for domestic production remains a hurdle. Moreover, the lack of investment in new production facilities hampers the region’s ability to achieve self-sufficiency. Many existing plants operate below full capacity due to outdated technology and limited access to financing. As a result, manufacturers face supply constraints during peak production periods, affecting the timely delivery of finished goods such as tires, plastics, and coatings.
Technological Gaps and Skilled Labor Shortages
Another significant challenge facing the LatiAmericanca carbon black market is the technological gap between regional producers and their global counterparts, compounded by a shortage of skilled labor in specialized manufacturing processes. The carbon black industry demands precise control over combustion parameters, particle size distribution, and surface chemistry—areas where many Latin American producers lag due to outdated equipment and limited R&D investment. According to the Organization of American States (OAS), technical training programs related to petrochemical and materials engineering remain underfunded in several Latin American countries. This results in a shortage of professionals capable of operating advanced carbon black production systems or developing next-generation products such as nano-structured carbon blacks and conductive composites. In addition, the absence of strong university-industry collaborations limits knowledge transfer and innovation. While institutions in Brazil and Argentina have made strides in material science research, the commercialization of lab-scale findings into industrial applications remains slow. Without adequate technical expertise, local manufacturers struggle to meet the quality and consistency expectations of global clients, particularly in high-end sectors like automotive and electronics.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
5.13% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Type, Application, Grade, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis; Segment-Level Analysis; DROC, PESTLE Analysis; Porter’s Five Forces Analysis; Competitive Landscape; Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
Brazil, Mexico, Argentina, Chile and Rest Of Latin America |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Cabot Corporation, Birla Carbon, Orion Engineered Carbons, Phillips Carbon Black Limited, Tokai Carbon Co. Ltd., Continental Carbon Company, Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation, Imerys SA, Longxing Chemical, Jiangxi Black Cat Carbon Black Inc. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Type Insights
The furnace black segment dominated the Latin American carbon black market by accounting for an estimated 68.7% of total consumption in 2024. This dominance is primarily attributed to its widespread use in tire manufacturing, where it serves as a reinforcing agent that enhances mechanical strength, abrasion resistance, and thermal stability. The tire industry remains the largest consumer of furnace black in the region, especially in Brazil and Mexico, where automotive production has seen consistent growth over the past few years. According to Brazil’s National Association of Vehicle Manufacturers (ANFAVEA), the country produced more than 2.5 million vehicles in 2023, with tire manufacturers such as Pirelli and Bridgestone heavily relying on furnace black for high-performance tire treads. Additionally, furnace black is extensively used in industrial rubber goods beyond tires, including conveyor belts, hoses, and seals, which are critical components in mining and agriculture—two major sectors across Latin America. Moreover, advancements in production technologies have allowed manufacturers to tailor furnace black grades for specific performance characteristics, making it a preferred choice over other types.
The acetylene black is emerging as the fastest-growing segment in the Latin American carbon black market, projected to expand at a CAGR of 9.4%. Unlike traditional carbon black types, acetylene black offers superior electrical conductivity and surface area, making it highly suitable for specialized applications in electronics, batteries, and conductive polymers. One of the key drivers of this growth is the rising adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) in countries like Chile and Colombia, which has spurred demand for lithium-ion batteries containing acetylene black as a conductive additive. In addition, the electronics manufacturing sector in Mexico is increasingly using acetylene black in printed circuit boards and anti-static packaging materials. Mexican export-oriented electronics firms have expanded their presence in global supply chains, particularly with North American clients, leading to higher domestic consumption of specialty-grade carbon black. Universities and research institutions in Argentina and Brazil are also exploring novel uses for acetylene black in supercapacitors and energy storage systems.
By Application Insights
The tire application segment accounted for 62.7% of the Latin American carbon black market in 2024 which was driven by the region's strong automotive and transportation industries. Carbon black plays a crucial role in enhancing tire durability, traction, and resistance to wear, making it indispensable in tire manufacturing. Brazil stands out as the largest consumer in this segment, with tire production exceeding 50 million units annually, as reported by the Brazilian Tyre Industry Association (ANIP). Major tire manufacturers such as Michelin, Goodyear, and Continental maintain production facilities in the country, contributing significantly to carbon black consumption. The country's strategic location and access to raw materials support a robust tire export business, particularly to North America and Africa. Mexico also contributes substantially to this segment, given its status as one of the top ten vehicle producers globally. As per the Mexican Automotive Industry Association (AMIA), the country manufactured over 3 million vehicles in 2023, many of which were exported. Since each vehicle requires multiple tires, the downstream demand for carbon black remains strong. Moreover, road infrastructure development projects across Argentina and Peru are boosting the need for commercial vehicle tires, further supporting carbon black consumption.
The plastics application segment is experiencing rapid expansion in the Latin American carbon black market, projected to grow at a CAGR of 8.7%. This growth is primarily fueled by the increasing use of carbon black as a UV stabilizer and coloring agent in plastic products used across packaging, agriculture, and construction. In Brazil, the plastics industry has seen steady growth, with production volumes surpassing 6 million tons in 2023, as reported by the Brazilian Plastics Industry Association (ABIPLAST). Carbon black is widely used in agricultural films, irrigation pipes, and outdoor containers due to its ability to protect against UV degradation, extending the lifespan of these materials. Colombia and Chile have also witnessed a surge in demand for carbon black in food packaging and flexible film applications. Furthermore, environmental regulations promoting the use of UV-protected plastics in outdoor applications are encouraging manufacturers to incorporate carbon black into their formulations.
By Grade Insights
The standard-grade carbon black held the largest share of the Latin American market in 2024. This influence is basically due to its extensive use in conventional tire and rubber applications, where cost-effectiveness and availability outweigh the need for specialized performance properties. Tire manufacturers in Brazil and Mexico form the core consumer base for standard-grade carbon black, leveraging its reinforcing capabilities to produce durable and economical tires suited for both domestic and export markets. Beyond tires, standard-grade carbon black is widely used in general-purpose rubber products such as hoses, conveyor belts, and industrial seals, which are essential components in mining, agriculture, and construction—key economic sectors in Latin America. Moreover, price sensitivity among small and medium-sized manufacturers continues to favor standard grade over premium alternatives.
The specialty grade carbon black is coming out as the swiftest advancing segment in the Latin American market, projected to expand at a CAGR of 10.2%. Unlike standard grade variants, specialty grades offer enhanced properties such as improved conductivity, dispersion, and color purity, making them ideal for advanced applications in electronics, coatings, and battery manufacturing. One of the primary growth drivers is the rise of electric mobility in the region, particularly in Chile and Colombia, where lithium-ion battery production is gaining momentum. Conductive specialty carbon black is used as an additive in battery electrodes to enhance electron transport efficiency. In addition, the paints and coatings industry in Argentina and Peru is increasingly adopting specialty grades to achieve better pigment dispersion and weather resistance in architectural and industrial coatings. Furthermore, academic institutions and R&D centers in Brazil are experimenting with specialty carbon blacks in nanocomposites and conductive polymers for aerospace and medical device applications.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
Brazil was at the forefront of the Latin American carbon black market by accounting for 38.8% of total regional consumption in 2024. As the region’s largest economy and a key player in automotive manufacturing, Brazil drives significant demand for carbon black, particularly in tire and rubber applications. The country’s tire industry is a major consumer, with annual production surpassing 50 million units, as reported by the Brazilian Tyre Industry Association (ANIP). Domestic and multinational tire manufacturers, including Michelin, Goodyear, and Pirelli, operate large-scale production facilities that rely heavily on carbon black for tire reinforcement and durability. Beyond tires, Brazil’s expanding plastics and packaging industry is contributing to increased carbon black usage. Additionally, the country is investing in sustainable carbon black initiatives, with universities and startups exploring bio-based and recycled feedstocks.
Mexico is another key player in the market. Its strategic location, strong automotive sector, and proximity to North American markets make it a key hub for carbon black consumption. The automotive industry is the primary driver. A significant portion of these vehicles are exported, necessitating a continuous supply of tires and rubber components, all of which depend on carbon black for performance enhancement. In addition to automotive applications, Mexico’s electronics and packaging industries are expanding rapidly, particularly in northern states near the U.S. border. Companies involved in printed circuit board manufacturing and conductive polymers are increasingly using specialty-grade carbon black, diversifying demand beyond traditional tire applications. Mexican manufacturers also benefit from well-established logistics networks and foreign direct investment in industrial zones, facilitating efficient procurement of carbon black and related materials.
Despite economic fluctuations, Argentina maintains a stable industrial base, particularly in tire manufacturing and agrochemicals, which drive consistent demand for carbon black. The country’s tire industry benefits from both domestic consumption and exports, particularly to neighboring Mercosur nations. Beyond tires, Argentina’s growing plastics sector is contributing to increased carbon black usage. Moreover, Argentina is actively pursuing sustainable alternatives to traditional carbon black, with research institutions exploring pyrolysis-based methods using waste tires. Government-backed initiatives encourage circular economy practices, providing incentives for companies developing greener carbon black solutions.
Chile contributed majorly to the total Latin American carbon black consumption in 2024. While not a major producer, Chile’s industrial growth and increasing focus on electric mobility are shaping its carbon black demand dynamics. One of the key drivers is the country’s push toward electric vehicles (EVs), which has led to rising demand for conductive carbon black in lithium-ion batteries. Local battery assembly plants are beginning to source specialty-grade carbon black for electrode formulations. Additionally, Chile’s mining industry utilizes carbon black in various rubber-based components, including conveyor belts and protective linings. The country is also home to academic institutions researching alternative carbon sources, including bio-derived and recycled materials. These initiatives align with Chile’s broader sustainability goals and could influence future carbon black consumption patterns.
Colombia’s growing manufacturing sector, particularly in tire and plastic production, is fueling demand for carbon black across multiple industries. The tire industry is a major contributor, with domestic manufacturers supplying both local and regional markets. In parallel, Colombia’s plastics industry is expanding, driven by rising demand for packaging and agricultural films. Moreover, the government is promoting the use of sustainable materials through policy incentives, encouraging companies to explore alternative carbon black production methods. Research collaborations between universities and private firms are investigating ways to convert agricultural waste into value-added carbon materials.
LEADING PLAYERS IN THE LATIN AMERICA CARBON BLACK MARKET
Cabot Corporation
Cabot Corporation is a leading global producer of carbon black with a strong presence across Latin America. The company offers a wide range of standard and specialty carbon black products tailored for tire, rubber, plastics, and electronics applications. In Latin America, Cabot serves major automotive and industrial clients by providing high-performance materials that enhance product durability and functionality. Its commitment to innovation and sustainability has positioned it as a trusted supplier in the region. Cabot also collaborates with local research institutions to develop advanced formulations that meet evolving industry needs, reinforcing its leadership in both regional and global markets.
Orion Engineered Carbons S.A.
Orion Engineered Carbons plays a significant role in the Latin American carbon black market through its diverse product portfolio and strategic regional partnerships. The company specializes in producing high-quality carbon black used in tire reinforcement, conductive polymers, and specialty coatings. Orion’s focus on customized solutions enables it to cater to niche applications in growing sectors such as electric mobility and packaging. By investing in sustainable production practices and expanding its distribution network, Orion strengthens its foothold in Latin America while contributing to global advancements in carbon black technology and environmental responsibility.
Birla Carbon
Birla Carbon is a key player in the Latin American carbon black industry, known for its extensive manufacturing capabilities and customer-centric approach. The company supplies a broad spectrum of carbon black grades that support industries ranging from tire manufacturing to ink formulation. In Latin America, Birla Carbon has built strong relationships with automotive and industrial clients, ensuring reliable supply and technical support. Through continuous investment in R&D and process optimization, the company enhances product performance and sustainability. Birla Carbon’s active engagement with regional stakeholders helps drive innovation and maintain its competitive edge in the dynamic global carbon black landscape.
TOP STRATEGIES USED BY KEY MARKET PARTICIPANTS
One of the primary strategies adopted by key players in the Latin American carbon black market is expanding production capacities and regional footprints. Companies are investing in new manufacturing facilities or upgrading existing ones to ensure a stable supply chain and reduce dependency on imports. This allows them to respond more efficiently to local demand fluctuations and regulatory requirements.
Another crucial strategy involves developing sustainable and alternative carbon black solutions With increasing environmental concerns and stricter emissions regulations, manufacturers are focusing on bio-based, recycled, and low-emission carbon black variants. These efforts not only align with global sustainability goals but also appeal to environmentally conscious customers in industries like automotive and packaging.
A third key approach is strengthening partnerships with downstream industries and research institutions. By collaborating with tire manufacturers, polymer producers, and academic centers, companies can better understand application-specific needs and co-develop tailored products. These alliances also facilitate knowledge exchange and accelerate the commercialization of innovative carbon black technologies in Latin America.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS AND COMPETITION OVERVIEW
Major Players in the Latin America Carbon black market include Cabot Corporation, Birla Carbon, Orion Engineered Carbons, Phillips Carbon Black Limited, Tokai Carbon Co. Ltd., Continental Carbon Company, Mitsubishi Chemical Corporation, Imerys SA, Longxing Chemical, Jiangxi Black Cat Carbon Black Inc.
The Latin America carbon black market is characterized by a mix of global leaders and regional players competing to meet the rising demand from automotive, tire, plastics, and specialty industries. While multinational corporations such as Cabot Corporation, Orion Engineered Carbons, and Birla Carbon dominate due to their established infrastructure and technological expertise, local firms are increasingly gaining traction by offering cost-effective and region-specific solutions. The competition is particularly intense in Brazil and Mexico, where the automotive and tire industries form the backbone of carbon black consumption. However, emerging economies like Colombia and Chile are witnessing increased activity as companies look to diversify their regional exposure. Strategic investments in production capacity, sustainability initiatives, and specialized product development are shaping the competitive landscape. Additionally, the shift toward specialty-grade carbon blacks for electric vehicle batteries and conductive polymers is prompting players to innovate and differentiate their offerings. As environmental regulations tighten and demand for high-performance materials grows, the battle for market share is intensifying, with companies adapting through localized strategies and collaborative ventures.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THE MARKET
- In February 2024, Cabot Corporation announced a strategic collaboration with a Brazilian research institute to develop next-generation carbon black derived from renewable feedstocks. This initiative aims to offer eco-friendly alternatives for tire and polymer applications, aligning with regional sustainability goals and strengthening Cabot’s leadership in green material innovation.
- In May 2024, Orion Engineered Carbons expanded its logistics network in Mexico by establishing a new distribution hub near Monterrey. This move was designed to improve delivery efficiency and ensure a timely supply of carbon black to key automotive and industrial customers in northern Mexico.
- In October 2024, Birla Carbon launched a dedicated technical service center in Argentina to provide localized support to tire manufacturers and plastic converters. The center focuses on optimizing carbon black formulations for specific applications, enhancing customer satisfaction, and reinforcing Birla’s presence in South America.
- In January 2025, a joint venture between a European carbon black producer and a Colombian chemical company led to the establishment of a new compounding facility near Bogotá. The facility caters to growing demand from the packaging and agricultural film industries, enabling faster access to customized carbon black solutions.
- In March 2025, Orion Engineered Carbons partnered with a Chilean battery startup to explore the use of conductive carbon black in lithium-ion energy storage systems. This collaboration supports Chile’s push for clean energy technologies and positions Orion as a pioneer in specialty carbon black applications in the Andean region.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the Latin America Carbon Black Market has been segmented and sub-segmented based on type, application, grade, and region.
By Type
- Furnace Black
- Acetylene Black
By Application
- Tire
- Plastics
By Grade
- Standard Grade
- Specialty Grade
By Region
- Brazil
- Mexico
- Argentina
- Chile
- Rest Of Latin America
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is driving the growth of the carbon black market in Latin America?
The market growth is driven by increasing demand from the automotive industry (especially tire manufacturing), rising use of plastic production, and growing infrastructure development in the region.
2. Which countries in Latin America have the largest demand for carbon black?
Major markets include Brazil, Mexico, Argentina, and Colombia, with Brazil leading due to its robust automotive and manufacturing sectors.
3. Who are the major players in the Latin America carbon black market?
Key players include Cabot Corporation, Birla Carbon, Orion Engineered Carbons, Phillips Carbon Black Limited, and Tokai Carbon Co. Ltd.
4. How is the market responding to sustainability trends?
There is a growing shift toward sustainable and green carbon black production, including recycling-based methods and efforts to reduce carbon footprints.
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 1600
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: sales@marketdataforecast.com