Latin America Generic Injectables Market Research Report – Segmented By Therapeutic Area (Anti-infectives, Oncology), Container Type, Distribution Channel & Country (Mexico, Brazil, Argentina, Chile and Rest of Latin America) - Industry Analysis From 2025 to 2033
Latin America Generic Injectables Market Size
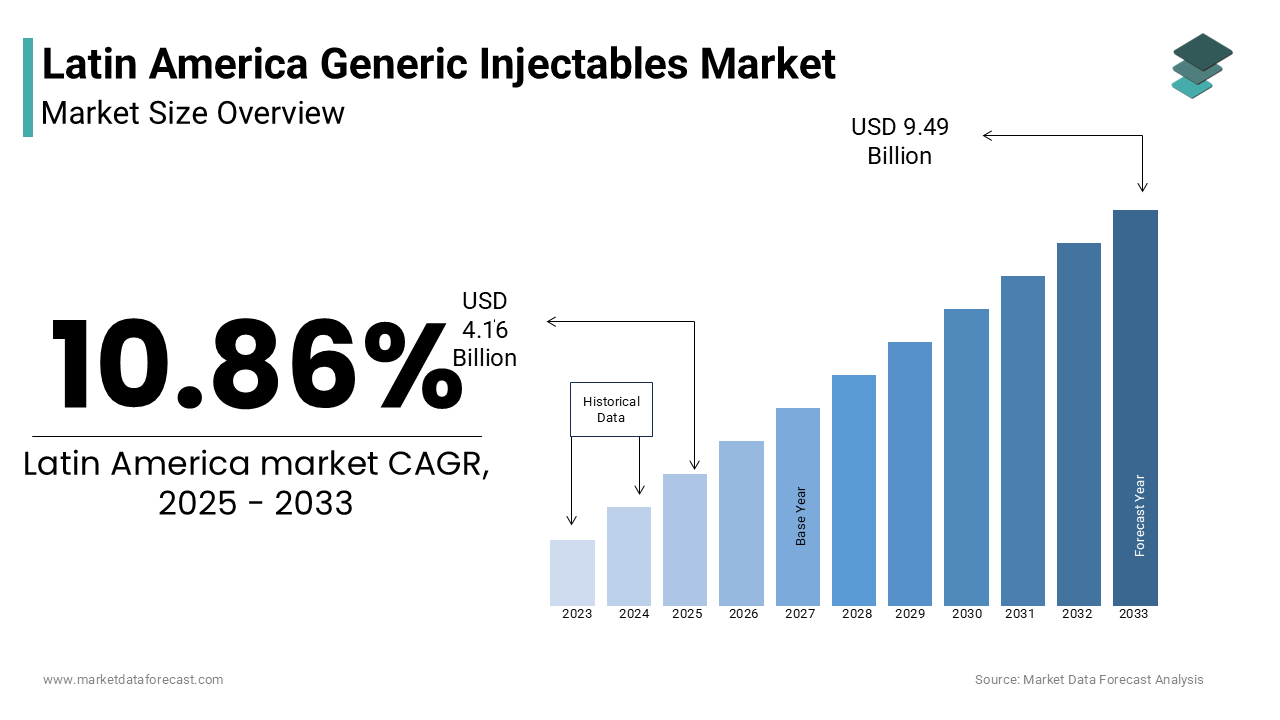
The Latin America generic injectables market was worth USD 3.75 billion in 2024. The Latin America market is expected to reach USD 9.49 billion by 2033 from USD 4.16 billion in 2025, rising at a CAGR of 10.86% from 2025 to 2033.
The Latin America generic injectables market covers off-patent, bioequivalent versions of branded injectable drugs used in hospitals, clinics, and ambulatory care centers. These products are administered intravenously, intramuscularly, or subcutaneously to treat acute and chronic conditions such as infections, cancer, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders. The market is driven by increasing demand for affordable healthcare solutions, government support for local manufacturing, and growing hospitalization rates across the region. As per the World Bank, rising prevalence of non-communicable diseases has led to increased reliance on injectable therapies, especially in countries like Brazil and Mexico where chronic illness management is a growing public health priority. Moreover, regulatory agencies such as ANVISA in Brazil and COFEPRIS in Mexico have implemented frameworks to fast-track approvals for high-quality generic injectables, encouraging domestic production and import substitution.
MARKET DRIVERS
Rising Healthcare Expenditure and Government Emphasis on Cost-effective Therapies
One major driver of the Latin America generic injectables market is the increasing focus on cost containment within public healthcare systems, which are under pressure to manage rising disease burdens and budget constraints. In Brazil, for example, the Ministry of Health mandates the substitution of branded injectables with bioequivalent generics whenever available, leading to higher adoption in public hospitals and primary care units. Similarly, in Argentina, the National Administration of Drugs, Foods and Medical Devices (ANMAT) has streamlined approval processes for generic injectables to accelerate their availability and reduce treatment costs. As per PAHO, a significant portion of injectable medicines used in national immunization programs and maternal health initiatives are sourced from domestic generic manufacturers due to their affordability and compliance with WHO standards.
Expansion of Hospital Infrastructure and Inpatient Treatment Demand
Another key driver of the Latin America generic injectables market is the expansion of hospital infrastructure and the corresponding rise in inpatient treatment requirements. According to the Latin American Hospital Association (LAHA), the number of hospital beds in the region increased notably over the past five years, particularly in urban centers of Colombia, Chile, and Peru. This growth has been accompanied by a surge in surgical procedures, chemotherapy sessions, and intensive care admissions, all of which rely heavily on injectable medications. Also, private hospital chains in Brazil and Ecuador have expanded their outpatient infusion centers, further boosting demand for cost-effective injectable therapies. With continued investment in healthcare infrastructure and rising patient inflows, injectable drug utilization remains a core component of clinical treatment protocols across Latin America.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
Stringent Regulatory Requirements and Bioequivalence Challenges
A significant restraint affecting the Latin America generic injectables market is the stringent regulatory framework governing the approval and quality assessment of injectable formulations. Unlike oral dosage forms, injectables require rigorous demonstration of bioequivalence, sterility, and stability, making the pathway to market entry more complex and time-consuming. Similarly, in Mexico, COFEPRIS mandates comparative dissolution studies and in vivo assessments for certain parenteral products, increasing development costs for manufacturers. These hurdles limit the participation of smaller domestic firms and delay the availability of affordable injectable alternatives in both public and private healthcare settings, constraining overall market growth.
Limited Manufacturing Capabilities and Quality Control Concerns
Another critical challenge in the Latin America generic injectables market is the limited presence of high-quality manufacturing facilities capable of producing sterile injectable drugs at scale. Injectable formulations require highly controlled environments, including clean rooms and advanced filling lines, which many local manufacturers lack due to high capital expenditure and technical complexity. Furthermore, quality control issues have been frequently cited in product recalls and regulatory rejections. Without substantial investment in technology upgrades and process validation, the region will continue to face shortages and supply disruptions, limiting the scalability of its generic injectables sector.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Increasing Adoption of Biosimilars and Complex Injectables
An emerging opportunity in the Latin America generic injectables market is the growing interest in biosimilars and complex injectable formulations, particularly in oncology, autoimmune disorders, and endocrinology. As patents expire on high-cost biologics, governments and healthcare institutions are increasingly turning to biosimilar versions to expand patient access without straining budgets. Similarly, in Brazil, the Ministry of Health has included several biosimilar monoclonal antibodies in its public procurement tenders, signaling strong institutional backing.
Rise in Public-Private Partnerships and Local Production Initiatives
Another promising avenue for growth in the Latin America generic injectables market is the strengthening of public-private partnerships aimed at enhancing domestic production capabilities. Governments across the region are recognizing the strategic importance of local manufacturing in ensuring supply security, reducing import dependency, and controlling medicine prices. Additionally, multilateral organizations such as PAHO and the World Bank have facilitated technology transfer agreements between international pharmaceutical firms and local producers to boost capacity building.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Supply Chain Disruptions and Raw Material Shortages
A major challenge confronting the Latin America generic injectables market is the vulnerability of its supply chain to global disruptions and raw material shortages. Many active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and excipients used in injectable formulations are sourced from Asia, particularly China and India, making the region susceptible to geopolitical tensions, trade restrictions, and logistical bottlenecks. Moreover, fluctuating exchange rates and customs clearance inefficiencies add financial unpredictability for manufacturers relying on imported materials. Without stronger vertical integration and regional sourcing strategies, the Latin American market will continue to face operational challenges that hinder consistent product availability and market expansion.
Price Controls and Margin Pressures Impacting Manufacturer Viability
Another pressing challenge in the Latin America generic injectables market is the imposition of aggressive price controls and tender-based procurement mechanisms, which often squeeze manufacturers margins and discourage investment in innovation. Public health authorities prioritize cost reduction in medicine procurement, sometimes at the expense of product quality and supplier sustainability. Unless balanced with incentives for quality assurance and long-term supply commitments, current pricing policies may undermine the competitiveness and resilience of the Latin American generic injectables industry.
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Application Insights
The anti-infectives segment dominated the Latin America generic injectables market by accounting for 28.3% of total consumption in 2024. This is primarily attributed to the high prevalence of bacterial and viral infections, increasing hospitalization rates, and the widespread use of intravenous antibiotics in both public and private healthcare settings. According to the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO), antimicrobial resistance remains a significant public health challenge in the region, leading to prolonged treatment durations and increased reliance on broad-spectrum injectable antibiotics. Additionally, government procurement programs such as Mexico’s INSABI and Argentina’s SUMAR have prioritized the supply of affordable generic injectable antibiotics to curb infectious disease spread in low-income populations.

The oncology injectables represent the fastest-growing segment in the Latin America generic injectables market, projected to expand at a CAGR of nearly 10.7%. This is driven by rising cancer incidence, expanding access to chemotherapy treatments, and increasing affordability through biosimilar adoption. According to the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), an estimated 1.2 million new cancer cases were diagnosed across Latin America in 2023, with breast, cervical, and colorectal cancers being the most prevalent. Moreover, governments are increasingly procuring generic oncology injectables to reduce treatment costs. In Chile, the Ministry of Health included several generic monoclonal antibodies in its national formulary, significantly lowering patient out-of-pocket expenses.
By Container Type Insights
The vials possessed the largest share in the Latin America generic injectables market by capturing 42.6% of total volume in 2024. Their influence is because of the widespread usage in hospitals, infusion centers, and compounding pharmacies where multi-dose administration is common. Vials offer advantages such as compatibility with various reconstitution techniques, extended shelf life, and ease of handling during large-scale dispensing. Furthermore, local manufacturers favor vials for their established production lines and lower packaging complexity compared to more advanced formats like prefilled syringes.
The prefilled syringes are coming up as the fastest-growing container segment in the Latin America generic injectables market, registering a projected CAGR of around 9.4% during the forecast period. This development is fueled by increasing demand for convenience, reduced dosing errors, and improved safety profiles, particularly in outpatient and self-administered therapies. In Argentina, the Ministry of Health introduced a pilot program promoting prefilled insulin syringes for diabetic patients, enhancing adherence and reducing needle-stick injuries among caregivers. Moreover, multinational pharmaceutical companies are investing in local filling and packaging partnerships to meet the rising demand for ready-to-use injectables.
By Distribution Channel Insights
Hospitals represented the biggest distribution channel in the Latin America generic injectables market by accounting for 68% of total sales in 2024. This dominance is attributed to the fact that injectable medicines are predominantly administered in institutional settings such as public hospitals, private clinics, and specialized treatment centers. Additionally, the Latin American Hospital Association (LAHA) reported that chemotherapy, anesthesia, and anti-infective injectables constitute the majority of hospital-based pharmaceutical expenditures.
Retail pharmacies are the quickest advancing distribution channel in the Latin America generic injectables market, projected to grow at a CAGR of around 7.9% over the next decade. This is driven by rising consumer preference for home-based therapies, increasing availability of disposable injection devices, and expanding insurance coverage for self-administered injectables. In Argentina, private health insurers have started reimbursing select injectable biologics dispensed through specialty pharmacies, encouraging greater outpatient treatment adoption. Moreover, e-pharmacy platforms are playing a crucial role in driving accessibility, particularly in Brazil, where digital health startups now offer temperature-controlled delivery of injectable medications.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
Brazil had the largest market share in the Latin America generic injectables sector by accounting for a 35% of total revenue in 2024. Positioned as the region's pharmaceutical hub, Brazil benefits from a well-established generic drugs industry, robust regulatory oversight, and a large public healthcare system that drives procurement volume. The Ministry of Health reported that in 2023, over 250 million units of generic injectables were distributed under the SUS program, covering antibiotics, analgesics, and chemotherapeutic agents. Moreover, ANVISA has implemented fast-track approval pathways for bioequivalent injectables, facilitating quicker market entry for domestic manufacturers.
Mexico ranks second in the Latin America generic injectables market with a market share of approximately 26% in 2023. The country’s strategic location, strong trade relationships, and growing healthcare expenditure support its competitive position in the regional market. Additionally, Mexico serves as a major production and export center for North America, benefiting from existing supply chain linkages with U.S. and Canadian markets. With continued policy support and infrastructure development, Mexico remains a pivotal player in the Latin American injectables landscape.
Argentina is placing itself as a key contributor due to its relatively advanced healthcare system and strong domestic pharmaceutical base. The country’s public health infrastructure, combined with a growing focus on cost-effective treatment options, supports sustained demand for injectable generics. Moreover, Argentina has been strengthening its regulatory alignment with international standards, allowing faster approvals for high-quality injectables.
Chile holds a notable market share of the Latin America generic injectables market, driven by high healthcare expenditure, strong regulatory oversight, and a well-developed private health insurance system. The country maintains one of the most efficient healthcare models in the region, ensuring broad access to essential injectable medicines. Apart from these, Chile has been proactive in adopting biosimilars and complex injectables, integrating them into national treatment protocols.
The Rest of Latin America (ROLA), comprising countries such as Colombia, Peru, Ecuador, Costa Rica, and Central American nations, collectively accounts for around 14% of the regional generic injectables market. While individually smaller in scale, these markets are experiencing rapid growth due to improving healthcare infrastructure, increasing government spending, and rising medical tourism. In Central America, countries like Costa Rica have emerged as medical tourism hubs, attracting patients from North America and the Caribbean for cost-effective injectable treatments.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS AND COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
Pfizer Inc., Viatris Inc., Biocon, Lupin Limited, Aurobindo Pharma Limited, Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Fresenius SE & Co. KGaA, Hikma Pharmaceuticals PLC, and Sandoz (a division of Novartis AG), Sanofi, Baxter International Inc., Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Cipla Inc., and Hospira are some of the key market players Latin America generic injectables market.
The Latin America generic injectables market features a competitive landscape characterized by the coexistence of global pharmaceutical giants and well-established regional players. Multinational companies such as Fresenius Kabi, Hikma, and Pfizer leverage their technological expertise, regulatory experience, and brand recognition to maintain a dominant presence in major markets like Brazil and Mexico. These firms often focus on innovation, biosimilar development, and scalable production models to secure long-term contracts with public and private healthcare providers.
At the same time, domestic manufacturers such as Laboratorio Elea in Argentina and Hypermarcas in Brazil play a crucial role in supplying cost-effective injectables tailored to local disease profiles and regulatory frameworks. These companies benefit from lower operational costs and deeper understanding of regional procurement dynamics.
Competition is further intensified by pricing pressures, increasing demand for high-quality sterile products, and regulatory convergence efforts across the region. As healthcare systems prioritize affordability and treatment access, players must continuously adapt their strategies to maintain relevance and capture market share in this evolving environment.
Top Players in the Latin America Generic Injectables Market
Fresenius Kabi (Germany-based, with strong presence across Latin America)
Fresenius Kabi is a global leader in hospital pharmaceuticals and plays a vital role in the Latin America generic injectables market. The company specializes in parenteral nutrition, infusion therapy, and critical care injectables, offering a wide range of high-quality generic products tailored to hospital needs. In Latin America, Fresenius Kabi has established itself through strategic partnerships, local manufacturing initiatives, and continuous investment in clinical education for healthcare professionals.
Hikma Pharmaceuticals (Jordan-based, expanding footprint in Latin American markets)
Hikma is a prominent player in the global generic injectables space and has been actively strengthening its position in Latin America. The company offers a diverse portfolio including antibiotics, analgesics, and oncology injectables, focusing on affordability and compliance with international quality standards. In Latin America, Hikma collaborates with regional distributors and participates in public health tenders to enhance product accessibility and expand its market reach.
Laboratorio Elea (Argentina-based, key domestic manufacturer)
Laboratorio Elea is one of Argentina’s leading producers of injectable medicines and a significant contributor to the Latin America generic injectables market. Known for its expertise in sterile manufacturing, the company supplies essential generic injectables to both public and private healthcare sectors. Elea plays a crucial role in ensuring medicine availability within Argentina and has begun exporting select products to neighboring countries, reinforcing its regional influence.
Top Strategies Used by Key Market Participants
One of the primary strategies employed by key players in the Latin America generic injectables market is expanding local manufacturing capabilities. Companies are investing in GMP-certified production facilities or partnering with domestic manufacturers to reduce import dependency, ensure faster supply cycles, and comply with evolving regulatory expectations.
Another widely adopted approach is participating in government procurement programs. Many multinational and regional firms align their commercial strategies with national health priorities by bidding for public tenders, which guarantees large-volume sales and long-term contracts with public health institutions.
Lastly, strengthening distribution networks through strategic alliances has become essential for market expansion. Firms are collaborating with regional wholesalers, hospital pharmacy groups, and e-pharmacy platforms to improve last-mile delivery and increase product visibility across both urban and rural healthcare settings.
RECENT MARKET DEVELOPMENTS
- In February 2024, Fresenius Kabi announced a joint venture with a Brazilian contract manufacturing organization to produce ready-to-use injectables locally, aiming to streamline supply chain operations and meet rising hospital demand.
- In July 2023, Hikma Pharmaceuticals expanded its distribution network in Colombia by entering into an exclusive agreement with a leading local wholesaler, enhancing its reach in both public and private healthcare segments.
- In January 2024, Laboratorio Elea launched a new line of oncology injectables approved under ANMAT guidelines, positioning itself as a key supplier for Argentina’s growing cancer treatment needs.
- In October 2023, Pfizer partnered with a Chilean biotech firm to develop biosimilar injectables, with plans to introduce them in Latin American markets over the next three years to capitalize on patent expirations.
- In May 2024, Baxter International inaugurated a regional logistics hub in Panama, aimed at improving distribution efficiency for its injectable products across Central and South America.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the Latin America generic injectables market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Therapeutic Area
- Anti-infectives
- Oncology
By Container Type
- Vials
- Prefilled Syringes
By Distribution Channel
- Hospitals
- Retail Pharmacy
By Country
- Mexico
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Chile
- Rest of Latin America
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the future growth outlook for the Latin America Generic Injectables Market?
The Latin America generic injectables market is projected to grow steadily due to rising demand for affordable treatments, government support for generics, and expansion in hospital-based therapies.
Which trends are shaping the future of this market?
Key trends include biosimilar expansion, rise in prefilled syringe usage, telehealth-driven home injection support, and localized manufacturing investments.
How is the competitive landscape expected to change?
More domestic players are expected to enter the market, and global firms are forming partnerships with local manufacturers to expand reach and reduce costs.
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from
$ 1600
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: sales@marketdataforecast.com
