Latin America Handicrafts Market Size, Share, Trends, Forecast, Research Report - Segmented By Product Type (Woodware, Artmetal Ware, Handprinted Textiles and Scarves, Embroidered and Crocheted Goods, Zari and Zari Goods, Imitation Jewelry, Sculptures, Pottery and Glass wares, Attars and Agarbattis, and Others), Distribution Channel, End-Use, and Region (Brazil, Mexico, Argentina, Chile & Rest of Latin America) – Regional Industry 2025 to 2033
Latin America Handicrafts Market Size
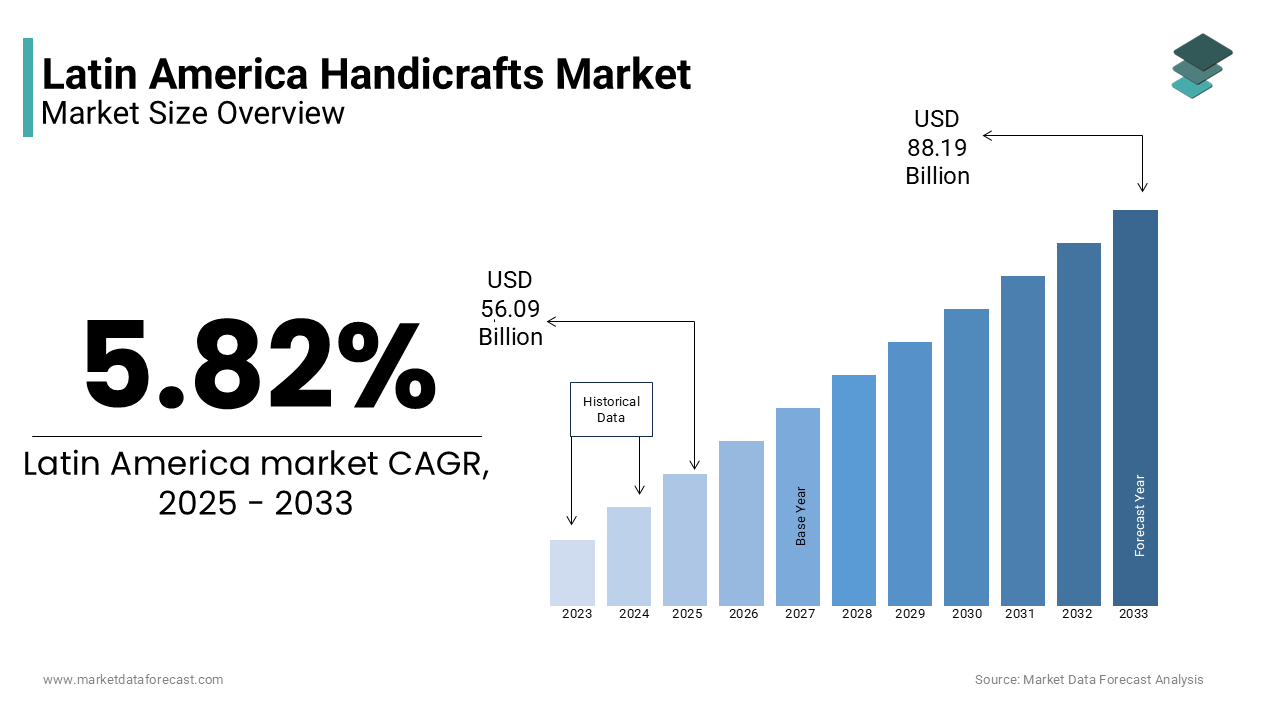
The Latin American handicrafts market was valued at USD 53.01 billion in 2024. The global market size is expected to reach USD 56.09 billion in 2025 and USD 88.19 billion by 2033, with a CAGR of 5.82% during the forecast period.
The Latin America handicrafts market encompasses a wide range of artisanal products crafted using traditional techniques and locally sourced materials. These include textiles, ceramics, woodwork, metalwork, jewelry, leather goods, and decorative arts, often reflecting indigenous heritage and cultural symbolism. Countries such as Mexico, Peru, Colombia, Brazil, and Guatemala are renowned for their rich craftsmanship traditions, which have been passed down through generations.
The preservation of these cultural practices has been supported by government initiatives and non-profit organizations focused on sustaining artisan livelihoods and promoting fair trade principles. This export growth reflects increasing international appreciation for authentic, handmade goods, particularly in North America and Europe.
In addition to international markets, domestic tourism plays a vital role in sustaining the handicraft sector. This dual reliance on tourism and global demand underscores the strategic importance of handicrafts in regional economies.
 MARKET DRIVERS
MARKET DRIVERS
Cultural Heritage and Indigenous Artisan Traditions
One of the primary drivers of the Latin America handicrafts market is the region’s deep-rooted cultural heritage and long-standing artisan traditions. Many countries in the region are home to indigenous communities whose craftsmanship has been preserved and passed down through generations, offering a unique value proposition in both domestic and international markets.
In Mexico, for instance, Oaxacan woodcarving and Zapotec rug weaving continue to be major contributors to the national handicraft economy. Similarly, in Peru, Quechua and Aymara communities maintain vibrant textile traditions that have gained recognition in global fashion and interior design circles. These artisanal traditions not only serve as symbols of national identity but also attract buyers seeking ethically produced, one-of-a-kind items.
Growth of E-commerce and Digital Marketplaces
A significant driver shaping the Latin America handicrafts market is the expansion of e-commerce platforms and digital marketplaces that enable artisans to reach broader audiences beyond local markets. Online selling channels have empowered small-scale producers to connect directly with international buyers, reducing dependency on intermediaries and improving profit margins.
According to GSMA Intelligence, internet adoption in Latin America surpassed 72% in 2023, enabling greater participation in digital commerce. Platforms like Etsy, Amazon Handmade, and regional sites such as MercadoLibre have facilitated cross-border sales, allowing Latin American artisans to showcase their work to a global customer base. As per the Colombian Institute of Technical Standards (ICONTEC), this initiative contributed to an increase in certified handicraft exports in the same year.
Mexico has also seen a surge in digital engagement among artisans, particularly those involved in silver jewelry and Talavera pottery. This shift toward digital integration is not only expanding market access but also enhancing brand storytelling, allowing artisans to share the cultural narratives behind their creations and build emotional connections with consumers worldwide.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
Limited Access to Formal Financial Services and Credit Facilities
A major restraint affecting the Latin America handicrafts market is the limited access to formal financial services and credit facilities for small-scale artisans, many of whom operate informally and lack collateral or business documentation required by banks. This financial exclusion hampers investment in raw materials, equipment upgrades, and market expansion.
According to the World Bank, a significant portion of adults in Latin America remain unbanked, with even higher rates observed among rural and indigenous populations who constitute a large portion of the artisan workforce. In Guatemala, where handicraft production is a key income source for Mayan communities, the Central Bank of Guatemala reported that less than 20% of artisans had access to formal loans in 2023.
As a result, many artisans rely on informal lenders who charge exorbitant interest rates, limiting profitability and long-term sustainability. Without improved access to affordable financing and tailored banking solutions, many skilled craftsmen struggle to transition from subsistence-level production to structured business models capable of competing in regional and international markets.
Intellectual Property Theft and Counterfeiting
Intellectual property theft and counterfeiting pose a serious threat to the Latin America handicrafts market, undermining the economic value of traditional designs and discouraging artisan innovation. Many indigenous and community-based craft patterns are replicated and sold without proper attribution or compensation, often by mass manufacturers seeking to capitalize on their aesthetic appeal. These imitations, often produced in low-cost manufacturing hubs outside the region, dilute the perceived authenticity of genuine handcrafted products.
In Peru, the National Institute for the Defense of Competition and the Protection of Intellectual Property (INDECOPI) recorded over 300 cases of unauthorized use of indigenous motifs in 2023 alone. Many of these instances involved foreign brands incorporating Andean textile designs into mass-produced apparel and accessories without acknowledging or compensating the original creators. These violations not only erode the economic returns for artisans but also threaten the integrity of cultural heritage.
 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Rise of Ethical Consumerism and Sustainable Sourcing
A major opportunity shaping the Latin America handicrafts market is the growing global trend of ethical consumerism and sustainable sourcing, which aligns closely with the region's artisan-led production model. Consumers, particularly in North America and Europe, are increasingly prioritizing eco-friendly, socially responsible, and fair-trade-certified products, creating new demand channels for Latin American handicrafts. This shift in consumer behavior has benefited Latin American artisans who often use natural, biodegradable materials and employ labor-intensive, low-impact production methods.
In response, several governments and NGOs have launched certification programs to help local artisans gain access to premium markets. In Colombia, Artesanías de Colombia introduced a traceability system in 2023 to verify the origin and sustainability of handcrafted products, thereby enhancing marketability abroad.
In apart from these, international retailers and lifestyle brands are integrating Latin American handicrafts into their product lines. For example, Anthropologie and Ten Thousand Villages have expanded their partnerships with cooperatives in Mexico and Guatemala to source ethically made home décor and fashion accessories.
Expansion of Tourism and Cultural Diplomacy Initiatives
Tourism and cultural diplomacy initiatives present a significant opportunity for the Latin America handicrafts market, as travelers seek authentic, locally made souvenirs that reflect the heritage of the regions they visit. Government-backed cultural promotion efforts further amplify the visibility of traditional crafts on the global stage.
According to the World Travel & Tourism Council, Latin America welcomed a significant number of international tourists in 2023, many of whom engaged in cultural experiences such as visiting artisan workshops, attending craft fairs, and purchasing locally made products. In Mexico, the Secretariat of Tourism reported that over 40% of surveyed visitors made at least one handicraft purchase during their stay, contributing significantly to artisan incomes.
In Peru, the Ministry of Foreign Trade and Tourism launched the “Peru Crafts Abroad” program in 2023, which included curated exhibitions in major cities across the United States and Europe. These events not only boosted international awareness but also led to increased online orders and wholesale inquiries for Peruvian textiles and ceramics. With continued investment in tourism-driven cultural promotion and international exposure, the Latin America handicrafts market stands to benefit from sustained global interest in authentic, handcrafted goods.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Supply Chain Fragmentation and Logistics Barriers
Supply chain fragmentation and logistics barriers represent a persistent challenge for the Latin America handicrafts market, hindering efficient production, distribution, and export capabilities. Many artisans operate independently or within small cooperatives, lacking the infrastructure to manage bulk orders or adhere to international shipping standards.
According to the Inter-American Development Bank, nearly 60% of small-scale artisans in Latin America rely on informal transportation networks to move their goods, leading to delays, damage, and inconsistent delivery times. In Ecuador, the Ministry of Production noted that remote artisan clusters, particularly in the Andean and Amazonian regions, face difficulties accessing centralized distribution centers, resulting in higher transportation costs and reduced competitiveness in export markets.
Furthermore, the lack of standardized quality control and labeling systems makes it challenging for Latin American handicrafts to meet the regulatory requirements of developed markets. Until improvements in logistics infrastructure and supply chain coordination are realized, many artisans will continue to face obstacles in scaling their businesses and reaching global buyers efficiently.
Declining Interest Among Younger Generations in Traditional Craft Professions
Another significant challenge facing the Latin America handicrafts market is the declining interest among younger generations in pursuing traditional craft professions, threatening the long-term sustainability of artisanal knowledge and skills. As urbanization and formal education expand, many young people view handicraft-making as economically unstable or outdated compared to more lucrative career paths in technology, finance, or service industries.
According to the study, few percentage of youth in rural areas expressed interest in continuing family-based artisan trades, citing limited financial security and the physically demanding nature of the work as deterrents. This generational gap poses a risk to the continuity of traditional weaving, dyeing, and embroidery techniques. Efforts to reverse this trend include educational programs that integrate handicraft skills into school curricula and initiatives that reframe artisanal work as a viable entrepreneurial path.
Intense Competition from Mass-Manufactured Alternatives
Intense competition from mass-manufactured alternatives presents a major challenge to the Latin America handicrafts market, as industrially produced goods flood local and international markets with cheaper, imitation versions of traditional designs. These machine-made replicas, often imported from Asia, undercut prices and reduce the incentive for consumers to invest in authentic, labor-intensive handmade products.
In Argentina, local artisans have struggled to compete with imported goods from China and India, which dominate department stores and bazaars at significantly lower price points. Even in export markets, Latin American handicrafts face stiff competition from industrialized producers who replicate traditional aesthetics at scale. This commoditization threatens the livelihoods of genuine artisans and undermines the value of culturally rooted craftsmanship. Unless stronger differentiation strategies and consumer education campaigns are implemented, the Latin America handicrafts market will continue to lose ground to synthetic substitutes that mimic appearance without honoring authenticity.
 REPORT COVERAGE
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
5.82% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Product Type, Distribution Channel, End-Use, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional, & Country Level Analysis; Segment-Level Analysis; DROC; PESTLE Analysis; Porter’s Five Forces Analysis; Competitive Landscape; Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
Latin America include Brazil, Argentina, Mexico, and the Rest of Latin America |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Fakih Group of Companies, Gangamani Fashions, Handicrafts Town, Dezaro, and others. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Product Type Insights
Handprinted textiles and scarves represented the largest segment in the Latin America handicrafts market, capturing 24.2% of total revenue in 2024. This dominance is attributed to the region’s rich tradition of textile weaving, dyeing, and embroidery, particularly among indigenous communities in Mexico, Peru, Guatemala, and Bolivia.
The use of natural dyes, intricate patterns, and culturally significant motifs has made these products highly desirable in global markets that value authenticity and heritage. The sector also benefits from government-backed certification programs that ensure traceability and fair-trade compliance. With strong cultural roots and growing demand for ethically sourced apparel, handprinted textiles and scarves remain the most prominent product type in the Latin America handicrafts market.
Imitation jewelry is emerging as the fastest-growing product segment in the Latin America handicrafts market, projected to expand at a CAGR of 9.8%. This growth is driven by rising global demand for fashion-forward, affordable accessories rooted in indigenous aesthetics and local artistry. Traditional techniques such as Huichol beadwork, Mixtec silver filigree, and Maya clay designs are being adapted into contemporary forms that resonate with both domestic and international buyers.
Additionally, social media influencers and ethical fashion bloggers have played a crucial role in amplifying visibility for these items. With increasing brand collaborations, digital exposure, and shifting consumer preferences toward unique, non-mass-produced accessories, imitation jewelry is poised for sustained high growth across Latin America.
By Distribution Channel
Independent retailers dominated the Latin America handicrafts distribution landscape, accounting for 33.3% of total sales in 2024. These small-scale shops, often located near tourist hubs or artisan cooperatives, play a critical role in connecting local producers with regional consumers and international visitors.
In Mexico, the Secretariat of Tourism reported that over 60% of surveyed tourists purchased handicrafts from independent stores rather than large retail chains , citing personalized service, direct interaction with artisans, and perceived authenticity as key decision factors.
Similarly, in Peru, the Ministry of Foreign Trade and Tourism found that artisan fairs and local boutiques accounted for nearly half of all craft sales, with popular destinations like Cusco and Arequipa hosting thousands of micro-retailers selling textiles, pottery, and jewelry.
In Brazil, the Ministry of Tourism noted that independent outlets in Salvador da Bahia and Recife were instrumental in promoting Afro-Brazilian and indigenous crafts. These retailers not only provide physical access points for tourists but also serve as cultural ambassadors, educating customers about the significance of each piece. Their proximity to production centers allows for faster inventory turnover and stronger relationships between artisans and sellers. As long as tourism remains a key driver of handicraft consumption, independent retailers will continue to hold the largest share of the market.
Online stores are the fastest-growing distribution channel in the Latin America handicrafts market, projected to expand at a CAGR of 12.4% through 2033. This surge is fueled by increased internet penetration, mobile commerce adoption, and a shift toward globalized purchasing behaviors that favor convenience and variety. Platforms like Etsy, Amazon Handmade, and MercadoLibre have facilitated cross-border transactions, allowing small-scale makers to reach buyers in North America, Europe, and Asia. With continued improvements in logistics, digital literacy, and financial inclusion, online stores are set to reshape how Latin American handicrafts reach global audiences.
By End-Use Insights
Residential use constituted the largest end-use segment in the Latin America handicrafts market by holding a 78% of total demand in 2024. Consumers primarily purchase handcrafted goods for home décor, personal wear, and functional items that reflect cultural identity and artistic expression.
Moreover, the trend of “slow living” and conscious consumption has led to increased appreciation for artisanal home goods that blend functionality with aesthetic storytelling. Given the deep-rooted cultural affinity for artisanal home décor and personal accessories, the residential segment will continue to drive the Latin America handicrafts mark
The commercial end-use segment is experiencing robust growth in the Latin America handicrafts market, projected to expand at a CAGR of 9.2% during the forecast period. This segment includes products sold to hotels, restaurants, spas, corporate offices, and retail stores seeking to incorporate authentic, culturally resonant elements into their environments. Additionally, global lifestyle brands sourcing Latin American handicrafts for resale in upscale interiors and fashion lines have contributed to this expansion. With the hospitality, wellness, and experiential retail sectors expanding, the commercial application of Latin American handicrafts is expected to grow steadily.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
Brazil
Brazil is positioning itself as a strategic exporter due to its diverse cultural influences and rich artisanal traditions. The country boasts a wide array of handicrafts, including Afro-Brazilian beaded items, Amazonian wood carvings, and Northeastern lacework. Brazil has also benefited from digital transformation. Despite economic challenges, Brazil maintains a strong foothold in the regional handicrafts industry, leveraging its cultural diversity and evolving digital infrastructure to sustain growth.
Mexico
Mexico led the Latin America handicrafts market with a 31.3% share in 2024, driven by its deep-rooted artisan traditions and well-established export infrastructure. The country’s handicraft sector is deeply intertwined with its national identity, featuring world-renowned styles such as Talavera pottery, Zapotec rugs, and Huichol beadwork.
The Mexican Secretariat of Economy reported that handicraft exports reached USD 1.1 billion in 2023 , with the United States, Canada, and Germany being the top destination markets. Traditional silver jewelry from Taxco and handwoven textiles from Oaxaca performed particularly well in specialty retail and online marketplaces. With strong government support, digital integration, and global recognition of its artisanal excellence, Mexico continues to lead the Latin American handicrafts market.
Argentina
Argentina is emerging as a notable exporter of gaucho-inspired leather goods, silver jewelry, and regional textiles. Despite economic volatility, the country maintains a dedicated artisan base that blends traditional craftsmanship with modern design sensibilities. Argentina has also seen success in international exhibitions, with Buenos Aires-based designers participating in curated showcases in Spain, Italy, and Japan, highlighting the country’s unique fusion of Spanish colonial and indigenous design elements. Furthermore, the rise of niche e-commerce platforms specializing in South American craftsmanship has enabled Argentine artisans to bypass intermediaries and sell directly to global buyers. While still smaller compared to other regional players, Argentina’s commitment to cultural preservation and design innovation positions it as a growing force in the Latin American handicrafts landscape.
Chile
Chile is distinguished by its strong representation of indigenous Mapuche culture and coastal artisan traditions. The country’s handicrafts sector is deeply tied to native identity, with government-backed initiatives supporting community-based production and export readiness.
The Ministry of Culture and Sports highlighted that Chilean handicrafts are increasingly featured in museums and cultural festivals, enhancing their appeal beyond mere commodities to symbols of historical and ethnic pride. Local cooperatives and NGOs such as Red de Artesanos de la Araucanía have been instrumental in preserving traditional techniques while adapting them to contemporary tastes. With a strong emphasis on authenticity, cultural diplomacy, and digital accessibility, Chile is strengthening its position as a custodian of indigenous craftsmanship in Latin America.
Rest of Latin America
The Rest of Latin America collectively accounted for notable share of the regional handicrafts market in 2024, encompassing countries like Colombia, Peru, Guatemala, Bolivia, Ecuador, and Central American nations. Each of these countries contributes distinct craft identities that enrich the overall market. Like, Peru’s Ministry of Foreign Trade and Tourism reported that Andean textiles and Chulucana ceramics were among the top-performing exports , with a 30% increase in international orders due to partnerships with global retailers and fashion houses.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS AND COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
Fakih Group of Companies, Gangamani Fashions, Handicrafts Town, Dezaro, are playing dominating role in the Latin America handicrafts market.
The Latin America handicrafts market is marked by a highly fragmented yet culturally rich competitive landscape. It features a mix of independent artisans, regional cooperatives, government-backed institutions, and private enterprises vying for domestic and international attention. While many artisans operate informally, especially in rural areas, there is a growing trend toward professionalization driven by digital platforms and institutional support.
Competition extends beyond product quality to include brand narrative, authenticity, and ethical production practices. International buyers increasingly prioritize transparency and sustainability, pushing Latin American producers to adopt certification mechanisms and digital visibility strategies. E-commerce has leveled the playing field, allowing smaller players to reach global audiences without needing large retail infrastructure.
However, challenges persist, including intellectual property theft, supply chain inefficiencies, and competition from mass-produced replicas. Despite these hurdles, the sector continues to evolve as artisans and institutions collaborate to preserve cultural heritage while adapting to modern consumer expectations and distribution models.
TOP PLAYERS IN THE MARKET
FONART (Mexico)
FONART, Mexico’s National Fund for the Development of Arts and Crafts, plays a central role in promoting traditional Mexican handicrafts both domestically and internationally. It supports artisans through training programs, market access initiatives, and certification processes that ensure authenticity and quality. FONART organizes major national and international events to showcase Mexican craftsmanship, enhancing global recognition. Its efforts have helped position Mexican crafts such as Talavera pottery, silver jewelry, and handwoven textiles as premium artisanal products in global markets.
Artesanías de Colombia (Colombia)
Artesanías de Colombia is instrumental in preserving and promoting the country’s diverse cultural heritage through its support of local artisans and craft cooperatives. The organization facilitates export readiness, product traceability, and brand positioning, enabling Colombian handicrafts to gain traction in North America and Europe. By integrating digital tools and e-commerce platforms, Artesanías de Colombia has empowered thousands of small-scale producers to reach international buyers while maintaining ethical sourcing standards and sustainable production practices.
PromPerú (Peru)
PromPerú actively promotes Peruvian handicrafts on the global stage, focusing on Andean textiles, ceramics, and jewelry rooted in indigenous traditions. Through curated exhibitions and international trade fairs, PromPerú enhances visibility and demand for authentic Peruvian crafts. The agency collaborates with designers and exporters to ensure compliance with fair-trade principles, contributing to Peru’s growing reputation as a source of ethically made, high-quality artisan goods in global lifestyle and fashion markets.
TOP STRATEGIES USED BY KEY MARKET PLAYERS
One of the primary strategies used by key players in the Latin America handicrafts market is cultural storytelling and branding, where artisans and organizations emphasize the historical significance, symbolism, and origin of each product to create emotional value and justify premium pricing in global markets.
Another crucial approach is digital transformation and e-commerce integration , which allows artisans to bypass intermediaries and connect directly with international consumers through platforms like Etsy, Amazon Handmade, and region-specific online marketplaces that enhance visibility and streamline transactions.
Lastly, certification and fair-trade alignment are being prioritized to build trust with conscious consumers who seek transparency in sourcing and labor practices. Organizations like FONART and Artesanías de Colombia have introduced labeling systems and traceability measures to differentiate genuine, handmade products from mass-produced imitations, ensuring long-term competitiveness and consumer confidence.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THE MARKET
- In February 2024, FONART launched an AI-powered translation tool for artisan websites, enabling real-time communication with international buyers and improving customer experience for small-scale Mexican craftsmen selling abroad.
- In May 2024, Artesanías de Colombia partnered with a fintech firm to offer microloans to rural artisans, helping them invest in raw materials, equipment upgrades, and digital storefronts without relying on informal lenders.
- In July 2024, PromPerú collaborated with a major U.S. department store chain to feature Andean textiles and Amazonian ceramics in exclusive holiday collections, significantly raising international awareness and driving seasonal sales.
- In September 2024, MercadoLibre announced a dedicated section for certified Latin American handicrafts, complete with seller verification and fair-trade badges, enhancing credibility and consumer trust in online purchases.
- In November 2024, Etsy expanded its Latin America-focused creator program, providing free digital marketing training, shipping subsidies, and legal advisory services to 5,000 artisans across Mexico, Colombia, and Guatemala, empowering them to scale globally.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the Latin America handicrafts market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Product Type
- Woodware
- Artmetal Ware
- Handprinted Textiles and Scarves
- Embroidered and Crocheted Goods
- Zari and Zari Goods
- Imitation Jewelry
- Sculptures
- Pottery and Glass wares
- Attars and Agarbattis
- Others
By Distribution Channel
- Mass Retailers
- Departmental Stores
- Independent Retailers
- Specialty Stores
- Online Stores
- Others
By End-Use
- Residential
- Commercial
By Country
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the market size and CAGR of the Latin American handicrafts market?
The market is projected to grow from USD 56.09 billion in 2025 to USD 88.19 billion by 2033, at a CAGR of 5.82%.
2. What is driving the growth of the handicrafts market in Latin America?
Rising global demand for handmade goods and growing tourism are major growth drivers.
3. Which product types dominate the Latin American handicrafts market?
Textiles, pottery, woodwork, and jewelry are among the most popular and widely sold product types.
4. How does tourism influence the handicrafts market in Latin America?
Tourists often purchase local crafts, boosting sales in markets, fairs, and cultural destinations.
5. What are the key trends in the handicrafts market?
Eco-friendly materials, traditional designs with modern touches, and online craft platforms are trending.
6. Which countries lead the Latin American handicrafts industry?
Mexico, Peru, Colombia, and Brazil are leading producers and exporters of traditional crafts.
7. What challenges does the market face?
Mass production, lack of market access for artisans, and low international visibility are challenges.
8. How is e-commerce impacting the handicrafts market?
Online platforms are expanding reach and allowing artisans to sell directly to global consumers.
9. What role does sustainability play in handicraft production?
Many artisans use sustainable, recycled, and locally sourced materials to appeal to eco-conscious buyers.
10. Who are the primary buyers of Latin American handicrafts?
Collectors, tourists, interior designers, and retailers interested in unique and culturally rich items.
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from
$ 1600
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: sales@marketdataforecast.com