Latin America Smart Grid Security Market Size, Share, Trends, Forecast, Research Report - Segmented By Solution, Subsystem (SCADA/ICS, AMI, Demand Response, and Home Energy Management), Security Type, and Region (Brazil, Mexico, Argentina, Chile & Rest of Latin America) – Regional Industry 2025 to 2033
Latin America Smart Grid Security Market Size
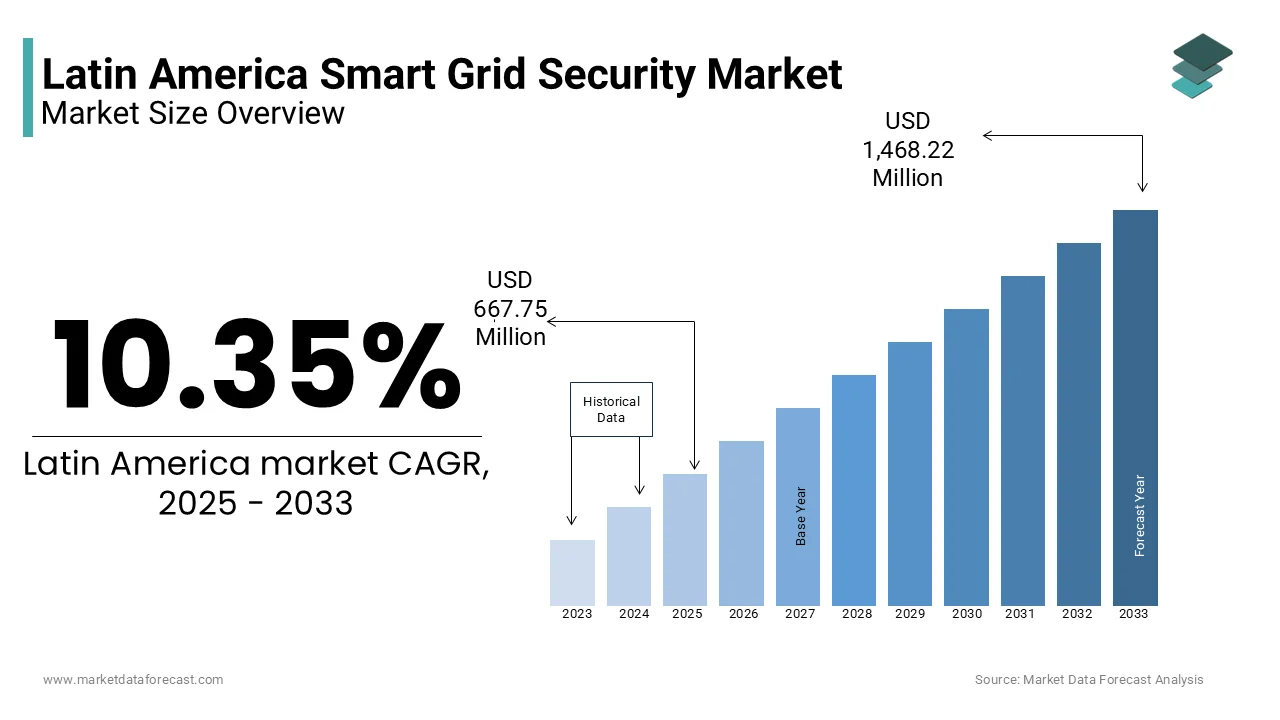
The Latin American smart grid security market was valued at USD 605.12 million in 2024. The global market size is expected to reach USD 667.75 million in 2025 and USD 1,468.22 million by 2033, with a CAGR of 10.35% during the forecast period.
The Latin America smart grid security market is the integration of advanced cybersecurity solutions within modernized electricity distribution networks that leverage digital technologies for real-time monitoring, automation, and data exchange. As countries in the region expand their smart grid infrastructure to enhance energy efficiency and incorporate renewable energy sources, the need for robust security frameworks has become critical. However, this digital transformation exposes power utilities to cyber threats such as ransomware attacks, unauthorized access, and system disruptions. In response, governments and energy regulators across the region are introducing policies to strengthen grid resilience.
MARKET DRIVERS
Increasing Cybersecurity Threats Targeting Energy Infrastructure
One of the primary drivers fueling growth in the Latin America smart grid security market is the escalating frequency and sophistication of cyberattacks targeting energy infrastructure. Power grids, especially those incorporating IoT-enabled devices and remote monitoring systems, have become attractive targets for cybercriminals seeking to disrupt national energy supplies. In Brazil, there is a significant increase in ransomware attacks against utility providers, including a major breach affecting the São Paulo state power grid in late 2023. Similarly, Colombia recorded a 45% year-over-year surge in attempted intrusions into smart grid systems , highlighting growing vulnerabilities. These incidents have prompted regulatory bodies and utility companies to invest heavily in intrusion detection systems, secure communication protocols, and network segmentation strategies.
 Expansion of Smart Grid Deployments and Renewable Integration
Expansion of Smart Grid Deployments and Renewable Integration
Another key driver of the Latin America smart grid security market is the rapid deployment of smart grid technologies and the increasing integration of renewable energy sources. Governments across the region are investing in smart meters, grid automation, and distributed energy resource management systems to improve grid reliability and support sustainable development goals. The decentralized nature of modern energy systems increases exposure to cyber risks, prompting utilities and regulators to prioritize security investments.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
Limited Cybersecurity Expertise and Skilled Workforce Shortages
A significant restraint impeding the growth of the Latin America smart grid security market is the lack of skilled professionals with expertise in both cybersecurity and energy infrastructure. The complexity of securing smart grids requires specialized knowledge in industrial control systems (ICS), threat intelligence, and incident response—areas where regional talent pools remain underdeveloped. Additionally, frequent staff turnover and limited training initiatives further exacerbate the skills gap. Without sustained investment in workforce development and collaboration between academia and industry stakeholders, the ability to implement and maintain robust smart grid security systems will remain constrained across the region.
Fragmented Regulatory Frameworks and Compliance Challenges
Another critical challenge facing the Latin America smart grid security market is the fragmented regulatory environment, which varies significantly across countries. Each nation has its own set of guidelines governing cybersecurity standards for critical infrastructure, leading to inconsistencies in enforcement, reporting requirements, and technical specifications. Also, on energy regulation in Latin America, only Brazil, Mexico, and Chile have established comprehensive cybersecurity mandates for the energy sector, while other countries operate under loosely defined or outdated frameworks. Furthermore, cross-border coordination remains limited, complicating efforts to address transnational cyber threats that could affect interconnected power systems.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Rise of Public-Private Partnerships for Smart Grid Cybersecurity Initiatives
One of the most promising opportunities shaping the Latin America smart grid security market is the increasing collaboration between government entities and private sector players to enhance cybersecurity capabilities. Recognizing the strategic importance of securing national energy infrastructure, several countries have initiated public-private partnerships aimed at developing localized cybersecurity ecosystems. These initiatives not only facilitate knowledge transfer but also encourage innovation in security technologies tailored to Latin American energy infrastructures. Moreover, regional cooperation through forums such as the Latin American Energy Organization (OLADE) has fostered information sharing and best practice adoption among member states.
Adoption of AI and Machine Learning for Threat Detection and Response
The growing adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in cybersecurity presents a significant opportunity for the Latin America smart grid security market. Traditional rule-based security systems often struggle to detect sophisticated, zero-day cyberattacks that target energy infrastructure. AI-driven anomaly detection and predictive analytics offer a more proactive approach to identifying threats before they escalate. Meanwhile, Brazil’s largest utility, Eletrobras, deployed ML algorithms to monitor grid behavior and flag suspicious activities indicative of potential cyber intrusions. These advancements are being supported by global tech firms expanding their presence in the region, offering scalable cloud-based security platforms tailored to smart grid applications.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Vulnerability of Legacy Systems and Aging Grid Infrastructure
A pressing challenge in the Latin America smart grid security market is the coexistence of legacy infrastructure with modern digital systems, creating significant security vulnerabilities. Many power distribution networks in the region still rely on decades-old supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems that were not originally designed with cybersecurity in mind. In Venezuela, aging infrastructure combined with outdated security protocols led to multiple grid failures attributed to cyber sabotage in recent years. Retrofitting these legacy systems with modern security features poses financial and technical challenges, particularly for publicly owned utilities with limited budgets.
High Implementation Costs and Budget Constraints
Another major challenge affecting the Latin America smart grid security market is the high cost of implementing advanced cybersecurity solutions, which poses a barrier for many utility providers, especially in lower-income economies. Securing smart grids involves deploying firewalls, encryption tools, intrusion prevention systems, and continuous monitoring platforms—all of which require significant capital investment. In countries like Honduras and Paraguay, where public investment in energy infrastructure remains limited, many utility companies allocate less share of their annual budget to IT and cybersecurity. Even in larger markets such as Argentina, economic instability has constrained government spending on grid modernization programs. Private-sector participation is often hindered by regulatory uncertainty and unclear return-on-investment models for cybersecurity expenditures.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
10.35% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Solution, Subsystem, Security Type, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional, & Country Level Analysis; Segment-Level Analysis; DROC; PESTLE Analysis; Porter’s Five Forces Analysis; Competitive Landscape; Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
Latin America include Brazil, Argentina, Mexico, and the Rest of Latin America |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
BAE Systems, IBM Corporation, Cisco Systems, Intel Corporation, Siemens AG, Symantec Corporation, N-Dimension Solutions, Leidos Holdings, AT&T Cybersecurity, Schneider Electric, and others. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Solution Insights
The Solutions segment had the largest share of the Latin America smart grid security market, accounting for approximately 58% in 2024. This dominance is primarily due to the increasing deployment of cybersecurity technologies directly embedded into grid infrastructure components such as smart meters, industrial control systems (ICS), and supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems. In Brazil, where ANEEL has mandated compliance with cybersecurity standards for all regulated utilities, the procurement of intrusion detection systems and encryption tools grew. Additionally, the adoption of next-generation firewalls and threat intelligence platforms has surged in response to rising cyber incidents targeting energy networks. These solutions are critical for securing communication protocols across distributed grid assets and ensuring real-time monitoring capabilities remain uncompromised.
The Cloud-based deployment mode is the fastest-growing component of the Latin America smart grid security market, projected to expand at a CAGR of 17.9%. This rapid expansion is attributed to the scalability, cost-effectiveness, and centralized management advantages offered by cloud-native security architectures. As utilities increasingly adopt IoT-enabled grid devices and remote monitoring applications, the need for agile and updatable security frameworks has intensified. The ability to integrate artificial intelligence for anomaly detection and leverage shared threat intelligence across regions makes cloud-based deployment a strategic priority for modernizing smart grid security in Latin America.
By Subsystem Insights
The SCADA/ICS subsystem dominated the Latin America smart grid security market by holding an estimated market share of 42.7% in 2024. This leading position is due to critical role these systems play in managing electricity generation, transmission, and distribution networks. SCADA systems are widely used across national grids in countries like Brazil, Mexico, and Argentina, making them prime targets for cyberattacks aimed at disrupting power supply. In Brazil, ANEEL issued new directives requiring all SCADA operators to implement multi-factor authentication and secure remote access protocols, leading to a increase in cybersecurity solution procurement among state-owned utilities. Given the strategic importance of securing these foundational grid control systems, SCADA/ICS remains the most heavily protected subsystem in the region’s smart grid security landscape.
The Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) subsystem is the swiftest advancing segment in the Latin America smart grid security market, projected to rising at a CAGR of 19.3%. This surge is driven by the widespread rollout of smart meters designed to enable real-time energy consumption tracking, dynamic pricing, and remote service management. However, the proliferation of millions of connected metering endpoints has introduced significant cybersecurity risks, including device spoofing, data interception, and denial-of-service attacks. In response, utility providers have accelerated investments in secure firmware updates, end-to-end encryption, and device authentication mechanisms. As digitalization progresses, the need to secure billions of interconnected metering devices will continue to drive robust demand for advanced cybersecurity solutions tailored to AMI deployments.
By Security Type Insights
The Network Security segment commanded the largest share of the Latin America smart grid security market, capturing about 37.3% in 2024. This dominance is attributable to the growing complexity of grid communication networks, which rely on extensive fiber-optic backbones, wireless sensor nodes, and IP-based transmission protocols. Ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of data exchanged between grid components—such as substations, control centers, and distributed energy resources—requires robust network-level protections. As smart grid networks expand and interconnectivity increases, the imperative to secure these pathways remains a top priority for regulators and utility operators alike.

The Endpoint Security segment is the quickest surging within the Latin America smart grid security market, projected to expand at a CAGR of 20.1%. This rapid growth is fueled by the exponential rise in endpoint devices integrated into smart grid ecosystems, including smart meters, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), and remote terminal units (RTUs). These devices serve as entry points for potential cyber intrusions, necessitating advanced protection measures such as behavioral analysis, firmware hardening, and zero-trust authentication. Meanwhile, Brazil’s AES Sul partnered with Fortinet to roll out micro-segmentation techniques that isolate compromised endpoints before threats can spread. As the number of connected grid assets continues to multiply, securing these endpoints becomes essential for maintaining the overall resilience of smart grid operations.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
Brazil occupied the top position in the Latin America smart grid security market, commanding an estimated 36% market share in 2024. The country's progress is attributed to its early adoption of smart grid technologies and proactive regulatory initiatives aimed at strengthening cybersecurity. Additionally, Brazil’s participation in global cybersecurity coalitions, such as the World Economic Forum’s Centre for Cybersecurity, has facilitated knowledge exchange and capacity building. As digital transformation accelerates, Brazil remains at the forefront of smart grid security innovation in Latin America.
Mexico’s strong focus on grid modernization and cross-border energy cooperation has positioned it as a key player in regional cybersecurity development. Also, partnerships with global cybersecurity firms such as Cisco and Palo Alto Networks have supported the implementation of real-time threat monitoring systems. As renewable integration expands and cyber threats evolve, Mexico is actively reinforcing its defenses to safeguard national energy assets.
Argentina’s market expansion is driven by increasing investments in smart metering and industrial control system (ICS) security. Additionally, the government introduced new fintech regulations in 2023 aimed at encouraging innovation while ensuring compliance with financial oversight. Despite macroeconomic challenges, Argentina is emerging as a dynamic player in the regional payments landscape.
Chile is distinguished by its technologically advanced energy infrastructure and high levels of digital adoption. It has also been a pioneer in adopting AI-driven threat detection systems, with Enel implementing machine learning algorithms to analyze grid behavior and flag anomalies in real time. With renewables accounting for nearly 40% of total electricity generation , the need to secure bidirectional energy flows and decentralized assets remains a central focus for regulators and industry stakeholders.
The “Rest of Latin America” category, comprising countries such as Colombia, Peru, Ecuador, and Central American nations. While individual economies may not match the scale of Brazil or Mexico, the collective growth potential is significant. Meanwhile, Honduras and Guatemala saw a rise in telemedicine-based diagnostics , creating demand for centralized automated labs capable of processing remote samples. This diversified yet rapidly evolving market presents unique opportunities for automation vendors aiming to expand beyond traditional hubs.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS AND COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
Key players in the Latin America smart grid security market are BAE Systems, IBM Corporation, Cisco Systems, Intel Corporation, Siemens AG, Symantec Corporation, N-Dimension Solutions, Leidos Holdings, AT&T Cybersecurity, and Schneider Electric.
The competition in the Latin America smart grid security market is intensifying as both global cybersecurity giants and emerging regional players vie for dominance in a rapidly evolving sector. International firms such as Siemens Energy, Cisco, and Fortinet maintain a strong presence due to their technological expertise and established partnerships with national utilities. At the same time, niche cybersecurity vendors and local system integrators are gaining traction by offering cost-effective, region-specific security solutions tailored to the unique regulatory and operational landscapes of individual countries. Government agencies and state-owned energy enterprises are increasingly prioritizing cybersecurity investments, creating opportunities for both domestic and foreign players to innovate and expand. Collaboration between public and private stakeholders is becoming more common, with joint ventures and pilot projects aimed at enhancing grid resilience against cyber threats. While urban centers and developed markets like Brazil and Mexico lead in adoption, emerging economies are catching up, driven by rising awareness of cyber risks and growing investments in grid modernization. This dynamic environment fosters continuous innovation, making the Latin American smart grid security market one of the most strategically important regions in the global energy cybersecurity landscape.
TOP PLAYERS IN THE MARKET
Siemens Energy
Siemens Energy is a global leader in energy infrastructure and plays a pivotal role in strengthening smart grid security across Latin America. The company provides comprehensive cybersecurity solutions tailored for industrial control systems, SCADA networks, and grid automation platforms. In Latin America, Siemens collaborates with national utilities and regulators to implement secure communication protocols, intrusion detection systems, and real-time monitoring tools. Its presence in countries like Brazil, Mexico, and Chile has been instrumental in enhancing grid resilience against cyber threats. By leveraging its global expertise and localized deployment capabilities, Siemens contributes significantly to the advancement of secure and intelligent power networks in the region.
Cisco Systems
Cisco Systems is a key player in securing critical infrastructure, including smart grids, across Latin America. The company offers advanced network security solutions that help protect grid communications, data integrity, and remote access points. In Latin America, Cisco works closely with utility providers to deploy secure SD-WAN architectures, zero-trust frameworks, and threat intelligence platforms. It also supports government-led initiatives aimed at building national cybersecurity ecosystems for energy infrastructure. With a strong focus on innovation and digital transformation, Cisco continues to shape the future of smart grid security by integrating cutting-edge networking and cyber defense technologies into evolving grid systems across the region.
Fortinet
Fortinet is a leading cybersecurity provider actively engaged in securing smart grid deployments in Latin America. The company delivers end-to-end security solutions designed for industrial environments, including firewalls, endpoint protection, and secure access services. In Latin America, Fortinet partners with energy firms and technology integrators to safeguard grid operations from cyber threats targeting smart meters, substations, and control centers. The company's commitment to education and capacity building through training programs enhances local readiness to manage cyber risks. As digitalization accelerates, Fortinet’s scalable and adaptive security architecture plays a crucial role in protecting the region’s expanding smart energy infrastructure.
TOP STRATEGIES USED BY THE KEY MARKET PLAYERS
Key players in the Latin America smart grid security market are employing strategic initiatives to solidify their competitive edge. One major approach is expanding regional partnerships with local governments and utility operators , allowing companies to align their offerings with national cybersecurity policies and gain deeper market access. Another prevalent strategy is investing in research and development to create industry-specific security solutions that address the unique challenges of smart grid infrastructures, such as securing distributed assets and managing legacy systems. Additionally, companies are focusing on enhancing service portfolios with managed security services and consulting , enabling utilities to outsource complex aspects of cybersecurity while ensuring continuous threat monitoring and compliance adherence. These strategies collectively help firms strengthen their foothold and respond effectively to the dynamic demands of the Latin American smart grid security landscape.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THE MARKET
- In February 2024, Siemens Energy launched a new regional cybersecurity center in São Paulo, Brazil, dedicated to supporting utility companies in detecting and mitigating cyber threats targeting smart grid infrastructure.
- In April 2024, Cisco Systems partnered with Mexico’s Comisión Federal de Electricidad (CFE) to deploy a secure SD-WAN framework across multiple substations, aiming to enhance network visibility and reduce vulnerabilities in grid communications.
- In June 2024, Fortinet announced a collaboration with Argentina’s National Institute of Industrial Technology (INTI) to develop a specialized cybersecurity curriculum focused on securing industrial control systems used in the energy sector.
- In August 2024, Efacec, a Portuguese energy technology firm with a strong presence in Latin America, expanded its cybersecurity division in Chile to provide customized grid security solutions for renewable energy integration projects.
- In October 2024, IBM Security entered into a strategic alliance with Brazil’s AES Sul to implement an AI-driven threat intelligence platform designed to monitor and respond to cyber incidents in real time across the utility’s smart grid network.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the Latin America smart grid security market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Solution
- Antivirus and antimalware
- Firewall
- Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Encryption
- Security and vulnerability management
- Intrusion Detection System/Intrusion Prevention System (IDS/IPS)
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS)
- Others (Data Loss Prevention (DLP), incident response, fraud detection, and Security Information and Event Management (SIEM))
By Subsystem
- Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA)/Industrial Control System (ICS)
- Advanced metering infrastructure
- Demand response
- Home energy management
By Security Type
- Endpoint security
- Network security
- Application security
- Database security
By Country
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Mexico
- Rest of Latin America
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is driving the growth of the smart grid security market in Latin America?
The growth is primarily driven by the increasing implementation of smart grid technologies, which necessitate advanced security solutions to protect against cyber threats. Additionally, government initiatives promoting energy efficiency and grid modernization contribute to market expansion.
2. Which countries in Latin America are leading in smart grid adoption?
Countries like Brazil and Mexico are at the forefront, with significant investments in smart grid infrastructure and security measures.
3. What are the main challenges facing the smart grid security market in the region?
Key challenges include the high cost of implementing advanced security solutions, lack of standardized regulations across countries, and the need for skilled cybersecurity professionals.
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 1600
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: sales@marketdataforecast.com