North America Vertical Farming Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report, Segmented By Growth Mechanism, Structure, Offering, Crop Type And By Country (The USA, Canada, Mexico and Rest of North America), Industry Analysis From 2025 to 2033
North America Vertical Farming Market Size
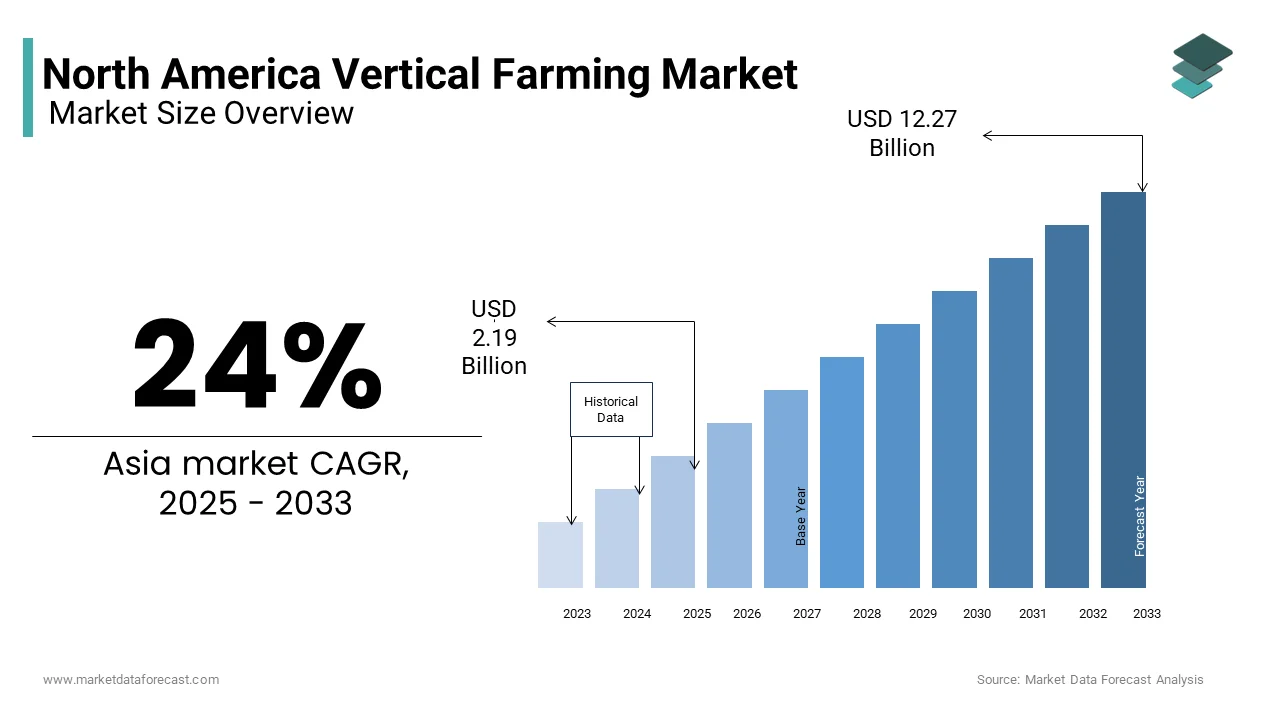
The North American vertical farming market was valued at USD 1.77 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 2.19 billion in 2025 from USD 12.27 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 24% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2033.
The North America vertical farming market refers to the practice of cultivating crops in vertically stacked layers using controlled-environment agriculture (CEA) technologies such as hydroponics, aeroponics, and aquaponics. This innovative approach enables year-round production with minimal land use, making it particularly suitable for urban environments where space is limited. Vertical farms utilize LED lighting, climate control systems, and automated nutrient delivery to optimize plant growth while significantly reducing water consumption compared to traditional agriculture. In Canada, the Canadian Agricultural Partnership reports that investments in controlled environment agriculture have surged, which is driven by growing interest in sustainable food production and local sourcing. The integration of artificial intelligence, IoT-enabled monitoring, and robotics into vertical farming operations has further enhanced efficiency and scalability. As per Statistics Canada, consumer demand for pesticide-free, locally grown produce has risen steadily, prompting major retailers and food service providers to source from urban vertical farms.
MARKET DRIVERS
Rising Urbanization and Demand for Locally Grown Produce
One of the key drivers of the North America vertical farming market is the rapid pace of urbanization and the corresponding rise in demand for locally grown, fresh produce. Vertical farming offers a viable solution by enabling crop cultivation in high-density urban settings without reliance on large tracts of farmland. According to the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, over 82% of the U.S. population now resides in urban areas, with similar trends observed in Canada. This concentration of consumers fosters proximity-based supply chains, which allow vertical farms to deliver farm-to-table freshness with reduced transportation emissions.
Additionally, city governments are actively promoting urban agriculture initiatives to enhance food security and reduce dependence on long-distance imports. For instance, New York City and Toronto have introduced zoning incentives and grant programs to support the establishment of indoor farms.
Technological Advancements Enhancing Operational Efficiency
Another significant driver of the North American vertical farming market is the continuous advancement of technology that enhances operational efficiency, productivity, and sustainability. Innovations in LED lighting, automation, artificial intelligence, and climate control systems have transformed vertical farming into a highly scalable and data-driven industry capable of delivering consistent yields with minimal resource inputs. According to a 2024 report by McKinsey & Company, the adoption of AI-powered monitoring systems in vertical farms has improved energy efficiency by up to 30%, which is allowing operators to fine-tune environmental conditions for optimal plant growth. Additionally, the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) sensors enables real-time tracking of temperature, humidity, and nutrient levels, reducing manual intervention and minimizing waste.
According to the U.S. Department of Energy, next-generation LED grow lights consume significantly less electricity than traditional horticultural lighting while providing tailored light spectra that boost photosynthesis and accelerate plant development. Furthermore, companies like AeroFarms and Plenty have pioneered fully automated vertical farming models that use machine learning algorithms to predict harvest cycles and adjust irrigation schedules dynamically. These technological strides not only lower production costs but also make vertical farming more financially viable, which is attracting investment from both agribusinesses and venture capital firms.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Initial Capital Investment and Operating Costs
One of the major restraints affecting the North American vertical farming market is the substantial initial capital investment and ongoing operational expenses associated with setting up and maintaining high-tech indoor farms. Unlike traditional agriculture, vertical farming requires significant expenditures on infrastructure, climate control systems, LED lighting, automation, and advanced nutrient delivery mechanisms. These costs often deter small-scale entrepreneurs and startups from entering the market, limiting the sector’s expansion to well-funded enterprises or government-backed initiatives.
Moreover, the energy-intensive nature of vertical farming contributes to elevated operating costs. As noted by the U.S. Department of Energy, electricity accounts for nearly 25–30% of total running expenses in most vertical farms, primarily due to continuous LED lighting and climate control needs. While advancements in energy-efficient technologies are helping to mitigate this issue, the financial burden remains a considerable barrier to widespread adoption for independent growers seeking profitability in competitive markets.
Limited Crop Diversity and Yield Constraints
Another key restraint in the North American vertical farming market is the limited range of commercially viable crops and yield constraints that hinder large-scale production. Most vertical farms currently focus on leafy greens, herbs, and microgreens due to their short growth cycles, compact size, and high market value. However, staple crops such as wheat, corn, and soybeans remain unsuitable for vertical farming due to space limitations, growth complexity, and economic feasibility concerns. According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), less than 15% of all agricultural commodities in North America can be efficiently cultivated using the vertical farming technique, restricting the industry’s potential to replace conventional farming at scale. Additionally, while vertical farms offer higher yield density per square foot, they face challenges in achieving cost parity with field-grown alternatives for bulk commodities. Furthermore, the Society of Indoor AgTech reports that scaling beyond niche produce categories often leads to diminishing returns due to increased infrastructure and labor demands, making it difficult for vertical farms to compete with large-scale outdoor operations on price.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for Precision Farming
A major opportunity driving the North America vertical farming market is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to enable precision farming, enhancing productivity, resource efficiency, and yield consistency. These technologies allow vertical farms to analyze vast amounts of real-time data related to plant health, nutrient levels, lighting intensity, and climate conditions, optimizing every aspect of the growing process.
According to the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), AI-driven analytics platforms are now capable of predicting plant stress indicators before visible symptoms appear, which is allowing farmers to intervene early and prevent crop losses. Companies like Bowery Farming and Infarm have deployed proprietary AI systems that continuously adapt growing conditions based on historical performance data, ensuring optimal output with minimal human intervention.
Moreover, according to the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), machine learning algorithms can improve energy efficiency by dynamically adjusting LED lighting and HVAC systems based on real-time crop requirements by reducing power consumption by up to 25%. As these technologies become more accessible and affordable, even smaller vertical farms can leverage AI and ML to refine their operations, increase profitability, and scale sustainably across North America.
Expansion of Government Support and Sustainability Incentives
Another emerging opportunity for the North America vertical farming market is the growing availability of government support and sustainability-focused incentive programs aimed at promoting controlled environment agriculture. Policymakers at federal, state, and municipal levels are increasingly recognizing vertical farming as a strategic tool for improving food security, which is reducing environmental impact, and strengthening local food systems.
According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), several states, including California, Illinois, and New Jersey, have launched grant programs and tax incentives to encourage the establishment of urban indoor farms. In Canada, the Canadian Agricultural Partnership (CAP) has allocated millions of dollars toward research and development initiatives focused on indoor farming technologies, particularly in urban centers like Toronto and Vancouver. According to Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada, vertical farming projects receiving public funding have demonstrated a 20–30% reduction in water usage and carbon footprint compared to traditional greenhouses by reinforcing their alignment with national sustainability goals. With continued policy support and targeted subsidies, vertical farming is poised for accelerated growth across North America.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Energy Consumption and Carbon Footprint Concerns
One of the foremost challenges facing the North American vertical farming market is the high energy consumption associated with indoor farming operations, which raises concerns regarding sustainability and overall carbon footprint. Unlike traditional agriculture, which relies on natural sunlight, vertical farms depend heavily on artificial lighting, climate control systems, and ventilation equipment, all of which contribute to significant electricity demand. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, vertical farms consume approximately 10 times more energy per square meter compared to conventional greenhouses, primarily due to continuous LED lighting and environmental regulation. While advances in energy-efficient lighting and smart controls have mitigated some of these concerns, many facilities still rely on grid-based electricity, which may not always come from renewable sources. Additionally, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) notes that unless vertical farms transition to clean energy sources such as solar, wind, or geothermal, their environmental benefits, such as reduced transportation emissions and water savings, may be offset by high carbon outputs. Some companies have begun investing in on-site renewable energy generation and off-grid solutions, but widespread adoption remains limited due to cost barriers and infrastructure constraints, which is posing a significant challenge to the industry’s long-term viability.
Supply Chain and Distribution Limitations
Another significant challenge confronting the North American vertical farming market is the complexity of integrating into existing supply chains and ensuring efficient distribution to retail and foodservice outlets. Despite the advantages of localized production, many vertical farms struggle with logistics, storage, and last-mile delivery, which can impact product freshness and cost competitiveness.
According to the Food Marketing Institute (FMI), over 50% of fresh produce in North America moves through centralized wholesale distribution networks, which is making it difficult for smaller vertical farms to gain direct access to large retail chains. Without established cold chain infrastructure and distribution partnerships, perishable crops like lettuce and herbs risk spoilage before reaching consumers.
Moreover, the Harvard Business Review highlights that many vertical farms lack the economies of scale necessary to negotiate favorable logistics contracts, which is leading to higher transportation costs relative to traditional suppliers. This challenge is particularly pronounced in rural and suburban areas where urban farms cannot easily reach their target markets. Unless vertical farming companies develop robust logistics strategies and collaborate with regional distributors, their ability to scale profitably may remain constrained.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
24% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Growth Mechanism, Structure, and Offering |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
The US, Canada, and the Country |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Illumitex Inc. (U.S.), Aerofarms (U.S.), Koninklijke Philips N.V. (The Netherlands), and Sky Greens (Singapore), among others. |
SEGMENT ANALYSIS
By Growth Mechanism Insights
The hydroponics segment dominated the North America vertical farming market by capturing 62.1% of the share in 2024. One key driver behind hydroponics' dominance is its established track record and ease of integration into commercial vertical farming operations. Unlike aeroponics or aquaponics, which require more complex systems, hydroponics relies on well-understood nutrient delivery mechanisms that have been refined over decades. Another major factor contributing to its market position is the high yield potential and water efficiency offered by hydroponic systems.
The aeroponics segment is projected to expand at a CAGR of 28.3% during the forecast period. A primary growth driver is the superior resource efficiency of aeroponic systems, which deliver nutrients directly to plant roots through misting, eliminating the need for soil or substrate. According to NASA’s research on advanced agricultural methods, aeroponic systems can reduce water usage by up to 98% compared to conventional farming, which is making them highly appealing in drought-prone regions such as California and Arizona.
Additionally, the ability of aeroponics to support high-value crop production in compact environments is attracting interest from both startups and institutional investors. As reported by the International Society for Horticultural Science (ISHS), aeroponic farms have demonstrated up to 30% faster growth rates for leafy greens and herbs by enhancing profitability for commercial growers.
By Structure Insights
The buildings segment dominated the North America vertical farming market share in 2024. One of the leading factors driving this segment's growth is the need for stable environmental controls and infrastructure customization. Unlike temporary structures or mobile units, permanent buildings offer superior insulation, climate regulation, and integration capabilities with HVAC, LED lighting, and automation systems. Another significant contributor is the availability of government incentives and zoning approvals for building-based agricultural facilities. As reported by the National Conference of State Legislatures (NCSL), several stateincluding Illinois, New Jersey, and Massachusetts, have introduced policies encouraging the conversion of vacant commercial buildings into vertical farms. These initiatives provide financial support and streamline permitting processes, which reinforces the attractiveness of building-based structures for serious vertical farming enterprises across North America.
The shipping containers segment is likely to register a CAGR of 24.6% during the forecast period. A key driver behind this growth is the flexibility and portability offered by container-based vertical farms, allowing deployment in diverse settings such as city centers, rooftops, food deserts, and disaster relief zones. Additionally, shipping container farms are increasingly being used by startups, educational institutions, and small-scale entrepreneurs due to their lower initial setup costs and quicker deployment times. As noted by the Urban Agriculture Network, container farms can be fully operational within six weeks of installation by offering a fast-track entry into the vertical farming sector.
By Offering Insights
The hardware segment dominated the North America vertical farming market by capturing 58.3% of the share in 2024. One of the key reasons for hardware’s dominant position is the high initial capital expenditure associated with setting up vertical farms, which heavily rely on specialized equipment for optimal performance. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, LED lighting alone accounts for nearly 30–40% of the upfront investment in a typical vertical farm, which reflects its critical role in plant growth and energy efficiency. Another major contributing factor is the continuous demand for upgrades and replacements as technology evolves. As reported by McKinsey & Company, over 65% of vertical farm operators invest in new hardware every 2–3 years to enhance productivity and reduce operational inefficiencies.
The software segment is projected to expand at a CAGR of 26.8% during the forecast period. A primary driver behind this segment’s expansion is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into farm management systems, enabling precise control over environmental conditions, nutrient levels, and crop health. According to the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), AI-powered analytics platforms have improved yield predictability by up to 40% by reducing waste and optimizing harvest schedules. Additionally, the adoption of cloud-based farm management tools is accelerating due to their scalability and accessibility, allowing farmers to remotely monitor and adjust parameters from any location. As per data from the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), over 50% of newly established vertical farms in 2023 deployed cloud-connected software solutions, facilitating seamless integration with supply chain logistics and compliance reporting.
COUNTRY ANALYSIS
The United States was the largest contributor of the North American farming market with 7a 6.4% share in 2024. One of the key drivers of vertical farming adoption in the U.S. is the expanding consumer preference for locally sourced, pesticide-free produce, particularly among millennials and Gen Z demographics. Additionally, government-backed initiatives and private investments are fueling industry expansion.
Canada was next by capturing 18.7% of the North America vertical farming market share in 2024. One of the primary drivers of vertical farming growth in Canada is the need to address food insecurity in northern and remote communities where access to fresh produce is limited due to harsh weather conditions and logistical constraints. Another important factor is the rising number of public-private partnerships aimed at scaling vertical farming technologies.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
The key players involved in the progress of the North America vertical farming market are Illumitex Inc. (U.S.), Aerofarms (U.S.), Koninklijke Philips N.V. (The Netherlands), and Sky Greens (Singapore,e), among others.
Top Players in the Market
One of the leading players in the North American farming market is AeroFarms, a pioneering company known for its advanced indoor vertical farming techniques using aeroponic systems. Headquartered in New Jersey, AeroFarms has developed proprietary technologies that enable high-yield, resource-efficient crop production without the need for soil or sunlight. The company's contributions extend beyond North America, influencing global standards in sustainable agriculture through innovations in seed genetics, lighting, and data analytics.
Another key player is Plenty, a San Francisco-based vertical farming enterprise that focuses on scaling high-tech indoor farms to supply fresh, pesticide-free produce to urban centers. Plenty leverages AI-driven climate control and precision irrigation to optimize plant growth, which is ensuring consistent quality and flavor. Its partnerships with major retailers and investors have positioned it as a model for commercial scalability in controlled environment agriculture, inspiring similar ventures worldwide.
Bowery Farming is also a major participant, recognized for its fully automated, software-driven vertical farming platform known as BoweryOS. This system integrates AI, computer vision, and IoT sensors to manage every aspect of the growing process remotely. With facilities in multiple U.S. locations, Bowery Farming is advancing the integration of technology and agriculture, setting new benchmarks for efficiency, traceability, and sustainability across the global food production landscape.
Top Strategies Used by Key Market Participants
A primary strategy employed by key players in the North America vertical farming market is expanding strategic partnerships with technology firms, retailers, and research institutions. These collaborations allow vertical farming companies to access cutting-edge innovations, streamline supply chain integration, and enhance product offerings tailored to consumer preferences.
Another critical approach is investing heavily in R&D to develop proprietary technologies that improve yield predictability, energy efficiency, and automation capabilities. Companies are continuously refining their growing systems, nutrient delivery mechanisms, and climate control algorithms to reduce operational costs and increase scalability.
The scaling operations through modular farm deployments in urban centers are gaining traction among industry leaders. By utilizing repurposed buildings and shipping containers, vertical farming firms can establish proximity-based production hubs that minimize transportation time while maximizing freshness and accessibility. These strategies collectively reinforce market prominence and long-term competitiveness in a rapidly evolving agricultural landscape.
COMPETITION OVERVIEW
The competition in the North American vertical farming market is intense and rapidly evolving, shaped by the convergence of agricultural expertise, technological innovation, and investment capital. Established players such as AeroFarms, Plenty, and Bowery Farming continue to dominate due to their sophisticated infrastructure, proprietary technologies, and strong retail partnerships. However, they face increasing pressure from emerging startups and agri-tech incubators offering niche solutions tailored to specific crops, climates, and distribution models.
Innovation remains a key battleground, with companies racing to develop more efficient LED lighting, AI-driven monitoring systems, and water-saving cultivation methods. The race to scale profitability while maintaining environmental benefits has led to a wave of strategic acquisitions, joint ventures, and government-backed initiatives aimed at accelerating commercial viability. At the same time, traditional greenhouse operators and hydroponic suppliers are adapting their business models to compete in the controlled-environment agriculture space.
Market participants are also differentiating themselves through brand positioning, supply chain integration, and sustainability messaging. As consumer demand for transparency and local sourcing grows, vertical farming firms must continuously refine their value propositions and expand their service footprints to maintain relevance in an increasingly crowded and capital-intensive industry.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THE MARKET
- In February 2024, AeroFarms announced a new partnership with a leading U.S. grocery retailer to supply locally grown leafy greens exclusively to select regional markets, which is reinforcing its commitment to hyper-local food distribution and strengthening its retail presence.
- In May 2024, Plenty launched a pilot program with a major university research center to develop next-generation plant varieties specifically optimized for vertical farming environments by aiming to enhance taste profiles, nutritional content, and growth efficiency.
- In July 2024, Bowery Farming introduced a new line of branded ready-to-eat salad kits featuring traceable, sustainably grown ingredients, expanding its consumer engagement strategy and deepening relationships with health-conscious shoppers.
- In September 2024, Infarm opened its first integrated regional distribution hub in Chicago, designed to streamline logistics and ensure fresher, faster delivery of vertically farmed produce to restaurants and supermarkets across the Midwest.
- In November 2024, Gotham Greens expanded its facility footprint by converting a former industrial warehouse into a state-of-the-art vertical greenhouse, combining hydroponics with AI-assisted climate controls to serve growing demand in the Northeastern United States.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the North America vertical farming market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Growth Mechanism
- Hydroponics
- Aeroponics
- Aquaponics
By Structure
- Buildings
- Shipping Containers
By Offering
- Hardware
- Software
- Service
By Country
- The US
- Canada
- Mexico
- Rest of North America
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the projected CAGR of the North America Vertical Farming Market from 2025 to 2033?
The North America vertical farming market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 24% from 2025 to 2033 , driven by rising urbanization, water scarcity concerns, and demand for locally grown produce with reduced supply chain risks.
Which country leads in vertical farming adoption within North America?
The U.S. accounts for over 85% of total vertical farming investments , with major hubs in California, New Jersey, and Illinois , where companies like AeroFarms, Plenty, and Bowery Farming operate large-scale indoor farms.
How much area in North America is currently under vertical farming operations?
As of 2024, over 6.2 million square feet of indoor growing space is dedicated to vertical farming across the U.S. and Canada, with New York City and Toronto seeing the fastest growth in facility installations.
Which crop dominates production in North American vertical farms?
Leafy greens (e.g., lettuce, kale, arugula) account for over 70% of all vertical farm output, due to their short growth cycle, high margin, and compatibility with hydroponic and aeroponic systems.
What percentage of urban grocery stores in the U.S. now stock locally grown vertical farm produce?
Over 42% of major urban supermarkets in cities like Boston, Chicago, and Los Angeles now carry fresh produce from local vertical farms, reflecting increased consumer preference for traceable, pesticide-free greens.
How has artificial lighting efficiency improved vertical farming economics since 2020?
Advancements in LED lighting technology have reduced energy consumption per pound of produce by up to 35% since 2020, making vertical farming more economically viable even in high-cost electricity regions.
Which states in the U.S. offer the most favorable incentives for vertical farming startups?
States like New York, California, and Michigan provide the most supportive policies, including tax credits, renewable energy grants, and zoning flexibility , to encourage urban agriculture and food resilience.
How much has venture capital investment in vertical farming companies grown since 2022?
VC funding in North American vertical farming startups rose by over 50% in 2023 , with major deals going to companies integrating AI-driven climate control, robotics, and modular farm designs .
What role does vertical farming play in reducing food deserts in North American cities?
Urban vertical farms have helped improve access to fresh produce in underserved neighborhoods, with Detroit, Baltimore, and Oakland launching community-integrated farms that supply local schools and food banks.
How is automation changing labor costs in North American vertical farms?
Automation technologies, including robotic harvesting and AI-based monitoring, have reduced labor expenses by nearly 40% in large-scale vertical farms, improving profitability and scalability.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from
$ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: sales@marketdataforecast.com