Global Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report - Segmented By Drug Type (Vitamin E and Pioglitazone Ocaliva Elafibranor Selonsertib & Cenicriviroc), Sales Channel, Region (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, And Middle East & Africa) - Industry Analysis (2025 to 2033)
Global Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) Market Size
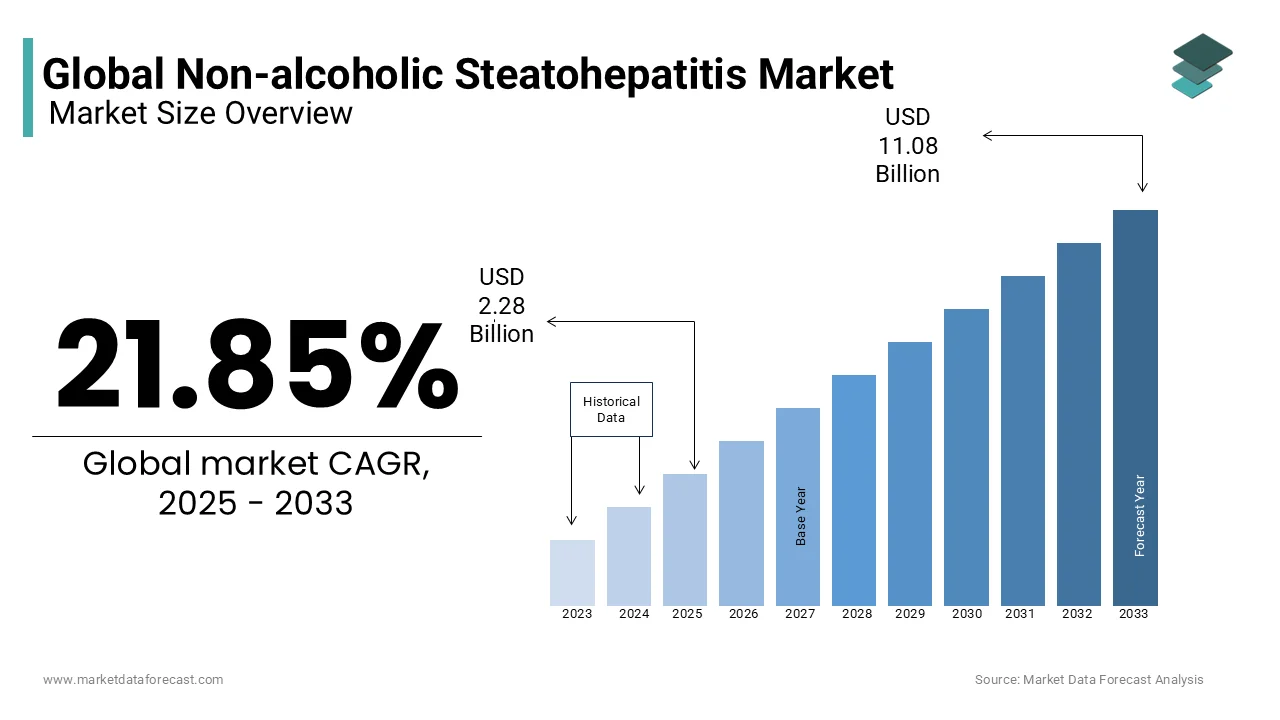
The global Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) market size was valued at USD 1.87 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 11.08 billion by 2033 from USD 2.28 billion in 2025. The market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 21.85%.
MARKET DRIVERS
Rising Prevalence of Obesity and Diabetes
One of the primary drivers of the Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) market is the escalating prevalence of obesity and type 2 diabetes, both of which are major risk factors for Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH). According to the World Health Organization (WHO), global obesity rates have nearly tripled since 1975, with over 650 million adults classified as obese in 2021. Similarly, the International Diabetes Federation reports that diabetes affects approximately 537 million people worldwide with projections reaching 783 million by 2045.
These conditions create a fertile ground for Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) progression. As per a study published in The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology, individuals with obesity are five times more likely to develop Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) compared to those with normal body weight. Additionally, the economic burden of managing complications such as cirrhosis and liver failure is staggering, which is estimated at $103 billion annually in the U.S. alone. This growing patient pool drives demand for effective Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) treatments by positioning the market for sustained growth.
Advancements in Diagnostic Technologies
Advancements in diagnostic technologies represent another key driver propelling the Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) market forward. Early detection of Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) is critical for preventing irreversible liver damage, yet traditional methods like liver biopsies are invasive and costly. For example, FibroScan, an ultrasound-based technology, offers a painless alternative for assessing liver stiffness and fat accumulation. A study in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology found that FibroScan accurately identifies advanced fibrosis in 90% of cases by improving patient outcomes. Similarly, blood-based biomarkers like cytokeratin-18 (CK-18) enable cost-effective screening by reducing diagnosis costs by 30%.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Costs of Treatment Development
A significant restraint facing the Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) market is the exorbitant cost associated with developing effective treatments. According to Deloitte, the average cost of bringing a new drug to market exceeds $2.6 billion, with Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) therapies being particularly challenging due to complex disease mechanisms and high clinical trial failure rates. For instance, Genfit’s elafibranor, once considered a promising candidate, failed Phase III trial by resulting in losses exceeding $500 million. Additionally, regulatory hurdles further exacerbate costs. The FDA mandates extensive long-term studies to evaluate safety and efficacy, delaying approvals by several years.
Lack of Awareness and Late Diagnosis
Limited awareness about Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) and its symptoms poses another major restraint, which is leading to delayed diagnosis and treatment. According to a survey conducted by the Global Liver Institute, less than 30% of patients with NAFLD or Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) are aware of their condition due to asymptomatic progression in early stages. This lack of awareness results in missed opportunities for timely intervention, worsening patient outcomes. For example, a study in Hepatology Communications reveals that over 60% of Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) cases are diagnosed only after significant liver damage has occurred, which is increasing healthcare costs by 40%. Additionally, misconceptions about liver health among healthcare providers delay referrals to specialists.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Expansion into Personalized Medicine
One promising opportunity lies in the development of personalized medicine approaches tailored to individual patient profiles, which is enhancing treatment efficacy and outcomes. Genetic testing and biomarker analysis enable precise targeting of underlying causes, which is addressing heterogeneity in disease progression. For instance, Intercept Pharmaceuticals’ obeticholic acid (OCA) demonstrates efficacy in specific patient subgroups with advanced fibrosis, which is achieving a 23% reduction in liver scarring in clinical trials. Similarly, collaborations between AI firms and biotech companies enhance drug discovery processes, which is reducing development timelines by 30%. These innovations position personalized medicine as a transformative force by fostering innovation and meeting evolving market demands.
Growth in Emerging Markets
Another lucrative opportunity exists in expanding Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) treatments to emerging markets, where rising obesity and diabetes rates create immense demand. According to Statista, the Asia-Pacific region accounts for over 60% of global diabetes cases, with India and China leading the charge. Government initiatives like India’s National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases, and Stroke (NPCDCS) aim to improve awareness and access to care. For example, partnerships between multinational pharma companies and local healthcare providers enhance affordability and distribution. Additionally, advancements in telemedicine enable remote consultations, addressing infrastructure gaps.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Complexity of Disease Pathogenesis
The complexity of Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) pathogenesis represents a significant challenge by complicating drug development and treatment standardization. According to Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) involves multiple pathways, including inflammation, insulin resistance, and oxidative stress, which is making it difficult to target with single-agent therapies. For instance, Allergan’s cenicriviroc is designed to address fibrosis that failed Phase III trials despite promising preclinical data. This multifactorial nature increases clinical trial durations and costs. Additionally, the lack of universally accepted biomarkers hinders progress.
Regulatory Uncertainty and Approval Delays
Regulatory uncertainty and approval delays further complicate the Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) market for novel therapies requiring extensive validation. According to BioPharma Dive, the FDA mandates long-term studies to evaluate safety and efficacy that delays approvals by up to 5 years. For example, Madrigal Pharmaceuticals’ resmetirom faced scrutiny over cardiovascular risks by prolonging its review process. Additionally, inconsistent guidelines across regions create barriers for global market entry.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
21.85% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Drug Type, Sales Channel, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional, & Country Level Analysis; Segment-Level Analysis; DROC; PESTLE Analysis; Porter’s Five Forces Analysis; Competitive Landscape; Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Genfit SA, One Way Liver S.L., BioPredictive S.A.S., Cadila Pharmaceuticals Ltd., Prometheus Laboratories, Siemens Healthineers AG, Intercept Pharmaceuticals Inc., Novartis AG, Galmed Pharmaceuticals, and Laboratory Corporation of America Holdings, and others. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Drug Type Insights
The vitamin E and Pioglitazone segment was the largest and held 35.4% of the Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) market share in 2024 due to their established efficacy in reducing liver fat and inflammation, which is making them a preferred choice for early-stage Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) management. According to a study published in The New England Journal of Medicine, combination therapy with Vitamin E and Pioglitazone achieves a 30% reduction in hepatic steatosis in patients with Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH). Key factors propelling this dominance include affordability and widespread availability. For instance, generic versions of Pioglitazone are priced up to 50% lower than novel therapies by enhancing accessibility for low-income populations. Additionally, regulatory approvals and extensive clinical validation support their adoption by reinforcing their stronghold in the market.
The ocaliva (Obeticholic Acid) segment is likely to register a CAGR of 18.7% throughout the forecast period with its ability to target fibrosis, a critical unmet need in advanced Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) cases. According to a study in The Lancet, Ocaliva reduces liver fibrosis progression by 23%, which is appealing to specialists managing severe cases. Emerging trends in personalized medicine further accelerate adoption. For example, collaborations between biotech firms and AI platforms enhance patient stratification, improving treatment outcomes. Additionally, regulatory incentives like FDA Fast Track designation expedite approvals, fostering rapid market penetration. These innovations position Ocaliva as a transformative force in the Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) market.
By Sales Channel Insights
The hospital pharmacies segment was the largest by capturing 45.6% of the Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) market share in 2024 with the critical role hospitals play in diagnosing and managing Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) for advanced cases requiring specialized care. According to the American Liver Foundation, over 60% of Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) patients receive their initial diagnosis and treatment plans in hospital settings. A major factor propelling this dominance is the integration of advanced diagnostic tools and multidisciplinary care teams. For instance, hospitals equipped with FibroScan technology offer non-invasive assessments by improving patient outcomes by 20%. Additionally, partnerships with pharmaceutical companies ensure steady supply chains by addressing logistical challenges effectively.
The online providers segment is projected to register a CAGR of 22.5% throughout the forecast period with the rising adoption of telemedicine and e-commerce platforms for healthcare products. Emerging trends in subscription-based models further accelerate adoption. For example, companies like PillPack and Capsule offer curated Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) treatment packages by enhancing convenience for chronic patients. Additionally, collaborations with insurance providers reduce costs, which is making treatments more accessible. These innovations position online providers as a key contributor to market expansion.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
North America was the top performer in the Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) market with 45.4% of share in 2024 with the increasing prevalence rates of obesity and diabetes. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), over 42% of U.S. adults are obese, which is creating immense demand for therapeutic solutions. A key factor propelling the market growth is the presence of advanced healthcare infrastructure and robust R&D investments in US. For instance, the FDA’s Fast Track designation expedites approvals for innovative therapies, fostering innovation. Additionally, awareness campaigns by organizations like the Global Liver Institute enhance early diagnosis rates by addressing unmet needs effectively.
Europe held 25.4% of the global Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) market share with countries like Germany, France, and Italy emerging as key contributors. According to Eurostat, Europe’s aging population and sedentary lifestyles contribute to rising Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) cases, with over 20% of adults affected by NAFLD. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) mandates rigorous clinical trials, ensuring safety and efficacy. A major driver is the integration of personalized medicine approaches. For example, collaborations between biotech firms and research institutions enhance drug discovery processes, reducing timelines by 30% . Additionally, government initiatives promote preventive measures, addressing lifestyle-related risk factors. These efforts position Europe as a hub for innovation and adoption in the Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) market.
Asia-Pacific Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) market growth is anticipated to grow at higher rate in the next coming years. India and China lead adoption, driven by urbanization, rising obesity rates, and increasing awareness about liver health. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), Asia-Pacific accounts for over 60% of global diabetes cases, which is creating immense demand for Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) treatments. Technological advancements further boost growth. For instance, partnerships between multinational pharma companies and local healthcare providers enhance affordability and distribution. Additionally, government initiatives like India’s NPCDCS improve awareness and access to care.
Latin America, with Brazil and Mexico as primary contributors. According to the Pan American Health Organization, rising obesity rates and sedentary lifestyles drive Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) prevalence, with over 30% of adults affected by metabolic syndrome. Government programs promoting healthy lifestyles address risk factors effectively. Key drivers include increasing investments in healthcare infrastructure and rising awareness about liver health. For example, partnerships with international organizations enhance local expertise, ensuring compliance with quality standards. These efforts position Latin America as a growing player in the Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) market.
The Middle East and Africa Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) market growth is deemed to grow with the rising government initiatives to modernize healthcare. Meanwhile, South Africa’s focus on preventive measures addresses food security challenges. A major driver is the rise of public health campaigns targeting obesity and diabetes. Additionally, collaborations with international organizations enhance local expertise by ensuring compliance with quality standards.
KEY MARKET PARTICIPANTS AND COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
Key players in the non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) market are Genfit SA, One Way Liver S.L., BioPredictive S.A.S., Cadila Pharmaceuticals Ltd., Prometheus Laboratories, Siemens Healthineers AG, Intercept Pharmaceuticals Inc., Novartis AG, Galmed Pharmaceuticals, and Laboratory Corporation of America Holdings.
The Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) market is characterized by intense competition, with established giants and emerging players vying for dominance. Key participants leverage their expertise in drug development, diagnostics, and personalized medicine to differentiate themselves. Consolidation through mergers and acquisitions is common, enabling companies to expand geographically and diversify product portfolios. For instance, Intercept Pharmaceuticals’ acquisition of a biotech startup strengthened its pipeline for fibrosis-targeting therapies.
Meanwhile, startups disrupt traditional dynamics by introducing plant-based and AI-driven solutions, appealing to health-conscious consumers. Regional players also pose a threat, capitalizing on localized expertise to challenge global leaders. This competitive landscape drives continuous innovation, benefiting end-users through improved product quality, affordability, and sustainability.
TOP 3 PLAYERS IN THE MARKET
Intercept Pharmaceuticals
Intercept Pharmaceuticals is a global leader in Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) therapeutics, known for its flagship product Ocaliva (Obeticholic Acid). The company focuses on addressing fibrosis, a critical unmet need in advanced Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) cases. Intercept collaborates with regulatory bodies to expedite approvals, ensuring timely market entry. Intercept continues to innovate by meeting evolving patient needs with a strong emphasis on clinical validation.
Genfit
Genfit specializes in developing novel therapies for Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH), leveraging its expertise in metabolic diseases. The company’s lead candidate, elafibranor, targets inflammation and fibrosis, addressing disease complexity effectively. Genfit invests heavily in R&D, ensuring robust clinical trial designs.
Madrigal Pharmaceuticals
Madrigal Pharmaceuticals excels in developing innovative Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) therapies, particularly resmetirom, which targets liver fat reduction. The company prioritizes safety and efficacy, conducting extensive long-term studies. Madrigal collaborates with healthcare providers to enhance accessibility, particularly in underserved regions.
STRATEGIES USED BY THE MARKET PLAYERS
Strategic Collaborations
Leading players prioritize strategic collaborations to enhance innovation and scalability. For example, Intercept Pharmaceuticals partnered with AI firms to develop predictive models for patient stratification, improving treatment outcomes by 25% . Such collaborations not only streamline workflows but also foster knowledge sharing, addressing regional challenges effectively.
Product Innovation
To stay ahead, companies invest heavily in R&D to develop cutting-edge solutions. Genfit, for instance, introduced novel biomarkers for early diagnosis, reducing costs by 30% . Similarly, Madrigal Pharmaceuticals developed resmetirom, achieving a 20% reduction in liver fat in clinical trials. These innovations address unmet needs while fostering customer loyalty.
Geographic Expansion
Expanding into emerging markets strengthens market presence and operational efficiency. In April 2024, Genfit launched new diagnostic clinics in sub-Saharan Africa, targeting underserved populations. This move enhances supply chain resilience and fosters inclusivity by meeting diverse customer needs globally.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THE MARKET
- In April 2024, Intercept Pharmaceuticals acquired a biotech startup specializing in fibrosis-targeting therapies. This move expanded its pipeline in advanced Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) treatments.
- In June 2024, Genfit launched a new line of diagnostic tools powered by AI, targeting early-stage Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) detection. This initiative diversified its offerings and addressed shifting consumer preferences.
- In August 2024, Madrigal Pharmaceuticals partnered with a telemedicine provider to enhance accessibility for chronic patients. This collaboration reduced treatment costs by 20% by aligning with affordability goals.
- In October 2024, Gilead Sciences announced a $1 billion investment in long-term clinical trials for selonsertib by improving safety and efficacy data. This reinforced its commitment to innovation.
- In December 2024, Novo Nordisk signed a distribution agreement with Amazon, enabling direct-to-consumer sales of its Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) treatments. This partnership expanded accessibility and tapped into the booming e-commerce segment.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the global Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) market has been segmented and sub-segmented based on drug type, sales channel, and region.
By Drug Type
- Vitamin E and Pioglitazone
- Ocaliva
- Elafibranor
- Selonsertib & Cenicriviroc
By Sales Channel
- Hospital Pharmacy
- Online Provider
- Retail Pharmacy
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What was the value of the global NASH market in 2024?
The market was valued at USD 1.87 billion in 2024.
2. What factors are driving growth in the NASH market?
Key drivers include the increasing prevalence of obesity and type 2 diabetes, rising awareness of liver diseases, and ongoing drug development efforts.
3. What regions are expected to see the highest growth in the NASH market?
North America currently leads due to strong R&D and diagnostics infrastructure, but Asia Pacific is expected to witness significant growth due to lifestyle changes and rising disease burden.
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2500
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]
