North America Biogas Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report By Application (Electricity Generation, Biofuel Production, Heat Generation), Feedstock (Livestock Manure, Sewage, Food Waste, Crop Residues, Energy Crops), and Country (United States, Canada, Mexico, Rest of North America) – Industry Analysis From 2025 to 2033.
North America Biogas Market Size
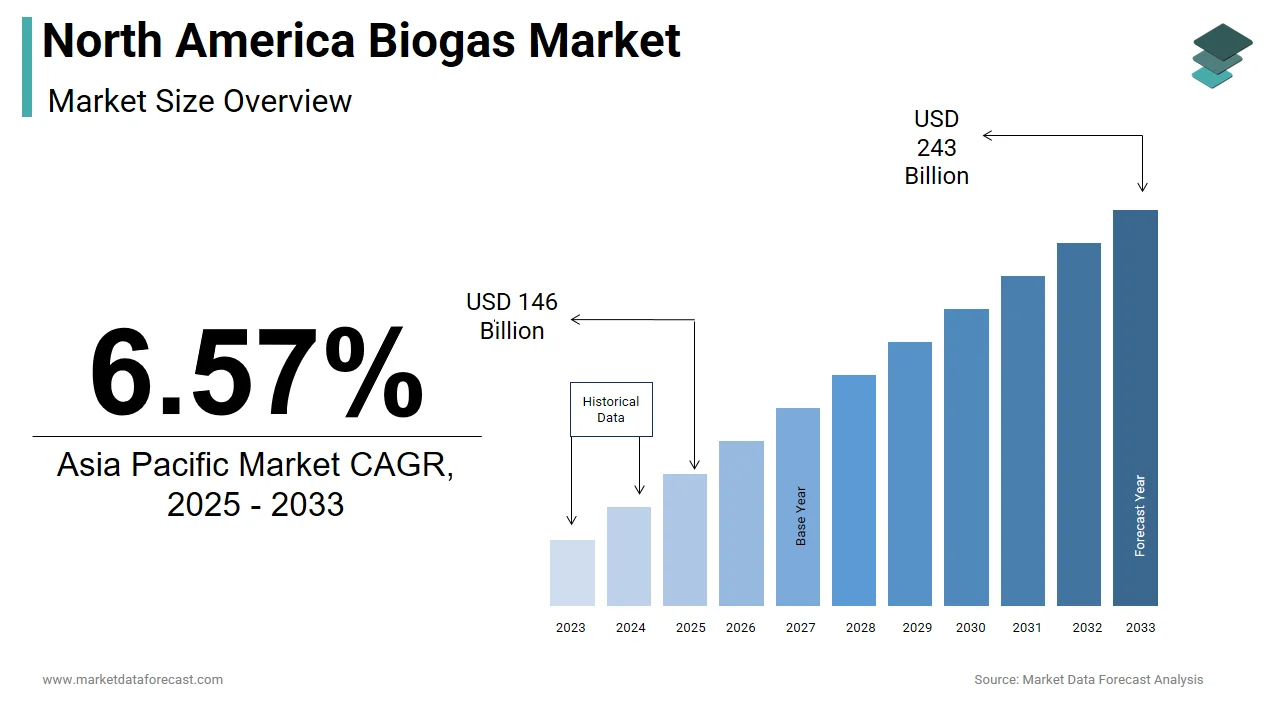
The size of the North America biogas market was worth USD 137.32 billion in 2024. The North America market is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 6.57% from 2025 to 2033 and be worth USD 243 billion by 2033 from USD 146 billion in 2025.
The North America biogas market refers to the production, processing, and utilization of biogas—a renewable energy source generated through the anaerobic digestion of organic materials such as agricultural waste, food scraps, sewage sludge, and livestock manure. Biogas primarily consists of methane and carbon dioxide, which can be used for electricity generation, heating, transportation fuel (in the form of biomethane), and grid injection after purification. The region’s increasing focus on decarbonization, coupled with growing investments in circular economy models, has positioned biogas as a strategic alternative to fossil fuels. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, biogas systems not only provide clean energy but also help mitigate greenhouse gas emissions by capturing methane that would otherwise be released into the atmosphere. As per Environment and Climate Change Canada, over 250 biogas facilities were operational across Canada in 2023, reflecting rising momentum in the sector. In the United States, states like California, New York, and Wisconsin have implemented targeted incentive programs to promote farm-based digesters and landfill gas-to-energy projects.
MARKET DRIVERS
Rising Emphasis on Renewable Energy and Decarbonization Policies
A significant driver of the North America biogas market is the growing emphasis on transitioning toward renewable energy sources and reducing carbon emissions from traditional fossil fuels. Governments at both the federal and state levels in the U.S. and Canada have introduced policies aimed at promoting cleaner energy alternatives. For instance, the Canadian government’s Pan-Canadian Framework on Clean Growth and Climate Change includes specific targets for reducing methane emissions from agriculture and waste sectors—key feedstock sources for biogas. Similarly, in the U.S., the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) of 2022 offers tax credits and financial incentives for biogas project developers under its clean energy provisions. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), methane capture through biogas systems can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 95% compared to conventional waste management practices. Also, the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) has launched the Partnerships for Climate-Smart Commodities initiative, allocating over USD 3 billion to support biogas infrastructure on farms. These policy-driven interventions are encouraging private investment and accelerating the deployment of biogas plants, particularly in regions with high agricultural activity and landfill operations.
Expansion of Organic Waste Diversion and Circular Economy Initiatives
Another key factor driving the North America biogas market is the increasing adoption of organic waste diversion strategies and circular economy principles aimed at converting waste into valuable resources. Municipalities and industries across the continent are implementing regulations to divert food waste, yard trimmings, and other organic materials from landfills to anaerobic digestion facilities. In California, Senate Bill 1383 mandates a 75% reduction in organic waste disposal by 2025, directly stimulating the growth of biogas production. As per the California Air Resources Board, this regulation is expected to result in the establishment of over 100 new biogas facilities by 2030. Meanwhile, in Canada, provinces such as Ontario and Quebec have introduced organics recycling mandates that require municipalities to collect and process organic waste separately. According to a 2023 report by the Institute for Local Self-Reliance, cities like Toronto and Montreal have significantly expanded their curbside organic waste collection programs, enhancing feedstock availability for biogas producers. Moreover, major corporations including Kroger, Starbucks, and Unilever have committed to zero-waste goals, partnering with biogas companies to convert food waste into energy and fertilizer.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Capital Investment and Long Payback Periods
One of the primary constraints affecting the North America biogas market is the substantial capital expenditure required for setting up anaerobic digestion facilities and upgrading biogas to biomethane. Constructing a commercial-scale biogas plant involves significant upfront costs related to digester tanks, gas cleaning equipment, pipeline connections, and compliance with environmental regulations. Similarly, municipal wastewater treatment plants seeking to implement biogas recovery systems often face multimillion-dollar investments. While long-term savings and revenue from energy sales or renewable identification numbers (RINs) exist, the payback period can extend beyond seven to ten years, deterring smaller investors and cooperatives from entering the market. In addition, financing options remain limited, especially for rural and independent operators who may lack access to credit or collateral. As reported by the USDA, less number of eligible agricultural biogas projects receive full funding due to budgetary constraints and competitive grant allocations.
Lack of Standardized Regulations and Inconsistent Policy Support
Regulatory inconsistency across jurisdictions poses a significant challenge to the growth of the North America biogas market. Unlike mature renewable energy sectors such as wind and solar, biogas faces fragmented regulatory frameworks that vary widely between U.S. states and Canadian provinces. Some regions offer favorable incentives, while others lack clear interconnection standards or certification processes for injecting biomethane into natural gas pipelines. According to the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), only some U.S. states have established comprehensive biomethane injection guidelines, creating uncertainty for developers seeking to expand beyond pilot projects. Similarly, in Canada, while provinces like British Columbia and Quebec have robust green gas mandates, others have yet to define formal procurement mechanisms for renewable natural gas (RNG). The absence of uniform technical specifications and grid access rules increases project development risks and complicates investor confidence. Furthermore, policy reversals or changes in administration priorities can disrupt long-term planning, as seen when certain U.S. state-level renewable energy subsidies faced budget cuts in recent years.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Integration of Biogas with Transportation Fuel Markets
A major opportunity emerging in the North America biogas market is its increasing use as a clean transportation fuel, particularly in the heavy-duty trucking and public transit sectors. As governments push for low-carbon mobility solutions, biomethane—upgraded from raw biogas—has gained prominence as a viable alternative to diesel. According to the International Council on Clean Transportation (ICCT), biomethane-powered trucks can achieve lifecycle greenhouse gas reductions of up to 400% compared to conventional diesel vehicles when sourced from dairy and landfill waste. In response, fleet operators and logistics companies are investing heavily in RNG-fueled vehicle fleets. For example, UPS has committed to purchasing 170 million gallon equivalents of RNG through 2026, while Clean Energy Fuels operates more than 50 renewable natural gas stations across the U.S. In Canada, BC Transit and Metro Vancouver have adopted RNG for public buses, supported by provincial mandates requiring 15% renewable content in transportation fuels by 2030. The expansion of RNG refueling infrastructure, combined with federal and state-level incentives such as California’s Low Carbon Fuel Standard (LCFS), is making biogas an increasingly attractive option for decarbonizing transport.
Utilization of Biogas in Industrial Heat and Power Applications
Industrial applications represent another promising growth area for the North America biogas market, particularly in heat and power generation for manufacturing, food processing, and greenhouse cultivation. Many large-scale industries are turning to biogas as a reliable and locally sourced energy alternative to fossil fuels, driven by corporate sustainability goals and rising energy costs. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, anaerobic digestion systems installed at food processing plants can supply a significant portion of onsite energy needs, reducing dependency on grid electricity and lowering carbon footprints. Companies like General Mills and Tyson Foods have partnered with biogas developers to convert organic waste from their operations into usable energy. Also, agricultural co-operatives are leveraging biogas for greenhouse heating, as demonstrated by large-scale projects in British Columbia and Ontario. With increasing pressure to meet net-zero targets and comply with emissions regulations, industries are actively exploring biogas as a scalable, decentralized energy solution.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Feedstock Availability and Seasonal Variability
A critical challenge facing the North America biogas market is the inconsistent availability and seasonal fluctuations of organic feedstock needed for continuous biogas production. Anaerobic digestion relies heavily on a stable supply of agricultural residues, food waste, and manure, which can vary based on farming cycles, weather conditions, and waste collection efficiency. According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), manure availability from dairy farms—among the most common feedstocks—can drop by up to 30% during dry seasons or periods of reduced livestock activity. Similarly, fluctuations in municipal organic waste collection due to holidays, supply chain disruptions, or changes in consumer behavior affect biogas plant operations. In colder regions like Canada, winter months often result in lower biogas yields due to slower microbial activity in digesters. A study found that biogas output in some provinces declined during peak winter months. To address these challenges, biogas producers are exploring co-digestion strategies by blending multiple feedstocks; however, securing diverse and consistent inputs remains a logistical and economic hurdle.
Technical Complexity and Maintenance Requirements of Biogas Systems
Operating and maintaining biogas systems presents a significant technical challenge that hampers broader adoption across North America. Unlike conventional energy systems, anaerobic digesters require precise control of temperature, pH levels, and microbial balance to ensure optimal performance. Any imbalance or contamination in the feedstock can lead to process inhibition, reduced gas yield, or even system failure. According to a 2023 report by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), approximately 25% of biogas installations in the U.S. experience operational downtime due to poor maintenance practices or insufficient operator expertise. In rural areas, where many farm-based digesters are located, access to skilled technicians and spare parts can be limited, increasing repair delays and operational costs. Also, the need for regular desulfurization, solids removal, and equipment inspections adds to the complexity of managing biogas facilities. In Canada, the Ontario Biogas Association noted that small-scale biogas operators often struggle with high maintenance expenses and a shortage of trained personnel. Despite technological advancements, the operational intensity of biogas systems remains a deterrent for potential adopters, particularly those without prior experience in energy management.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
Segments Covered |
By Application, Feedstock, and Region. |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional and Country-Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, Drivers, Restraints, Opportunities, Challenges; PESTLE Analysis; Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Countries Covered |
United States, Canada, Mexico, and the Rest of North America. |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Engie SA, Bekon GmbH, DMT International, EnviTec Biogas AG, and AEV Energy GmbH. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Application Insights

Electricity generation is the largest application segment in the North America biogas market by accounting for 47.3% of total market revenue in 2024. This dominance is due to the increasing integration of renewable energy into national grids and the growing adoption of decentralized power generation models. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, the number of biogas-powered electricity facilities across the United States in 2023 was around 2251, with landfill gas and agricultural digesters contributing significantly to this capacity. In Canada, provinces like Ontario and Quebec have prioritized biogas-based power projects under their green energy mandates. A key driver behind this segment’s leadership is the support from federal and state-level incentive programs. Additionally, utilities are increasingly purchasing renewable energy credits (RECs) linked to biogas-derived electricity. The EPA’s AgSTAR program has also played a pivotal role in promoting on-farm biogas systems that generate electricity while reducing methane emissions.
Biofuel production is emerging as the fastest-growing application in the North America biogas market, projected to grow at a CAGR of 12.4%. This rapid expansion is primarily driven by the transportation sector’s shift toward low-carbon fuels and supportive regulatory frameworks encouraging the use of renewable natural gas (RNG). In the U.S., California’s Low Carbon Fuel Standard (LCFS) has been instrumental in stimulating demand for RNG as vehicle fuel, with companies like UPS and Waste Management investing heavily in RNG-powered fleets. As per the California Air Resources Board, over 90 million gasoline gallon equivalents of RNG were used in transport in 2023. Similarly, Canadian provinces such as British Columbia and Alberta have introduced renewable content mandates for transportation fuels, accelerating biofuel adoption. Major oil and gas companies including Shell and Enbridge have entered the RNG market, further boosting investment.
By Feedstock Insights
Livestock manure is the largest feedstock segment in the North America biogas market by holding a 39.8% of the total market share in 2024. This influence is attributed to the vast availability of animal waste, particularly from the dairy and beef cattle industries, which serve as consistent and high-methane-yield sources for anaerobic digestion. The widespread deployment of farm-based digesters has been a major catalyst for this segment's growth. In Wisconsin, New York, and Vermont, numerous dairy farms have installed anaerobic digestion systems supported by USDA grants and state-level subsidies. As indicated by the American Biogas Council, a large number of agricultural biogas systems were operational in the U.S., most of which relied primarily on livestock manure. In Canada, the province of Quebec has actively promoted manure-to-energy projects through its Programme d’Énergie Renouvelable, leading to increased RNG production. Besides, environmental regulations aimed at curbing methane emissions from concentrated animal feeding operations (CAFOs) have incentivized manure capture and conversion into biogas.
Food waste is the fastest-growing feedstock segment in the North America biogas market, anticipated to expand at a CAGR of 13.8%. This accelerated growth is driven by increasing municipal and commercial efforts to divert organic waste from landfills, where it contributes significantly to methane emissions. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), food waste accounts for nearly 24% of landfill contents in the U.S. , making it a priority area for waste valorization strategies. Several cities across North America have implemented mandatory organic waste diversion policies to curb landfill usage and promote biogas generation. For example, California’s Senate Bill 1383 mandates a 75% reduction in organic waste disposal by 2025, directly stimulating investments in food waste-fed biogas facilities. In Canada, Toronto and Montreal have expanded curbside organic collection programs, supplying steady volumes of food scraps to regional biogas plants. Furthermore, partnerships between grocery chains, restaurants, and biogas producers have enhanced feedstock supply consistency.
COUNTRY-WISE ANALYSIS
The United States held the dominant position in the North America biogas market by capturing an estimated 82.7% of regional market value in 2024. This lead position is attributed to a combination of robust policy support, abundant organic feedstock availability, and extensive infrastructure development across multiple sectors, including agriculture, wastewater treatment, and landfill gas utilization. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, more than 2,200 biogas systems were either operational or under development in 2023, including over 250 farm-based digesters and 1,000 landfill gas recovery sites. Federal initiatives such as the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) and the Rural Energy for America Program (REAP) have provided significant financial incentives for biogas developers. Besides, state-level programs like California’s Low Carbon Fuel Standard (LCFS) and New York’s Climate Leadership and Community Protection Act (CLCPA) have spurred investment in renewable natural gas (RNG) production. As per the American Biogas Council, the U.S. biogas sector generated over 17 billion kWh of electricity and displaced nearly 1.2 billion gallons of diesel equivalent in transportation fuels in 2023.
Canada is contributing a notable share of the total market value in 2024. The country’s biogas industry is experiencing steady growth due to increasing environmental awareness, favorable government policies, and growing municipal and agricultural participation. Provincial governments have played a crucial role in fostering biogas development. Ontario, Quebec, and British Columbia have implemented aggressive renewable gas mandates and funding programs to encourage biomethane injection into natural gas pipelines. The Province of Quebec, for instance, requires utilities to source a certain percentage of their natural gas supply from renewable sources by 2030, as outlined by Régie de l’énergie du Québec. Moreover, Environment and Climate Change Canada has emphasized biogas as a key tool for achieving national methane reduction targets under the Global Methane Pledge.
The remaining North American countries are emerging markets with high growth potential. Although still in the early stages of development, these markets are showing promising signs of growth due to increasing environmental concerns, urban waste management challenges, and emerging policy frameworks supporting renewable energy. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), Mexico had approximately 40 operational biogas plants in 2023, primarily serving the agro-industrial and wastewater treatment sectors. Mexico’s Ministry of Energy (SENER) has included biogas in its National Development Plan, aiming to increase renewable gas penetration in the energy matrix. Several large-scale projects are underway, including the development of biogas-to-power installations at sugarcane mills and livestock farms. In addition, the Mexican government has introduced clean energy certificates (CELs) to incentivize biogas generation. Meanwhile, the Caribbean region is exploring small-scale biogas solutions to improve energy security and reduce reliance on imported fossil fuels. As per a 2024 World Bank report, Jamaica and Trinidad and Tobago have initiated pilot programs to convert food and agricultural waste into biogas for rural electrification and transport applications.
MARKET KEY PLAYERS
Companies playing a dominant role in the North America biogas market profiled in this report are Engie SA, Bekon GmbH, DMT International, EnviTec Biogas AG, and AEV Energy GmbH.
TOP LEADING PLAYERS IN THE MARKET
One of the leading players in the North America biogas market is Waste Management, Inc., a major environmental services provider in the U.S. The company plays a pivotal role in landfill gas-to-energy projects, converting methane emissions from waste into usable energy. Waste Management has been instrumental in developing and operating biogas recovery systems at its landfill sites, contributing significantly to renewable fuel supply chains and corporate sustainability goals.
Another key player is A Better Routeplanner (ABR) , which, while primarily known for route optimization software, has made strategic moves to integrate biogas fueling infrastructure into its logistics solutions. ABR supports fleet operators transitioning to renewable natural gas (RNG), helping companies identify RNG refueling stations across North America and optimize transportation routes accordingly.
Enbridge Inc., a Canadian energy infrastructure giant, has emerged as a major force in the biogas sector by investing heavily in RNG production and distribution. Enbridge works closely with agricultural and municipal partners to develop biogas upgrading facilities and inject biomethane into existing natural gas pipelines. The company’s initiatives support large-scale decarbonization efforts in both residential and commercial sectors, positioning it as a key contributor to the growth of the North American biogas market.
TOP STRATEGIES USED BY KEY MARKET PARTICIPANTS
One of the primary strategies employed by key players in the North America biogas market is strategic partnerships with agricultural, municipal, and industrial stakeholders. By collaborating with waste generators and landowners, companies ensure a consistent supply of organic feedstock, which is essential for continuous biogas production. These alliances also help in securing long-term off-take agreements for renewable energy or fuel.
Another critical approach is expanding RNG processing and pipeline injection capabilities. Leading firms are investing in upgrading facilities that transform raw biogas into pipeline-quality biomethane, allowing seamless integration into existing natural gas networks and expanding market reach beyond localized operations.
Lastly, leveraging government incentives and regulatory frameworks is a key tactic used by top participants. Companies actively engage with policymakers and utilize federal and state-level grants, tax credits, and low-carbon fuel programs to finance new projects and enhance profitability, ensuring sustainable growth in a competitive landscape.
COMPETITION OVERVIEW
The competition in the North America biogas market is characterized by a mix of established energy firms, specialized biogas developers, and emerging startups striving to capture a growing share of the renewable energy landscape. While traditional utility and waste management companies leverage their existing infrastructure and scale to dominate the space, new entrants bring innovative technologies and niche applications that challenge conventional models. The market is witnessing increasing collaboration between industry players, research institutions, and public agencies to accelerate technology deployment and streamline regulatory compliance. With rising demand for renewable fuels, especially in the transport and power generation sectors, companies are differentiating themselves through advanced feedstock management, RNG purification techniques, and digital monitoring tools. Additionally, vertical integration strategies—where firms control everything from waste sourcing to energy distribution—are becoming more prevalent. This evolving competitive environment fosters innovation, enhances operational efficiency, and drives broader adoption of biogas as a viable alternative to fossil-based energy sources across the region.
RECENT MARKET DEVELOPMENTS
- In February 2024, Enbridge signed a long-term agreement with a major Ontario dairy cooperative to develop an anaerobic digestion facility that will convert livestock manure into renewable natural gas (RNG) for grid injection, strengthening Enbridge’s position in the Canadian biogas space.
- In May 2024, Clean Energy Fuels announced the expansion of its Redeem™ RNG fueling station network across several U.S. states, aiming to provide greater accessibility for truck fleets and reinforcing its leadership in the transportation-focused biogas sector.
- In July 2024, Brightmark acquired a biogas project development firm based in the Midwest, enhancing its capabilities in farm-based digester deployment and accelerating its ability to deliver integrated biogas solutions across rural America.
- In September 2024, Waste Management launched a pilot program to co-digest food waste with landfill gas at select sites, aiming to boost RNG yields and expand its renewable energy portfolio while aligning with state-level organics diversion mandates.
- In November 2024, CRB Group partnered with a European biogas equipment manufacturer to introduce modular digester technology tailored for small- to mid-sized farms, improving scalability and lowering entry barriers for independent agricultural producers seeking to adopt biogas systems.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the North America biogas market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Application
- Electricity Generation
- Biofuel Production
- Heat Generation
By Feedstock
- Livestock Manure
- Sewage
- Food Waste
- Crop Residues
- Energy Crops
By Country
- United States
- Canada
- Mexico
- Rest of North America
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Which country dominates the North America Biogas Market?
The United States is the regional leader due to a vast network of digesters and supportive policies, followed by Canada’s focus on agricultural and industrial biogas, while Mexico’s market is emerging
2. What are the main applications of biogas in North America?
Biogas is primarily used for electricity generation, vehicle fuel (biofuel), heat production, and as renewable natural gas (RNG) for grid injection
3. What feedstocks are most commonly used in the North America Biogas Market?
Key feedstocks include livestock manure, municipal solid waste, food waste, crop residues, sewage, and energy crops
4. How do government policies impact the North America Biogas Market?
Policies such as the Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) and state-level renewable portfolio standards incentivize biogas production and integration into energy systems
5. What role does biogas play in reducing greenhouse gas emissions in North America?
Biogas systems capture methane from waste, reducing emissions and providing a renewable alternative to fossil fuels, supporting climate goals
6. What are the major challenges facing the North America Biogas Market?
Challenges include high initial investment, limited public awareness, regulatory complexity, and competition from low-cost fossil fuels
7. What technological innovations are shaping the North America Biogas Market?
Innovations include advanced anaerobic digestion, improved gas purification, and integration with smart energy grids
8. What are the future trends and opportunities in the North America Biogas Market?
Trends include growth in RNG facilities, integration with existing gas infrastructure, and expanding biogas use in agriculture, industry, and transportation
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from
$ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: sales@marketdataforecast.com