North America Monoclonal Antibodies Market Research Report – Segmented By Source (Humanized , Human ), Indication, End-User, Application, Country (US, Canada and Rest of North America) - Industry Analysis (2025 to 2033)
North America Monoclonal Antibodies Market Size
The North America Monoclonal Antibodies Market was valued at USD 16.91 billion in 2024. The North America Monoclonal Antibodies Market is expected to have 6.24% CAGR from 2024 to 2033 and be worth USD 29.36 billion by 2033 from USD 17.97 billion in 2025.
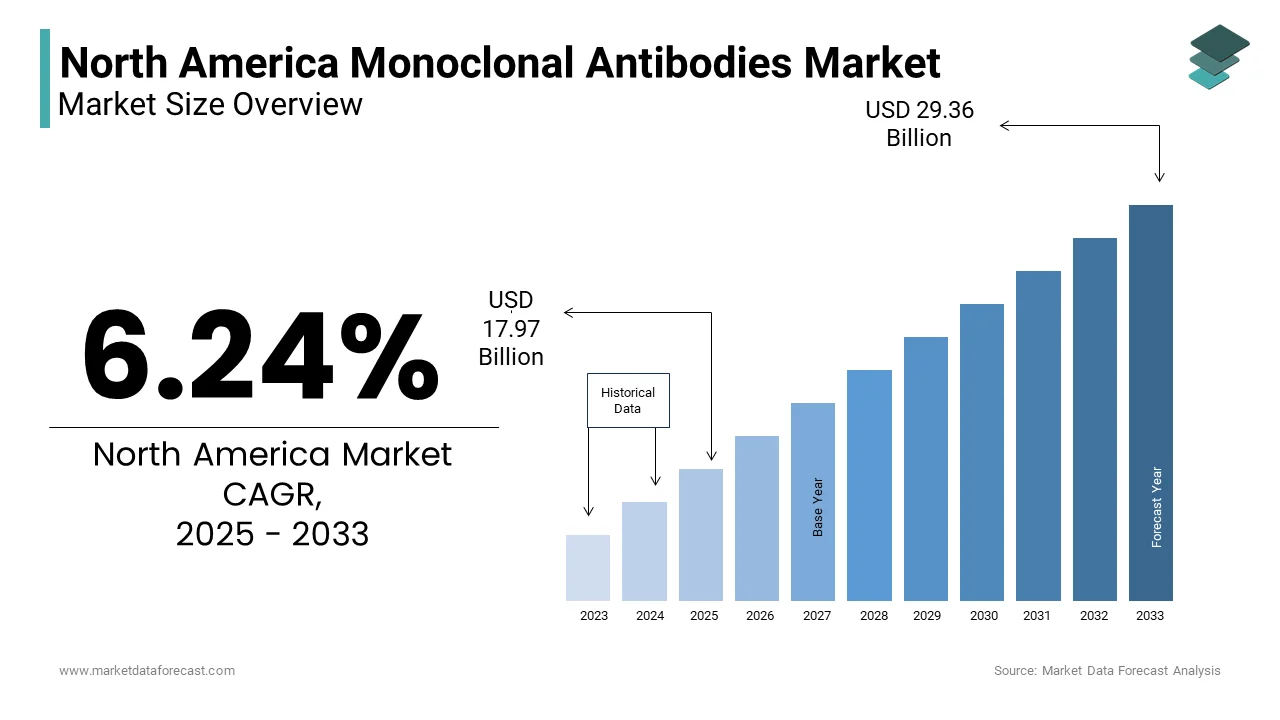
The North America monoclonal antibodies market represents a critical segment of the biopharmaceutical industry, involving laboratory-produced molecules engineered to mimic the immune system’s ability to fight disease. These therapeutic agents are widely used in the treatment of oncology, autoimmune disorders, infectious diseases, and inflammatory conditions. With their high specificity and targeted mechanisms of action, monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) have become integral to modern medicine, particularly in personalized and precision therapies.
According to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), over 100 monoclonal antibody-based drugs had been approved for clinical use in the United States by the end of 2023, with more than 600 in various stages of development globally. In Canada, Health Canada reported an increase in the number of mAb biosimilars under review, reflecting growing interest in cost-effective alternatives to branded biologics. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) emphasized the expanding role of monoclonal antibodies in addressing unmet medical needs, particularly in oncology and immunotherapy applications.
Additionally, advancements in antibody engineering, such as bispecific antibodies and antibody-drug conjugates, have broadened the scope of therapeutic applications. As per the Biotechnology Innovation Organization, the U.S. remains the global leader in biopharmaceutical R&D investments, accounting for nearly 40% of all new monoclonal antibody drug approvals worldwide.
MARKET DRIVERS
Rising Prevalence of Chronic Diseases
One of the primary drivers fueling the North America monoclonal antibodies market is the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases such as cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and autoimmune disorders. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), chronic diseases account for approximately 70% of all deaths in the United States, making them the leading cause of mortality and disability in the region. A key factor behind this growth is the aging population in both the U.S. and Canada, which is more susceptible to chronic illnesses requiring long-term management. The National Institute on Aging reported that the proportion of Americans aged 65 and older increased significantly in 2023, contributing to higher incidence rates of age-related cancers and degenerative conditions. Additionally, patient registries maintained by the American Cancer Society indicated that over 1.9 million new cancer cases were diagnosed in the U.S. in 2023 alone, reinforcing the need for advanced treatment options.
Expansion of Biosimilars and Cost-Reduction Initiatives
Another major driver influencing the North America monoclonal antibodies market is the rapid expansion of biosimilars, which offer cost-effective alternatives to expensive originator biologics while maintaining comparable safety and efficacy profiles. This trend is being supported by regulatory reforms aimed at accelerating biosimilar approval pathways and encouraging market competition. A 2023 report published by the RAND Corporation found that the introduction of biosimilars had led to price reductions of up to 35% for certain mAb treatments, which is making them more accessible to a broader patient base. In Canada, Health Canada and the Patented Medicine Prices Review Board (PMPRB) have implemented pricing reforms to promote the adoption of biosimilars, resulting in increased prescriptions and hospital procurement. Additionally, payer organizations and insurers have launched educational campaigns to build physician and patient confidence in biosimilar usage.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Development and Manufacturing Costs
A significant restraint affecting the North America monoclonal antibodies market is the high cost associated with research, development, and large-scale manufacturing of these complex biologic therapeutics. This financial burden limits the entry of smaller biotech firms and constrains investment in novel therapeutic targets. Additionally, the production process for monoclonal antibodies is highly intricate, involving mammalian cell culture, purification, and stringent quality control measures that contribute to elevated manufacturing expenses. In Canada, the Canadian Generic Pharmaceutical Association noted that the complexity of biosimilar development also posed challenges in achieving cost parity with originator drugs, despite regulatory incentives.
Stringent Regulatory Requirements and Approval Delays
Another critical constraint impacting the North America monoclonal antibodies market is the presence of stringent regulatory frameworks and lengthy approval processes imposed by health authorities such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and Health Canada. According to the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER), the average time required for the approval of a new monoclonal antibody therapy in the U.S. extends beyond seven years, including extensive clinical trial phases and post-marketing surveillance.
These prolonged timelines pose a challenge for manufacturers aiming to introduce novel therapies in a timely manner. A 2023 analysis by the Duke Margolis Center for Health Policy found that delays in regulatory submissions and inspections contributed to an average lag of 18 months between European and U.S. market entries for several monoclonal antibody products. Additionally, evolving guidelines around biosimilar interchangeability and analytical comparability testing have added layers of complexity to product development strategies. In Canada, Health Canada’s implementation of stricter biosimilar evaluation criteria in early 2023 further extended review durations for new entrants.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Advancements in Immuno-Oncology and Targeted Therapies
An emerging opportunity in the North America monoclonal antibodies market is the rapid progress in immuno-oncology and targeted cancer therapies, where monoclonal antibodies play a pivotal role in enhancing immune response and delivering cytotoxic agents directly to malignant cells. This trend is being driven by breakthroughs in antibody engineering, including the development of bispecific T-cell engagers (BiTEs) and antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), which improve treatment precision and reduce off-target effects. Additionally, academic and industry collaborations such as those facilitated by the Parker Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy are accelerating the discovery of novel checkpoint inhibitors and adoptive cell therapies incorporating monoclonal antibodies.
Increased Government Funding and Public-Private Collaborations
Another significant opportunity shaping the North America monoclonal antibodies market is the growing influx of government funding and public-private partnerships aimed at advancing biopharmaceutical innovation and pandemic preparedness. The Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) announced in 2023 a multi-year initiative to bolster domestic manufacturing capabilities for monoclonal antibodies, ensuring supply chain resilience and faster deployment during future health emergencies. In Canada, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) allocated over $150 million to support biologics research and commercialization efforts, strengthening the regional biopharma ecosystem.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Complex Manufacturing Infrastructure and Supply Chain Constraints
A pressing challenge currently facing the North America monoclonal antibodies market is the complexity of manufacturing infrastructure and the limitations in scaling production to meet growing demand. Moreover, supply chain disruptions—particularly in the availability of raw materials such as cell culture media components and single-use bioprocessing equipment—have created bottlenecks in production timelines. In Canada, the National Research Council’s Industrial Research Assistance Program (NRC-IRAP) noted that small and mid-sized biotech firms faced particular difficulties in securing reliable sourcing channels for critical inputs.
Reimbursement Barriers and Pricing Pressures
Another significant challenge impeding the growth of the North America monoclonal antibodies market is the increasing pressure on pricing and reimbursement policies, particularly within publicly funded healthcare systems and insurance networks. In response, managed entry agreements and value-based pricing models are becoming more prevalent, especially in the U.S. Medicare and Medicaid programs. A 2023 study published in Health Affairs found that nearly half of newly launched monoclonal antibody therapies faced restricted formulary placement due to cost concerns, limiting patient access.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
6.24 % |
|
Segments Covered |
By Source , Indication, End-User, Application and Country. |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis; DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter's Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Country Covered |
The U.S., Canada and Rest of North America |
|
Market Leader Profiled |
GlaxoSmithKline plc, Novartis AG, Pfizer Inc., Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Source Insights
The humanized monoclonal antibodies segment was the largest and held 45.3% of the North America monoclonal antibodies market share in 2024. According to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), over 60% of newly approved monoclonal antibody therapies between 2020 and 2023 were classified as humanized, reflecting a strong industry shift away from murine and chimeric sources. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) reported that humanized antibodies demonstrate significantly lower risk of immune rejection compared to earlier generations, which is allowing for longer treatment durations and better clinical outcomes. Additionally, advancements in recombinant DNA technology and phage display platforms have enabled more precise engineering of humanized antibodies, enhancing their binding specificity and therapeutic efficacy.
The human monoclonal antibodies segment is emerging with the a CAGR of 11.2% throughout the forecast period. A primary driver behind this rapid growth is the increasing adoption of human monoclonal antibodies in novel therapeutics targeting chronic and rare diseases. According to the Biotechnology Innovation Organization, the number of human monoclonal antibody-based drugs under clinical development increased by 25% in 2023 compared to the previous year, with a significant portion focused on oncology and neurology applications. In Canada, Health Canada reported a surge in regulatory submissions for human-derived mAbs, particularly in immuno-oncology and Alzheimer’s disease treatment pipelines.
By Indication Insights
The cancer segment was the largest and held 48.6% of the North America monoclonal antibodies market share in 2024. This dominance is attributed to the high incidence of malignancies such as breast, lung, colorectal, and hematological cancers, which require targeted and often long-term biological interventions. One of the key drivers behind this segment’s dominance is the integration of monoclonal antibodies into standard-of-care regimens, including checkpoint inhibitors, antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), and bispecific T-cell engagers (BiTEs). The National Cancer Institute emphasized that monoclonal antibodies now represent over 60% of all biologic treatments used in oncology, with drugs like Herceptin, Keytruda, and Enhertu playing pivotal roles in both solid tumor and blood cancer management. Additionally, rising government funding and private sector investments are fueling innovation in cancer immunotherapy. A 2023 white paper published by the Parker Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy noted that over $1.2 billion was allocated to monoclonal antibody research in oncology during the past fiscal year.
The autoimmune diseases segment is likely to grow with a CAGR of 10.8% in the next coming years. According to the American Autoimmune Related Diseases Association (AARDA), over 50 million Americans suffer from autoimmune disorders, making them one of the leading causes of chronic illness in the United States. A 2023 study published in Arthritis & Rheumatology found that biologic therapies including TNF-alpha inhibitors like Humira and IL-17 inhibitors were prescribed in nearly 30% of moderate-to-severe rheumatoid arthritis cases, demonstrating strong clinical adoption.
In Canada, the Canadian Institute for Health Information (CIHI) reported a 12% increase in monoclonal antibody prescriptions for autoimmune indications in 2023, supported by expanded public reimbursement policies and biosimilar entry into the market. Additionally, the growing recognition of personalized medicine approaches has led to the development of newer mAbs tailored to individual biomarker profiles, further driving demand.
By End-User Insights
The hospitals and clinics segment held a dominant share of the North America monoclonal antibodies market in 2024. According to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), over 3 million monoclonal antibody infusions were administered in U.S. hospitals and outpatient facilities in 2023, covering indications ranging from cancer to autoimmune disorders. The high cost and complexity of these therapies necessitate professional oversight, making hospitals and specialty clinics the preferred setting for treatment delivery.
The research institutes segment is likely to grow with a CAGR of 12.4% from 2025 to 2033. According to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), federal funding for monoclonal antibody research exceeded $2.5 billion in fiscal year 2023, supporting initiatives in vaccine development, cancer immunotherapy, and neurodegenerative disease studies. Additionally, the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology (FASEB) reported a 20% increase in grant allocations for antibody engineering and discovery projects, reflecting heightened scientific interest in this field.
By Application Insights
The medical application segment dominated the North America monoclonal antibodies market with largest share in 2024. According to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), over 100 monoclonal antibody-based drugs had been approved for clinical use by the end of 2023, with more than 600 in various stages of clinical development. These therapies are being deployed across hospitals, specialty clinics, and home infusion services, emphasizing their critical role in modern healthcare. In Canada, Health Canada reported a 12% increase in the prescription of monoclonal antibodies for chronic disease treatment in 2023, supported by expanded insurance coverage and biosimilar adoption. A 2023 white paper published by CADTH found that over 70% of surveyed physicians considered monoclonal antibodies essential for managing complex conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and metastatic cancers.
The experimental segment is lucratively to grow with a CAGR of 13.1% during the forecast period. A primary driver behind this trend is the surge in academic and corporate investment in monoclonal antibody discovery platforms, including phage display, transgenic mice, and AI-assisted antibody engineering. In Canada, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) reported a 15% increase in monoclonal antibody-related publications and pilot studies in 2023, signaling robust academic engagement. A 2023 white paper from the Ontario Institute for Cancer Research found that experimental mAb therapies demonstrated promising results in early-phase trials for glioblastoma and pancreatic cancer.
COUNTRY LEVEL ANALYSIS
The United States was the top performer in the North America monoclonal antibodies market by accounting for 82.3% of share in 2024. According to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), over 100 monoclonal antibody therapies had received approval by the end of 2023, with an additional 600 in various phases of clinical development. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) reported that federal funding for monoclonal antibody research exceeded $2.5 billion in fiscal year 2023, supporting advancements in immuno-oncology, neurology, and infectious disease prevention. Additionally, the presence of major biopharma players such as Roche (Genentech), Amgen, and AbbVie ensures a robust ecosystem of drug development, manufacturing, and distribution.
Canada ranked second with 14.3% of the North America monoclonal antibodies market share in 2024. One of the key drivers of market expansion is the implementation of national biosimilars uptake strategies by provinces such as British Columbia, Quebec, and Ontario, aimed at reducing treatment costs while maintaining therapeutic efficacy. Academic institutions like the University of Toronto and McMaster University have also strengthened partnerships with global biopharma firms to advance therapeutic discovery.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS AND COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
Some of the major companies dominating the market by their products include GlaxoSmithKline plc, Novartis AG, Pfizer Inc., Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Eli Lilly and Company, Seattle Genetics, Bristol-Myers Squibb, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., and Biogen Inc.
The competition in the North America monoclonal antibodies market is intense and highly dynamic, driven by a mix of established pharmaceutical giants, emerging biotech firms, and biosimilar developers. Leading multinational corporations such as Roche, Johnson & Johnson, and Amgen dominate with deep expertise, extensive product portfolios, and robust distribution networks. These companies continuously invest in next-generation antibody technologies, including bispecifics, ADCs, and Fc-engineered variants, to stay ahead in an evolving landscape.
At the same time, biosimilar manufacturers like Samsung Bioepis, Sandoz, and Pfizer’s Hospira unit are reshaping the market by offering cost-effective alternatives that challenge originator brands. Their growing presence is influencing pricing strategies and reimbursement policies in the U.S. and Canada. Additionally, smaller biotech firms are carving out niche positions by focusing on novel targets, innovative delivery mechanisms, and platform-based discovery methods that allow for faster development cycles.
Contract development and manufacturing organizations (CDMOs) are also playing a critical role by enabling smaller players to scale up production without heavy capital investment. As demand for monoclonal antibodies expands across therapeutic areas, companies are differentiating themselves through technological innovation, adaptive regulatory engagement, and strategic lifecycle
Top Players in the Market
Roche (Genentech)
Roche, through its subsidiary Genentech, is a global leader in monoclonal antibody development and commercialization. In North America, Roche plays a pivotal role in oncology and autoimmune disease treatment with flagship products like Herceptin, Tecentriq, and Ocrevus. The company’s commitment to innovation and personalized medicine has made it a dominant force in biologics research and therapy development.
Johnson & Johnson
Johnson & Johnson, under its Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies division, is a major player in the North America monoclonal antibodies market, known for developing therapies across oncology, immunology, and infectious diseases. Its portfolio includes key drugs such as Stelara, Darzalex, and Simponi, which have become essential treatments in chronic inflammatory and hematologic malignancies.
Amgen
Amgen is a leading innovator in the North America monoclonal antibodies market, with a strong focus on oncology and rheumatology indications. The company has developed widely used therapies such as Blincyto and Enbrel, contributing significantly to the advancement of targeted biological treatments. Amgen also invests heavily in biosimilars by enhancing accessibility and affordability in the biopharmaceutical space.
Top Strategies Used by Key Players
One major strategy employed by leading players in the North America monoclonal antibodies market is expanding therapeutic pipelines through internal R&D and strategic acquisitions by allowing companies to maintain a competitive edge by introducing novel and differentiated monoclonal antibody-based treatments across multiple disease areas.
Another key approach is leveraging partnerships and collaborations with academic institutions, biotech firms, and contract manufacturing organizations by enabling faster discovery, development, and production of complex monoclonal antibody therapies while reducing time-to-market.
Lastly, focusing on biosimilar development and lifecycle management of existing blockbuster drugs is increasingly being utilized to sustain revenue streams and broaden patient accessin response to patent expirations and increasing pressure from payers and regulatory bodies to reduce healthcare costs.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THE MARKET
In February 2023, Roche announced a partnership with AbCellera to co-develop next-generation monoclonal antibodies targeting emerging infectious diseases, which is leveraging AI-powered discovery platforms to accelerate development timelines and enhance therapeutic specificity.
In July 2023, Amgen entered into a strategic collaboration with BeiGene to explore combination therapies using monoclonal antibodies in oncology by aiming to improve patient outcomes in hematological malignancies and solid tumors through synergistic immune activation.
In January 2024, AbbVie acquired Teneobio, a California-based biotech firm specializing in ultra-specific monoclonal antibodies, strengthening its pipeline in oncology and autoimmune diseases while advancing capabilities in bispecific and multispecific antibody formats.
In June 2024, Johnson & Johnson expanded its biologics manufacturing capacity in Pennsylvania, investing over $500 million to scale production of key monoclonal antibody drugs and support anticipated demand from newly approved indications.
In November 2024, Merck KGaA partnered with a U.S.-based synthetic biology startup to develop protein-engineered monoclonal antibodies with enhanced stability and longer half-life, which is aiming to reduce dosing frequency and improve patient adherence in chronic disease management.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the north america monoclonal antibodies market has been segmented & sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Source
- Humanized
- Human
By Indication
- Cance
- Autoimmune Diseases
By End-User
- Hospitals/Clinics
- Research Institute
By Application
- Medical
- Experimental
By Country
- The U.S.
- Canada
- Rest of North America
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors are driving the growth of the monoclonal antibodies market in North America?
Key drivers include increasing prevalence of chronic diseases (like cancer and autoimmune disorders), advancements in biotechnology, strong R&D investment, and favorable regulatory policies.
Which therapeutic areas are majorly targeted by monoclonal antibodies in North America?
Monoclonal antibodies are widely used in oncology, autoimmune diseases (like rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn’s disease), infectious diseases, and cardiovascular conditions.
What are the leading countries contributing to the North American monoclonal antibodies market?
The United States dominates the market due to high healthcare expenditure, presence of major pharmaceutical companies, and advanced infrastructure. Canada also contributes significantly.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from
$ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: sales@marketdataforecast.com
