North America Steam Turbine Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report By Capacity (>300 MW, <150 MW), End User and Country (The United States, Canada and Rest of North America), Industry Analysis From 2025 to 2033
North America Steam Turbine Market Size
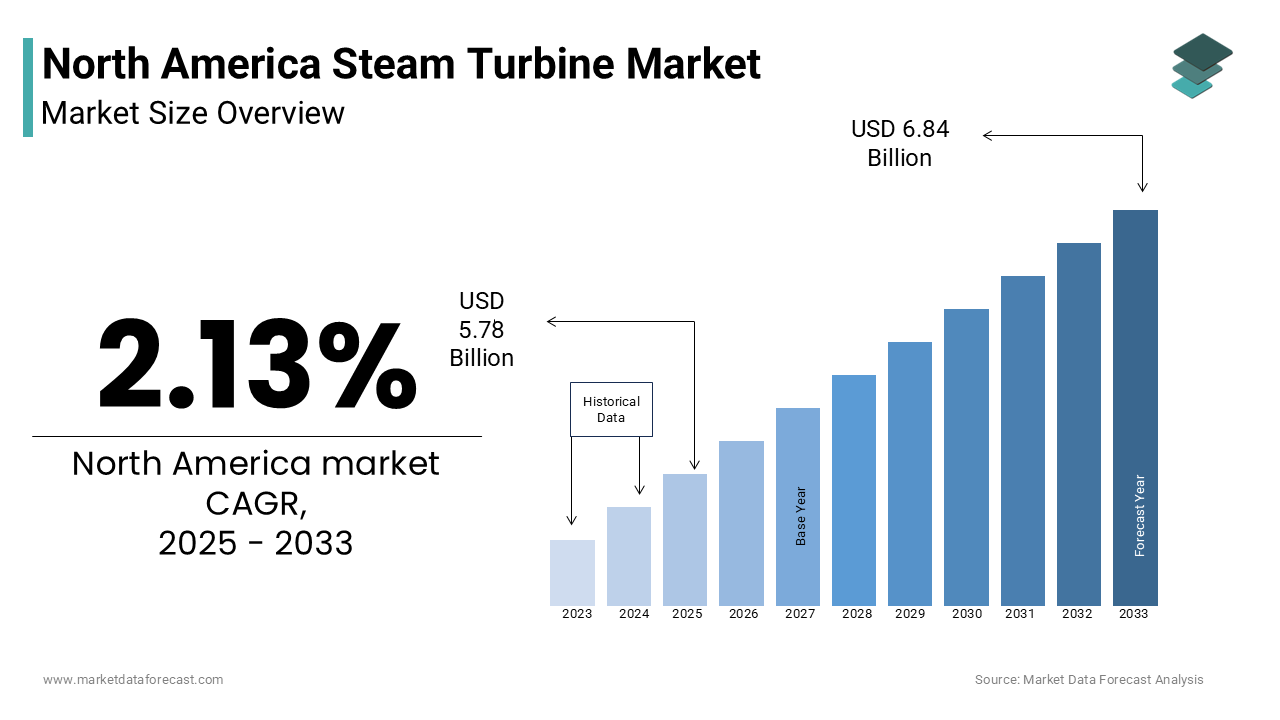
The North America Steam Turbine Market was worth USD 5.66 billion in 2024. The North America market is expected to reach USD 6.84 billion by 2033 from USD 5.78 billion in 2025, rising at a CAGR of 2.13% from 2025 to 2033.
The North America steam turbine market involves the design, manufacturing, and deployment of steam turbines used primarily for electricity generation across thermal power plants, industrial facilities, and cogeneration units. Steam turbines convert thermal energy from pressurized steam into mechanical work, which is then transformed into electrical energy through generators. These turbines remain a cornerstone of baseload power supply despite the ongoing transition toward renewable energy sources.
Beyond utility-scale applications, steam turbines are extensively deployed in industrial sectors such as refining, chemicals, pulp and paper, where they support both process heating and onsite power generation. The aging fleet of steam turbines across North America has prompted increased investment in retrofitting, efficiency upgrades, and replacement projects.
MARKET DRIVERS
Aging Thermal Power Infrastructure Requiring Upgrades
One of the primary drivers of the North America steam turbine market is the aging thermal power generation fleet, particularly in the United States, which necessitates extensive modernization and replacement programs. This aging infrastructure has led utilities to invest in high-efficiency steam turbines capable of improving plant performance while reducing environmental impact.
In response, companies like General Electric and Siemens have introduced advanced ultra-supercritical (USC) steam turbines that operate at higher temperatures and pressures, achieving efficiency gains.
Demand for Industrial Cogeneration and Process Heating Applications
A significant driver of the North America steam turbine market is the widespread adoption of cogeneration (combined heat and power or CHP) systems across industrial sectors such as refining, petrochemicals, and food processing. These industries require both electrical power and thermal energy for manufacturing processes, making steam turbines an integral component of efficient energy utilization.
The International Energy Agency (IEA) reports that the United States leads globally in installed CHP capacity, with over 110 gigawatts operational as of 2023. Many of these installations rely on back-pressure and extraction steam turbines that enable simultaneous electricity generation and process heating, thereby enhancing overall energy efficiency beyond 80%.
Similarly, Irving Oil’s Saint John refinery utilizes custom-designed steam turbines to optimize energy recovery and reduce dependence on external power supplies.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
Regulatory Pressure and Environmental Concerns
A major restraint affecting the North America steam turbine market is the increasing regulatory scrutiny surrounding greenhouse gas emissions from fossil-fueled power generation. Governments at both federal and state levels have introduced stringent environmental policies aimed at reducing carbon dioxide emissions, leading to a decline in new coal-fired power plant construction and accelerating the retirement of aging units. According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), coal-fired generation capacity in the United States declined by over 25 gigawatts between 2020 and 2023 due to compliance costs and climate policy mandates.
The Canadian government has also enforced aggressive decarbonization targets, including a commitment to phase out traditional coal-fired electricity generation by 2030.
While some utilities have opted for repowering with natural gas, which still relies on steam turbines in combined cycle configurations, the long-term outlook for fossil-based generation remains uncertain.
High Capital Investment and Long Project Timelines
The high capital expenditure required for steam turbine installation, along with extended project development timelines, presents a significant barrier to market growth. Unlike modular technologies such as gas turbines or renewable energy systems, steam turbines necessitate complex integration with boiler systems, condensers, and auxiliary equipment, leading to substantial upfront costs.
Additionally, regulatory permitting and environmental assessments often prolong project execution. Such delays deter investor interest and increase financial risk, particularly in markets where policy uncertainty prevails.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Retrofitting and Life Extension of Existing Plants
A significant opportunity for the North America steam turbine market lies in the retrofitting and life extension of aging thermal power plants. Many coal and gas-fired stations currently operating across the continent were built several decades ago and are experiencing declining efficiency and increased maintenance costs.
General Electric and Siemens have developed specialized retrofit packages that include high-efficiency blades, improved sealing systems, and digital monitoring solutions to enhance performance and extend operational lifespans.
With rising pressure to balance reliability and sustainability, retrofitting represents a viable pathway for extending asset longevity and preserving steam turbine demand in North America’s evolving power landscape.
Integration with Carbon Capture and Storage Technologies
An emerging opportunity for the North America steam turbine market is the integration of steam-based power generation with carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies. As governments and utilities seek pathways to decarbonize fossil fuel-based generation, CCS-equipped power plants are gaining traction as a transitional solution.
In Canada, the Boundary Dam Carbon Capture Project in Saskatchewan has demonstrated the technical viability of integrating CCS with coal-fired steam turbines. With enhanced tax incentives and regulatory backing, the convergence of steam turbine technology with CCS offers a compelling avenue for sustained market growth.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Declining Investment in Coal-Based Generation
A key challenge confronting the North America steam turbine market is the persistent decline in investment towards coal-based power generation. Over the past decade, numerous coal-fired power plants have been retired or converted to natural gas due to economic, environmental, and regulatory pressures. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), coal-fired generation capacity in the United States fell by nearly 30% between 2015 and 2023, with no new coal plants coming online in the same period.
This trend is largely driven by the increasing competitiveness of natural gas and renewables, which offer lower operating costs and reduced carbon footprints. The International Energy Agency (IEA) reports that natural gas-fired power generation surpassed coal in the U.S. in 2016 and has maintained dominance ever since. Consequently, steam turbine manufacturers that traditionally catered to coal-fired plants face shrinking demand unless they adapt to alternative applications.
Competition from Alternative Power Generation Technologies
The North America steam turbine market is increasingly challenged by competition from alternative power generation technologies, particularly gas turbines and renewable energy systems. Gas turbines, especially those used in combined cycle configurations, offer quicker startup times, greater flexibility, and lower emissions compared to traditional steam-based systems. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), a notable share of new utility-scale power additions in the United States between 2020 and 2023 were based on natural gas, reflecting a preference for gas turbine technology in new build scenarios. Renewables, particularly wind and solar photovoltaic systems, pose another formidable challenge.
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Capacity Insights
The >300 MW capacity segment dominated the North America steam turbine market, accounting for a 58.2% of total market value in 2024. This segment is primarily driven by its widespread use in large-scale utility power plants that provide baseload electricity across the continent.
According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), over 60% of coal and gas-fired power plants operating in the United States have generating capacities exceeding 300 MW, with many relying on high-capacity steam turbines for efficient energy conversion. These units are essential for maintaining grid stability, especially in regions where intermittent renewable sources require backup generation.
Additionally, the International Energy Agency (IEA) reports that large fossil-fueled plants continue to contribute significantly to dispatchable generation, reinforcing demand for high-capacity steam turbines.
Furthermore, repowering initiatives—such as Duke Energy’s Cliffside Unit 6 upgrade in North Carolina—have demonstrated the economic viability of deploying advanced ultra-supercritical turbines in this capacity range.
The <150 MW capacity segment is projected to grow at the fastest CAGR of 5.7%. This growth is largely attributed to increasing adoption in industrial cogeneration (CHP) applications, district heating systems, and small modular power plants.
According to the U.S. Department of Energy, a significant share of industrial combined heat and power (CHP) installations in North America utilize steam turbines below 150 MW, particularly in sectors like pulp and paper, food processing, and chemical manufacturing. These industries benefit from simultaneous electricity and thermal energy production, achieving high efficiencies.
Moreover, the rise in biomass and waste-to-energy power plants—many of which operate within this capacity range—is driving demand. With growing emphasis on decentralized energy systems and circular economy principles, the <150 MW segment is gaining momentum as a key growth driver in the North American steam turbine market.
By End-use Insights
The power and utility end-use segment had the largest share of the North America steam turbine market, estimated at 62.3% in 2024. This dominance is primarily due to the continued reliance on coal and gas-fired power plants for baseload electricity generation across the region.
Many of these plants depend on steam turbines for converting thermal energy into mechanical work, making them indispensable components of the power infrastructure.
Despite ongoing decarbonization efforts, provinces like Alberta and Saskatchewan still rely on coal and gas-based generation to maintain grid reliability during periods of low renewable output.
Additionally, retrofitting and modernization programs aimed at improving efficiency and reducing emissions are sustaining demand. With utilities seeking to balance reliability and sustainability, the power and utility segment remains the primary consumer of steam turbine technology in North America.
The industrial end-use segment is expected to grow at the highest CAGR of 6.2%. This accelerated growth stems from the expanding deployment of steam turbines in industrial cogeneration (combined heat and power or CHP) systems, particularly in refining, petrochemicals, pulp and paper, and food processing sectors.
These systems offer enhanced energy efficiency by simultaneously producing electricity and thermal energy, reducing overall fuel consumption and emissions.
In Canada, Suncor Energy and Irving Oil have implemented customized steam turbine solutions to improve energy self-sufficiency at their refineries. As manufacturers prioritize energy resilience and cost optimization, the industrial segment is emerging as a strong growth engine for the North America steam turbine market.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
The United States maintained a dominant position in the North America steam turbine market, holding an estimated market share of 76.7% in 2024. This leading position is due to the country’s extensive coal and gas-fired power generation fleet, aging thermal infrastructure requiring modernization, and strong industrial base reliant on cogeneration systems.
Many of these plants rely on steam turbines for power production, highlighting their continued relevance in the region's energy infrastructure. In addition to utility-scale applications, the industrial sector plays a significant role in sustaining steam turbine demand.
Moreover, retrofitting and life extension programs are gaining traction as utilities seek to enhance efficiency and comply with evolving emissions standards. With continued investment in both power generation and industrial applications, the United States remains the central hub for steam turbine activity in North America.
Canada is emerging as a key player in the North America steam turbine market due to sustained industrial demand, thermal power plant retrofits, and regional policy support for energy efficiency. Provinces such as Alberta and Saskatchewan, which rely heavily on fossil-based generation, have initiated turbine modernization programs to align with federal emission reduction targets.
Beyond utility applications, the industrial sector remains a critical driver of steam turbine demand. Companies like Resolute Forest Products and Kruger Inc. have deployed custom-designed steam turbines to optimize energy recovery and reduce dependence on external power supplies
The Rest of North America, encompassing Mexico and select Caribbean nations, currently accounts for a smaller share of the regional steam turbine market in 2024. While still in early stages compared to the U.S. and Canada, this region is witnessing gradual adoption driven by industrial expansion, thermal power development, and cross-border investments.
In the Caribbean, countries such as Jamaica and Trinidad and Tobago are investing in small-scale thermal and biomass power plants equipped with steam turbines to enhance energy security and reduce dependency on imported fuels. Despite challenges such as limited technical expertise and financial constraints, the Rest of North America presents promising opportunities for steam turbine vendors, particularly as international aid and private equity investments begin to flow into the region’s power sector.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS AND COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
GE Vernova (General Electric), Siemens Energy, Mitsubishi Power, Elliott Group, MAN Energy Solutions, Toshiba Energy Systems & Solutions, Fuji Electric, Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Chola Turbo Machinery International, and Turbine Generator Maintenance, Inc. are some of the key market players names
The competition in the North America steam turbine market is shaped by a blend of established global leaders and niche regional players striving to maintain relevance amid evolving energy policies and technological advancements. Major international manufacturers dominate due to their deep technical expertise, comprehensive service portfolios, and longstanding relationships with utility operators. However, the declining share of coal-based generation and increasing preference for flexible, low-carbon alternatives have prompted these firms to pivot toward retrofitting, efficiency enhancements, and integrated digital solutions. In parallel, industrial demand for cogeneration systems has opened opportunities for specialized turbine suppliers to carve out competitive positions. The market also sees growing influence from software-focused firms entering through partnerships or acquisitions, offering digital asset management tools that complement traditional turbine offerings. While large multinational corporations continue to lead in scale and innovation, the shift toward sustainability and digitalization is reshaping competitive dynamics, requiring continuous adaptation to remain relevant in the North American energy ecosystem.
Top Players in the North America Steam Turbine Market
General Electric (GE Vernova)
General Electric, now operating as GE Vernova in the energy sector, is a leading global provider of steam turbine technology with a strong footprint in North America. The company delivers high-efficiency turbines for utility-scale power plants and industrial applications, emphasizing performance optimization and emissions reduction. GE has played a pivotal role in advancing ultra-supercritical steam turbine technology, which enhances plant efficiency and supports sustainability goals. Its extensive service network and digital solutions, including predictive maintenance and remote diagnostics, have reinforced its position as a preferred partner for utilities and industrial clients across the region.
Siemens Energy
Siemens Energy is a major contributor to the North America steam turbine market, offering a broad portfolio of steam turbines tailored for coal, gas, and combined cycle power plants. The company focuses on integrating advanced materials, aerodynamics, and digital monitoring systems to improve reliability and reduce downtime. Siemens has been instrumental in supporting modernization projects that extend the life of aging thermal assets while aligning with evolving environmental regulations. Its commitment to innovation and strategic collaborations with key utilities continues to strengthen its presence in the North American power generation landscape.
Mitsubishi Power (a subsidiary of Mitsubishi Heavy Industries)
Mitsubishi Power plays a significant role in the North America steam turbine market by providing high-performance turbines designed for both new installations and retrofitting existing power plants. The company emphasizes efficiency, flexibility, and low-emission operations through its advanced steam turbine designs. Mitsubishi’s integration of digital twin technology and lifecycle management services has enhanced operational transparency and asset longevity for customers. With a focus on decarbonization pathways such as carbon capture-ready turbines, Mitsubishi Power is well-positioned to support the transition toward cleaner thermal generation in North America.
Top Strategies Used by Key Market Participants
One of the primary strategies employed by leading players in the North America steam turbine market is technology innovation and digital integration, focusing on enhancing efficiency, reducing emissions, and enabling predictive maintenance through smart analytics. Companies are embedding digital twins, AI-driven diagnostics, and IoT-based monitoring into their turbine offerings to improve performance and customer value.
Another crucial approach is strategic partnerships and joint ventures with utility providers, engineering firms, and research institutions. These collaborations help manufacturers align product development with regional regulatory requirements and grid modernization initiatives, ensuring long-term relevance in a shifting energy landscape.
Lastly, retrofitting and life extension programs have become central to maintaining market presence. As new coal-fired plant construction declines, companies are increasingly focused on upgrading existing turbines to meet efficiency and environmental standards, allowing operators to extend asset lifecycles without full replacement.
RECENT MARKET DEVLEOPMENTS
- In February 2024, General Electric (GE Vernova) launched an updated line of ultra-supercritical steam turbines optimized for North American coal and gas-fired power plants, aiming to enhance efficiency and support emissions reduction goals for aging thermal fleets.
- In May 2024, Siemens Energy announced a collaboration with a leading U.S. utility to retrofit multiple coal-fired power stations with digitally enabled steam turbines, improving reliability and compliance with evolving environmental standards.
- In July 2024, Mitsubishi Power introduced a new steam turbine service center in Houston, Texas, designed to provide localized technical support, spare parts logistics, and field engineering services for power plant operators across North America.
- In September 2024, Baker Hughes entered into a strategic alliance with a Canadian industrial energy firm to deploy compact steam turbines for cogeneration applications in the pulp and paper sector, expanding its presence in industrial energy solutions.
- In November 2024, Ansaldo Energia acquired a U.S.-based turbine control systems developer to enhance its digital capabilities, integrating real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance features into its steam turbine offerings for North American customers.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the North America steam turbine market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Capacity
- >300 MW
- <150 MW
By End-use
- Power & Utility
- Industrial
By Country
- The United States
- Canada
- Rest of North America
Frequently Asked Questions
What is driving the growth of the steam turbine market in North America?
Growth is being driven by rising demand for reliable power generation, aging thermal power infrastructure upgrades, and continued use of steam turbines in industrial and combined heat & power (CHP) applications.
What challenges does the North American steam turbine market face?
Major challenges include competition from gas turbines and renewable energy, regulatory pressure on emissions, and the high capital cost of turbine installation and maintenance.
What is the outlook for the steam turbine market over the next decade?
While large-scale coal-based installations may decline, the market will remain stable due to industrial demand, CHP projects, and opportunities in retrofitting and servici
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from
$ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: sales@marketdataforecast.com