North America Commercial Vehicle Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report By Vehicle Type (Commercial Vehicles) and by Propulsion Type, and Country (The United States, Canada, and Rest of North America), Industry Analysis From 2025 to 2033
North America Commercial Vehicle Market Size
The Commercial Vehicle market size in North America was valued at USD 557.33 billion in 2024 and is predicted to be worth USD 859.43 billion by 2033 from USD 584.81 billion in 2025 and grow at a CAGR of 4.93% from 2025 to 2033.
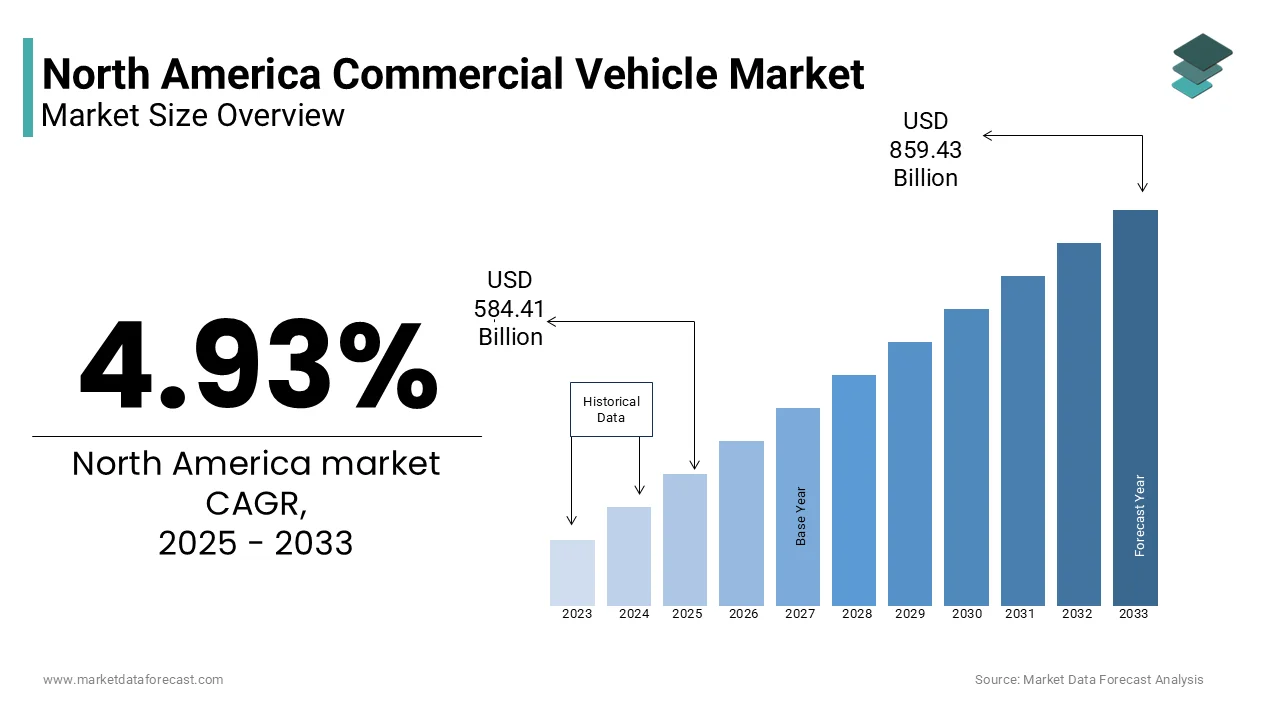
The North America Commercial Vehicle market covers a broad range of vehicles designed for transporting goods, passengers, or equipment as part of business operations. This includes heavy-duty trucks, medium-duty delivery vans, buses, construction vehicles, and specialized transport units used across logistics, public transportation, agriculture, and industrial sectors. The market is driven by both economic demand for freight movement and policy frameworks aimed at modernizing infrastructure and reducing emissions.
The United States and Canada form the core of this market, supported by robust manufacturing ecosystems, strong trade networks, and a growing emphasis on electrification and smart mobility solutions. Moreover, the rise in e-commerce and just-in-time delivery models has intensified demand for last-mile delivery vehicles, encouraging manufacturers to innovate in fuel efficiency, connectivity, and automation. Companies like UPS, FedEx, and Amazon have committed to integrating electric delivery fleets.
MARKET DRIVERS
Growth of E-Commerce and Last-Mile Delivery Demand
One of the primary drivers of the North America commercial vehicle market is the rapid expansion of e-commerce and the corresponding surge in demand for last-mile delivery solutions. The shift toward online shopping, accelerated by changing consumer behavior and advancements in logistics technology, has led to a significant increase in freight volume requiring efficient and timely delivery solutions. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, retail e-commerce sales in the U.S. exceeded $1 trillion in 2023, representing a year-over-year growth of nearly 10%. This trend has created an urgent need for a larger and more agile fleet of commercial vehicles, particularly light and medium-duty delivery vans tailored for urban logistics. Major logistics companies such as Amazon, UPS, and FedEx have responded by expanding their fleets with new and electrified vehicles to meet delivery demands while complying with sustainability goals. As reported by BloombergNEF, Amazon alone plans to deploy 100,000 electric delivery vans in North America by 2030 through its partnership with Rivian Automotive. Apart from these, the proliferation of micro-fulfillment centers and local distribution hubs has further intensified the requirement for compact, high-efficiency commercial vehicles capable of navigating city traffic and adhering to emission regulations.
Government Investment in Infrastructure and Fleet Modernization
Another key driver influencing the North America commercial vehicle market is the substantial government funding directed toward infrastructure development and fleet modernization initiatives. In recent years, federal and state-level policies have prioritized the upgrading of transportation networks, promoting cleaner and more technologically advanced commercial fleets. The Bipartisan Infrastructure Law (BIL), enacted in 2021, allocated $7.5 billion for electric vehicle charging infrastructure, including support for electrifying commercial fleets. According to the Federal Highway Administration (FHWA), over $110 billion was earmarked under BIL for roads, bridges, and major transportation projects, creating favorable conditions for increased freight movement and demand for commercial vehicles. Moreover, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) introduced stricter emissions standards, prompting fleet operators to replace aging diesel vehicles with newer, low-emission alternatives. In Canada, similar efforts are underway. Provinces like Ontario and Quebec have also launched subsidies for commercial fleet electrification.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
Supply Chain Disruptions and Component Shortages
A significant restraint affecting the North America commercial vehicle market is the ongoing impact of supply chain disruptions and component shortages, particularly in semiconductor chips, steel, and battery materials. The global semiconductor shortage, exacerbated by pandemic-related factory shutdowns and geopolitical tensions, has delayed production timelines for both traditional and electric commercial vehicles. According to the Center for Automotive Research (CAR), major truck manufacturers faced an average delay of six to nine months in vehicle deliveries due to parts unavailability in 2023. Steel and aluminum price volatility has further compounded these challenges. For electric commercial vehicles, lithium, cobalt, and nickel shortages have constrained battery production capacity, slowing the pace of fleet electrification. The International Energy Agency (IEA) notes that global lithium demand outpaced supply in 2023, leading to bottlenecks in EV battery manufacturing. These supply-side constraints have led to extended lead times, higher acquisition costs, and reduced inventory availability for commercial fleet buyers.
High Acquisition and Maintenance Costs for Electric Commercial Vehicles
Another key challenge restraining the North America commercial vehicle market is the elevated acquisition and maintenance costs associated with electric commercial vehicles (ECVs), which pose financial barriers for fleet operators, particularly small and mid-sized businesses. Although electric trucks and vans offer long-term savings in fuel and emissions compliance, their upfront purchase price remains significantly higher than conventional diesel-powered counterparts. Beyond initial costs, the lack of standardized service infrastructure and trained technicians for ECV maintenance adds to operational complexity. Battery replacement, software updates, and specialized diagnostics require investments in training and tools, increasing total cost of ownership. In addition, many fleet managers cite uncertainty about battery longevity and residual value as deterrents to full-scale adoption. While government incentives such as tax credits and rebates help offset some expenses, widespread cost parity between electric and diesel commercial vehicles is still projected to be several years away.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Electrification of Public Transit and School Bus Fleets
One of the most promising opportunities for the North America commercial vehicle market lies in the electrification of public transit and school bus fleets, driven by environmental mandates and federal funding initiatives. Governments at both federal and state levels are increasingly prioritizing the transition from diesel-powered buses to zero-emission alternatives to reduce urban air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. Federal programs such as the Low-No Emission (Low-No) Grant Program and the Clean School Bus Program have allocated billions of dollars to support the procurement of electric buses. Leading manufacturers such as Blue Bird Corporation, Lion Electric, and Proterra have ramped up production to meet growing demand, securing contracts with major school districts and municipal transit agencies. Canada has mirrored this momentum.
Expansion of Connected and Autonomous Commercial Vehicles
Another significant opportunity for the North America commercial vehicle market is the growing adoption of connected and autonomous vehicle technologies, which promise to enhance fleet efficiency, safety, and operational scalability. The convergence of artificial intelligence, telematics, and real-time data analytics is transforming how commercial vehicles are managed, monitored, and deployed across logistics, transportation, and delivery sectors. Major automotive and technology firms—including Waymo, TuSimple, Aurora Innovation, and Embark Trucks—are actively testing and deploying autonomous semi-trucks and delivery vans on U.S. highways and regional routes. Several states, including Arizona, Texas, and California, have already permitted limited autonomous trucking operations under regulatory supervision. Simultaneously, the integration of vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication and predictive maintenance systems is enhancing fleet uptime and reducing unplanned repair costs.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Regulatory Compliance and Emissions Standards
A major challenge facing the North America commercial vehicle market is the increasing complexity of regulatory compliance and tightening emissions standards imposed by federal and state authorities. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the California Air Resources Board (CARB) have introduced progressively stringent emissions requirements, mandating reductions in nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter, and carbon dioxide (CO₂) from commercial fleets. As per EPA guidelines, new heavy-duty vehicle emissions standards set for 2027 aim to cut NOx emissions by approximately 80% compared to current levels, necessitating significant engineering adaptations. Compliance with these regulations requires manufacturers to invest heavily in advanced after-treatment systems, clean-diesel engines, and hybrid or electric powertrains, which increases vehicle costs and development timelines. Additionally, CARB's Advanced Clean Trucks (ACT) rule mandates that a percentage of new commercial vehicle sales must be zero-emission by specific deadlines, compelling fleet owners to reassess purchasing strategies. Navigating this evolving regulatory landscape poses a dual challenge: ensuring environmental compliance while maintaining affordability and operational efficiency.
Skilled Labor Shortage in Commercial Vehicle Manufacturing and Maintenance
Another critical challenge confronting the North America commercial vehicle market is the persistent shortage of skilled labor in both manufacturing and post-sale service operations. The industry faces a widening skills gap due to an aging workforce, declining vocational training enrollment, and the increasing technical complexity of modern commercial vehicles—especially those incorporating electric drivetrains and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). Manufacturers are also grappling with production delays caused by labor shortages on assembly lines and in component fabrication plants. The American Trucking Associations highlights that wage competition and workforce retention issues have become pressing concerns for original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) aiming to scale output.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
4.93% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Vehicle Type, Propulsion Type, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
The United States, Canada, Mexico, and Rest of North America |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Daimler AG, Paccar Inc, Volvo Group, Navistar International Corporation, Ford Motor Company, General Motors Company, Nissan Motor Co., and others |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Vehicle Type Insights
The light commercial vehicle (LCV) segment dominated the North America commercial vehicle market by accounting for 42% of total market revenue in 2024. This is primarily driven by the widespread use of LCVs in last-mile delivery, urban logistics, and small business transportation needs, particularly within the e-commerce, food delivery, and service industries. One of the key factors behind this dominance is the rapid expansion of online retail and same-day delivery services, which has significantly increased demand for compact, fuel-efficient delivery vans and trucks. Companies such as Amazon, FedEx, and UPS have placed large orders for both conventional and electric light commercial vehicles to meet growing consumer expectations. Another major contributor to the segment's growth is the increasing adoption of fleet-as-a-service models and vehicle leasing programs , making it easier for small businesses and entrepreneurs to access commercial transport solutions without high upfront costs.
The heavy commercial vehicle segment is emerging as the fastest-growing category within the North America commercial vehicle market, projected to expand at a CAGR of 6.8%. While traditionally slower to evolve due to longer replacement cycles, heavy-duty trucks are now undergoing significant transformation driven by regulatory pressures, technological innovation, and freight industry dynamics. A primary driver behind this rapid growth is the increased demand for long-haul freight transportation, fueled by cross-border trade under the USMCA agreement and the continued expansion of just-in-time supply chain models. According to the American Trucking Associations (ATA), over 72% of all freight tonnage moved in the U.S. is transported by truck, with Class 8 tractor-trailers playing a dominant role. The ATA also reports that freight volumes grew by nearly 5% in 2023, reinforcing the need for new and more efficient heavy commercial vehicles. Additionally, the accelerated development and deployment of electric and hydrogen-powered semi-trucks is reshaping the market landscape. Companies such as Tesla Semi, Nikola Corporation, and Daimler Trucks North America are investing heavily in zero-emission heavy-duty platforms, supported by federal incentives under the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law.
By Propulsion Type Insights
The internal combustion engine (ICE) segment continued to command the North America commercial vehicle market by capturing substantials share of total propulsion type market share in 2024. Despite growing interest in alternative fuel technologies, ICE vehicles—primarily diesel-powered—remain the backbone of freight and logistics operations due to their proven reliability, extensive refueling infrastructure, and cost-effectiveness for long-haul applications. One of the key drivers of this segment’s continued dominance is the established support network and operational familiarity among fleet operators, particularly in sectors like construction, agriculture, and intercity freight transport. Diesel engines offer high torque, durability, and range capabilities that are still unmatched by many electric alternatives. A different factor sustaining ICE market leadership is the relatively lower acquisition cost compared to hybrid and electric commercial vehicles, making them more accessible to independent haulers and smaller logistics firms.
The hybrid and electric commercial vehicle segment is seeing the swiftest growth rate in the North America commercial vehicle market, progress to grow at a CAGR of 14.2%. This rapid expansion is largely attributed to aggressive government policies promoting zero-emission transportation, coupled with increasing corporate commitments to sustainability and carbon neutrality. A notable aspect behind this growth is the implementation of state-level mandates and incentive programs aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions from the transportation sector. California’s Advanced Clean Trucks (ACT) rule, for instance, requires manufacturers to ensure that a certain percentage of commercial vehicle sales are zero-emission, starting with 40% for medium- and heavy-duty vehicles by 2035. Additionally, the growing investment in EV charging infrastructure and fleet electrification initiatives by major logistics companies is accelerating market adoption.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
United States led the North America commercial vehicle market by capturing a 82.5% of regional market share in 2024. As the largest economy in the region and a global hub for logistics, manufacturing, and transportation, the U.S. maintains a vast commercial vehicle fleet supporting domestic and international trade, urban delivery services, and industrial operations. A main driver of the U.S. market is the explosive growth of e-commerce and digital supply chain systems, which have dramatically increased demand for delivery vans, cargo trucks, and logistics fleet modernization. Another key factor supporting market growth is the strong presence of major commercial vehicle manufacturers and suppliers, including Navistar International, PACCAR Inc., and Cummins Inc. These companies are actively developing advanced propulsion systems, connected vehicle technologies, and autonomous driving features tailored for North American road conditions.
Canada plays a vital role in cross-border freight movement, regional logistics, and public transportation, contributing to steady commercial vehicle demand across multiple sectors. A major driver behind Canada’s market position is the expanding adoption of zero-emission commercial vehicles, supported by federal and provincial government funding initiatives. Provinces like Ontario and Quebec have introduced additional subsidies and procurement targets, with Quebec aiming to replace 100% of its diesel-powered public buses with electric models by 2035. Another contributing factor is the growth of interprovincial freight corridors and logistics hubs , particularly along the Windsor-Quebec corridor and the British Columbia-Alberta trade routes.
Mexico is reflecting a relatively smaller but gradually evolving presence in the regional transportation ecosystem. Although traditionally overshadowed by the U.S. and Canada, Mexico is beginning to see increased commercial vehicle activity driven by industrial expansion, nearshoring trends, and logistical upgrades. A basic aspect influencing Mexico’s market trajectory is the growing integration of Mexican manufacturing into North American supply chains, particularly in automotive, aerospace, and electronics sectors. In addition, the expansion of nearshoring initiatives—where U.S.-based companies relocate production closer to home—has heightened the need for cross-border freight movement, boosting commercial vehicle utilization. Other assisting point is the emerging focus on fleet modernization and alternative fuels, particularly in urban centers like Mexico City and Monterrey. While challenges related to infrastructure and regulatory alignment persist, Mexico’s evolving industrial base suggests a cautious but promising outlook for commercial vehicle adoption in the coming years.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS AND COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
Daimler AG, Paccar Inc, Volvo Group, Navistar International Corporation, Ford Motor Company, General Motors Company, and Nissan Motor Co., Ltd. are key players in the North America commercial vehicle market.
The North America commercial vehicle market is characterized by intense competition driven by technological advancements, shifting regulatory landscapes, and evolving customer expectations. A mix of established automotive giants, emerging electric vehicle startups, and global conglomerates are vying for dominance, each bringing distinct strengths in engineering, manufacturing scale, and innovation. Traditional players like PACCAR, Daimler Truck North America, and Navistar continue to leverage their deep-rooted industry expertise and robust distribution networks, while newer entrants such as Tesla, Nikola Corporation, and Rivian are disrupting the space with ambitious electrification roadmaps and digital-first approaches.
Market dynamics are further influenced by increasing demand for smart, connected, and autonomous commercial vehicles that enhance fleet performance and reduce environmental impact. Competition extends beyond vehicle sales to encompass total cost of ownership, service ecosystems, and software-enabled features such as route optimization and predictive maintenance. Additionally, government policies on emissions, trade agreements, and infrastructure investments play a crucial role in shaping competitive positioning. With rapid technological evolution and growing emphasis on sustainability, the North America commercial vehicle market remains highly dynamic, fostering both rivalry and collaboration among industry participants.
TOP PLAYERS IN THE MARKET
PACCAR Inc
PACCAR Inc. is a leading manufacturer of premium commercial vehicles, known for its renowned brands Peterbilt, Kenworth, and DAF. The company plays a pivotal role in shaping the North America commercial vehicle market through continuous innovation in fuel efficiency, aerodynamics, and driver comfort. PACCAR’s strong dealer network, advanced telematics solutions, and commitment to sustainability have made it a preferred choice among fleet operators across the U.S. and Canada.
Freightliner (Daimler Truck North America)
Freightliner (Daimler Truck North America) holds a dominant presence in the heavy-duty truck segment and significantly influences market trends in North America. As a subsidiary of Daimler Truck AG, Freightliner leads in developing electric and hydrogen-powered commercial vehicles, aligning with global decarbonization goals. The company's investment in connected vehicle technology and extensive after-sales service infrastructure has reinforced its leadership position in both traditional and emerging propulsion segments.
Navistar International
Navistar International, now part of TRATON GROUP, contributes substantially to the North American commercial vehicle landscape through its innovative Class 6–8 truck offerings. Navistar is recognized for its bold design philosophy, integrated powertrain development, and early adoption of alternative fuels. The company has played a key role in advancing autonomous driving partnerships and electrification strategies, making it a strategic player in the evolving commercial mobility ecosystem.
TOP STRATEGIES USED BY KEY PLAYERS
One of the primary strategies employed by key players is accelerated electrification and investment in zero-emission technologies, as manufacturers seek to align with regulatory mandates and corporate sustainability goals. Companies are developing battery-electric and hydrogen fuel cell trucks tailored for urban delivery, port operations, and long-haul transport, ensuring compliance with evolving emissions standards while meeting customer demand for cleaner fleets.
Another major approach is strategic partnerships and joint ventures with technology firms, charging infrastructure providers, and logistics companies to enhance product capabilities and ecosystem readiness. These collaborations help manufacturers validate new vehicle designs, optimize energy consumption, and expand service networks, ensuring seamless integration into commercial operations.
The third key strategy involves digital transformation and connected vehicle integration, where OEMs embed telematics, predictive maintenance systems, and over-the-air software updates into commercial fleets. By leveraging real-time data analytics and AI-driven diagnostics, companies improve fleet uptime, operational efficiency, and driver experience, reinforcing their competitive positioning in the rapidly evolving market landscape.
RECENT HAPPENINGS IN THE MARKET
- In January 2024, PACCAR announced a multi-million-dollar expansion of its Chillicothe, Ohio, manufacturing facility aimed at scaling production capacity for next-generation electric trucks, reinforcing its leadership in sustainable commercial mobility.
- In March 2024, Freightliner (Daimler Truck North America) launched an exclusive partnership with a major charging infrastructure provider to deploy over 100 high-speed commercial EV charging stations along key freight corridors, enhancing support for fleet electrification.
- In June 2024, Navistar introduced a new suite of connected vehicle services powered by AI-based diagnostics, offering fleet operators real-time insights into vehicle health, fuel efficiency, and driver safety to improve overall operational performance.
- In September 2024, Cummins Inc. unveiled a dedicated hydrogen engine production line in Indiana, marking a strategic shift toward diversifying propulsion options for commercial vehicles beyond battery-electric platforms.
- In November 2024, Tesla Semi commenced limited deliveries of its long-range electric semi-truck to select logistics partners in California and Texas, signaling the beginning of large-scale deployment and intensifying competition in the zero-emission freight sector.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the North America commercial vehicle market has been segmented and sub-segmented based on the following categories.
By Vehicle Type
- Commercial Vehicles
By Propulsion Type
- Hybrid Vehicles
- Electric Vehicles
- Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) Vehicles
By Country
- The United States
- Canada
- Rest of North America
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is considered a commercial vehicle in North America?
A commercial vehicle includes trucks, vans, buses, and other vehicles used for transporting goods or passengers for business purposes.
2. Which types of commercial vehicles are most common in North America?
Light commercial vehicles (LCVs), heavy-duty trucks, and buses are among the most common types in this market.
3. What factors are driving demand for commercial vehicles in North America?
Key drivers include e-commerce growth, construction activity, last-mile delivery needs, and fleet upgrades.
4. Who are the major manufacturers in the North American commercial vehicle market?
Leading players include Daimler AG, Paccar Inc, Ford Motor Company, General Motors, Volvo Group, and Navistar.
5. What role does electric mobility play in the commercial vehicle segment?
Electric commercial vehicles are gaining traction due to sustainability goals, fuel savings, and stricter emission regulations.
6. How is the commercial vehicle market segmented in North America?
The market is segmented by vehicle type, fuel type, end-user (logistics, construction, etc.), and country.
7. Which industries are the largest users of commercial vehicles in the region?
Logistics, construction, mining, public transportation, and retail are major end-user industries.
8. Are autonomous commercial vehicles being developed in North America?
Yes, several companies are investing in autonomous trucking and delivery solutions, especially for long-haul routes.
9. How does government regulation impact the commercial vehicle industry?
Emissions standards, safety regulations, and transport policies significantly influence manufacturing and operations.
10. Is there a growing trend toward connected commercial vehicles?
Yes, telematics, GPS tracking, and fleet management solutions are increasingly adopted to improve efficiency and safety.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from
$ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: sales@marketdataforecast.com