Global Warehouse Robotics Market Size, Share, Trends, & Growth Forecast Report Segmented By Product (Mobile Robots, Articulated Robots, Cylindrical Robots, Scara Robots, Parallel Robots, and Cartesian Robots), Function, Payload Capacity, Component, Software, Application Capacity, and Region (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East & Africa), Industry Analysis From 2024 to 2033
Global Warehouse Robotics Market Size
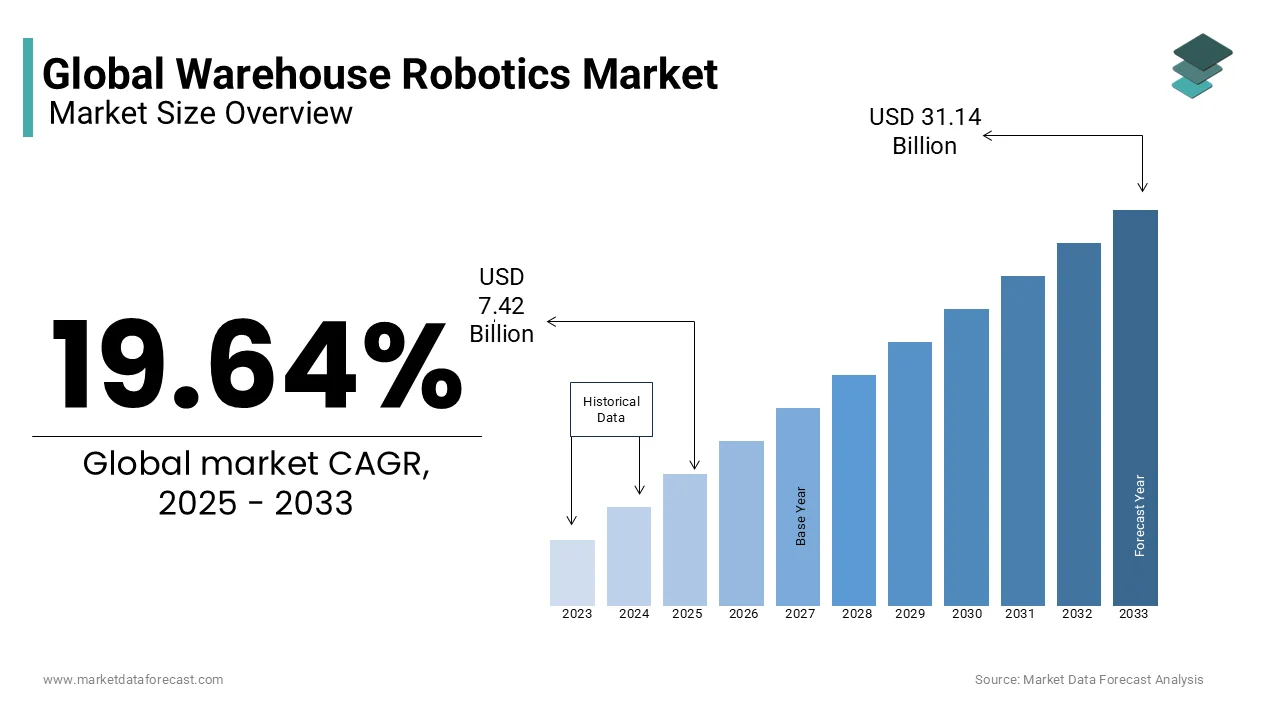
The global warehouse robotics market was valued at USD 6.20 billion in 2024. The global market is expected to reach USD 31.14 billion by 2033 from USD 7.42 billion in 2025, rising at a CAGR of 19.64% from 2025 to 2033.
Warehouse robotics involves using automated machines to perform tasks like picking, sorting, and transporting goods within warehouse settings. These robots aim to boost efficiency, reduce errors, and address labor shortages in the logistics sector. The rise of e-commerce has significantly increased the demand for such automation. According to the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD), global e-commerce sales reached $26.7 trillion in 2019 showcases the vast scale of online transactions. This surge has prompted businesses to adopt robotic solutions to manage higher order volumes efficiently.
Labor dynamics in the transportation and warehousing sectors further drive the need for automation. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects about 1.9 million job openings annually in these sectors from 2023 to 2033, due to growth and worker replacements. This substantial turnover underscores challenges in maintaining a stable workforce, making robotics an attractive solution to ensure consistent operations.
Workplace safety is another critical factor. The warehousing landscape faces various occupational hazards including overexertion and repetitive motion injuries. Implementing robotics can mitigate these risks by taking over physically demanding tasks is leading to a safer work environment.
Advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning have enhanced the capabilities of warehouse robots and enables them to handle complex tasks with greater autonomy. This technological progress allows for more efficient warehouse operations as robots can adapt to dynamic environments and optimize workflows.
MARKET DRIVERS
Rising E-commerce Demand
The exponential growth of e-commerce is a key driver for warehouse robotics adoption. The U.S. Census Bureau reports that e-commerce sales in the United States grew by 14.2% in 2022 alone, reaching $1.03 trillion. This surge necessitates faster order fulfillment and precise inventory management, which robotics excel at providing. According to the Federal Reserve System, warehouses using automated systems reduce operational downtime by 25%, ensuring timely deliveries during peak seasons. Additionally, according to the International Labour Organization, repetitive manual tasks lead to a 30% higher error rate compared to robotic systems. These factors underscore the critical role of robotics in meeting consumer expectations for speed and accuracy while optimizing supply chain efficiency.
Labor Shortages and Rising Costs
Labor shortages are propelling the adoption of warehouse robotics globally. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projects a 20% decline in available warehouse workers by 2030 due to aging populations and shifting workforce preferences. Simultaneously, wage inflation is rising, with the National Employment Law Project reporting an average 5% annual increase in logistics wages over the past five years. Automation offers a cost-effective solution as robots can operate continuously without fatigue or salary hikes. Furthermore, the World Economic Forum states that automation technologies could offset labor shortages by fulfilling up to 40% of repetitive tasks currently performed by humans. This makes robotics indispensable for maintaining productivity amidst tightening labor markets.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Initial Investment Costs
The substantial upfront costs associated with implementing warehouse robotics act as a significant restraint. The U.S. Department of Commerce estimates that deploying a single robotic system can cost between $50,000 and $100,000, depending on complexity. For small and medium enterprises, this financial burden often outweighs perceived benefits, especially when cash flow constraints exist. A report by the Small Business Administration reveals that only 30% of SMEs have access to sufficient capital for advanced technological upgrades. Additionally, maintenance expenses add another layer of financial strain, with the National Institute of Standards and Technology stating that annual upkeep costs range from 10% to 20% of initial investment. These barriers hinder widespread adoption, particularly among smaller players.
Technical Complexity and Integration Challenges
Integrating robotics into existing warehouse systems presents technical challenges that deter adoption. The European Union Agency for Cybersecurity warns that 60% of companies face compatibility issues when merging new robotic systems with legacy infrastructure. Such integration requires specialized expertise, which is scarce, according to the International Labour Organization, noting a global shortage of 40 million skilled tech workers by 2030. Furthermore, cybersecurity risks escalate with interconnected devices, as spotlighted by the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency, which recorded a 300% rise in cyberattacks targeting industrial automation systems since 2020. These complexities create hesitation among businesses despite potential long-term gains.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Advancements in Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence advancements present immense opportunities for warehouse robotics innovation. The National Science Foundation states that AI-powered robots can improve decision-making accuracy by 45% through real-time data analysis and predictive capabilities. Machine learning algorithms enable these systems to adapt dynamically to changing workflows, enhancing operational flexibility. Moreover, the U.S. Department of Energy shows that AI-driven optimization reduces energy consumption by 25% in automated facilities, aligning with sustainability goals. Governments worldwide are also supporting AI development, with China’s Ministry of Science and Technology allocating $15 billion annually toward AI research, further accelerating its integration into robotics. These developments position AI as a transformative force driving smarter and more efficient warehousing solutions.
Expansion into Emerging Markets
Emerging markets offer untapped potential for warehouse robotics expansion. The World Bank reports that urbanization rates in developing countries will reach 68% by 2050, creating massive demand for efficient logistics infrastructure. India’s Ministry of Commerce forecasts a 25% annual growth in e-commerce, requiring scalable automation solutions to handle increased volumes. Similarly, Africa’s rapid industrialization, supported by initiatives like the African Continental Free Trade Area Agreement, boosts warehousing needs. The United Nations Industrial Development Organization notes that investing in robotics in these regions could enhance productivity by 30%, addressing both economic and logistical challenges. This geographic diversification opens lucrative avenues for robotics providers seeking global growth.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Regulatory Compliance and Standardization Issues
Navigating regulatory frameworks poses a major challenge for warehouse robotics deployment. The International Organization for Standardization emphasizes that inconsistent safety standards across regions complicate international operations. For instance, Europe mandates stricter compliance under the Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC, requiring rigorous testing before implementation. Additionally, the U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration enforces stringent workplace safety regulations, imposing additional costs on manufacturers. Non-compliance risks penalties and operational delays, further complicating market entry. Harmonizing global standards remains elusive, hindering seamless cross-border adoption despite growing demand for unified guidelines.
Resistance to Change Among Workforce
Workforce resistance to adopting robotics is a persistent challenge in the market. The International Labour Organization finds that 70% of employees express concerns about job displacement due to automation, leading to pushback during implementation phases. Training programs aimed at upskilling workers often face low participation rates, as noted by the U.S. Department of Labor, which reports only 40% employee engagement in reskilling initiatives. Furthermore, cultural resistance in traditional industries slows acceptance of new technologies. For example, Japan’s Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry reports that older generations in manufacturing sectors exhibit reluctance to embrace change, impacting overall productivity. Overcoming this psychological barrier is crucial for successful robotics integration.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
19.64% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Product, Function, Payload Capacity, Component, Software, Application Capacity, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
ABB, Bastian Solutions LLC, Daifuku Co. Ltd., Dematic, Fetch Robotics Inc., Honeywell International Inc, KNAPP AG, KUKA AG, OMRON Corporation, YASKAWA Electric Corporation, and FANUC Corporation. |
SEGMENT ANALYSIS
By Product Insights
The Mobile robots segment dominated the warehouse robotics market with a share of 40.1% in 2024 due to their ability to navigate dynamic environments and optimize workflows. As per the U.S. Department of Commerce, warehouses using mobile robots achieve a 25% increase in operational efficiency. For instance, Amazon deploys over 750,000 mobile robots globally to streamline order fulfillment. These robots are pivotal for e-commerce operations ensuring faster delivery times and reducing labor costs.
The Articulated robots segment exhibit a fastest CAGR of 18.5% driven by advancements in multi-axis technology. Their flexibility allows them to handle complex tasks like palletizing and packaging efficiently. A study by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) reveals that articulated robots reduce labor costs by up to 30%. Industries like automotive rely heavily on these systems due to their precision and adaptability. With global manufacturing output projected to grow at 3.5% annually, according to the World Bank, this segment is set to expand rapidly.
By Function Insights
The Pick & place operations segment held a 45.6% of the market share in 2024 emphasizing their critical role in streamlining warehouse activities. This function reduces human error by 50% while increasing throughput speeds significantly. E-commerce fulfillment centers benefit greatly, as they ensure timely order processing during peak seasons. According to the Federal Reserve System, businesses leveraging pick-and-place robots achieve a 20% reduction in operational downtime, making them indispensable for high-volume operations.
The Transportation segment within warehouses grows at a CAGR of 20.5% and is fueled by innovations in autonomous guided vehicles. Rising urbanization has led to shorter delivery windows, pushing companies to adopt efficient internal transport solutions. The U.S. Census Bureau reports a 60% surge in same-day deliveries since 2020, demostrates the need for seamless material movement inside facilities. Furthermore, transportation robots minimize energy consumption by 25%, per the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), positioning them as sustainable choices for future-ready warehouses.
By Payload Capacity Insights
The below 10 kg payload category commanded 50.3% of the market share in 2024 owing to its suitability for lightweight goods prevalent in e-commerce. Lightweight items constitute nearly 70% of online retail sales globally, per the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD). These robots excel in sorting small packages, enhancing accuracy rates by 35%. Their affordability and ease of deployment make them ideal for SMEs, contributing to widespread adoption across diverse sectors.
The Above 900 kg payload robots segment boast a CAGR of 22.8% propelled by heavy-duty applications in industries like automotive and construction. The U.S. Department of Energy indicates that large payload robots improve load-handling efficiency by 40%, reducing workplace injuries. As infrastructure projects gain momentum globally, valued at $15 trillion by Oxford Economics, this segment will continue expanding, addressing growing demands for robust mechanized solutions capable of managing bulky materials safely and effectively.
By Component Insights
The Hardware segment led the market with a 65.8% market share in 2024 backed by tangible assets like robotic arms, sensors, and actuators. Investment in durable hardware components ensures long-term reliability, essential for uninterrupted warehouse operations. The European Union’s Horizon 2020 program found that hardware-centric automation increases productivity by 30%, validating its central role in achieving scalable efficiencies. Given the capital-intensive nature of robotics, hardware remains foundational, driving sustained growth in the sector.
The Software segment shows a CAGR of 25.7% influenced by advancements in AI and machine learning capabilities, outlines Accenture Strategy. Real-time analytics offered by sophisticated software enhance decision-making processes, improving overall equipment effectiveness by 20%, based on findings from the National Science Foundation (NSF). Cloud integration trends also contribute to rapid software adoption, enabling remote monitoring and predictive maintenance functionalities crucial for optimizing resource allocation in modern supply chains.
By Software Insights
The WMS segment captured 55.1% of the software category in 2024 propelled by its comprehensive inventory tracking and order management features. Organizations using WMS experience a 25% improvement in stock accuracy levels, ensuring better customer satisfaction. Additionally, WMS integrates seamlessly with IoT devices, facilitating real-time updates vital for agile supply chain operations. Its widespread implementation underscores its importance as a cornerstone for digital transformation initiatives in warehousing.
The WES segment sees a CAGR of 30.1% bolstered by its ability to synchronize multiple warehouse functions simultaneously. By combining task prioritization with workforce optimization, WES enhances throughput by 40%, according to Manufacturing USA studies. Growing emphasis on omnichannel strategies amplifies the need for cohesive execution platforms capable of adapting to fluctuating consumer demands. As retailers strive for greater agility, WES emerges as a key enabler bridging gaps between planning and execution layers.
By Application Capacity Insights
The E-commerce segment moved ahead with a 50.6% market share in 2024 reflecting its dependence on automated systems for swift order fulfillment. Online shopping accounts for 20% of total retail sales globally, per the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), underscoring the necessity of robotics in meeting escalating consumer expectations. Automated picking and packing solutions tailored for e-commerce reduce cycle times by 35%, ensuring competitive advantage amidst fierce market dynamics.
The Healthcare applications grow at a CAGR of 27.5% spurred by stringent regulatory requirements and increased demand for sterile handling solutions, elaborates Frost & Sullivan. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that medical errors cost healthcare systems $42 billion annually, emphasizing the value of precise robotic interventions. Robots in pharmaceutical distribution centers boost accuracy rates by 45%, minimizing contamination risks. With an aging population projected to double by 2050, per United Nations projections, healthcare robotics will play a transformative role in safeguarding public health outcomes.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
North America was at the forefront of the warehouse robotics market with a 35.7% share in 2024 which was driven by its advanced technological infrastructure and high adoption of automation in logistics. The U.S. Department of Commerce reports that over 60% of warehouses in the region have implemented robotic systems and is boosting operational efficiency by 30%. E-commerce giants like Amazon and Walmart heavily invest in robotics, with Amazon deploying over 750,000 robots globally, many in North America. The region’s robust R&D ecosystem and strong presence of key players make it pivotal for innovation and market leadership.
Asia-Pacific exhibits highest CAGR of 22.2% fueled by rapid industrialization and the booming e-commerce sector, states McKinsey & Company. China alone accounts for 40% of global e-commerce sales, per the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD). Governments in the region such as India and Japan are investing heavily in smart manufacturing initiatives, with Japan’s Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry allocating $1 billion annually to robotics development. Rising labor costs and urbanization further accelerate adoption, making Asia-Pacific a hotspot for future growth.
Europe is poised for steady growth which is supported by stringent labor regulations and a focus on sustainability. The European Union’s Horizon Europe program allocates €95 billion to digital transformation including robotics ensures long-term market expansion. According to Eurostat, over 50% of EU-based warehouses plan to adopt robotics by 2025 to meet environmental targets. Germany is a manufacturing hub that leads adoption with an estimated 30% annual increase in robotic installations. Europe’s emphasis on precision and eco-friendly solutions positions it as a key contributor to global advancements.
Latin America shows moderate growth potential propelled by rising investments in logistics infrastructure. The Inter-American Development Bank revealed a $10 billion investment pipeline in regional warehousing projects, fostering robotics adoption. Brazil, the largest economy, reports a 15% annual rise in automated systems usage, per the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics. While challenges like limited technical expertise persist, increasing trade volumes and urbanization will propel demand.
The Middle East and Africa shows gradual adoption backed by government-led smart city initiatives. Dubai’s Smart City 2025 strategy aims to automate 25% of municipal services, including warehousing, says the Dubai Government. South Africa’s Department of Trade and Industry projects a 10% annual increase in robotics investments due to mining and retail sector demands. Despite slower initial uptake, growing urban populations and infrastructure development will drive steady growth.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
The major players in the global warehouse robotics market include ABB, Bastian Solutions LLC, Daifuku Co. Ltd., Dematic, Fetch Robotics Inc., Honeywell International Inc, KNAPP AG, KUKA AG, OMRON Corporation, YASKAWA Electric Corporation, and FANUC Corporation.
TOP 3 PLAYERS IN THE MARKET
Amazon Robotics (formerly Kiva Systems)
Amazon Robotics is a leader in warehouse automation, revolutionizing logistics with its advanced robotic systems. Acquired in 2012 as Kiva Systems, the company has deployed over 750,000 robots across Amazon’s fulfillment centers. These robots handle sorting, picking, and transportation, significantly reducing human workload and enhancing delivery speed. Notable innovations include Proteus, Amazon’s first fully autonomous robot, and Sparrow, an AI-driven robotic arm capable of handling diverse inventory. With a focus on artificial intelligence, Amazon Robotics continues to invest in improving efficiency, optimizing storage space, and reducing operational costs. This expansion aligns with Amazon’s strategy to dominate the e-commerce logistics space through automation and AI-powered robotics.
ABB Ltd.
ABB Ltd. is a global leader in automation and industrial robotics, providing solutions that enhance warehouse efficiency and reduce reliance on human labor. ABB's robotic arms and AI-driven automation systems assist in material handling, palletizing, sorting, and packing operations. The company’s presence in logistics, manufacturing, and distribution sectors makes it a key player in warehouse robotics. ABB’s FlexPicker robots and collaborative robots (cobots) enable businesses to automate repetitive warehouse tasks with high precision. With strong market positioning in Europe, Asia-Pacific, and North America, ABB continues to invest in AI, cloud-based automation, and machine learning, ensuring scalable and adaptable solutions for warehouses worldwide.
KUKA AG
KUKA AG is a German robotics company specializing in warehouse automation and provides intelligent robotic solutions for logistics as well as manufacturing. Its robotic arms and mobile automation platforms help optimize warehouse efficiency by automating palletizing, sorting, and picking operations. KUKA’s AI-driven automation software enables warehouses to manage high-order volumes with minimal human intervention. The company has a strong presence in Europe and Asia where its robots streamline supply chain processes. KUKA also focuses on collaborative robotics (cobots) to work alongside human workers, improving safety and productivity. With continuous R&D investments, KUKA remains a leading innovator in AI-driven robotics, shaping the future of warehouse automation.
TOP STRATEGIES USED BY THE KEY MARKET PARTICIPANTS
AI-Powered Robotics and Automation
Key players like Amazon Robotics, ABB Ltd., and KUKA AG are heavily investing in AI-powered robotics to enhance warehouse efficiency and adaptability. AI-driven robots, such as Amazon's Sparrow and Proteus, leverage computer vision and machine learning to optimize picking, sorting, and transportation of goods. ABB's FlexPicker robots and KUKA's AI-driven automation systems use real-time data analysis to improve warehouse productivity. These advancements allow companies to reduce operational costs, improve accuracy, and speed up order fulfillment. AI-powered robotics also enable predictive maintenance, preventing system failures and reducing downtime, which is crucial for e-commerce giants and large-scale logistics operations.
Strategic Acquisitions and Partnerships
Mergers, acquisitions, and partnerships have played a crucial role in strengthening market presence. Amazon acquired Kiva Systems in 2012, rebranded it as Amazon Robotics, and has since dominated warehouse automation. ABB and KUKA have formed strategic alliances with AI and sensor technology firms to enhance robotic capabilities. These collaborations help companies integrate cutting-edge innovations into their existing solutions while expanding their global footprint. Such acquisitions allow firms to access new technologies, diversify their product offerings, and enter emerging markets while keeping a competitive edge in warehouse automation.
Expansion of Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)
Warehouse robotics leaders are focusing on developing and deploying Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) to revolutionize warehouse efficiency. Amazon’s Proteus, an AMR designed for seamless warehouse navigation, reduces human intervention while improving safety. ABB and KUKA have also introduced intelligent AMRs that adapt to changing warehouse environments and optimize material transport. These robots leverage advanced sensors, LiDAR, and AI algorithms to autonomously navigate warehouse floors, avoiding obstacles and optimizing workflows. The adoption of AMRs allows companies to scale operations, handle increasing order volumes, and meet the growing demand for faster, more efficient logistics.
COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
The warehouse robotics market is seeing intense competition as companies race to automate warehouses and meet the increasing demand for faster as well as more efficient logistics. The growth of e-commerce, supply chain complexities, and labor shortages has been turning businesses to robotics to improve operations. Major players like Amazon Robotics, ABB Ltd., and KUKA AG dominate the market, but several other companies are also making their mark by innovating with AI, automation, and intelligent robotic solutions.
Amazon Robotics spearheads with its vast network of autonomous robots, efficiently handling picking, sorting, and transportation in fulfillment centers worldwide. On the other hand, ABB Ltd. and KUKA AG specialize in industrial and collaborative robots, catering to various industries beyond e-commerce including manufacturing and logistics. These companies invest heavily in AI-powered automation, cloud integration, and smart robotics to stay ahead.
Smaller players and startups are also emerging by offering cost-effective and flexible robotics solutions to compete with market giants. The market is witnessing rapid technological advancements, with companies focusing on scalability, real-time data processing, and autonomous mobile robots (AMRs). As demand for faster fulfillment, reduced costs, and smarter warehouses continues to grow, the competition in warehouse robotics is only getting more intense and innovation-driven.
RECENT MARKET DEVELOPMENTS
- In February 2025, Agility Robotics deployed humanoid robots called "Digit" in a Spanx warehouse in Flowery Branch, Georgia. This innovation signifies a shift toward more flexible and capable robotic systems in warehouse operations, leveraging AI advancements to enhance automation.
- In February 2025, Amazon announced plans to invest up to $25 billion in robotics and AI for its retail operations. This investment aims to enhance warehouse automation, reduce operational costs, and improve delivery efficiency to compete with low-cost rivals.
- In February 2025, Hai Robotics introduced the HaiPick Climb, a robotic solution designed to simplify goods-to-person automation. This development allows warehouses and distribution centers to retrofit existing facilities with automation without major infrastructure changes.
- In March 2025, Amazon advanced its warehouse automation efforts by developing AI-powered picking robots like Robin and Sparrow. These robots use artificial intelligence and computer vision to autonomously retrieve products from shelves, improving efficiency and reducing operational costs.
- In December 2024, John Lewis implemented autonomous warehouse robots to enhance operations during the Christmas season. The deployment of 60 ten-meter-high Hai robots helped streamline picking, packing, and sorting processes, increasing warehouse productivity and storage capacity.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the global warehouse robotics market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Product
- Mobile Robots
- Articulated Robots
- Cylindrical Robots
- Scara Robots
- Parallel Robots
- Cartesian Robots
By Function
- Pick & Place
- Palletizing & De-palletizing
- Transportation
- Packaging
By Payload Capacity
- Below 10 kg
- 11 kg to 80 kg
- 81 kg to 400 kg
- 401 kg to 900 kg
- Above 900 kg
By Component
- Hardware
- Software
By Software
- Warehouse Management System
- Warehouse Control System
- Warehouse Execution System
By Application Capacity
- E-commerce
- Automotive
- Consumer Electronics
- Food & Beverage
- Healthcare
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia-Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
Which industries are the primary users of warehouse robotics?
Key industries include e-commerce, automotive, food and beverage, electronics, and pharmaceuticals.
What are the main functions performed by warehouse robots?
Warehouse robots primarily handle picking and placing, sorting and packaging, palletizing and depalletizing, and transportation tasks.
What factors are driving the growth of the warehouse robotics market?
Growth is driven by the expansion of e-commerce, labor shortages, and the need for increased efficiency in warehouse operations.
How is artificial intelligence impacting warehouse robotics?
AI enhances warehouse robotics by improving navigation, object recognition, and decision-making capabilities, leading to more efficient operations.
What is the future outlook for the warehouse robotics market?
The market is expected to continue growing, with ongoing advancements in AI and robotics technology leading to more widespread adoption.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from
$ 2500
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: sales@marketdataforecast.com