Global Immunoglobulins Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report Segmented By Type (Normal Immune Globulins Hyperimmune Globulins), Route of Administration and Region (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America and Middle East & Africa), Industry Analysis From 2025 to 2033
Global Immunoglobulins Market Size
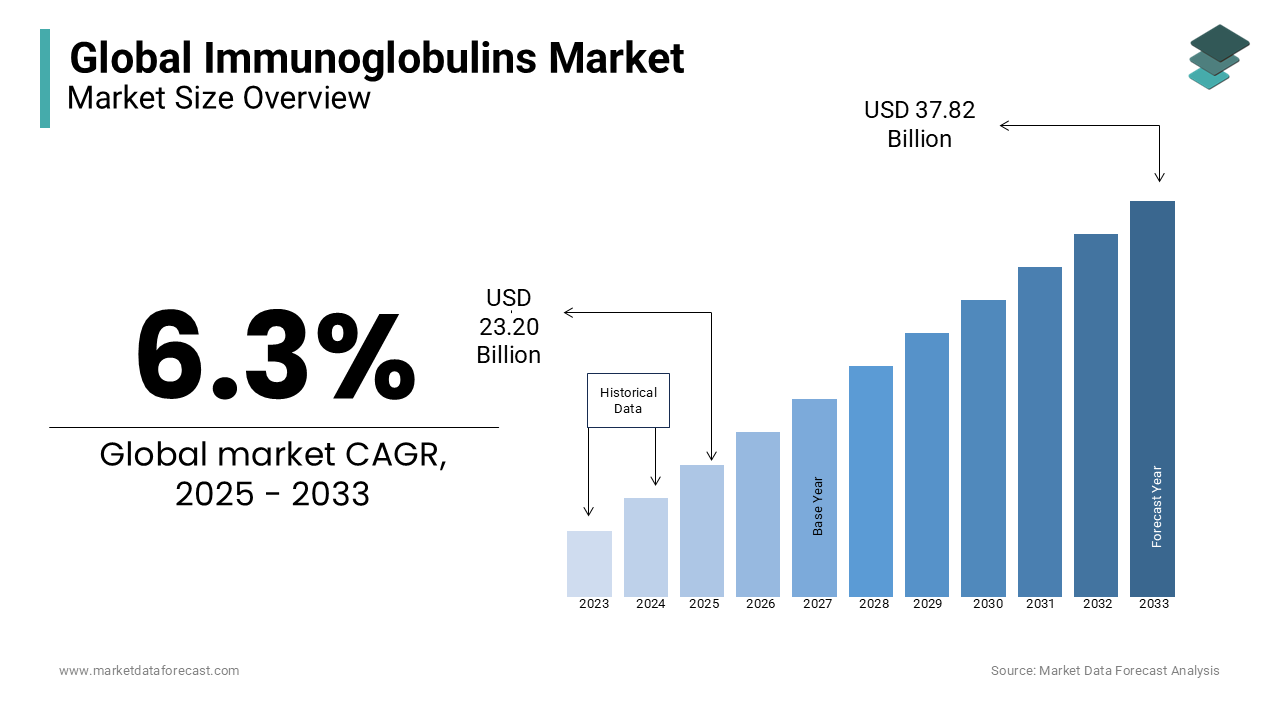
The global immunoglobulins market size was estimated at USD 21.83 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 37.82 billion by 2033 from USD 23.20 billion in 2025, growing at a CAGR of 6.3% from 2025 to 2033.
The Immunoglobulins focuses on therapies derived from antibodies that play a critical role in the immune system. Immunoglobulins, or antibodies, are used to treat a range of conditions, including primary immunodeficiency disorders (PIDD), autoimmune diseases, and certain neurological conditions. Approximately 6 million people globally suffer from PIDD by highlighting the importance of immunoglobulin therapies.
Neurological applications, such as treating Guillain-Barré syndrome and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP), are significant contributors to market growth with CIDP affecting 1-2 per 100,000 people annually. Advancements in production techniques have improved the safety and efficacy of immunoglobulin products by reducing adverse reactions.
MARKET DRIVERS
Rising Prevalence of Autoimmune Diseases
The increasing prevalence of autoimmune diseases is a key driver for the immunoglobulins market. Conditions such as multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, and lupus require immunoglobulin therapies to modulate immune responses. For instance, an estimated 4 million people globally live with multiple sclerosis, many of whom benefit from immunoglobulin treatments. Advances in diagnostics are improving early detection rates that is driving the demand to the extent. The use of immunoglobulins in managing inflammation and preventing immune-mediated damage continues to grow with autoimmune conditions become more common due to genetic and environmental factors is boosting the market significantly.
Expansion of Subcutaneous Immunoglobulin (SCIG) Therapies
The shift toward subcutaneous immunoglobulin (SCIG) therapy is another major driver. SCIG offers patients greater flexibility with at-home administration and fewer side effects compared to intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) therapies. This convenience has led to higher adoption rates, especially for chronic conditions like primary immunodeficiency disorders (PIDD). Studies indicate that SCIG reduces hospital visits by 30-40% by improving patients’ quality of life while reducing healthcare costs. The development of advanced SCIG delivery devices is further fueling its adoption by making it a significant growth factor in the immunoglobulins market.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Cost of Immunoglobulin Therapies
The high cost of immunoglobulin therapies is a significant restraint for the market. Treatments like intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) and subcutaneous immunoglobulin (SCIG) are expensive, with annual costs ranging from $25,000 to $50,000 per patient by depending on the condition and dosage. This financial burden limits accessibility, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. Additionally, the need for regular administration in chronic conditions further escalates expenses for patients and healthcare systems. High production costs is due to involving plasma collection and complex purification processes which contribute to these high prices by posing a barrier to widespread adoption of immunoglobulin therapies.
Limited Plasma Supply
Immunoglobulin therapies rely on human plasma as the primary raw material, making limited plasma supply a critical challenge. Collecting plasma is time-consuming, with over 1,000 plasma donations required to treat a single patient with PIDD annually. The rising global demand for immunoglobulins outpaces the supply of plasma, creating shortages in some regions. Factors like donor availability, strict regulatory requirements, and high production standards exacerbate the issue. This imbalance between supply and demand restricts the growth of the market and emphasizes the need for alternative manufacturing solutions.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Emerging Applications in Infectious Disease Treatments
The use of immunoglobulins in treating infectious diseases is gaining traction, particularly for emerging viral infections like respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), severe influenza, and COVID-19. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), RSV causes over 33 million lower respiratory tract infections annually in children under five, with 3.6 million requiring hospitalization. Immunoglobulins, such as hyperimmune globulins, have shown promise in providing passive immunity during outbreaks. For example, during the 2014 Ebola outbreak, hyperimmune globulin therapy demonstrated a 40% reduction in mortality rates in clinical trials. Similarly, during the COVID-19 pandemic, convalescent plasma therapy was widely used, with over 500,000 units administered in the U.S. alone by 2021, according to the FDA. As global healthcare systems prioritize pandemic preparedness, the demand for immunoglobulin-based treatments is expected to grow, creating opportunities for manufacturers to expand their portfolios and address unmet medical needs.
Advancements in Recombinant Immunoglobulin Technologies
Recombinant immunoglobulin production is emerging as a promising solution to overcome plasma supply constraints. Unlike traditional plasma-derived immunoglobulins, recombinant technologies use advanced cell culture systems to produce antibodies, ensuring consistent quality and scalability. These innovations can reduce reliance on human plasma, addressing shortages while offering a more sustainable supply chain. For instance, CSL Behring and Takeda Pharmaceuticals are investing heavily in recombinant technologies, with Takeda’s rIX-FP (recombinant factor IX) already approved for hemophilia B treatment. Recombinant products are also being developed for specific autoimmune and rare diseases, expanding their therapeutic applications. As this technology gains acceptance, it opens opportunities for manufacturers to cater to unmet clinical needs and enhance market growth with innovative and next-generation immunoglobulin therapies.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Complex Regulatory Requirements
Navigating stringent regulatory frameworks is a significant challenge in the immunoglobulins market. The production of immunoglobulin therapies involves plasma collection, purification, and testing, all under strict regulations to ensure safety and efficacy. These processes are time-consuming and costly by delaying market entry for new products. For example, the average time to develop and approve a plasma-derived therapy can exceed 7-10 years by creating barriers for smaller companies. Additionally, regional differences in regulatory standards further complicate global distribution by making it difficult for manufacturers to expand into new markets efficiently.
Adverse Reactions and Side Effects
Adverse reactions associated with immunoglobulin therapies pose a challenge to their adoption. While generally effective, these treatments can cause side effects such as headaches, nausea, and severe allergic reactions in some patients. 10-20% of patients receiving intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) experience mild to moderate side effects. Managing these risks requires careful monitoring and individualized dosing by adding to healthcare provider burdens. Concerns about potential long-term effects, such as thrombotic events are discouraging some patients and clinicians from considering immunoglobulin therapies by highlighting the need for safer formulations and improved administration methods.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
Segments Covered |
By Type, Route of Administration, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis; DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter's Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Market Leader Profiled |
Grifols, S.A., CSL Behring, Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, Kedrion Biopharma Inc., Octapharma AG, Biotest AG, LFB S.A., China Biologic Products Holdings, Inc., Baxter International Inc.M, ADMA Biologics, Inc. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Type Insights
Normal Immune Globulins dominate the global immunoglobulins market with 70-75% of the market share in 2024. This segment’s leadership is driven by its widespread use in treating primary immunodeficiency disorders (PIDs), which affect over 6 million people globally, according to the Immune Deficiency Foundation (IDF). Normal immune globulins, such as intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) and subcutaneous immunoglobulin (SCIG) are also critical for managing chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) and multifocal motor neuropathy (MMN). The U.S. FDA has approved over 20 IVIG products for these conditions. The segment’s growth is further supported by the rising prevalence of autoimmune diseases and the increasing adoption of immunoglobulin therapies in emerging markets.

The Hyperimmune Globulins segment is projected to grow at a CAGR of 12% from 2025 to 2033. This growth is fueled by their targeted use in treating infectious diseases and specific immune deficiencies. For instance, hyperimmune globulins are critical in managing hepatitis B, rabies, and tetanus, with the World Health Organization (WHO) reporting over 59,000 global deaths annually from rabies alone. The segment has also gained prominence during the COVID-19 pandemic, with convalescent plasma therapy being used in over 500,000 cases in the U.S., according to the FDA. Additionally, hyperimmune globulins are being developed for emerging infectious diseases, such as Zika and Ebola by highlighting their importance in pandemic preparedness. The segment’s rapid growth is driven by increasing R&D investments and the urgent need for effective treatments against infectious threats.
By Route of Administration Insights
Intravenous (IV) Administration is the largest segment, accounting for approximately 71.2% of the global market share as of 2024. This dominance is due to its established efficacy in treating various immunodeficiency disorders and autoimmune diseases. IV administration allows for rapid delivery of immunoglobulins, making it suitable for acute care settings. Its widespread adoption in hospitals and clinics underscores its critical role in managing conditions like primary immunodeficiency and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy.
Subcutaneous (SC) Administration is the fastest-growing segment, with a projected Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 9.3% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2033. This growth is driven by the convenience of at-home administration, improved patient compliance, and a lower incidence of systemic side effects compared to IV administration. SC administration empowers patients with chronic conditions to manage their therapy more independently, reducing the need for frequent hospital visits and enhancing their quality of life.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
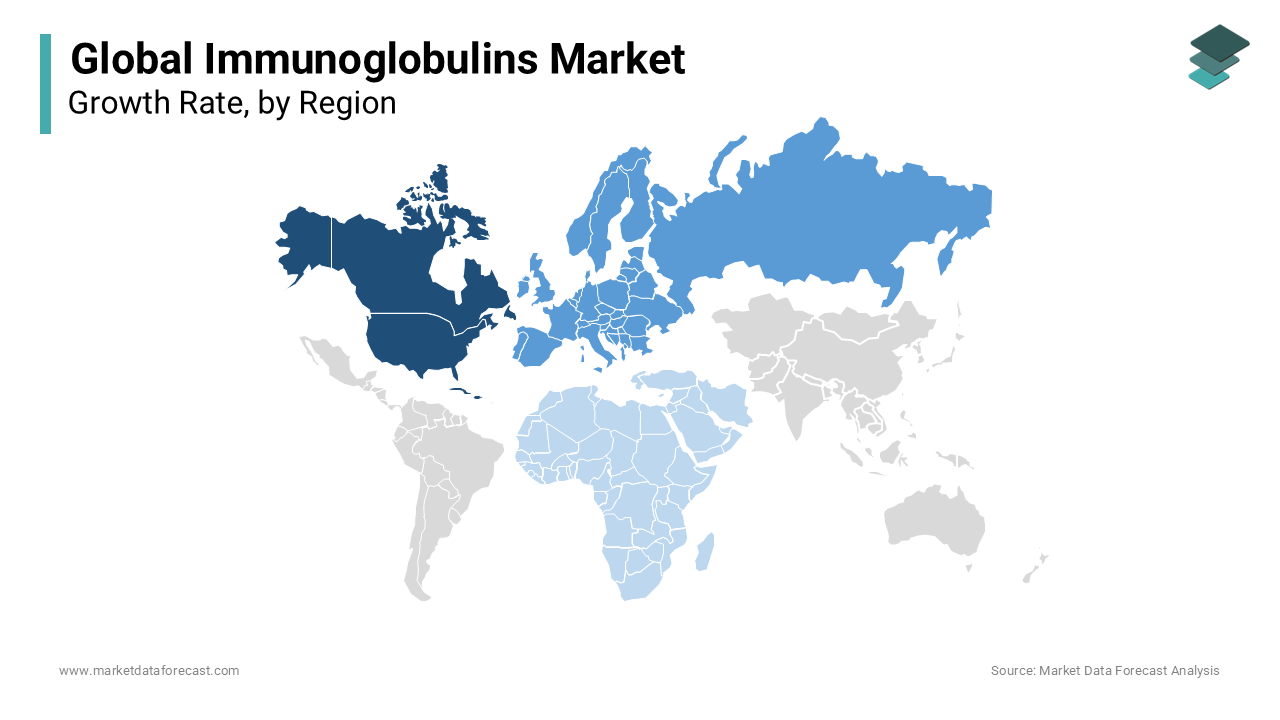
North America holds the largest share of the global immunoglobulins market at 40% during the forecast period 2025-2033. This is driven by advanced healthcare infrastructure and the high prevalence of immunodeficiency disorders like primary immunodeficiency disorders (PIDD), which affect over 250,000 individuals in the U.S. Neurological applications such as CIDP treatment are also significant, with CIDP affecting 1-9 per 100,000 people annually. The adoption of subcutaneous immunoglobulin (SCIG) therapy will reduce hospital visits by 30-40% which further strengthens the region's position.
Europe accounts for 30% of the global market share and is projected to grow at a significant CAGR. Germany, France, and the UK lead due to robust healthcare systems and government reimbursement policies. The region sees strong demand for immunoglobulin therapies to manage autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis, which affects over 2.8 million people globally, many of whom reside in Europe. Germany’s annual healthcare innovation investment exceeds €20 billion by fostering access to advanced therapies.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region, with a projected CAGR of 9% during the forecast period. Rising healthcare spending and improved diagnostic capabilities in countries like China, Japan, and India are driving growth. Over 30 million people in Asia suffer from immunodeficiency-related conditions. China, for example, increased healthcare funding by 7% in 2024 is expanding access to therapies for rare diseases.
Latin America immunoglobulins market is growing steadily. Brazil and Mexico lead, driven by increased awareness and healthcare investment. In Brazil, over 40,000 cases of Guillain-Barré syndrome treatable with immunoglobulins, are reported annually. Improvements in diagnostic infrastructure are enhancing access to immunoglobulin therapies across the region.
Middle East and Africa (MEA) represent with a significant CAGR. Limited adoption is due to infrastructure challenges, but Saudi Arabia’s $500 billion NEOM project, which includes advanced medical facilities is driving progress. In South Africa, awareness campaigns have led to a 10% increase in early diagnosis of immunodeficiency disorders which is showing signs of gradual market growth in the region.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS & COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
Grifols, S.A., CSL Behring, Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, Kedrion Biopharma Inc., Octapharma AG, Biotest AG, LFB S.A., China Biologic Products Holdings, Inc., Baxter International Inc.M, ADMA Biologics, Inc. are some of the key market players.
The Immunoglobulins Market is highly competitive, with established global players and emerging regional companies vying for market dominance. Key players like Grifols, CSL Behring, and Takeda Pharmaceutical hold significant shares due to their extensive product portfolios, robust distribution networks, and investment in R&D. These companies are focusing on innovation, such as the development of subcutaneous immunoglobulin (SCIG) therapies, which offer greater convenience and patient compliance compared to intravenous options.
Smaller players, including Kedrion Biopharma and Octapharma, are gaining ground by addressing unmet needs in niche therapeutic areas, such as rare diseases and off-label applications. Geographic expansion into emerging markets, particularly in Asia-Pacific and Latin America, is another strategy employed by these companies to capture growth opportunities.
The competition is also driven by advancements in recombinant technologies, which promise a sustainable alternative to plasma-derived products. For example, research into cell culture-based immunoglobulin production is intensifying as companies seek to address the ongoing plasma supply constraints.
Pricing pressure and regulatory challenges further intensify the competitive landscape, pushing manufacturers to focus on cost-efficiency while meeting stringent safety and quality standards. Overall, the market is characterized by innovation, strategic partnerships, and a growing emphasis on improving patient access to life-saving therapies globally.
RECENT MARKET DEVELOPMENTS
- In 2021, CSL Behring launched Hizentra, a subcutaneous immunoglobulin therapy, in Japan. This launch addressed the needs of primary immunodeficiency patients and expanded CSL’s product portfolio in the region.
- In 2021, Kedrion Biopharma partnered with Kamada Ltd. to commercialize a plasma-derived immunoglobulin product for COVID-19 treatment. This partnership expanded Kedrion’s therapeutic portfolio and addressed pandemic-related needs.
- In 2021, Biotest AG began constructing a new plasma protein plant in Dreieich, Germany. This project aims to double Biotest's immunoglobulin production capacity.
- In 2021, Baxter International Inc. launched Cuvitru, a subcutaneous immunoglobulin therapy, in the U.S. This launch provided more treatment options and strengthened Baxter’s product line.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the immunoglobulins market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Type
- Normal Immune Globulins
- Hyperimmune Globulins
By Route of Administration
- Intravenous (IV) Administration
- Subcutaneous (SC) Administration
- Others
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the major challenges in the immunoglobulins market?
Challenges include the high cost of therapies, limited availability of plasma, stringent regulatory requirements, and potential side effects such as allergic reactions and thrombotic events.
What are the recent developments in the immunoglobulins market?
Recent developments include advancements in plasma fractionation techniques, increased investment in plasma collection, the development of recombinant immunoglobulins, and improved immunoglobulin formulations with better efficacy and safety profiles.
Which region holds the largest market share?
North America holds the largest market share due to advanced healthcare infrastructure, high awareness, and the presence of key players.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from
$ 2500
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: sales@marketdataforecast.com
