North America Digital Substation Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report By Module (Hardware, Fiber-optic Communication Networks, SCADA), Insulation (Transmission Substation, Distribution Substation), Voltage (Up to 220kV, 220-500kV, Above 500kV), Application (Utility, Heavy Industries, Transportation, Others), and Country (United States, Canada, Mexico, Rest of North America) – Industry Analysis From 2025 to 2033.
North America Digital Substation Market Size
The size of the North America digital substation market was worth USD 2.53 billion in 2024. The North America market is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 7.01% from 2025 to 2033 and be worth USD 4.66 billion by 2033 from USD 2.71 billion in 2025.
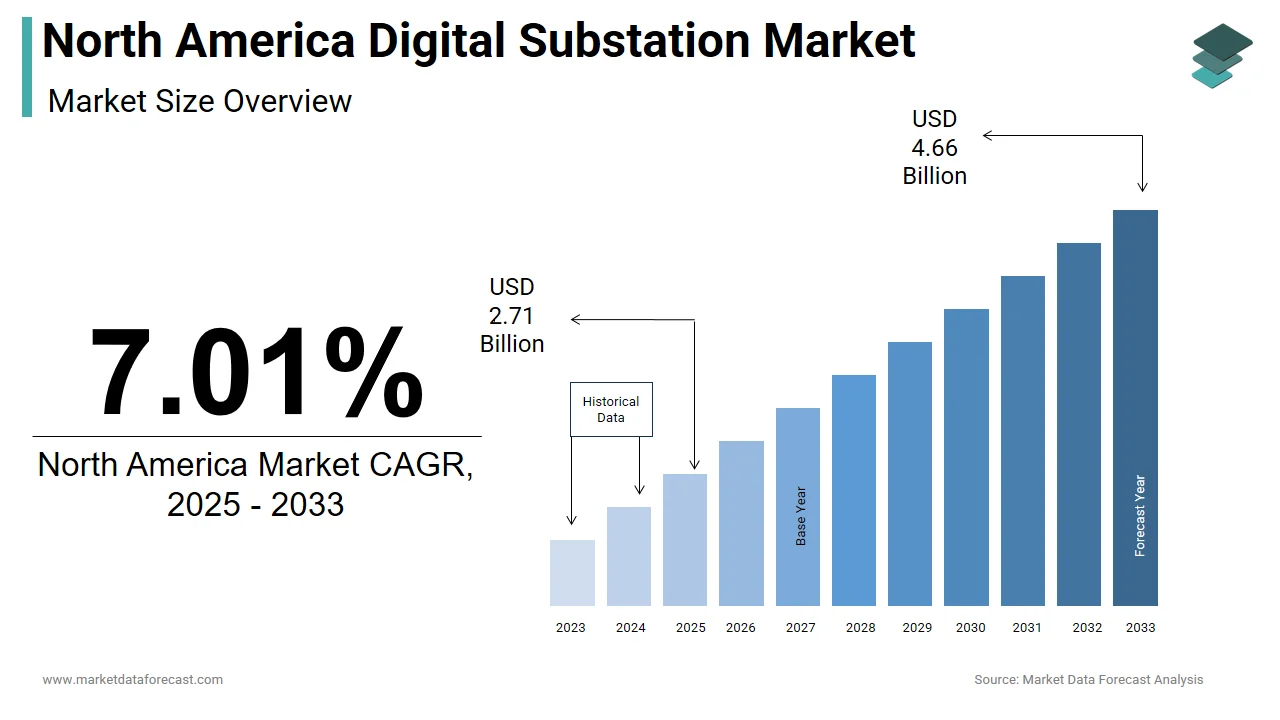
The North America digital substation market refers to the integration of intelligent electronic devices (IEDs), communication technologies, and automation systems within electrical substations to enhance grid reliability, operational efficiency, and real-time monitoring. These substations leverage IEC 61850 standards for seamless interoperability among components such as protection relays, control systems, and remote monitoring units. As power utilities modernize aging infrastructure and integrate renewable energy sources, the shift from conventional to digital substations has gained momentum across the United States and Canada.
In addition, the Canadian Electricity Association reported that approximately 75% of Canada’s electricity infrastructure requires modernization by 2030. These aging assets, combined with increasing demand for a reliable power supply and smart grid technologies, are driving the adoption of digital substations. Furthermore, the growing deployment of distributed energy resources (DERs) and electric vehicle charging stations necessitates advanced substation capabilities to manage bidirectional power flows and ensure system stability.
MARKET DRIVERS
Modernization of Aging Power Infrastructure
One of the primary drivers of the North America digital substation market is the urgent need to modernize aging power infrastructure. The U.S. Department of Energy estimates that nearly 70% of the country’s transmission and distribution lines were constructed in the 1970s or earlier, leading to frequent outages and inefficiencies. According to the American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE), the U.S. power grid received a grade of “C-” in its 2021 Infrastructure Report Card, underscoring the necessity for technological upgrades to improve resilience and performance. Digital substations offer a viable solution by enabling predictive maintenance, reducing downtime, and enhancing overall system reliability.
Digital substations play a critical role in this modernization effort by integrating advanced sensors, automation, and analytics to monitor equipment health and optimize operations. For instance, Ontario's Independent Electricity System Operator (IESO) has already initiated several digital substation pilot projects aimed at improving grid flexibility and reducing maintenance costs. With escalating investments in grid modernization and regulatory support for smart infrastructure development, the North American market for digital substations is experiencing robust growth driven by infrastructure renewal needs.
Integration of Renewable Energy Sources
The increasing penetration of renewable energy sources into the North American power grid is another significant driver of the digital substation market. As per the International Energy Agency (IEA), renewable energy accounted for over 20% of total electricity generation in the United States in 2023, with wind and solar contributing significantly to this growth. Canada, too, has made substantial progress, with hydroelectric, wind, and solar energy collectively providing over 80% of the country’s electricity generation, according to Natural Resources Canada.
Unlike traditional centralized power generation, renewable energy systems often involve decentralized and intermittent power sources such as rooftop solar panels and wind farms. This shift necessitates a more flexible and responsive grid infrastructure capable of managing bidirectional power flows, voltage fluctuations, and dynamic load balancing. Digital substations address these challenges through real-time data acquisition, automated control mechanisms, and advanced communication protocols like IEC 61850. They enable precise coordination between distributed energy resources (DERs) and grid operators, ensuring grid stability and efficient energy dispatch.
For example, the Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT) has implemented digital substation technology to better manage the influx of wind energy into the state’s grid.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Initial Investment Costs
Despite the long-term benefits associated with digital substations, one of the key restraints impeding their widespread adoption in North America is the high initial investment required for implementation. Unlike conventional substations that rely on analog systems and manual controls, digital substations incorporate advanced hardware such as intelligent electronic devices (IEDs), merging units, and fiber-optic communication networks, all of which significantly increase capital expenditures.
Like, the cost of deploying a fully digital substation can be up to 40% higher than that of a traditional substation. This includes not only equipment costs but also expenses related to software licensing, cybersecurity integration, and workforce training. While digital substations reduce operational and maintenance costs over time, many utility providers, especially smaller municipal and rural cooperatives, face budgetary constraints that delay investment decisions.
In Canada, the situation is similar. A study conducted by Manitoba Hydro found that retrofitting an existing substation with digital infrastructure could cost between CAD 1.5 million and CAD 3 million per unit, depending on complexity and scale.
Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities
Cybersecurity concerns represent a significant restraint in the expansion of the North America digital substation market. As digital substations rely heavily on interconnected IT/OT systems, they become increasingly susceptible to cyber threats that can compromise grid integrity and operational continuity. According to the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC), there was a 67% increase in reported cybersecurity incidents targeting the bulk power system in 2023 compared to the previous year. This rising threat landscape poses a major challenge for utilities adopting digital infrastructure.
Digital substations use standardized communication protocols such as IEC 61850, which, while facilitating interoperability, also expose systems to potential vulnerabilities if not properly secured. A breach in substation cybersecurity can lead to unauthorized access, equipment malfunction, or even large-scale blackouts. In 2021, the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) issued multiple advisories warning of exploitable flaws in industrial control systems used in substations, emphasizing the urgent need for robust security measures.
Moreover, implementing comprehensive cybersecurity protections adds to the complexity and cost of digital substation deployments. Utilities must invest in secure communication architectures, continuous monitoring systems, and employee training programs.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Expansion of Smart Grid Initiatives
The proliferation of smart grid initiatives across North America presents a significant opportunity for the digital substation market. Governments and utility providers are increasingly investing in smart grid technologies to enhance grid reliability, improve energy efficiency, and accommodate the growing share of renewable energy sources. According to the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), over $8 billion has been allocated since 2009 to support smart grid investments through the Smart Grid Investment Grant (SGIG) program, benefiting more than 100 utilities across the country.
Smart grids rely on real-time data exchange and automation to optimize power distribution, detect faults, and enable demand-side management. Digital substations serve as the backbone of these intelligent networks by integrating advanced sensing, communication, and control functionalities. For instance, Southern California Edison has deployed digital substations equipped with IEC 61850-compliant systems to facilitate seamless integration with its broader smart grid framework, improving fault detection response times.
Increasing Demand for Predictive Maintenance Solutions
The growing emphasis on predictive maintenance in the power sector offers a compelling opportunity for the expansion of the North America digital substation market. Traditional preventive maintenance practices are being replaced by data-driven approaches that leverage real-time diagnostics and machine learning algorithms to anticipate equipment failures before they occur. Digital substations, equipped with intelligent electronic devices (IEDs) and condition-based monitoring systems, play a crucial role in enabling this transition.
According to the Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI), predictive maintenance can reduce equipment downtime by up to 50% and lower maintenance costs by 25–30%. These efficiencies are particularly valuable in North America, where aging infrastructure and increasing service demands place pressure on utilities to maintain high levels of reliability.
Similarly, in Canada, BC Hydro has adopted digital substation platforms that provide continuous asset health assessments using sensor-based data streams.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Regulatory and Standardization Complexities
A major challenge facing the North America digital substation market is the evolving landscape of regulatory requirements and standardization frameworks. While digital substations offer superior performance and interoperability through protocols such as IEC 61850, the lack of uniform adoption and enforcement of industry-wide standards across different jurisdictions complicates implementation efforts.
In the United States, regulatory authority over power infrastructure is divided between federal agencies such as the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) and state-level public utility commissions. This fragmented governance structure leads to inconsistencies in compliance mandates, procurement policies, and cybersecurity benchmarks. According to the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC), variations in regional reliability standards can delay project approvals and create additional administrative burdens for utilities deploying digital substations.
These regulatory hurdles pose a significant challenge to market participants aiming to scale digital substation deployments efficiently across the region.
Skilled Workforce Shortage
Another pressing challenge confronting the North America digital substation market is the shortage of skilled professionals capable of designing, installing, and maintaining advanced digital infrastructure. As utilities transition from conventional electromechanical systems to digitized, protocol-driven environments, the demand for expertise in areas such as IEC 61850 configuration, cybersecurity, and system integration has surged.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), employment in the electrical power-line worker sector is projected to grow by 6% between 2022 and 2032, yet the availability of specialized personnel with digital substation experience remains limited.
Educational institutions and industry associations have responded by expanding training programs focused on smart grid technologies, however, the pace of workforce development lags behind the rapid adoption of digital substations.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
Segments Covered |
By Module, Insulation, Voltage, Application, and Region. |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional and Country-Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, Drivers, Restraints, Opportunities, Challenges; PESTLE Analysis; Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Countries Covered |
United States, Canada, Mexico, and the Rest of North America. |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
ABB Ltd., Siemens AG, General Electric Company, Schneider Electric, Honeywell International Inc., Cisco Systems Inc., Eaton Corporation plc, Emerson Electric Co., NR Electric Co. Ltd., Hitachi Energy Ltd, and others. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Module Insights
The hardware segment dominated the North America digital substation market, accounting for approximately 65% of the total market value in 2024. This dominance is primarily attributed to the foundational role that physical components such as intelligent electronic devices (IEDs), merging units, and protection relays play in enabling real-time monitoring, automation, and control within digital substations.
According to the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), over 70% of the country’s transmission infrastructure is aging, with many substations requiring comprehensive upgrades to meet modern reliability standards. As part of these modernization efforts, utilities are increasingly investing in advanced hardware components that support interoperability under IEC 61850 protocols.
The fiber-optic communication networks segment is projected to grow at the fastest CAGR of 9.4% from 2025 to 2033. This rapid expansion is driven by the critical need for secure, high-speed data transmission across digital substations, which rely on real-time communication between intelligent electronic devices (IEDs) and supervisory control systems.
As North American utilities integrate renewable energy sources and distributed energy resources (DERs), the demand for reliable and low-latency communication infrastructure has surged. A study by the Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI) found that fiber-optic networks reduce signal interference and improve system resilience compared to traditional copper wiring, making them ideal for digital substation environments.
By Insulation Insights
The transmission insulation segment had the largest market share, estimated at around 58% in 2024. This superiority is supported by the extensive investment in upgrading high-voltage transmission infrastructure to accommodate increasing electricity demand and the integration of renewable energy sources.
For example, the Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA) has allocated over $2 billion toward transmission system upgrades through 2027, incorporating digital substations equipped with high-performance insulation technologies.
Moreover, the rise in cross-border electricity trade between the U.S. and Canada has increased the reliance on ultra-high-voltage (UHV) transmission corridors, which mandate superior insulation materials. Companies like ABB and Schneider Electric have reported rising orders for gas-insulated switchgear (GIS) and vacuum interrupters tailored for transmission applications, reinforcing this segment’s leading position in the market.
The distribution insulation segment is anticipated to register the highest CAGR of 8.9% during the forecast period. This growth is fueled by the rapid electrification of rural areas, the proliferation of electric vehicles (EVs), and the increasing deployment of distributed energy resources (DERs) across urban centers.
Data from the International Energy Agency (IEA) indicates that EV sales in North America surpassed 1.5 million units in 2023, significantly increasing localized load demands on distribution networks. To accommodate this surge, utilities are investing in compact, modular insulation solutions suitable for digital substations located in densely populated zones.
Additionally, the Canadian Urban Transit Research & Innovation Consortium (CUTRIC) reports that public transit agencies are expanding fast-charging EV infrastructure, further boosting demand for efficient distribution insulation systems.
Furthermore, the push toward microgrid development driven by state-level incentives in states like California and Texas is enhancing the importance of distribution-level insulation. This convergence of DER integration and decentralized power generation is propelling the distribution insulation segment into a high-growth trajectory.
By Voltage Insights
The 220–500 kV voltage range led the regional market, representing a 48.8% of the North America digital substation market in 2024. This segment serves as the backbone of regional power grids, connecting major generation hubs to load centers while ensuring stable bulk power transmission.
Aging infrastructure is a key driver. Utilities such as PJM Interconnection have launched multi-billion-dollar grid modernization programs, prioritizing digital substations within this voltage class to enhance grid resilience and cyber-secure operations.
In Canada, Manitoba Hydro has undertaken several digital retrofits in 230 kV substations to support interprovincial power exchanges with Ontario and Saskatchewan. The Canadian Standards Association (CSA) also emphasizes the growing preference for gas-insulated switchgear (GIS) in this voltage category due to its compact footprint and reduced maintenance needs.
The up to 220 kV segment is poised to accelerate at the highest CAGR of 9.7% during the forecast period. This acceleration is largely driven by the rapid expansion of local distribution networks, the integration of distributed energy resources (DERs), and the rise in microgrid deployments.
According to the U.S. Department of Energy, a significant portion of new digital substation installations between 2021 and 2023 occurred in the sub-220 kV range, primarily serving commercial hubs, industrial parks, and residential communities. The proliferation of rooftop solar installations has necessitated intelligent substations capable of managing bidirectional power flow and maintaining voltage stability at lower voltage levels.
Similarly, Toronto Hydro has integrated more than 30 digital substations in the 138 kV range to support electric vehicle charging infrastructure expansion.
Moreover, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) reports that cities adopting climate action plans such as Los Angeles, Chicago, and Boston are increasingly opting for digital substations in this voltage class to enable smart grid functionalities and real-time asset monitoring.
COUNTRY-WISE ANALYSIS
The United States maintained a lead position in the North America digital substation market, holding an estimated market share of 76.3% in 2024. This superiority is anchored in the country’s large-scale grid modernization initiatives, aggressive renewable energy integration, and federal funding programs aimed at enhancing grid resilience.
Additionally, the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA) of 2021 allocates $73 billion to upgrade the nation’s power infrastructure, including digital substation deployment.
Utilities such as Southern California Edison and Dominion Energy have actively rolled out digital substations compliant with IEC 61850 standards, improving real-time diagnostics and reducing unplanned downtime. Furthermore, the rise in distributed energy resource (DER) integration, particularly in states like Texas and California, has necessitated intelligent substation infrastructure capable of handling variable power flows.
Canada is emerging as a key player in the North America digital substation market due to proactive government policies, aging infrastructure renewal programs, and the expansion of clean energy sources.
Provinces such as Ontario and Alberta have taken the lead, with the Independent Electricity System Operator (IESO) initiating multiple pilot projects to test digital substation capabilities in real-world conditions.
Hydro-Québec, one of North America’s largest electricity producers, has deployed over 50 digital substations since 2021, leveraging fiber-optic communication networks to enhance grid reliability and cybersecurity. Moreover, the Canadian Centre for Cyber Security (CCCS) has issued guidelines encouraging utilities to adopt standardized digital infrastructure to mitigate cyber risks, further accelerating adoption.
The Rest of North America, encompassing Mexico and select Caribbean nations, currently accounts for a significant share of the regional digital substation market in 2024. While still in early stages compared to the U.S. and Canada, this region is gaining traction due to increasing foreign investments, evolving regulatory frameworks, and growing emphasis on grid reliability.
In the Caribbean, countries such as Jamaica and Trinidad and Tobago are investing in microgrid-enabled digital substations to enhance energy security and reduce dependency on imported fuels. Despite challenges such as limited technical expertise and financial constraints, the Rest of North America presents promising opportunities for digital substation vendors, particularly as international aid and private equity investments begin to flow into the region’s power sector.
MARKET KEY PLAYERS
Companies playing a dominant role in the North America digital substation market profiled in this report are ABB Ltd., Siemens AG, General Electric Company, Schneider Electric, Honeywell International Inc., Cisco Systems Inc., Eaton Corporation plc, Emerson Electric Co., NR Electric Co. Ltd., Hitachi Energy Ltd, and others.
TOP LEADING PLAYERS IN THE MARKET
Siemens Energy
Siemens Energy is a leading global player in the digital substation market and holds a strong presence across North America. The company provides comprehensive digital substation solutions that integrate intelligent electronic devices, automation systems, and advanced cybersecurity protocols. Siemens has been instrumental in setting industry benchmarks through its adoption of IEC 61850 standards and its focus on interoperability and grid resilience. In North America, Siemens collaborates closely with major utilities to deploy next-generation substations that support renewable integration and smart grid initiatives.
General Electric (GE Vernova)
GE Vernova, formerly part of General Electric’s energy division, plays a pivotal role in shaping the digital transformation of power infrastructure in North America. With its robust portfolio of digital protection relays, control systems, and analytics platforms, GE offers scalable solutions tailored for both transmission and distribution applications. The company emphasizes predictive maintenance and real-time asset monitoring, enabling utilities to enhance operational efficiency and reduce downtime. GE’s strategic partnerships and localized service networks have strengthened its foothold in the region’s evolving digital substation landscape.
Schneider Electric
Schneider Electric is a key contributor to the North America digital substation market through its EcoStruxure Grid platform, which enables end-to-end digitization of electrical infrastructure. The company focuses on delivering modular, secure, and interoperable digital substation systems that support grid modernization and sustainability goals. Schneider’s commitment to innovation is evident in its integration of IoT-enabled sensors, cloud-based analytics, and cybersecurity frameworks into substation designs. By supporting utility decarbonization strategies and digital transformation programs, Schneider continues to expand its influence in North American power markets.
TOP STRATEGIES USED BY KEY MARKET PARTICIPANTS
One of the primary strategies employed by key players in the North America digital substation market is strategic partnerships and collaborations with utility providers, regulatory bodies, and research institutions. These alliances help companies align their product development with regional grid modernization goals and compliance requirements while gaining deeper insights into local market dynamics.
Another widely adopted approach is technology innovation and R&D investments, particularly in areas such as AI-driven diagnostics, edge computing, and cybersecurity enhancements. Companies are continuously refining their digital substation architectures to meet evolving performance and security standards, ensuring long-term competitiveness.
Lastly, expansion through acquisitions and localized service centers is a crucial growth strategy. By acquiring niche technology firms or establishing regional support hubs, market leaders can accelerate deployment timelines, improve customer responsiveness, and strengthen their presence in high-growth areas within the North American power sector.
COMPETITION OVERVIEW
The competition in the North America digital substation market is characterized by intense rivalry among established global players and emerging regional firms striving to capture market share through technological differentiation and strategic positioning. Leading vendors are increasingly focusing on enhancing product portfolios with integrated digital solutions that offer superior interoperability, scalability, and cybersecurity features. As utilities continue to prioritize grid modernization and renewable energy integration, companies are investing heavily in research and development to deliver more intelligent, adaptive, and resilient substation technologies. The market also sees growing participation from software-focused firms entering the space through partnerships or acquisitions, further diversifying the competitive landscape. While large multinational corporations maintain dominance due to their extensive resources and global expertise, smaller innovators are leveraging niche capabilities in automation, analytics, and communication systems to challenge the status quo. This dynamic environment fosters continuous innovation and drives the evolution of digital substations as a critical enabler of the future power grid.
RECENT MARKET DEVELOPMENTS
- In February 2024, Siemens Energy launched a new line of compact digital secondary substations designed specifically for urban distribution networks in North America. This product introduction aimed at addressing space constraints in metropolitan areas while supporting grid modernization efforts.
- In May 2024, General Electric (GE Vernova) announced a strategic collaboration with a major U.S. utility to deploy IEC 61850-compliant digital substations across several Midwestern states, reinforcing its position as a preferred technology partner for grid modernization projects.
- In July 2024, Schneider Electric expanded its EcoStruxure Grid ecosystem with the introduction of a cloud-based substation management platform tailored for North American utilities, offering enhanced remote monitoring and predictive maintenance capabilities.
- In September 2024, ABB opened a dedicated digital substation training and innovation center in Toronto, Canada, aimed at equipping engineers and utility personnel with specialized skills required for deploying and maintaining next-generation digital infrastructure.
- In November 2024, Eaton Corporation acquired a U.S.-based industrial cybersecurity firm to bolster its digital substation offerings, integrating advanced threat detection and secure communication protocols into its existing power management solutions for the North American market.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the North America digital substation market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Module
- Hardware
- Fiber-optic Communication Networks
- SCADA
By Insulation
- Transmission Substation
- Distribution Substation
By Voltage
- Up to 220kV
- 220-500kV
- Above 500kV
By Application
- Utility
- Heavy Industries
- Transportation
- Others
By Country
- United States
- Canada
- Mexico
- Rest of North America
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the main drivers fueling the North America Digital Substation Market?
Key drivers include grid modernization, rising energy demand, renewable energy integration, regulatory support for smart grids, and the need for improved reliability and cybersecurity
2. What role does renewable energy play in the North America Digital Substation Market?
The shift toward renewables like wind and solar drives demand for digital substations to manage variable power inputs and ensure stable, flexible grid operations
3. How is IoT technology transforming the North America Digital Substation Market?
IoT enables real-time data analytics, remote monitoring, and predictive maintenance, boosting operational efficiency and grid resilience
4. What trends are shaping the North America Digital Substation Market in 2025 and beyond?
Trends include IEC 61850 adoption, cloud-based solutions, advanced cybersecurity, automation, and increased integration of distributed energy resources
5. How does the market address cybersecurity challenges in digital substations?
Utilities are investing in advanced cybersecurity measures to protect critical infrastructure from rising cyber threats and ensure grid security
6. What is the significance of government initiatives in the North America Digital Substation Market?
Government funding and regulatory frameworks are crucial for promoting smart grid development, grid modernization, and adoption of digital technologies
7. What are the main challenges facing the North America Digital Substation Market?
Challenges include high initial investment, complexity of upgrading legacy systems, and the need for skilled personnel in digital operations
8. Which companies are key players in the North America Digital Substation Market?
Major players include ABB, Cisco, Emerson Electric, Hitachi Energy, and CG Power & Industrial Solutions, among others
9. How are industrial sectors benefiting from digital substations in North America?
Industrial users gain from enhanced power management, automation, and integration of renewables, improving efficiency and reducing downtime
10. What future opportunities exist in the North America Digital Substation Market?
Opportunities include further automation, AI-driven analytics, expansion into emerging markets, and ongoing upgrades to support the clean energy transition
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from
$ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: sales@marketdataforecast.com