Asia Pacific Cell Line Development Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report By Type (Primary Cell Line, Hybridomas, Continuous Cell Lines, Recombinant Cell Line), By Product (Equipment, Media & Reagent), By Application (Drug Discovery, Bioproduction, Tissue Engineering), and Country (India, China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, Rest of APAC) – Industry Analysis From 2025 to 2033.
Asia Pacific Cell Line Development Market Size
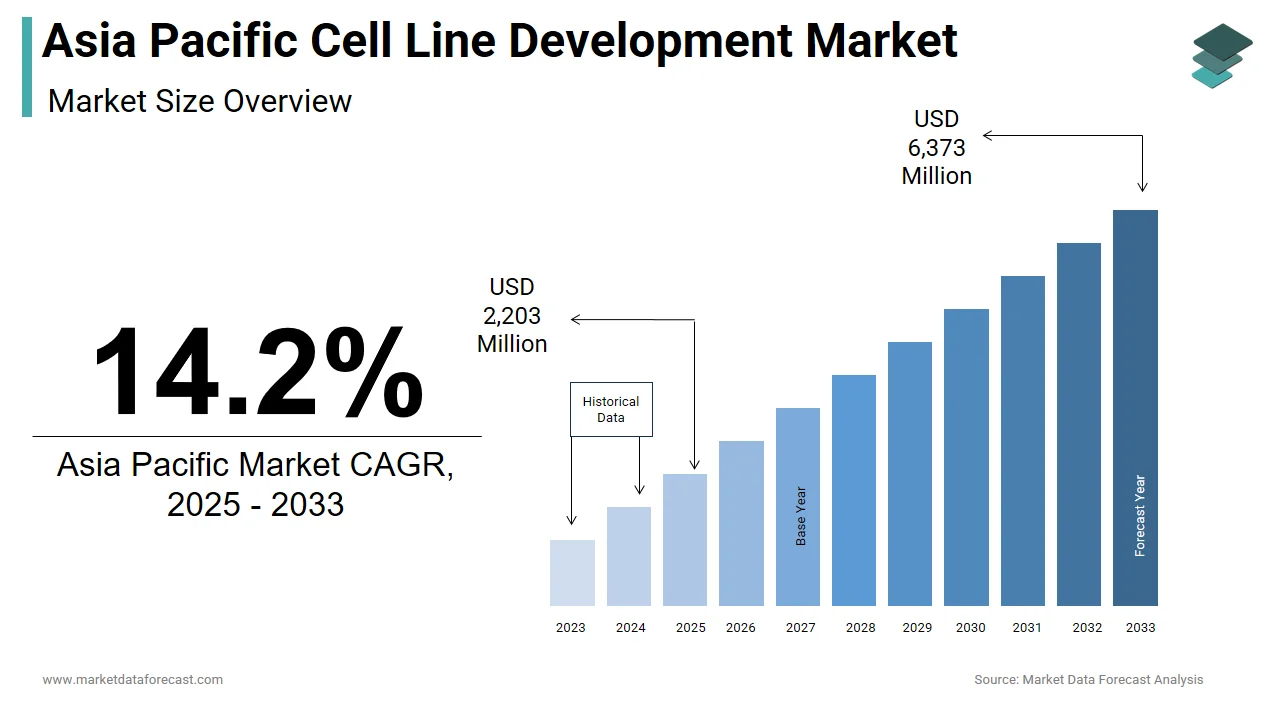
The size of the Asia Pacific cell line development market was worth USD 1,929 million in 2024. The Asia Pacific market is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 14.2% from 2025 to 2033 and be worth USD 6,373 million by 2033 from USD 2,203 million in 2025.
The cell line development process involves the genetic modification and selection of host cells primarily mammalian such as Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cells is to produce monoclonal antibodies, vaccines, and other biologics used in precision medicine and disease treatment. According to the International Society for Cell & Gene Therapy, over 40% of all new drug approvals by the U.S. FDA between 2015 and 2023 were biologics, many of which originated from advanced cell line platforms developed in Asia. Furthermore, government initiatives aimed at strengthening domestic biopharma capabilities, coupled with rising demand for biosimilars and personalized therapeutics, are reshaping the competitive landscape.
MARKET DRIVERS
Expansion of Biopharmaceutical Research and Development Activities
One of the primary drivers fueling the growth of the Asia Pacific cell line development market is the rapid expansion of biopharmaceutical research and development activities across the region. As governments and private enterprises increase investment in biotechnology, there is a corresponding rise in demand for high-quality, scalable cell lines capable of producing complex therapeutic proteins such as monoclonal antibodies and recombinant enzymes.
South Korea has also emerged as a leader in this space, with companies such as Samsung Biologics and Celltrion investing heavily in next-generation cell line platforms. As per the Korean Biomedical Review, the country’s biologics pipeline now includes over 60 candidates in clinical development, each requiring robust and stable expression systems.
Rising Demand for Biosimilars and Personalized Therapies
Another significant driver of the Asia Pacific cell line development market is the growing demand for biosimilars and personalized therapeutic approaches, which require highly optimized and reproducible cell lines for large-scale production. Biosimilars offer cost-effective alternatives to patented biologics, which is making them particularly attractive in emerging markets where affordability and accessibility are key considerations. In Japan, where an aging population drives demand for chronic disease treatments, the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare has actively encouraged the adoption of biosimilars through pricing reforms and reimbursement incentives. As per the Japan Bioindustry Association, the domestic biosimilars market grew by 22% in 2023, necessitating greater capacity for efficient and scalable cell line generation.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Cost and Complexity of Advanced Cell Line Development Technologies
A major restraint affecting the widespread adoption of cell line development services in the Asia Pacific region is the high cost and technical complexity associated with advanced technologies. Developing stable, high-yielding cell lines requires sophisticated tools such as gene-editing platforms, flow cytometry, high-throughput screening, and automated bioreactors, all of which demand substantial capital investment and technical expertise. For smaller biotech firms and academic institutions in countries like Indonesia, Vietnam, and the Philippines, these costs can be prohibitive, limiting access to cutting-edge development platforms.
Additionally, the complexity of maintaining regulatory compliance and ensuring reproducibility in cell line characterization adds another layer of challenge. As per the Asia Pacific Biotech Review, only 12% of biotech startups in Southeast Asia possess the internal capability to conduct full-scale cell line development independently, forcing them to rely on expensive CRO partnerships.
Shortage of Skilled Professionals and Limited Training Programs
Another critical barrier to the growth of the Asia Pacific cell line development market is the shortage of skilled professionals and limited availability of structured training programs in cellular engineering and bioprocessing. Cell line development is a highly specialized discipline that requires expertise in molecular biology, genetics, bioinformatics, and fermentation technology, yet there is a significant gap between industry demand and workforce readiness. As per the Asian Society for Molecular and Cellular Biology, less than 5% of life sciences graduates in the region receive formal training in industrial cell line development methodologies. In India, despite having a large pool of biotechnology students, only a handful of institutions offer dedicated courses in mammalian cell culture and transgenic cell engineering, according to the All India Council for Technical Education. Moreover, in countries like Thailand and Malaysia, the lack of industry-academia collaborations limits exposure to real-world applications of cell line technologies. According to a 2023 report by the Singapore Economic Development Board, nearly 70% of biotech firms operating in the region face challenges in recruiting personnel with hands-on experience in cell line optimization.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Growth of Contract Research Organizations (CROs) Specializing in Cell Line Services
The rapid expansion of contract research organizations (CROs) offering specialized cell line development services presents a significant opportunity for market growth in the Asia Pacific region. According to McKinsey & Company, the Asia Pacific CRO market grew by over 18% in 2023, with cell line development and biologics production emerging as key service areas. In China, companies like WuXi AppTec and Shanghai GenScript have expanded their cell engineering divisions to serve both domestic and international clients, leveraging lower labor and infrastructure costs to gain a competitive edge. India has also become a preferred outsourcing destination due to its strong scientific talent base and favorable regulatory environment. As per the Association of Biotechnology Led Enterprises, more than 30 CROs in India now offer comprehensive cell line development packages, supporting biosimilar and monoclonal antibody projects for global pharma firms.
Advancements in Gene Editing and Synthetic Biology Techniques
Advancements in gene editing and synthetic biology are opening new avenues for innovation in the Asia Pacific cell line development market. Technologies such as CRISPR-Cas9, TALENs, and base editing are enabling researchers to create highly specific, stable, and high-yielding cell lines with greater efficiency than traditional methods. These breakthroughs are transforming the landscape of therapeutic protein production and accelerating the development of next-generation biologics.
According to a 2023 report by the Asia Pacific Genome Editing Consortium, CRISPR-based cell line engineering is being adopted in over 60 research institutions across Japan, South Korea, and Singapore, with several commercial applications already in clinical development. In Japan, the University of Tokyo and Osaka University have launched collaborative projects with biopharma firms to develop novel CHO cell lines engineered for enhanced protein expression and reduced immunogenicity.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Regulatory Complexity and Divergent Approval Pathways
One of the most pressing challenges facing the Asia Pacific cell line development market is the presence of fragmented and inconsistent regulatory frameworks across different countries. Each nation within the region has its own regulatory authority, such as the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) in China, the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) in Japan, and the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) in India. These agencies impose varying requirements for the validation, documentation, and safety testing of genetically modified cell lines, complicating the commercialization process for developers.
According to a 2023 report by the Asia Pacific Regulatory Harmonization Initiative, the time required to obtain regulatory clearance for cell line-derived biologics can differ significantly, ranging from 12 months in Singapore to over 24 months in some ASEAN nations. This variability discourages multinational biotech firms from entering certain markets, which is limiting access to innovative cell line technologies and slowing down product development cycles. Additionally, the lack of standardized guidelines for gene-edited cell lines creates uncertainty regarding intellectual property rights and data submission protocols.
Intellectual Property Disputes and Patent Protection Issues
Intellectual property (IP) disputes and inadequate patent protection pose a significant challenge to the Asia Pacific cell line development market, particularly as innovation accelerates in gene editing and synthetic biology. While advancements in CRISPR, recombinant DNA technology, and proprietary cell engineering methods drive market growth, they also lead to overlapping claims, legal ambiguities, and enforcement difficulties across different jurisdictions.
According to the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), patent litigation involving biotechnology assets in the Asia Pacific region has increased by 25% over the past five years. In China, concerns about IP theft and weak enforcement mechanisms have prompted several global biotech firms to delay technology transfers or restrict access to proprietary cell line platforms. Similarly, in India, while the Patent Act provides a legal framework for biotech inventions, the interpretation of patent eligibility for genetically modified organisms remains ambiguous, leading to prolonged legal battles. In South Korea and Japan, although IP laws are more mature, the rapid pace of innovation often outpaces regulatory updates, resulting in conflicts over ownership of gene-edited cell lines. As per the Korea Invention Promotion Association, over 40% of recent biotech patents in the country have faced opposition or invalidation proceedings within two years of filing.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
Segments Covered |
By Type, Product, Application, and Region. |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional and Country-Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, Drivers, Restraints, Opportunities, Challenges; PESTLE Analysis; Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Countries Covered |
India, China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, New Zealand, Thailand, Malaysia, Vietnam, Philippines, Indonesia, Singapore, Rest of APAC |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Merck KGaA, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., SELEXIS, WuXi AppTec, General Electric, Lonza, and Corning Incorporated. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Type Insights

The recombinant cell line segment held the largest share of the Asia Pacific cell line development market with 38.3% in 2024. According to the Asian Society for Molecular and Cellular Biology, over 70% of approved biologics in the region rely on recombinant Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cells for large-scale production. In China, where biopharma investment has surged in recent years, more than 150 companies are actively engaged in developing recombinant-based therapeutics, as reported by the Chinese Biopharmaceutical Association. Moreover, technological advancements such as CRISPR-mediated gene editing and synthetic biology approaches have enhanced the efficiency and yield of recombinant cell lines, which is making them highly desirable for industrial applications. As per the Singapore Economic Development Board, local biotech firms have increasingly adopted automated cell line screening platforms that reduce development timelines by up to 40%.
The continuous cell lines segment is likely to gain huge traction with a CAGR of 12.6% throughout the forecast period. This growth is driven by their extensive use in high-throughput drug screening, viral vaccine production, and cancer research, where consistent and reproducible results are critical.
According to the Asia Pacific Biotech Review, continuous cell lines such as HEK293 and Vero cells are being widely used in preclinical studies and biomanufacturing workflows across India and South Korea. Furthermore, increasing collaboration between academic institutions and industry players is accelerating the development of novel immortalized cell models tailored for disease-specific applications. As per a 2023 report by the Korean Biomedical Research Foundation, South Korean biotech startups have launched more than 20 new continuous cell line platforms in the past two years alone.
By Product Insights
The media & reagents segment was the largest share of the Asia Pacific cell line development market with 54.7% in 2024. Nearly 80% of cell line development workflows require customized media solutions to support optimal cell growth and protein expression. In China, the National Medical Products Administration reported a surge in demand for chemically defined and animal-component-free media, with imports and domestic production both rising sharply in response to biopharma expansion. Additionally, government initiatives promoting indigenous bioprocessing capabilities have led to increased investments in local media manufacturing. As per the Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce and Industry (FICCI), India’s domestic media production capacity expanded by over 25% in 2023, reinforcing the sector’s foundational role in sustaining the region's cell line development ecosystem.
The equipment segment is projected to expand at a CAGR of 13.4% in the next coming years. In South Korea, where digital transformation in life sciences is advancing rapidly, leading institutions like KAIST and Samsung Biologics have integrated robotic liquid handling systems and AI-driven clone selection tools into their workflows. Japan’s Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) has also observed a shift toward modular bioreactor setups, which enhance process flexibility and reduce contamination risks. As per the Japan Bioindustry Association, over 40% of new biopharma facilities established in the country since 2021 feature next-generation bioreactors designed for scalable cell culture.
By Application Insights
The bioproduction segment led the Asia Pacific cell line development market with 47.6% of share in 2024. According to the Asia Pacific Biotech Review, over 85% of approved biologics in the region depend on mammalian cell lines primarily CHO and HEK293 for large-scale production. In China, where the biopharma sector has experienced exponential growth, the National Medical Products Administration recorded more than 200 active biologics development programs in 2023, each requiring dedicated cell line engineering efforts.
Additionally, the expansion of contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs) offering cell line development services has further boosted adoption. The bioproduction remains the most influential application area in the Asia Pacific cell line development market with increasing global demand for biosimilars and personalized therapies.
The drug discovery segment is projected to expand at a CAGR of 14.1% in the next coming years. This surge is driven by the increasing use of genetically engineered cell lines in target validation, high-throughput screening, and mechanism-of-action studies during early-stage pharmaceutical research.
According to the Asian Society for Molecular and Cellular Biology, over 60% of academic and industry-led drug discovery projects in the region now incorporate CRISPR-edited or reporter-expressing cell lines to enhance assay accuracy and predictability. In India, the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) has launched several collaborative initiatives with biotech firms to develop disease-specific cell models for oncology and infectious disease research.
COUNTRY LEVEL ANALYSIS
China was the largest contributor in the Asia Pacific cell line development market by accounting for 29.3% in 2024 due to its aggressive investments in biopharmaceutical research, rapid expansion of contract development and manufacturing organizations (CDMOs), and strong government backing for indigenous drug discovery. Companies like WuXi AppTec, Shanghai GenScript, and Sinocelltech have scaled up their offerings to serve both domestic and international clients, leveraging cost advantages and technical expertise.
Japan was positioned second with 18.4% of the Asia Pacific cell line development market share in 2024. The growth of the market in this country is leveraged by its advanced biotech infrastructure, mature pharmaceutical industry, and strong academic-industry collaborations. The country has long been a leader in regenerative medicine and precision therapeutics, fostering a conducive environment for cutting-edge cell line engineering. Government agencies such as the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) have implemented fast-track approval pathways for innovative biologics, encouraging greater investment in cell line development. As per the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, Japan’s biopharma exports reached record levels in 2023, with cell-based products forming a significant portion.
South Korea cell line development market growth is driven by its strong focus on biotech innovation and strategic investments in research infrastructure. The country has established itself as a regional leader in monoclonal antibody production and gene-editing applications, supported by a cluster of world-class biopharma companies and research institutes.
India cell line development market growth is primarily driven by its cost-effective R&D infrastructure, strong scientific talent pool, and increasing participation in global biopharma partnerships. According to the Department of Biotechnology, India has over 50 contract research organizations (CROs) offering cell line development services, many of which specialize in CHO-based expression systems and hybridoma technology. Companies like Biocon, Syngene, and Piramal Pharma Solutions have expanded their capabilities to support biosimilar and monoclonal antibody development for international markets.
Australia cell line development market is likely to be driven by its well-developed healthcare system, strong regulatory framework, and focus on translational research. The country maintains some of the highest clinical and quality control standards in the region, ensuring safe and effective deployment of cell line technologies. Universities such as Monash and the University of Melbourne are actively engaged in stem cell research and regenerative medicine, providing a strong foundation for future applications in drug discovery and personalized therapies. As per Deloitte’s 2023 healthcare report, Australia serves as a regional testing ground for global biotech firms seeking to introduce new cell line platforms in the Asia Pacific. This strategic positioning reinforces Australia’s role as a key contributor to the regional market.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
Some of the noteworthy companies in the APAC cell line development market profiled in this report are Merck KGaA, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., SELEXIS, WuXi AppTec, General Electric, Lonza, and Corning Incorporated.
TOP LEADING PLAYERS IN THE MARKET
Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
Thermo Fisher Scientific is a global leader in life sciences research and plays a pivotal role in the Asia Pacific cell line development market. The company offers an extensive portfolio of cell culture media, reagents, bioreactors, and gene-editing tools that support both academic and industrial applications. In the Asia Pacific region, Thermo Fisher has established strong distribution networks and collaborates with major biotech firms to provide end-to-end solutions for stable cell line generation. Its commitment to innovation and customer support has positioned it as a preferred partner across research institutions and pharmaceutical companies.
Merck KGaA (MilliporeSigma)
Merck KGaA, operating under the brand name MilliporeSigma in the U.S. and Canada, is a key player in the global and regional cell line development landscape. The company provides advanced cell engineering platforms, including CRISPR-based tools, transfection reagents, and chemically defined media tailored for high-yield protein production. In the Asia Pacific, Merck has expanded its technical service teams and launched localized training programs to enhance adoption among emerging biopharma firms. Its integrated offerings help streamline the development process from discovery to commercialization.
Lonza Group Ltd.
Lonza is a leading contract development and manufacturing organization (CDMO) with a strong presence in the Asia Pacific cell line development market. The company specializes in customized cell line services, particularly for monoclonal antibody and vaccine production. Lonza supports clients through every stage of development, offering proprietary expression systems such as GS Xceed and scalable bioprocessing technologies.
TOP STRATEGIES USED BY KEY MARKET PARTICIPANTS
One of the primary strategies employed by leading players in the Asia Pacific cell line development market is technology innovation and platform integration , where companies continuously develop advanced tools and workflows to enhance efficiency and reproducibility in cell line generation. Another crucial approach is strategic partnerships and joint ventures , wherein manufacturers collaborate with academic institutions, biotech startups, and regulatory bodies to drive knowledge exchange and expand their application base.
COMPETITION OVERVIEW
The competition in the Asia Pacific cell line development market is characterized by a blend of global leaders and rapidly emerging regional players striving to capture a larger share of a dynamic and expanding industry. Multinational corporations dominate due to their comprehensive product portfolios, deep R&D capabilities, and well-established distribution networks. These companies invest heavily in next-generation technologies such as CRISPR, synthetic biology, and automated screening platforms to maintain technological superiority and accelerate client project timelines. At the same time, domestic firms are gaining momentum by offering cost-effective solutions, localized expertise, and agile service models tailored to the evolving needs of biopharmaceutical developers. As the demand for biosimilars, monoclonal antibodies, and regenerative therapies grows, so does the intensity of competition not only in terms of pricing but also in innovation, service delivery, and strategic positioning. Additionally, shifting regulatory landscapes and increasing collaboration between academia and industry further shape the competitive environment, requiring all participants to adapt quickly to sustain growth and relevance.
RECENT MARKET DEVELOPMENTS
- In March 2023, Thermo Fisher Scientific opened a new cell culture media manufacturing facility in Singapore aimed at enhancing supply chain resilience and supporting the rapid expansion of biopharma activities across Southeast Asia.
- In October 2023, Merck KGaA partnered with a leading Indian biotech firm to co-develop novel gene-editing protocols for high-yield cell lines, reinforcing its foothold in one of the fastest-growing R&D hubs globally.
- In May 2024, Lonza expanded its cell line development laboratory in Sydney, incorporating AI-driven clone selection tools to improve productivity and reduce development timelines for Australian and New Zealand-based clients.
- In November 2023, Bio-Techne launched a series of localized training workshops across South Korea to educate scientists on the latest advancements in recombinant cell line engineering and increase adoption of its proprietary media formulations.
- In February 2024, Sartorius AG acquired a majority stake in a Chinese CRO specializing in hybridoma technology, strengthening its ability to serve the growing monoclonal antibody development sector in the region.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This Asia Pacific cell line development market research report is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Type
- Primary Cell Line
- Hybridomas
- Continuous Cell Lines
- Recombinant Cell Line
By Product
- Equipment
- Media & Reagent
By Application
- Drug Discovery
- Bioproduction
- Tissue Engineering
By Country
- India
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Thailand
- Malaysia
- Vietnam
- Philippines
- Indonesia
- Singapore
- Rest Of APAC
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What drives the Asia Pacific cell line development market?
The Asia Pacific cell line development market is driven by rising demand for biopharmaceuticals, increased R&D investment, supportive government policies, and a growing focus on personalized medicine and biosimilars
2. What challenges affect the Asia Pacific cell line development market?
The Asia Pacific cell line development market faces challenges such as high development costs, regulatory complexities, ethical concerns over sourcing, and variability in product quality and standards across countries
3. What opportunities exist in the Asia Pacific cell line development market?
The Asia Pacific cell line development market offers opportunities in contract research and manufacturing, adoption of automation and high-throughput technologies, and expansion of biotech hubs supported by strategic collaborations
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: sales@marketdataforecast.com
