Europe Indoor Farming Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report By Facility Type (Greenhouses, Vertical Farms), Component (Hardware, Software, Services), Growing Mechanism (Aeroponics, Hydroponics, Aquaponics), Crop Category (Fruits, Vegetables & Herbs, Flowers & Ornamentals), and Country (Germany, UK, France, Italy, Rest of Europe) – Industry Analysis From 2025 to 2033.
Europe Indoor Farming Market Size
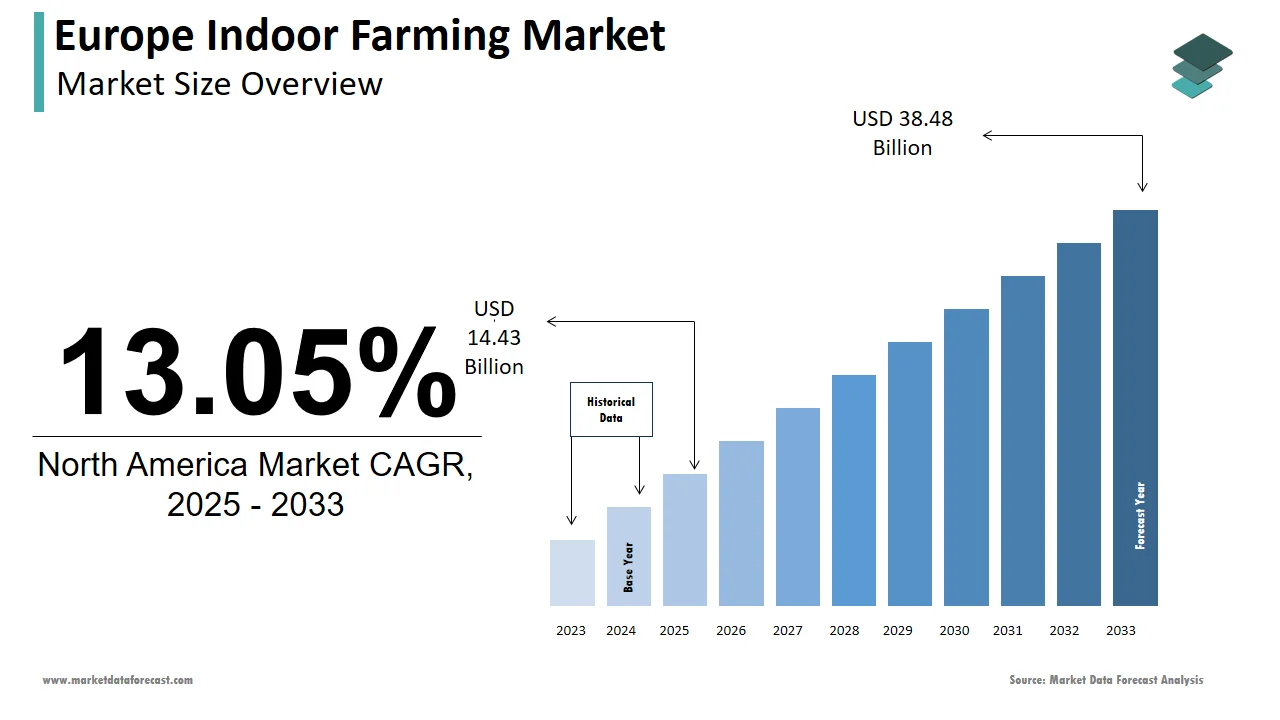
The indoor farming market size in Europe was valued at USD 12.76 billion in 2024. The European market is estimated to be worth USD 38.48 billion by 2033 from USD 14.43 billion in 2025, growing at a CAGR of 13.05% from 2025 to 2033.
The Europe indoor farming market is witnessing robust growth, driven by the increasing demand for sustainable agriculture and locally-grown produce. Countries like the Netherlands, Germany, and the UK are leading this transformation by owing to their advanced technological infrastructure and supportive government policies aimed at reducing carbon footprints in agriculture. According to Eurostat, urbanization in Europe has led to a reduction in arable land is creating opportunities for controlled-environment agriculture. This trend aligns with consumer preferences shifting toward pesticide-free and fresh produce. Additionally, as stated by the European Environment Agency, climate change concerns are pushing farmers to adopt resource-efficient methods that minimize water usage and energy consumption. The adoption of LED lighting and IoT-based monitoring systems further enhances productivity while ensuring sustainability.
MARKET DRIVERS
Growing Demand for Sustainable Food Production Systems
The Europe indoor farming market is being propelled by the increasing need for sustainable food production systems, driven by urbanization and population growth. According to projections by the European Commission, over 75% of Europe’s population is expected to live in urban areas by 2030 by leading to a significant reduction in arable land availability. The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) confirms that this urban shift has intensified pressure on traditional agriculture is making innovative solutions like indoor farming indispensable. Controlled-environment agriculture offers a viable alternative by enabling year-round cultivation while minimizing resource use. For instance, vertical farming systems, as per a study by the World Economic Forum, can produce up to 10 times more yield per square meter compared to conventional farming methods, while using 90% less water. This efficiency aligns with consumer preferences for locally sourced, pesticide-free produce, which has surged in demand across Europe.
Climate Change Mitigation and Agricultural Resilience
Another critical driver of the Europe indoor farming market is the urgent need to mitigate the adverse effects of climate change on agriculture. The European Environment Agency reports that extreme weather events have caused a 20% decline in crop yields across Southern Europe over the past decade. Indoor farming provides a robust solution by offering a controlled environment insulated from unpredictable climatic conditions. Technologies such as hydroponics and aeroponics, integral to indoor farming, optimize resource efficiency and reduce environmental impact. A report by McKinsey & Company emphasizes that the widespread adoption of these technologies could cut agricultural emissions by up to 30% is supporting the goals of the European Green Deal to achieve net-zero emissions. Additionally, government initiatives are further accelerating adoption; for example, subsidies for energy-efficient LED lighting in indoor farms lower operational costs and encourage investment.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Initial Investment and Operational Costs
One of the most significant restraints hindering the growth of the Europe indoor farming market is the high initial investment required to set up these advanced systems. According to a report by the International Finance Corporation (IFC), establishing a state-of-the-art vertical farm can cost between €5 million and €10 million, depending on the scale and technology used. This includes expenses for infrastructure, climate control systems, LED lighting, and automation tools. Such costs are often prohibitive for small-scale farmers or startups, limiting market entry to only well-funded enterprises. Furthermore, operational expenses remain a challenge due to the energy-intensive nature of indoor farming. The energy costs account for nearly 30% of the total operational expenses in indoor farms with artificial lighting and temperature control being the primary contributors.
Technological Complexity and Workforce Challenges
Another restraint is the technological complexity associated with indoor farming, coupled with a shortage of skilled labor. Indoor farming systems rely heavily on advanced technologies such as IoT sensors, AI-driven monitoring, and automated nutrient delivery systems. According to a study published by the European Centre for the Development of Vocational Training (CEDEFOP), nearly 40% of agricultural businesses in Europe struggle to find workers with expertise in precision agriculture and controlled-environment technologies. This skills gap poses a significant challenge, as improper management of these systems can lead to inefficiencies or crop failures. Additionally, the complexity of integrating multiple technologies increases the risk of technical malfunctions, which require specialized knowledge to resolve. The lack of standardized training programs further exacerbates this issue is leaving many potential adopters hesitant to invest in such systems. Moreover, as per insights from the European Innovation Partnership for Agricultural Productivity and Sustainability (EIP-AGRI), smaller farms often lack access to technical support networks, making it harder for them to overcome these challenges.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Integration of AI and Automation for Enhanced Efficiency
One of the most promising opportunities in the Europe indoor farming market lies in the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and automation technologies, which can significantly enhance operational efficiency and scalability. These technologies enable real-time monitoring of crop health, nutrient levels, and environmental conditions, allowing farmers to optimize resource use and maximize yields. For instance, automated irrigation systems powered by AI can reduce water consumption by up to 40%, as stated by the European Technology Platform for Sustainable Chemistry (SusChem). Moreover, robotics and machine learning algorithms are being deployed to automate labor-intensive tasks such as planting, harvesting, and packaging, reducing dependency on manual labor.
Expansion into Urban Areas and Localized Food Production
Another key opportunity for the Europe indoor farming market is the growing trend of urbanization and the increasing demand for localized food production. As per projections by the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE), urban areas will house 80% of Europe’s population by 2050, creating a pressing need for sustainable food systems within cities. Indoor farming offers a viable solution by enabling the cultivation of fresh produce in vertical farms located in urban centers, drastically reducing transportation costs and carbon emissions. A study by the Ellen MacArthur Foundation estimates that urban indoor farming could reduce food-related emissions by up to 28 million tons annually in Europe. Furthermore, consumer preferences are shifting toward locally grown, pesticide-free produce, with Nielsen reporting a 30% increase in demand for such products over the past five years. This trend is particularly pronounced in cities like London, Paris, and Berlin, where rooftop farms and vertical farming facilities are gaining traction.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Energy Dependency and Carbon Footprint Concerns
A significant challenge for the Europe indoor farming market is its heavy reliance on energy, which raises concerns about sustainability and carbon emissions. According to the European Environment Agency, indoor farming systems consume approximately 300-500 kWh of electricity per square meter annually, primarily for artificial lighting, climate control, and automation. While these systems are designed to optimize resource use, their energy-intensive nature can paradoxically contribute to higher carbon footprints if the electricity comes from non-renewable sources. For example, in countries like Poland and the Czech Republic, where coal still accounts for a significant share of the energy mix, indoor farming operations could inadvertently exacerbate environmental issues. According to a report by the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), transitioning to renewable energy sources could reduce emissions by up to 60%, but this shift requires substantial investment and policy support.
Limited Crop Diversity and Market Acceptance
Another pressing challenge is the limited crop diversity that indoor farming systems can currently support, which restricts their market potential. As per a study by Wageningen University & Research, indoor farms are predominantly used for cultivating leafy greens, herbs, and microgreens, which account for over 80% of the total produce. While these crops are well-suited for controlled environments, staples like grains, root vegetables, and fruits remain difficult to grow economically at scale due to their space and resource requirements. This lack of diversity limits the ability of indoor farming to meet broader dietary needs, potentially alienating segments of the consumer base. Furthermore, market acceptance remains a hurdle, as many consumers and retailers are unfamiliar with indoor-grown produce. A survey conducted by the European Consumer Organisation (BEUC) revealed that only 45% of European consumers are willing to pay a premium for indoor-farmed products, citing concerns about taste, texture, and nutritional value.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
13.05% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Facility Type, Component, Growing Mechanism, Crop Category, and Region. |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional and country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, Drivers, Restraints, Opportunities, Challenges; PESTLE Analysis; Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Countries Covered |
UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, Czech Republic, and the Rest of Europe. |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Argus Control Systems Ltd., Certhon, Richel Group, Netafim, General Hydroponics, Hydrodynamics International, Illumitex, Lumigrow, Signify Holding, Bowery Farming Inc, and others. |
SEGMENT ANALYSIS
By Facility Type Insights
The greenhouses segment dominated the Europe indoor farming market with highest share in 2024. The growth o the segment is driven by its established infrastructure and widespread adoption across key agricultural regions like the Netherlands, Spain, and Italy. The Netherlands, often referred to as the "greenhouse hub of Europe," contributes over 30% of the continent’s greenhouse-based produce, according to Wageningen University & Research. Greenhouses are favored for their versatility, enabling the cultivation of a wide range of crops, including tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers, which collectively represent over 70% of greenhouse production in Europe.
One of the primary factors driving this dominance is the high yield efficiency of greenhouses. According to a report by the European Commission, greenhouse farming can increase crop yields by up to 400% compared to traditional open-field farming while using significantly less water and land. Additionally, advancements in technologies such as climate control systems and hydroponics have further enhanced productivity. For instance, the integration of energy-efficient LED lighting has reduced operational costs by 25%, as stated by the International Energy Agency. Furthermore, government subsidies and incentives for sustainable agriculture have bolstered greenhouse adoption.
The vertical farms segment is projected to witness a CAGR of 15.8% from 2025 to 2033. This rapid expansion is fueled by urbanization and the increasing demand for hyper-localized food production in densely populated cities like London, Paris, and Berlin. According to Eurostat, urban areas in Europe are expected to house over 80% of the population by 2050 is creating a pressing need for innovative solutions to meet urban food demands. A key driver of this growth is the ability of vertical farms to maximize space utilization. A report by the World Economic Forum states that vertical farming systems can produce up to 10 times more yield per square meter than traditional farming methods by making them ideal for urban environments with limited arable land. Additionally, advancements in automation and AI have reduced labor costs and improved operational efficiency. For example, AI-driven nutrient delivery systems have cut resource wastage by 30%, as per PwC. Moreover, consumer preferences for pesticide-free and sustainably grown produce are propelling demand. Nielsen reports a 35% increase in sales of locally sourced, indoor-grown vegetables in Europe over the past three years. These factors, coupled with supportive government policies promoting urban agriculture, position vertical farms as the fastest-growing segment in the market.
By Component Insights
The hardware was the largest segment in the Europe indoor farming market with an estimated share of 55.3% in 2024. The growth of the segment is primarily driven by the extensive use of physical equipment such as LED grow lights, climate control systems, irrigation setups, and hydroponic infrastructure, which form the backbone of indoor farming operations. For instance, LED lighting alone accounts for nearly 30% of the hardware segment, with the Netherlands being a major adopter, using over 10 million LED fixtures in its greenhouse facilities, according to Wageningen University & Research. The demand for hardware is fueled by the need for precision agriculture tools that optimize resource efficiency. According to a report by the International Energy Agency, advanced LED lighting systems can reduce energy consumption by up to 40% compared to traditional lighting solutions, making them indispensable for indoor farms. Additionally, the growing adoption of automated systems for temperature, humidity, and nutrient control has further propelled hardware investments. According to Eurostat, hardware components account for nearly 60% of the initial setup costs for indoor farming facilities.
The software segment is augmented in holding a significant CAGR of 18.2% from 2025 to 2033. This rapid expansion is driven by the increasing integration of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and data analytics into farming operations, enabling real-time monitoring and decision-making. For example, AI-driven software platforms can predict crop health and optimize resource allocation with an accuracy rate of over 90%, as per PwC. A key factor fueling this growth is the rising complexity of indoor farming systems, which require sophisticated software for seamless operation. According to a study by the European Centre for the Development of Vocational Training (CEDEFOP), over 70% of indoor farms now rely on IoT-enabled software solutions to manage environmental parameters like lighting, temperature, and nutrient delivery. Moreover, the shift toward sustainability is amplifying demand for software that enhances energy efficiency. A report by the Ellen MacArthur Foundation notes that smart software systems have reduced energy usage by 25% in indoor farms across Europe. Additionally, the proliferation of cloud-based platforms has made these solutions more accessible to small and medium-sized enterprises.
By Growing Mechanism Insights
Thehydroponics segment held the dominant share of the Europe indoor farming market in 2024. The growth is driven by its versatility, scalability, and ability to produce high yields with minimal resource consumption. For instance, hydroponic systems can reduce water usage by up to 90% compared to traditional soil-based farming, as per the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). The Netherlands, a leader in hydroponic innovation, has adopted this method in over 70% of its greenhouse operations, producing crops like tomatoes, cucumbers, and lettuce that dominate European markets.
One of the primary factors driving hydroponics' is its compatibility with controlled-environment agriculture. A report by Wageningen University & Research states that hydroponic systems enable farmers to grow crops year-round, regardless of external weather conditions, ensuring consistent supply chains. Additionally, advancements in nutrient delivery systems have improved crop quality and productivity, with yields increasing by up to 25% in recent years. According to Eurostat, hydroponic farms also benefit from lower operational costs due to their reduced dependency on pesticides and fertilizers, which aligns with Europe’s stringent environmental regulations.
The aeroponics segment is swiftly emerging with a CAGR of 20.5% n the next coming years. This rapid expansion is fueled by the system's exceptional efficiency in resource utilization and its ability to produce premium-quality crops. For example, aeroponic systems use up to 98% less water than traditional farming methods, as stated by the World Economic Forum is making them particularly attractive in water-scarce regions like Southern Europe. The accelerated growth of aeroponics is driven by advancements in technology and increasing consumer demand for pesticide-free produce. According to a report by McKinsey & Company, aeroponic systems can achieve growth cycles that are 30% faster than hydroponics, enabling quicker harvests and higher profitability. Moreover, the system’s ability to grow crops without soil reduces contamination risks, appealing to health-conscious consumers. According to Nielsen, sales of aeroponically grown produce have surged by 40% in urban markets such as London and Paris over the past two years.
By Crop Category Insights
The vegetables and herbs segment dominated the Europe indoor farming market share in 2024. This segment's growth is driven by the high demand for fresh, pesticide-free produce in urban areas, where consumers are increasingly prioritizing health and sustainability. For instance, leafy greens such as lettuce, spinach, and kale represent over 50% of the vegetables grown indoors, according to Wageningen University & Research, due to their short growth cycles and adaptability to controlled environments.
One of the key factors propelling this dominance is the efficiency of indoor farming in producing nutrient-rich vegetables and herbs. As per a study by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), indoor-grown produce has 20% higher nutrient retention compared to conventionally farmed alternatives, appealing to health-conscious consumers. Additionally, the ability to cultivate these crops year-round, irrespective of seasonal constraints, ensures consistent supply chains. According to Eurostat, indoor vegetable production has grown by 35% over the past five years, with countries like the Netherlands and Germany leading the charge. Furthermore, government initiatives promoting sustainable agriculture have incentivized farmers to adopt indoor farming for vegetables and herbs, which aligns with the European Green Deal’s goals.
The Fruits segment is likely to gain huge traction with a CAGR of 17.3% from 2025 to 2033. This rapid expansion is fueled by advancements in indoor farming technologies that now enable the cultivation of fruit crops such as strawberries, blueberries, and even dwarf citrus varieties, which were previously challenging to grow in controlled environments.
The accelerated growth of this segment is driven by rising consumer demand for exotic and premium-quality fruits. A report by Nielsen reveals that sales of indoor-grown fruits have surged by 45% in urban markets like London and Paris over the past three years, as consumers seek locally sourced, pesticide-free options. Additionally, innovations in vertical farming systems and LED lighting have improved yield efficiencies for fruit crops by up to 30%, as per PwC. According to the European Environment Agency, indoor fruit farming also reduces water usage by 80% compared to traditional methods by making it an attractive option amid growing concerns about resource scarcity. Moreover, the increasing focus on reducing food miles and carbon footprints has further propelled investments in indoor fruit cultivation.
COUNTRY LEVEL ANALYSIS
The Netherlands was the largest contributor for the Europe indoor farming market with an estimated share of 30.1% in 2024. The country has positioned itself as a hub for innovation in controlled-environment agriculture. The Dutch government’s proactive support for sustainable farming practices has been instrumental in this success, with over €150 million invested annually in agricultural R&D, according to the Dutch Ministry of Agriculture, Nature, and Food Quality.
One of the key factors driving the Netherlands' dominance is its focus on export-oriented production. Eurostat data reveals that the country exports over €10 billion worth of greenhouse-grown vegetables annually, with tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers being the primary crops. Additionally, the Netherlands’ strategic adoption of hydroponics and vertical farming systems has enabled it to produce 10 times more yield per square meter than traditional farming methods. According to the European Environment Agency, Dutch indoor farms use 90% less water compared to conventional agriculture, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Germany indoor farming market is gaining huge traction with an esteemed CAGR of 15.4% in the foreseen years. The country’s emphasis on sustainability and resource efficiency has made it a hotspot for indoor farming innovations in urban areas like Berlin and Munich. Germany’s stringent environmental regulations have pushed farmers to adopt eco-friendly practices, with indoor farming emerging as a viable solution.
A major driver of Germany’s prominence is its strong integration of renewable energy in indoor farming operations. According to the Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems, over 40% of indoor farms in Germany now utilize solar and wind energy by reducing their carbon footprint significantly. Moreover, the growing consumer demand for organic and locally grown produce has fueled investments in vertical farming systems. Nielsen reports that sales of indoor-grown vegetables in Germany have increased by 30% over the past five years. Additionally, government subsidies for climate-smart agriculture have further accelerated adoption.
France is lucratively to grow with steady growth rate in the future period. While France has a long-standing tradition of open-field farming, it has embraced indoor farming as a means to address challenges such as urbanization, climate change, and food security. Cities like Paris and Lyon have become focal points for vertical farming startups is leveraging proximity to urban consumers.
A key factor driving France’s growth is its strong domestic demand for fresh, pesticide-free produce. According to Kantar Worldpanel, French consumers spent over €5 billion on organic and sustainably grown products in 2022, with indoor farming playing a pivotal role in meeting this demand. Additionally, the French government’s "Ecophyto Plan" aims to reduce pesticide usage by 50% by 2030 is encouraging farmers to adopt alternative methods like hydroponics and aeroponics. As per Eurostat, indoor farming in France has seen a 25% increase in adoption rates over the past three years.
Italy indoor farming market is to have the prominent growth opportunities in the next coming years. The country’s favorable climate and fertile soil have historically supported traditional farming, but the rise of urbanization and climate variability has spurred interest in indoor farming in regions like Lombardy and Emilia-Romagna.
One of the primary drivers of Italy’s growth is its focus on high-value crops such as basil, tomatoes, and strawberries, which thrive in controlled environments. According to the Italian Ministry of Agriculture, indoor farming has reduced water consumption by 70% while increasing yields by up to 300% for these crops. Furthermore, the Italian government’s "Green New Deal" initiative has allocated €2 billion toward sustainable agriculture projects, including indoor farming.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
Some notable companies that dominate the Europe indoor farming market profiled in this report are Argus Control Systems Ltd., Certhon, Richel Group, Netafim, General Hydroponics, Hydrodynamics International, Illumitex, Lumigrow, Signify Holding, Bowery Farming Inc, and others.
TOP LEADING PLAYERS IN THE MARKET
The Europe indoor farming market is dominated by innovative companies that have set benchmarks in sustainability and technological advancement. The top three players include Signify (formerly Philips Lighting), AeroFarms, and Plenty Unlimited.
AeroFarms, headquartered in the US but with significant operations in Europe, has revolutionized aeroponic systems by producing up to 390 times more yield per square foot than traditional farming. Plenty Unlimited, another US-based player expanding aggressively in Europe, focuses on vertical farming for leafy greens by supplying major retailers like Albert Heijn and Tesco. These companies contribute significantly to the global market by driving innovation in resource efficiency and scalability. For instance, Signify’s horticulture lighting solutions are used in over 50 countries, while AeroFarms’ patented technology reduces water usage by 95%.
TOP STRATEGIES USED BY KEY MARKET PARTICIPANTS
Key players in the Europe indoor farming market employ strategies such as partnerships, R&D investments, and acquisitions to strengthen their foothold. Collaborations with governments and universities are common; for example, Signify partners with Wageningen University to develop energy-efficient farming technologies. Companies also focus on expanding their product portfolios—AeroFarms launched modular aeroponic systems in 2023 to cater to small-scale farmers. Additionally, geographic expansion is a priority where Plenty Unlimited opened its first European facility in the UK in 2022. These strategies enhance market presence, drive innovation, and ensure compliance with regional regulations.
COMPETITION OVERVIEW
The Europe indoor farming market is highly competitive, characterized by rapid technological advancements and a focus on sustainability. Leading players like Signify, AeroFarms, and Plenty Unlimited dominate through innovation and strategic partnerships. Smaller startups, however, are gaining traction by offering affordable solutions for urban farming. According to Eurostat, competition is intensifying due to increasing demand for pesticide-free produce and government incentives for sustainable agriculture. Companies are investing heavily in R&D to differentiate themselves, with a particular emphasis on AI-driven automation and IoT integration. This dynamic landscape fosters innovation but also poses challenges for smaller players trying to compete with established giants.
TOP 5 MAJOR ACTIONS TAKEN BY KEY PLAYERS
- In April 2024, Signify partnered with the Dutch Ministry of Agriculture to launch a €50 million initiative aimed at promoting energy-efficient indoor farming technologies across Europe.
- In January 2023, AeroFarms acquired AgroSci, a UK-based vertical farming startup, to expand its footprint in Northern Europe and enhance its aeroponic system capabilities.
- In November 2022, Plenty Unlimited signed a supply agreement with Tesco to provide indoor-grown leafy greens exclusively to over 500 stores across the UK.
- In July 2023, Infarm, a Berlin-based vertical farming company, raised €200 million in Series D funding to scale its operations in Southern Europe, particularly Spain and Italy.
- In February 2024, Valoya, a Finnish LED lighting provider, collaborated with the Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences to develop next-generation LED grow lights optimized for Nordic climates.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This Europe indoor farming market research report is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Facility Type
- Greenhouses
- Vertical farms
- Shipping Container
- Building-based
- Others
By Component
- Hardware
- Climate Control Systems
- Lighting Systems
- Sensors
- Irrigation Systems
- Software
- Web-Based
- Cloud-Based
- Services
- System Integration & Consulting
- Managed Services
- Assisted Professional Services
By Growing Mechanism
- Aeroponics
- Hydroponics
- Aquaponics
By Crop Category
- Fruits, vegetables & herbs
- Tomato
- Lettuce
- Bell & Chili Peppers
- Strawberry
- Cucumber
- Leafy Greens
- Herbs
- Others
- Flowers & ornamentals
- Perennials
- Annuals
- Ornamentals
- Others
By Country
- UK
- France
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Russia
- Sweden
- Denmark
- Switzerland
- Netherlands
- Turkey
- Czech Republic
- Rest of Europe
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is driving the Europe indoor farming market?
Rising demand for fresh produce is driving the Europe indoor farming market.
2. Which technology is widely used in the Europe indoor farming market?
Hydroponics technology is widely used in the Europe indoor farming market.
3. What is a key trend in the Europe indoor farming market?
The adoption of vertical farming is a key trend in the Europe indoor farming market.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from
$ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: sales@marketdataforecast.com