Global Dicamba Herbicide Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report, Segmented By Crop Type (Cereals & Grains, Oilseeds & Pulses, And Pastures & Forage Crops), Formulation (Acid And Salt), Physical Form (Dry And Liquid), & Time Of Application (Pre- And Post-Emergence), And By Region (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and Middle East-Africa), Industry Analysis From (2025 to 2033)
Global Dicamba Herbicide Market Size
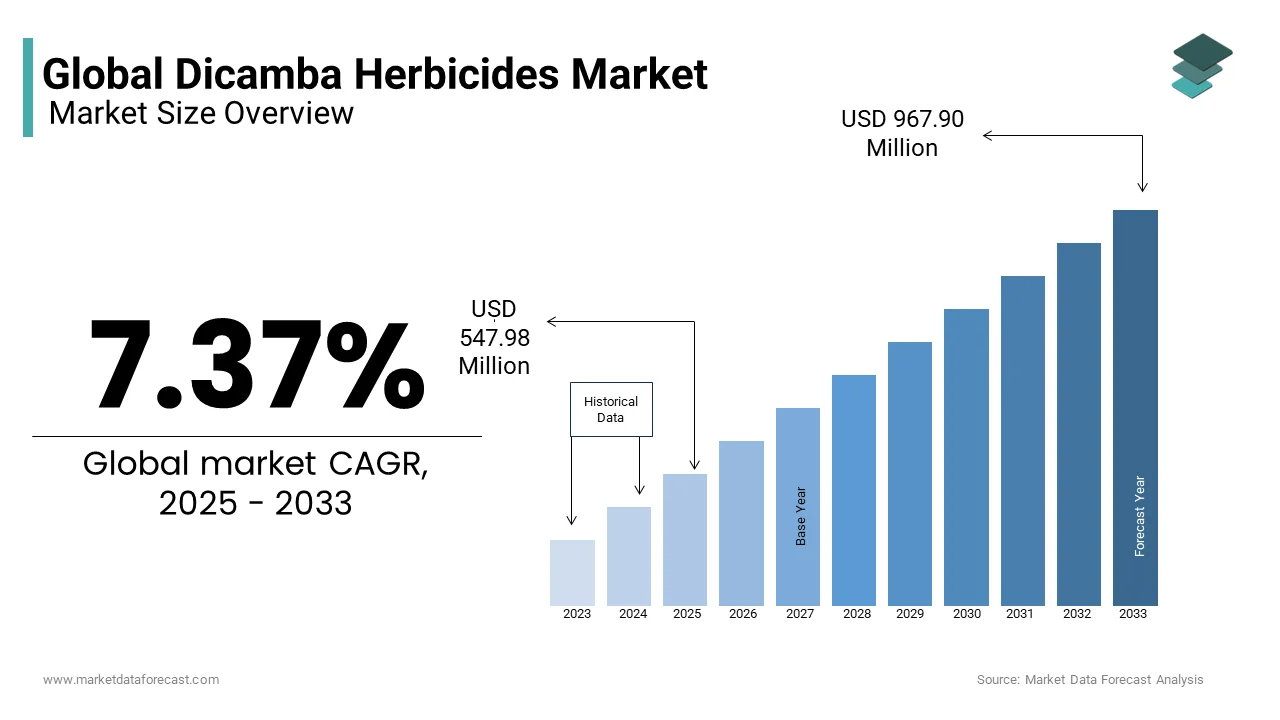
The global dicamba herbicide market was valued at USD 510.37 million in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 547.98 million in 2025 from USD 967.90 million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 7.37% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2033.
The market is expected to increase significantly owing to the growing demand for food security for the growing population, along with the limited availability of agricultural lands and a rise in crop loss due to weed problems.
Dicamba is a type of herbicide that is used to kill various types of Cin pastures, Rangelands, and Non-crop areas. Dicamba works by increasing plant growth rates. At sufficient amounts, the Plant outgrows its nutrient supplies and dies. Dicamba is generally used to kill Broadleaf weeds and annual and perennial rose weeds in grain crops and highlands.
MARKET DRIVERS AND RESTRAINTS
The growing need for food security for the rising populace and rising crop loss owing to weed problems, along with changing agricultural practices from traditional to conventional, are some of the factors driving the growth of the dicamba herbicide market. However, some of the factors like the volatility of Dicamba, Stringent regulatory approvals, and the growing organic food industry are restraining the market.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
CAGR |
7.37% |
|
Segments Covered |
By Crop Type, Formulation, Physical Form, Time of Application, and Region |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities |
|
Regions Covered |
North America, Europe, APAC, Latin America, Middle East & Africa |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Monsanto Company, BASF SE, Bayer Crop Science, E.I. du Pont de Nemours and Company, The Dow Chemicals Company, and Syngenta AG. |
REGIONAL ANALYSIS
Europe dominates the market during the forecast period. North America is the fastest-growing market and second-largest market owing to the rapidly advancing agricultural practices.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
This report includes a study of marketing and development strategies of leading companies such as Monsanto Company, BASF SE, Bayer Crop Science, E.I. du Pont de Nemours and Company, The Dow Chemicals Company, and Syngenta AG.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the global dicamba herbicide market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Crop Type
- Cereals & Grains
- Oilseeds & Pulses
- Pastures & Forage Crops
By Formulation
- Acid and Salt
- Based on Physical form
By Physical Form
- Dry
- Liquid
By Time of Application
- Pre- and Post-Emergence
- Cereals & grains
By Region
- North America
- Europe
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East and Africa
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Dicamba, and why is it widely used in agriculture?
Dicamba is a selective herbicide commonly used to control broadleaf weeds in crops like soybeans, corn, and cotton. Its popularity stems from its effectiveness against herbicide-resistant weed species, particularly in no-till and conservation farming systems.
What are the main factors driving the Dicamba herbicide market?
The market is driven by rising herbicide resistance to older chemicals (like glyphosate), expansion of genetically modified (GM) crops tolerant to Dicamba, and the growing need for effective pre- and post-emergent weed control in large-scale commercial farming.
What regulatory challenges affect the Dicamba herbicide market?
Dicamba faces strict regulatory scrutiny due to concerns over drift damage to non-target crops. Regulations around application timing, buffer zones, and spray technology are becoming more rigorous, particularly in the U.S. and Canada.
How is technology improving Dicamba application?
New spray drift-reduction technologies, vapor-control formulations, and precision application equipment are being adopted to minimize off-target movement and improve the safety and effectiveness of Dicamba usage.
What is the future outlook for the Dicamba herbicide market?
The future of the market depends on balancing weed management needs with environmental safety. Innovations in formulation, stricter use guidelines, and integration with other herbicide modes of action will define its role in sustainable crop protection.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2500
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]