Asia Pacific IoT Gateway Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report By Component (Processor, Sensor, Memory and Storage, Others), Connectivity (Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, ZigBee, Ethernet, Cellular, Others), End User (Automotive, Healthcare, Industrial, Consumer Electronics, BFSI, Oil & Gas, Retail, Aerospace & Defense, Others), and Country (India, China, Japan, South Korea, Australia) – Industry Analysis From 2025 to 2033.
Asia Pacific IoT Gateway Market Size
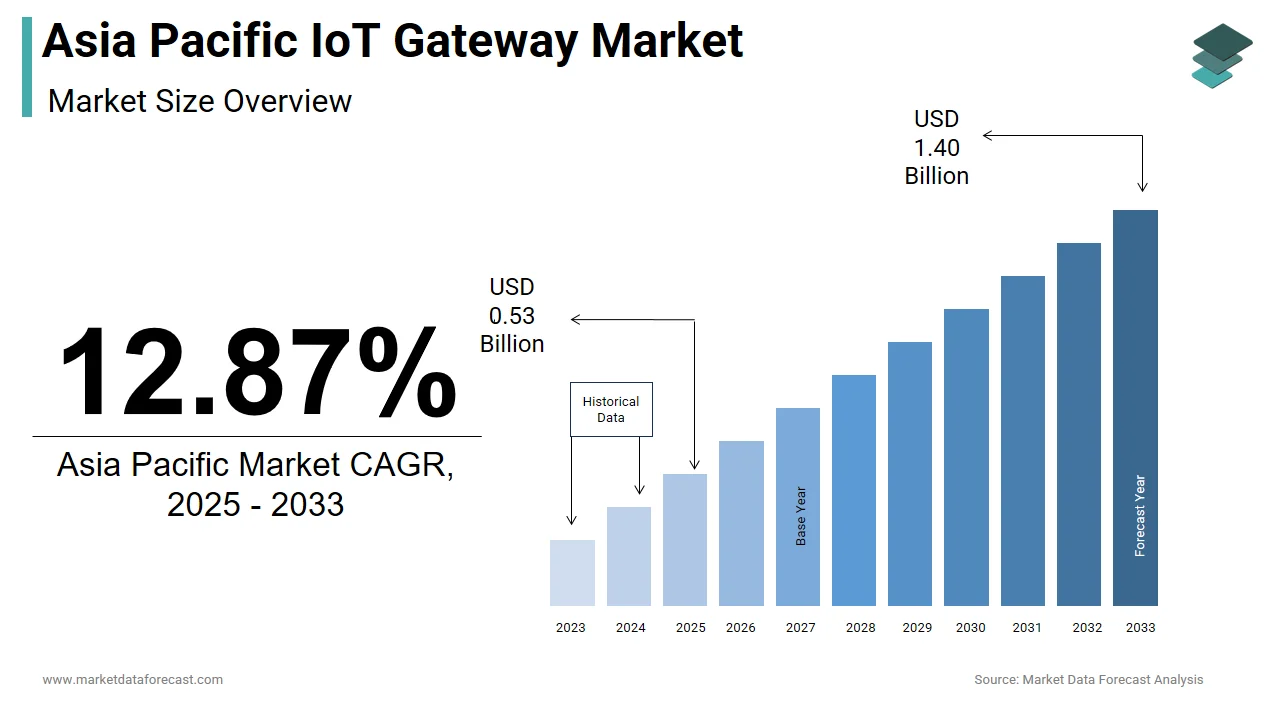
The size of the Asia Pacific IoT gateway market was worth USD 0.47 billion in 2024. The Asia Pacific market is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 12.87% from 2025 to 2033 and be worth USD 1.40 billion by 2033 from USD 0.53 billion in 2025.
The Asia Pacific IoT gateway market encompasses the deployment and integration of hardware and software solutions that enable secure connectivity, data processing, and communication between Internet of Things (IoT) devices and cloud platforms. IoT gateways act as intermediaries that aggregate sensor data, perform edge computing, filter unnecessary information, and transmit critical insights to centralized systems for further analysis. These gateways are essential in managing large-scale IoT ecosystems across industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, smart cities, agriculture, and logistics.
Asia Pacific has emerged as a pivotal region for IoT gateway adoption due to rapid digital transformation, increasing government initiatives toward smart infrastructure, and growing investments in Industry 4.0 technologies. According to ABI Research, the number of IoT-connected devices across the region surpassed 6 billion in 2023, highlighting the scale of demand for intelligent edge computing infrastructure like IoT gateways.
In India, for example, the Smart Cities Mission has spurred municipalities to deploy gateways for integrating traffic monitoring, waste management, and public safety systems. Similarly, in Japan, companies like Hitachi and NEC have integrated IoT gateways into their industrial automation frameworks to enhance predictive maintenance capabilities. South Korea, through its K-Networks strategy, is leveraging IoT gateways to support next-generation broadband connectivity and real-time analytics across urban environments.
As per IDC, enterprises in Australia and Southeast Asia are increasingly investing in hybrid IoT architectures where gateways play a central role in ensuring low-latency operations and improved network security. This evolving technological landscape underscores the growing strategic importance of IoT gateways in shaping the future of connected ecosystems across the Asia Pacific region.
MARKET DRIVERS
Surge in Industrial Automation and Smart Manufacturing Initiatives
One of the primary drivers fueling the growth of the Asia Pacific IoT gateway market is the widespread adoption of industrial automation and smart manufacturing practices. Governments and private enterprises across China, Japan, South Korea, and India are actively investing in digital transformation strategies aimed at enhancing production efficiency, reducing downtime, and improving supply chain visibility.
According to McKinsey & Company, over 70% of large-scale manufacturing firms in China have deployed IoT-enabled systems with integrated gateways to manage factory floor equipment, monitor machine health, and optimize energy consumption. In Japan, the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) has been promoting "Society 5.0," a vision that integrates cyber-physical systems with IoT gateways to streamline production workflows and enhance human-machine collaboration.
Similarly, in India, the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) reported a 40% increase in smart factory projects under the Make in India initiative in 2023, many of which rely on IoT gateways for real-time data aggregation and decision-making. In South Korea, automotive giants such as Hyundai and Kia are leveraging IoT gateways to support autonomous assembly lines, predictive maintenance, and remote diagnostics.
Moreover, companies like Siemens and Bosch have established regional innovation centers focused on developing localized gateway solutions tailored to small and medium-sized manufacturers in Southeast Asia. As per Frost & Sullivan, these trends indicate a strong correlation between industrial digitization efforts and the rising proliferation of IoT gateways across the manufacturing sector in the Asia Pacific region.
Expansion of Smart City and Urban Infrastructure Projects
Another significant driver of the Asia Pacific IoT gateway market is the rapid expansion of smart city initiatives and intelligent urban infrastructure development. Governments across the region are prioritizing digital transformation to improve public services, reduce environmental impact, and enhance city planning through interconnected IoT systems.
According to the Asian Development Bank, more than 200 smart city projects were underway across the Asia Pacific in 2023, with major implementations in Singapore, China, India, and Malaysia. These projects integrate IoT gateways to manage transportation networks, energy grids, surveillance systems, and environmental monitoring mechanisms.
In Singapore, the Smart Nation initiative has led to the deployment of thousands of IoT gateways enabling real-time traffic management, smart lighting, and air quality tracking. The Infocomm Media Development Authority (IMDA) reported that by mid-2023, over 90% of municipal services had been enhanced using IoT-driven data collected via gateways.
In India, the Smart Cities Mission has transformed urban governance in 100 designated cities, many of which utilize IoT gateways to connect streetlights, water distribution systems, and waste bins to centralized control centers. As per NITI Aayog, the country’s policy think tank, public utilities relying on IoT-based infrastructure saw a 30% improvement in operational efficiency in 2023.
Additionally, in China, cities like Shenzhen and Hangzhou have implemented large-scale IoT gateway networks to support AI-powered traffic optimization and emergency response coordination. These developments illustrate how urban modernization drives substantial demand for IoT gateway solutions across the Asia Pacific region.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Cost and Complexity of IoT Gateway Deployment
A key restraint impeding the growth of the Asia Pacific IoT gateway market is the high cost and technical complexity associated with deploying and maintaining these systems, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Unlike standard networking equipment, IoT gateways require specialized hardware configurations, embedded software, and seamless integration with existing IT and OT infrastructures, which can significantly escalate implementation costs.
According to Deloitte, the average investment required to set up an enterprise-grade IoT gateway system ranges from USD 15,000 to USD 50,000, depending on scalability and functionality. For budget-constrained organizations in emerging economies such as Indonesia, the Philippines, and parts of India, this represents a considerable financial burden.
Beyond initial setup costs, ongoing maintenance and software updates also pose challenges. Many IoT gateway solutions operate on proprietary platforms, requiring continuous licensing fees and technical support contracts. In Vietnam, for instance, the Vietnam Chamber of Commerce and Industry noted that only 18% of local manufacturers could afford full-fledged IoT gateway deployments without external funding or subsidies.
Moreover, the lack of standardized protocols across different IoT ecosystems creates interoperability issues, making it difficult for businesses to integrate multiple vendor solutions seamlessly. As per Gartner, approximately 35% of IoT project failures in the Asia Pacific region are attributed to compatibility problems between gateways and end devices, leading to operational inefficiencies and increased costs.
These financial and technical barriers continue to limit widespread adoption of IoT gateways, especially among SMEs and rural enterprises, thereby constraining market growth in several parts of the Asia Pacific.
Data Security and Privacy Concerns Across IoT Ecosystems
Data security and privacy concerns represent a major obstacle to the expansion of the Asia Pacific IoT gateway market. As IoT gateways serve as critical nodes in transmitting sensitive operational and user data, they become prime targets for cyberattacks, raising apprehensions among enterprises about the integrity and confidentiality of their digital assets.
According to the Ponemon Institute, cyberattacks targeting IoT infrastructure in the Asia Pacific region increased by nearly 45% in 2023 compared to the previous year. Many breaches originated from vulnerabilities in gateway firmware, insecure APIs, and weak authentication mechanisms. In Japan, the National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT) issued multiple advisories regarding compromised IoT gateways used in industrial control systems.
Moreover, regulatory uncertainty around data protection laws complicates compliance for multinational corporations operating across diverse jurisdictions in the Asia Pacific. Countries such as China and India have introduced stringent data localization requirements, mandating that certain categories of data be stored within national borders. This makes it challenging for global cloud providers and IoT gateway vendors to design unified solutions that meet varying legal standards.
In addition, a survey conducted by PwC found that nearly 60% of CIOs in ASEAN countries expressed hesitation in adopting IoT gateways due to fears of potential data leaks and ransomware attacks. As per Trend Micro, a cybersecurity firm headquartered in Tokyo, unsecured gateways were responsible for more than half of all IoT-related security incidents reported in the region in 2023.
Until stronger encryption methods, regular firmware updates, and comprehensive cybersecurity policies are universally adopted, security concerns will continue to hinder broader acceptance of IoT gateways across business sectors in the Asia Pacific.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Growth of Edge Computing and Decentralized Data Processing
One of the most promising opportunities for the Asia Pacific IoT gateway market lies in the expanding adoption of edge computing and decentralized data processing models. With the sheer volume of data generated by IoT devices increasing exponentially, enterprises are shifting away from centralized cloud-only architectures toward edge-based solutions that offer faster processing, lower latency, and improved operational efficiency.
According to IDC, by 2025, more than 40% of enterprise-generated data in the Asia Pacific region will be processed at the edge rather than in centralized cloud facilities. This transition necessitates robust IoT gateways capable of performing real-time analytics, filtering irrelevant data, and transmitting only actionable insights back to the cloud.
In China, tech giants such as Alibaba Cloud and Huawei have been investing heavily in edge computing infrastructure, offering customized IoT gateway solutions tailored for manufacturing, logistics, and smart grid applications. Huawei's Intelligent EdgeCloud platform, launched in 2023, enables businesses to deploy IoT gateways directly at factory sites, facilitating immediate decision-making without relying entirely on distant data centers.
Similarly, in India, startups such as ZenRobotics and VVDN Technologies have developed modular IoT gateways optimized for edge deployment in agriculture, energy, and retail sectors. As per NASSCOM, India’s premier industry association, over 200 new edge computing startups emerged in 2023 alone, many of which leveraged IoT gateways for distributed sensing and intelligent data handling.
Australia and New Zealand are also witnessing a surge in edge-centric IoT implementations, particularly in mining and agricultural monitoring, where real-time data processing is crucial for operational continuity. These developments highlight the transformative potential of edge computing in reshaping the future trajectory of the Asia Pacific IoT gateway market.
Integration of IoT Gateways in Renewable Energy and Smart Grid Systems
A rapidly emerging opportunity for the Asia Pacific IoT gateway market is the integration of these systems into renewable energy and smart grid infrastructure. Governments and utility providers across the region are investing heavily in sustainable energy solutions, driving the need for intelligent data aggregation, real-time monitoring, and bidirectional energy flow management—functions where IoT gateways play a central role.
According to BloombergNEF, renewable energy capacity in the Asia Pacific region is expected to grow by 60% between 2023 and 2030, with solar and wind power accounting for the majority of this expansion. To manage the variability and decentralization of renewable sources, utilities are deploying IoT gateways to facilitate smart metering, grid balancing, and fault detection.
In Japan, the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) has mandated the use of advanced IoT gateways in upcoming smart grid pilot projects designed to integrate household solar panels with national energy networks. Companies like Toshiba and Mitsubishi Electric have developed specialized gateways that enable real-time monitoring of electricity generation and consumption patterns.
South Korea, through its Fourth Industrial Revolution Strategy, has incorporated IoT gateways into its national energy storage and distribution framework. As part of this initiative, Korea Electric Power Corporation (KEPCO) has rolled out IoT-enabled substations equipped with gateways to optimize load distribution and prevent power outages during peak demand periods.
In Australia, state-level energy agencies have partnered with technology firms to implement IoT gateway-based microgrid solutions for remote communities and mining operations. These developments underscore the growing significance of IoT gateways in supporting the region’s clean energy transition and enhancing grid resilience.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Spectrum Allocation and Connectivity Constraints in Rural and Remote Areas
One of the foremost challenges facing the Asia Pacific IoT gateway market is the inconsistent availability of reliable spectrum and connectivity, particularly in rural and remote areas. While urban centers benefit from extensive 4G/5G coverage and fiber-optic infrastructure, vast regions across India, Indonesia, and the Philippines still suffer from poor network reach, limiting the effectiveness of IoT gateway deployments.
According to GSMA Intelligence, as of 2023, nearly 200 million people in the Asia Pacific region remained unconnected to mobile broadband networks, primarily residing in isolated or economically disadvantaged zones. Without stable internet access, IoT gateways cannot function optimally, restricting their ability to relay data to cloud platforms or receive real-time commands.
In India, despite the Digital India campaign, several states, including Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, and parts of the Northeas,t continue to face connectivity gaps, affecting the rollout of IoT-based agricultural monitoring and healthcare tracking systems. As per the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI), only 45% of rural towers had access to uninterrupted power and bandwidth in early 2023.
Similarly, in Indonesia, the archipelago's geographical diversity poses logistical hurdles in establishing uniform telecommunication coverage. The Indonesian Ministry of Communication and Information Technology acknowledged that many outer islands lacked LTE connectivity, limiting the performance of IoT gateways deployed for maritime surveillance and disaster warning systems.
To mitigate these challenges, governments and telecom operators are exploring Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) technologies such as LoRaWAN and NB-IoT, which require minimal infrastructure. However, achieving nationwide consistency remains a complex hurdle impacting the growth of the IoT gateway ecosystem in the Asia Pacific.
Lack of Standardization and Interoperability Among IoT Platforms
A critical challenge confronting the Asia Pacific IoT gateway market is the absence of universal standards and interoperability across IoT platforms. The presence of multiple proprietary ecosystems, communication protocols, and device specifications hampers seamless integration, leading to fragmented deployments and increased complexity for enterprises seeking scalable IoT solutions.
According to IEEE, there are currently over 30 different communication standards influencing IoT deployments globally, with limited consensus on which should dominate in the industrial, consumer, or commercial sectors. This fragmentation forces gateway developers to create custom firmware for each application, increasing both time-to-market and development costs.
In China, while state-backed initiatives promote domestic IoT standards such as China Mobile’s OneNET platform, foreign vendors often struggle to integrate their gateways with local cloud infrastructures due to non-compliance with regional certification norms. As per the China Electronics Standardization Institute, over 35% of IoT gateway imports faced compatibility challenges in 2023, delaying implementation timelines.
Similarly, in India, the lack of a unified national IoT framework results in inconsistent adoption of wireless protocols, forcing enterprises to invest in multiple gateway variants to accommodate different sensors and controllers. The Indian Institute of Standards and Quality Control (IISQC) highlighted in 2023 that interoperability issues accounted for nearly 28% of IoT project delays in industrial settings.
Regional standardization bodies across ASEAN nations have initiated discussions to harmonize IoT gateway requirements, but progress remains slow. Until a common framework emerges, the lack of interoperability will remain a persistent barrier to the widespread adoption of IoT gateways across the Asia Pacific.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
Segments Covered |
By Component, Connectivity, End User, and Region. |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional and Country-Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, Drivers, Restraints, Opportunities, Challenges; PESTLE Analysis; Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Countries Covered |
India, China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, New Zealand, Thailand, Malaysia, Vietnam, Philippines, Indonesia, Singapore, Rest of APAC |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Cisco Systems, Inc., Advantech Co., Ltd., Dell Inc., Microchip Technology Inc., and Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Component Insights

Among the various segments in the Asia Pacific IoT gateway market, Sensors hold the largest share, accounting for approximately 34% of total market revenue in 2023 , according to ResearchAndMarkets. The dominance of this segment is attributed to the widespread deployment of sensor-driven IoT applications across industrial automation, smart cities, and healthcare.
A primary growth driver is the increased integration of sensors into edge computing architectures, enabling real-time data acquisition and processing at the gateway level. In China, for instance, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology reported that over 65% of new IoT deployments in manufacturing plants involved gateways equipped with vibration, temperature, and pressure sensors to support predictive maintenance systems.
Another key factor is the rapid adoption of wireless sensor networks in agriculture and environmental monitoring. Countries like India and Indonesia are leveraging IoT gateways connected to soil moisture and weather sensors to optimize irrigation and crop yield management. According to the Indian Council of Agricultural Research, the use of smart sensors in precision farming initiatives expanded by 40% in 2023 compared to the previous year.
Additionally, smart city expansion programs in Singapore and Japan have led to large-scale installations of sensor-enabled IoT gateways for traffic flow analysis, air quality tracking, and public lighting control. As per the Singapore Economic Development Board, more than 80% of municipal IoT projects implemented in 2023 included sensor-integrated gateway units. These developments collectively reinforce the Sensor component as the leading segment in the regional IoT gateway ecosystem.
The Memory Devices segment is currently experiencing the highest growth rate, projected to expand at a CAGR of 15.7% between 2023 and 2030, as noted by Mordor Intelligence. This surge reflects the increasing demand for high-capacity local storage solutions within IoT gateways to support offline data processing and edge analytics.
A major growth enabler is the evolving need for on-device data retention and rapid retrieval capabilities, particularly in mission-critical applications such as autonomous vehicles, real-time industrial monitoring, and healthcare diagnostics. In South Korea, semiconductor firm SK Hynix reported a 28% increase in sales of embedded memory modules tailored for IoT gateways used in automotive telematics and AI-based surveillance systems.
Another significant factor is the adoption of flash-based and solid-state memory technologies in gateway hardware, which offer faster read/write speeds and improved reliability under harsh operating conditions. Japanese electronics manufacturer Renesas Electronics launched a new line of NAND flash memory chips in early 2023, specifically designed for industrial IoT gateways requiring high endurance and multi-year data integrity.
Moreover, the rise of decentralized analytics models has spurred demand for gateways with enhanced onboard memory, allowing them to store and process vast datasets without constant cloud connectivity. According to IDC, enterprises in Australia and New Zealand have started deploying edge gateways with built-in SSD storage to manage remote mining telemetry and offshore energy monitoring operations.
These factors illustrate how advancements in memory technology are reshaping the architecture of IoT gateways, making Memory Devices the fastest-growing component segment in the Asia Pacific market.
By Connectivity Insights
Wi-Fi remains the largest connectivity segment in the Asia Pacific IoT gateway market, capturing approximately 39% of total market share in 2023, as per Grand View Research. Its widespread adoption stems from its compatibility with existing infrastructure, ease of deployment, and suitability for both indoor and outdoor IoT applications.
One of the main reasons for Wi-Fi’s continued dominance is its prevalence in consumer and enterprise environments, where it serves as the primary access method for connecting smart devices to gateways. In India, the Smart Cities Mission has integrated Wi-Fi-enabled IoT gateways into public transport hubs and municipal buildings to facilitate seamless device communication and centralized monitoring.
Another contributing factor is the expansion of smart homes and commercial building automation, particularly in China and Southeast Asia. According to ABI Research, the number of Wi-Fi-connected IoT gateways used in residential security, HVAC control, and lighting systems surpassed 50 million units in 2023, driven by rising disposable incomes and growing awareness of home automation benefits.
Additionally, Wi-Fi 6 enhancements have boosted throughput and reduced latency, making it an attractive option for high-density IoT scenarios such as retail stores, hospitals, and logistics warehouses. In Australia, major retailers, including Woolworths and Kmart, deployed new generation IoT gateways with Wi-Fi 6 capabilities to support real-time inventory tracking and customer engagement platforms. These trends underline Wi-Fi’s entrenched position as the leading connectivity solution in the Asia Pacific IoT gateway landscape.
The Cellular connectivity segment is emerging as the fastest-growing, anticipated to expand at a CAGR of 18.2% between 2023 and 2030, as highlighted by MarketsandMarkets. This growth is driven by the rollout of 5G networks, the proliferation of mobile IoT applications, and the demand for always-connected services in remote and mobility-based deployments.
One key catalyst is the accelerated deployment of 5G infrastructure across China, Japan, and South Korea, which enables ultra-low latency and high-speed data transmission essential for advanced IoT gateway applications. According to the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology (CAICT), over 1.2 million 5G base stations were operational by mid-2023, directly supporting the adoption of cellular-connected IoT gateways in logistics, fleet management, and manufacturing.
Simultaneously, telecom operators in Southeast Asia are expanding their partnerships with IoT gateway vendors to offer bundled connectivity solutions for businesses. In Thailand, AIS (Advanced Info Service) collaborated with Huawei to launch a nationwide NB-IoT and LTE-M network aimed at supporting smart metering, asset tracking, and remote diagnostics via cellular IoT gateways.
Furthermore, cellular IoT gateways are gaining traction in transportation and outdoor applications, where wired or Wi-Fi connectivity is impractical. In India, the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways mandated the installation of GPS-enabled cellular gateways in all inter-city buses and freight trucks starting in 2023 to enhance safety and route optimization.
These developments underscore why Cellular connectivity is outpacing other options, offering unmatched mobility, scalability, and coverage that align well with evolving IoT use cases across the Asia Pacific region.
By End User Insights
Industrial constitutes the largest end-user segment, holding approximately 31% of the Asia Pacific IoT gateway market in 2023, as reported by Frost & Sullivan. This segment includes applications in manufacturing, oil and gas, utilities, and logistics, where IoT gateways play a critical role in enabling smart factory operations, remote equipment monitoring, and predictive maintenance.
A key contributor to this segment’s leadership is the widespread adoption of Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) across China, Japan, and South Korea, where manufacturers are increasingly integrating gateways into production lines for real-time data analytics and machine-to-machine communication. According to the China Machinery Industry Federation, over 70% of large-scale manufacturing firms adopted IIoT platforms in 2023, many of which relied on intelligent gateways for edge computing and data aggregation.
Another major factor is the growing investment in digital transformation programs by national governments, particularly in India and Indonesia, where industrial modernization is a strategic priority. Under India’s Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme, several companies in the electrical and mechanical sectors received subsidies to deploy IoT-based monitoring systems linked through secure gateways.
Moreover, oil and gas operators in Australia and Malaysia are leveraging IoT gateways for condition-based monitoring of offshore rigs and pipelines, ensuring operational continuity and reducing unplanned downtime. As per the Australian Petroleum Production & Exploration Association (APPEA), the industry recorded a 25% reduction in maintenance costs in 2023 due to the implementation of IoT gateway-enabled asset tracking.
These factors collectively reinforce the Industrial sector as the dominant end-user category in the Asia Pacific IoT gateway market.
The Healthcare segment is currently the fastest-growing, projected to expand at a CAGR of 17.4% from 2023 to 2030, as noted by Allied Market Research. The accelerating digitization of healthcare services, remote patient monitoring, and hospital automation has significantly increased reliance on IoT gateways for secure data transfer and real-time clinical insights.
A primary growth driver is the rising adoption of telehealth and wearable medical devices, especially post-pandemic, in countries like Singapore, Japan, and Australia. According to the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan, the number of remote health consultations utilizing IoT-enabled gateways surged by 35% in 2023, supported by government funding under the Digital Health Transformation Initiative.
Another crucial factor is the integration of IoT gateways in hospital infrastructure to streamline electronic health records (EHR), medical imaging, and medication dispensing systems. In India, Apollo Hospitals Group partnered with Intel to deploy intelligent gateways for centralizing diagnostic data from multiple departments, enhancing efficiency and treatment accuracy.
Additionally, government-backed investments in smart clinics and rural health kiosks have accelerated gateway adoption in underserved regions. In Indonesia, the Ministry of Health launched a pilot program in 2023 to install IoT gateways in 100 remote clinics to enable real-time transmission of vital signs and lab results to urban hospitals.
These interconnected developments highlight why the Healthcare segment is witnessing the most rapid uptake of IoT gateways across the Asia Pacific region.
COUNTRY-LEVEL ANALYSIS
China maintains the top position in the Asia Pacific IoT gateway market, accounting for approximately 38% of total regional demand in 2023, according to BloombergNEF. This leadership is primarily attributable to the country's aggressive push towards digital transformation, smart city development, and industrial automation.
A key growth lever is the scale of domestic IoT adoption, supported by extensive government initiatives such as the "Made in China 2025" strategy and the "Digital China" plan. According to the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology (CAICT), the number of IoT gateway deployments in manufacturing facilities alone exceeded 1.5 million units in 2023, reflecting the deepening integration of edge computing solutions.
Another important factor is the extensive rollout of 5G infrastructure, which has enabled widespread usage of cellular-connected IoT gateways in logistics, fleet management, and smart grid applications. As per the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, over 1.2 million 5G base stations were active by mid-2023, directly supporting next-generation gateway functionality.
Additionally, Chinese technology firms such as Huawei, ZTE, and Alibaba Cloud have developed localized gateway platforms tailored for both domestic and international markets. These companies continue to invest heavily in R&D, driving innovation in areas such as AI-powered gateways and secure data routing. These elements collectively affirm China’s dominant role in shaping the trajectory of the Asia Pacific IoT gateway sector.
India ranks second in the Asia Pacific IoT gateway market, contributing approximately 21% of total demand in 2023, as estimated by S&P Global Mobility. The country’s growth trajectory is strongly influenced by its ambitious infrastructure development plans and expanding digital economy.
A major growth driver is the Smart Cities Mission, launched by the Government of India, which involves deploying millions of IoT sensors and gateways across urban centers for traffic control, waste management, water distribution, and public safety. According to NITI Aayog, over 85% of these smart city projects now incorporate IoT gateways for real-time data aggregation and decision-making.
Another key factor is the National Digital Health Mission, which integrates IoT gateways in telemedicine and rural health infrastructure. As part of this initiative, thousands of primary health centers have been equipped with gateways that transmit biometric data to centralized cloud platforms, improving access to medical diagnostics in remote areas.
Additionally, India’s manufacturing sector is undergoing rapid digitization, with the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) reporting a 30% increase in smart factory implementations using IoT-enabled gateways in 2023. Companies like Wipro, Tata Consultancy Services, and L&T Technology Services are actively developing gateway-based industrial automation solutions for global clients.
These multi-sectoral developments position India as a rapidly emerging powerhouse in the IoT gateway space.
Japan holds the third-largest share in the Asia Pacific IoT gateway market, contributing roughly 11% of total demand in 2023, according to Fuji Keizai. The country’s market is distinguished by its focus on technological innovation, stringent regulatory standards, and early adoption of smart infrastructure.
A central growth driver is the accelerated transition to smart manufacturing and Society 5.0, a national vision that integrates cyber-physical systems with IoT gateways to streamline production workflows. According to the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI), over 60% of large-scale Japanese factories had implemented IoT gateway-based monitoring systems by 2023.
Another important factor is the expanding presence of IoT gateways in healthcare and elderly care services, given Japan’s aging population. The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare reported a 22% increase in the deployment of remote patient monitoring systems utilizing IoT gateways, helping caregivers track chronic conditions in real time.
Furthermore, Japanese telecom operators and hardware developers are collaborating to advance 5 G-enabled gateway solutions for automotive, logistics, and retail applications. NTT DOCOMO and NEC jointly launched a series of compact, low-power IoT gateways optimized for AIoT (Artificial Intelligence of Things) use cases, signaling deeper integration of intelligence into gateway functions.
These trends underline Japan’s progressive orientation toward sophisticated IoT gateway adoption.
South Korea secures the fourth-largest market share in the Asia Pacific IoT gateway segment, contributing approximately 7% of total demand in 2023, according to the Korea Communications Commission. The country’s market is characterized by a strong technology orientation and proactive policy measures aimed at fostering digital transformation.
One of the key growth levers is the K-Networks strategy, which promotes broad IoT adoption across urban infrastructure, transportation, and public services. As part of this initiative, Seoul has installed tens of thousands of IoT gateways for managing smart streetlights, parking systems, and environmental monitoring stations.
Another notable factor is the early commercialization of 5G and its integration with IoT gateways, particularly in automotive and industrial applications. Hyundai Mobis and Samsung SDS have introduced edge gateways capable of handling real-time vehicle diagnostics and factory floor analytics, leveraging ultra-low latency 5G connections.
Additionally, South Korea’s commitment to achieving net-zero emissions by 2050 is influencing gateway deployment strategies, with companies seeking to optimize energy consumption and reduce carbon footprints. LG Uplus, for example, has rolled out IoT gateways for smart grid applications that balance renewable energy supply and demand dynamically.
These developments highlight South Korea’s strategic positioning as a leader in next-generation IoT gateway integration.
Australia holds the fifth-largest share in the Asia Pacific IoT gateway market, contributing approximately 5% of total demand in 2023, according to IBISWorld. The country’s market is uniquely shaped by its vast geography and heavy reliance on resource extraction industries.
One of the primary drivers is the dominance of the mining and energy sectors, which require specialized IoT gateways to monitor equipment performance, track assets remotely, and ensure worker safety. According to the Minerals Council of Australia, nearly every major mine site now employs IoT gateways for real-time data collection from underground sensors and mobile machinery.
Another key factor is the continuous investment in smart cities and transportation infrastructure, particularly in Sydney, Melbourne, and Brisbane. The Smart Cities Council reported that over 70% of new urban development projects in 2023 included IoT gateway integrations for traffic optimization, energy-efficient lighting, and emergency response coordination.
Additionally, Australian tech firms and universities are actively researching AI-enhanced IoT gateways for applications ranging from agricultural monitoring to maritime surveillance. CSIRO, in collaboration with Telstra, has been testing AI-powered gateways for bushfire detection and climate modeling, demonstrating the country’s forward-thinking approach to IoT innovation.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
Some of the noteworthy companies in the APAC IoT gateway market profiled in this report are Cisco Systems, Inc., Advantech Co., Ltd., Dell Inc., Microchip Technology Inc., and Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
TOP LEADING PLAYERS IN THE MARKET
Cisco Systems is a global leader in networking solutions and holds a strong presence in the Asia Pacific IoT gateway market. The company offers secure, scalable, and intelligent gateway platforms that support a wide range of industrial and enterprise applications. Cisco plays a strategic role in enabling smart cities, connected transportation, and digital manufacturing through its IoT gateway technologies tailored for edge computing environments.
Hewlett-Packard Enterprise (HPE) is another key player contributing significantly to the growth of the Asia Pacific IoT gateway landscape. HPE provides edge-to-cloud IoT gateway solutions that allow businesses to process data closer to the source, reducing latency and enhancing operational efficiency. The company’s focus on hybrid IT infrastructure and AI-driven analytics makes it a preferred choice for enterprises undergoing digital transformation across the region.
Huawei Technologies is a dominant force in the Asia Pacific IoT gateway market due to its deep integration with national digitalization strategies, particularly in China and Southeast Asia. Huawei delivers high-performance IoT gateways optimized for 5G connectivity, smart grid systems, and industrial automation. With extensive R&D capabilities and government partnerships, the company is shaping the future of IoT ecosystems in the region.
TOP STRATEGIES USED BY KEY MARKET PARTICIPANTS
One of the primary strategies employed by leading players in the Asia Pacific IoT gateway market is strategic partnerships and ecosystem collaborations. Companies are actively engaging with telecom providers, cloud service vendors, and system integrators to create comprehensive IoT solutions that offer seamless deployment and end-to-end connectivity.
Another major approach is localized product development and regional customization, where global vendors adapt their IoT gateway offerings to meet country-specific regulatory requirements, network standards, and industry use cases. This enables them to better serve diverse markets such as India, Indonesia, and Australia, which have unique infrastructure demands.
Lastly, investment in edge intelligence and cybersecurity enhancements has become a priority for key players. As IoT deployments grow more complex, companies are embedding advanced processing capabilities and secure boot mechanisms into gateways to ensure data integrity, improve performance, and build enterprise trust in large-scale IoT implementations across the region.
COMPETITION OVERVIEW
The competition in the Asia Pacific IoT gateway market is dynamic and intensifying, driven by rapid technological advancements, increasing digital adoption, and growing demand for edge computing solutions. The market features a mix of global technology giants and emerging regional players, each striving to capture market share through innovation, strategic alliances, and localized product offerings.
Global firms such as Cisco, HPE, and Siemens maintain a strong foothold due to their established brand reputation, robust R&D capabilities, and extensive partner networks. These companies emphasize platform-based solutions that integrate seamlessly with cloud services and enterprise management tools, offering scalability and interoperability across industries.
At the same time, regional players like Huawei, Wipro, and Tata Elxsi are gaining traction by aligning closely with government initiatives and local infrastructure needs. These companies leverage their proximity to customers to deliver cost-effective, customized IoT gateway solutions tailored for specific verticals such as manufacturing, healthcare, and smart cities.
As the demand for secure, low-latency, and energy-efficient gateways rises, competition is shifting from hardware-centric offerings to value-added software and managed services. This evolution is prompting continuous innovation, with vendors increasingly focusing on AI-powered gateways, cybersecurity enhancements, and integrated IoT platform ecosystems to differentiate themselves in a rapidly maturing market.
RECENT MARKET DEVELOPMENTS
- In March 2024, Cisco launched a new line of compact, 5 G-enabled IoT gateways designed specifically for industrial edge computing applications in the Asia Pacific region. The product series was introduced in collaboration with major telecom operators in Japan and South Korea, aiming to enhance connectivity for smart manufacturing and logistics operations.
- In June 2024, HPE announced a joint venture with a leading Indian industrial automation firm to deploy IoT gateways integrated with AI-driven predictive maintenance capabilities. This initiative targeted improving operational efficiency in the country's rapidly expanding smart factory ecosystem.
- In August 2024, Huawei opened a dedicated IoT gateway research center in Singapore, focusing on developing next-generation edge computing solutions tailored for ASEAN markets. The facility emphasizes AI-enhanced data processing and security protocols suitable for mission-critical applications.
- In October 2024, Schneider Electric introduced a modular IoT gateway platform in Australia designed for energy and infrastructure monitoring. The solution supports real-time asset tracking and remote diagnostics, catering to mining and utility companies operating in remote locations.
- In December 2024, Tech Mahindra partnered with a Japanese cloud provider to launch an IoT gateway-as-a-service model targeting small and medium-sized enterprises. This initiative aimed to lower entry barriers for businesses looking to adopt digital transformation without significant upfront investment.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This Asia Pacific IoT gateway market research report is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Component
- Processor
- Sensor
- Memory and Storage Device
- Other Components
By Connectivity
- Bluetooth
- Wi-Fi
- ZigBee
- Ethernet
- Cellular
- Other Connectivity Types
By End User
- Automotive and Transportation
- Healthcare
- Industrial
- Consumer Electronics
- BFSI
- Oil and Gas
- Retail
- Aerospace and Defense
- Other End Users
By Country
- India
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- Australia
- New Zealand
- Thailand
- Malaysia
- Vietnam
- Philippines
- Indonesia
- Singapore
- Rest Of APAC
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What drives the Asia Pacific IoT gateway market?
The Asia Pacific IoT gateway market is driven by rapid industrial automation, smart city projects, and government digitalization initiatives, especially in manufacturing, urban infrastructure, and logistics
2. What challenges affect the Asia Pacific IoT gateway market?
The Asia Pacific IoT gateway market faces high deployment costs, technical complexity, lack of interoperability standards, and cybersecurity concerns, particularly for SMEs and rural areas
3. What opportunities exist in the Asia Pacific IoT gateway market?
The Asia Pacific IoT gateway market offers opportunities in edge computing, smart grid integration, renewable energy, and expanding IoT adoption in agriculture, healthcare, and smart cities
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from $ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: [email protected]