Europe Plant-based Food Market Size, Share, Trends & Growth Forecast Report By Type (Plant-based Meat, Fish, Dairy Alternatives, Condiments, Dressings, Mayo), Distribution Channel (Food Retail, Food Service, E-commerce), Nature (Organic, Conventional), Source (Soy, Wheat, Pea, Almond, Coconut, Others), and Country (UK, Germany, France, Italy, Spain, Netherlands, Rest of Europe) – Industry Analysis From 2025 to 2033.
Europe Plant-Based Food Market Size
The plant-based food market size in Europe was valued at USD 3.48 billion in 2024. The European market is estimated to be worth USD 9.17 billion by 2033 from USD 3.88 billion in 2025, growing at a CAGR of 11.36% from 2025 to 2033.
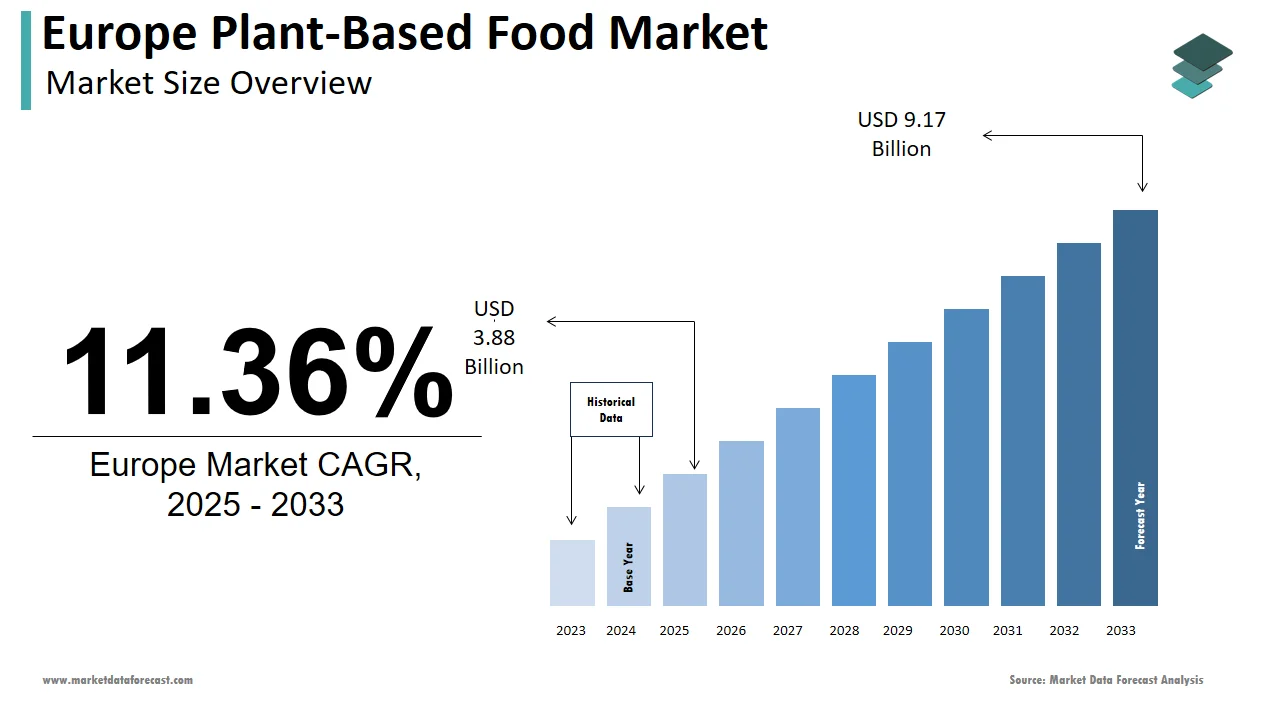
The Europe plant-based food market has emerged as a transformative force within the broader online food delivery ecosystem, driven by shifting consumer preferences toward sustainable and health-conscious eating. The plant-based food sales in Europe grew by 49, with Germany, France, and the UK leading adoption. Also, the rise of flexitarianism, coupled with increasing awareness of the environmental impact of animal agriculture, has positioned plant-based foods as a mainstream choice rather than a niche alternative. This trend is further amplified by the proliferation of online food delivery platforms like Deliveroo and Uber Eats, which have expanded their plant-based offerings to cater to this growing demand. Additionally, government initiatives promoting carbon-neutral lifestyles have incentivized consumers to adopt plant-based diets, creating a fertile ground for innovation and growth in this segment.
MARKET DRIVERS
Environmental Concerns
Environmental consciousness is a pivotal driver propelling the Europe plant-based food market forward. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), livestock farming contributes approximately 14.5% of global greenhouse gas emissions, prompting consumers to seek sustainable alternatives. Plant-based foods, which require significantly fewer natural resources compared to traditional animal-based products, align perfectly with this ethos. For instance, producing one kilogram of plant-based protein emits up to 90% less CO2 than its meat counterpart. This environmental advantage has resonated strongly with millennials and Gen Z, who prioritize eco-friendly choices. Furthermore, campaigns led by organizations like Greenpeace Europe have heightened awareness about the link between diet and climate change, further accelerating the shift toward plant-based consumption.
Rising Health Awareness
Health considerations represent another major driver for the Europe plant-based food market. As per the World Health Organization (WHO), non-communicable diseases such as obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular conditions are prevalent across Europe, accounting for close 77% of all deaths. Consumers are increasingly turning to plant-based diets as a preventive measure, given their association with lower cholesterol levels and reduced inflammation. A report by the European Society of Cardiology reveals that individuals adhering to plant-based diets exhibit a 25% lower risk of heart disease. Moreover, the pandemic-induced focus on immunity has spurred interest in nutrient-rich plant-based foods. For example, fortified plant-based milks and proteins are now widely consumed, particularly among urban professionals. These factors showcases how health awareness continues to shape consumer behavior in favor of plant-based options.
MARKET RESTRAINTS
High Price Sensitivity
Despite its growing popularity, the Europe plant-based food market faces challenges related to high price sensitivity among certain demographics. This pricing disparity stems from higher production costs associated with sourcing premium ingredients and advanced processing technologies. While affluent urbanites may willingly pay a premium for sustainability, rural populations and budget-conscious shoppers remain hesitant. Furthermore, economic uncertainties exacerbated by inflationary pressures have intensified scrutiny of discretionary spending, making affordability a critical barrier to widespread adoption. Without addressing these cost concerns, manufacturers risk alienating significant portions of the potential market.
Limited Taste and Texture Acceptance
Another notable restraint is the ongoing challenge of taste and texture acceptance among traditional meat and dairy consumers. Nearly 40% of first-time plant-based product users cite dissatisfaction with flavor and mouthfeel as reasons for discontinuing use. Mimicking the sensory experience of animal-derived foods remains a complex technical hurdle, particularly for plant-based meats and cheeses. Similarly, almond milk struggles to replicate the creaminess of cow’s milk, impacting its appeal in coffee and baking applications. While advancements in food technology are gradually bridging these gaps, the perception of inferior quality persists among skeptics. Overcoming these barriers requires sustained investment in R&D and consumer education to build trust and loyalty.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES
Expansion into Emerging Markets
The expansion of plant-based foods into emerging European markets presents a significant opportunity for growth. Eastern European countries like Poland and Romania are witnessing a gradual but steady rise in demand for plant-based options, driven by urbanization and exposure to Western dietary trends. This shift is further supported by local retailers like Auchan and Biedronka, which have begun stocking affordable plant-based items to cater to evolving preferences. Additionally, government initiatives promoting sustainable agriculture, such as Poland’s Green Deal Framework, create a conducive environment for market penetration. By tailoring products to regional tastes and affordability levels, manufacturers can unlock untapped potential in these burgeoning markets.
Collaboration with Food Delivery Platforms
Collaborations with online food delivery platforms offer another promising avenue for growth in the Europe plant-based food market. Partnering with platforms like Deliveroo, Uber Eats, and Glovo enables brands to reach tech-savvy millennials and Gen Z consumers who prioritize convenience and variety. For instance, partnerships with vegan-friendly restaurants and cloud kitchens have allowed companies like Beyond Meat and Oatly to expand their footprint without heavy infrastructure investments. Furthermore, personalized recommendations and promotional campaigns on these platforms enhance visibility and drive trial purchases.
MARKET CHALLENGES
Regulatory Hurdles and Labeling Requirements
Navigating stringent regulatory frameworks and labeling requirements poses a significant challenge for the Europe plant-based food market. The European Food Safety Authority mandates clear distinctions between plant-based and animal-derived products, often requiring detailed nutritional information and allergen disclosures. Such regulations complicate marketing strategies and limit the ability to appeal to traditional consumers. Additionally, compliance costs associated with certifications, such as organic or non-GMO labels, strain smaller players. Without streamlined processes, regulatory hurdles risk stifling innovation and increasing barriers to entry.
Cultural Resistance in Traditional Regions
Cultural resistance remains a persistent challenge, particularly in Southern and Eastern Europe, where traditional diets heavily feature animal-based products. Only 15% of Italians and 10% of Spaniards actively seek out plant-based alternatives, citing attachment to culinary heritage. Dishes like paella, lasagna, and moussaka are deeply ingrained in cultural identity, making it difficult for substitutes to gain acceptance. Moreover, skepticism about the authenticity and nutritional adequacy of plant-based foods persists among older generations. Overcoming this resistance requires localized marketing efforts and educational campaigns to bridge cultural gaps while respecting regional traditions.
REPORT COVERAGE
|
REPORT METRIC |
DETAILS |
|
Market Size Available |
2024 to 2033 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025 to 2033 |
|
Segments Covered |
By Type, Distribution Channel, Nature, Source, and Region. |
|
Various Analyses Covered |
Global, Regional and Country-Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, Drivers, Restraints, Opportunities, Challenges; PESTLE Analysis; Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities |
|
Countries Covered |
UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, Czech Republic, and the Rest of Europe. |
|
Market Leaders Profiled |
Beyond Meat Inc. (US), Impossible Foods Inc. (US), Atlantic Natural Foods LLC (US), Garden Protein International LLC (Canada), Kellogg's Company (US), and others. |
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS
By Type Insights
The dairy alternatives segment prevailed in the Europe plant-based food market by holding a share of 40.1% in 2024. This is due to its versatility, encompassing products like almond milk, oat milk, and soy yogurt, which seamlessly integrate into everyday diets. The growing prevalence of lactose intolerance, affecting nearly 15% of Europeans. Additionally, the reduced water usage and lower carbon emissions of plant-based dairy appeal to eco-conscious consumers. Retailers like Tesco and Carrefour have capitalized on this trend by expanding their private-label offerings, making dairy alternatives widely accessible. Their compatibility with coffee, baking, and cooking applications ensures consistent demand, solidifying their position as the largest segment.
The plant-based fish segment is moving ahead quickly, with a projected CAGR of 18.5%. This growth is driven by rising awareness of overfishing and marine ecosystem degradation, prompting consumers to seek sustainable seafood alternatives. Innovations in texture and flavor replication, such as Good Catch’s tuna and salmon analogs, have enhanced palatability and acceptance. Furthermore, partnerships with fine-dining chefs and upscale restaurants have elevated the segment’s image, appealing to affluent demographics. The convergence of sustainability, health, and culinary creativity ensures its rapid ascent in the market.
By Distribution Channel Insights
The food retail segment held the control share of the Europe plant-based food market i.e. 55% of sales in 2024. Supermarkets and hypermarkets like Aldi, Lidl, and Tesco play a pivotal role in driving accessibility and affordability. Their extensive distribution networks and strategic placement of plant-based products alongside conventional items enhance visibility and impulse purchases. Additionally, frequent discounts and bundled offers incentivize trial among price-sensitive buyers. The rise of this segment is further reinforced by collaborations with local farmers and suppliers, ensuring fresh and regionally relevant options. These factors collectively cement food retail’s leadership in the distribution landscape.
The E-commerce segment arose swiftly in the market and expected to have a CAGR of 22.7%. The convenience of home delivery and the ability to explore diverse product ranges attract digitally savvy consumers. Platforms like Amazon Fresh and Ocado have introduced dedicated plant-based sections, simplifying navigation for shoppers. A study by McKinsey notes that 45% of urban professionals rely on online grocery shopping, with plant-based foods being a top category. Subscription models and loyalty programs further enhance customer retention. Furthermore, social media integration and influencer endorsements amplify engagement, driving repeat purchases. As digital adoption accelerates, e-commerce is poised to redefine how plant-based foods are accessed and consumed across Europe.
By Nature Insights
The conventional plant-based foods segment attained the maximum growth in the Europe market with a 65.4% share in 2024. This segment’s growth is credited to its affordability and widespread availability, making it accessible to a broad demographic. Unlike organic variants, conventional products do not require stringent certifications, reducing production costs and enabling competitive pricing. Furthermore, major retailers like Aldi and Lidl have expanded their private-label conventional ranges, catering to budget-conscious shoppers. The expansion is further reinforced by its compatibility with mainstream culinary practices, ensuring consistent demand across households and foodservice channels.
The organic plant-based foods segment is having a quick rise with a CAGR of 14.8%. This progress is fueled by rising consumer awareness of sustainable agriculture and chemical-free ingredients. The segment’s premium positioning allows manufacturers to command higher prices, appealing to affluent urbanites who prioritize health and environmental impact. Additionally, government initiatives promoting organic farming, such as France’s Ecophyto Plan, have bolstered supply chains. Innovations in packaging and shelf-life extension further enhance appeal, driving rapid adoption among eco-conscious millennials and Gen Z consumers.
By Source Insights
The soy-based products segment commanded the Europe plant-based food market by capturing a 35.1% share in 2024. Soy’s versatility, high protein content, and established supply chain make it a preferred ingredient for plant-based meats, dairy alternatives, and condiments. Additionally, soy’s cost-effectiveness enables manufacturers to offer affordable options, appealing to price-sensitive buyers. Major brands like Impossible Foods and Alpro rely heavily on soy, further solidifying its leadership. Its widespread acceptance in both retail and foodservice channels ensures consistent demand, making it the cornerstone of the market.
The Pea-based products are the fastest-growing segment, with a CAGR of 20.5% . This development is caused by pea’s hypoallergenic properties and neutral taste, which appeal to health-conscious consumers. Innovations in extraction technologies have improved texture and flavor, enabling applications in diverse product categories like burgers, shakes, and snacks. Furthermore, pea cultivation requires fewer resources than soy, aligning with sustainability goals.
COUNTRY LEVEL ANALYSIS
Germany dominated the Europe plant-based food market in 2024, capturing a 28.1% share. The dominance is caused by strong consumer awareness of sustainability and animal welfare, supported by government incentives for plant-based diets. Berlin and Munich serve as hubs for veganism, with over 1.3 million Germans identifying as vegans in 2022. Retailers like Aldi and Lidl have expanded their plant-based offerings, ensuring accessibility.
France is the fastest-growing market, with a CAGR of 16.2%. This development is influenced by urbanization and a shift toward Mediterranean-inspired diets rich in plant-based ingredients. Paris and Lyon are at the forefront of adoption, with fine-dining chefs adding plant-based options to their menus. Government campaigns promoting reduced meat consumption have also accelerated adoption.
The UK benefits from strong online delivery platforms, driving steady growth. Italy faces resistance due to traditional cheese and meat preferences but shows gradual adoption. Spain’s younger population is embracing plant-based diets, particularly in coastal cities.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
A few notable companies operating in the Europe plant-based food market profiled in this report are Beyond Meat Inc. (US), Impossible Foods Inc. (US), Atlantic Natural Foods LLC (US), Garden Protein International LLC (Canada), Kellogg's Company (US), and others.
TOP LEADING PLAYERS IN THE MARKET
Beyond Meat
Beyond Meat dominates with its innovative plant-based meats. Its collaboration with fast-food chains like McDonald’s enhances visibility and accessibility.
Oatly
Oatly specializes in oat-based dairy alternatives. Its focus on sustainability and creative marketing resonates with eco-conscious consumers. Oatly’s European operations are strengthening its leadership in the dairy alternatives segment.
Alpro (Danone)
Alpro leverages its soy-based portfolio to cater to diverse demographics. Its strong retail presence ensures widespread distribution.
TOP STRATEGIES USED BY KEY MARKET PARTICIPANTS
Key players employ strategies such as product diversification, sustainability certifications, and partnerships with retailers and restaurants. For instance, Beyond Meat invests heavily in R&D to enhance texture replication, while Oatly prioritizes carbon-neutral production to appeal to eco-conscious buyers. Collaborations with major foodservice providers like Starbucks and McDonald’s amplify reach. Additionally, companies like Alpro focus on localized marketing campaigns to address regional preferences. These strategies collectively drive innovation, expand accessibility, and build brand loyalty, ensuring sustained growth in the competitive Europe plant-based food market.
COMPETITION OVERVIEW
The Europe plant-based food market is highly competitive, characterized by intense rivalry among global giants and niche players. Established brands like Beyond Meat and Oatly dominate through aggressive marketing and continuous innovation, while smaller companies focus on localized offerings to carve out niches. The market’s fragmentation is further exacerbated by the entry of private-label products from retailers like Tesco and Aldi, which offer affordable alternatives. Sustainability and health remain key differentiators, with companies investing heavily in eco-friendly packaging and nutritional advancements. This dynamic landscape fosters rapid innovation but challenges smaller players to maintain relevance amidst pricing pressures and evolving consumer preferences.
TOP 5 MAJOR ACTIONS TAKEN BY COMPANIES
- In April 2023, Beyond Meat launched a low-cost burger variant targeting budget-conscious consumers, enhancing affordability.
- In June 2023, Oatly partnered with Starbucks to introduce oat milk-based beverages across Europe, boosting visibility.
- In August 2023, Alpro introduced recyclable packaging, aligning with sustainability goals and enhancing brand image.
- In October 2023, Nestlé expanded its plant-based range with pea-based sausages, catering to flexitarians seeking variety.
- In December 2023, Just Eat integrated a dedicated “Vegan” filter on its app, simplifying access to plant-based options for users.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This Europe plant-based food market research report is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Type
- Plant-based Meat
- Plant-based Fish
- Dairy Alternatives
- Condiments
- Dressings
- Mayo
By Distribution Channel
- Food Retail
- Food Service
- E-commerce
By Nature
- Organic
- Conventional
By Source
- Soy
- Wheat
- Pea
- Almond
- Coconut
- Others
By Country
- UK
- France
- Spain
- Germany
- Italy
- Russia
- Sweden
- Denmark
- Switzerland
- Netherlands
- Turkey
- Czech Republic
- Rest of Europe
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What was the Europe Plant-Based Food market size in 2024?
The Europe Plant-Based Food market was valued at USD 3.48 billion in 2024. It's projected to reach USD 9.17 billion by 2033.
2. Which segment dominated the Europe Plant-Based Food market in 2024?
The dairy alternatives segment dominated the Europe Plant-Based Food market with a 40.1% share in 2024, driven by versatility and lactose intolerance.
3. Which country dominated the Europe Plant-Based Food market in 2024?
Germany dominated the Europe Plant-Based Food market in 2024 with a 28.1% share, driven by high consumer awareness and government support.
Related Reports
Access the study in MULTIPLE FORMATS
Purchase options starting from
$ 2000
Didn’t find what you’re looking for?
TALK TO OUR ANALYST TEAM
Need something within your budget?
NO WORRIES! WE GOT YOU COVERED!
Call us on: +1 888 702 9696 (U.S Toll Free)
Write to us: sales@marketdataforecast.com